您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹移動端效果之IndexList的實現方法,文中介紹的非常詳細,具有一定的參考價值,感興趣的小伙伴們一定要看完!
寫在前面
接著前面的移動端效果講,這次講解的的是IndexList的實現原理。效果如下:
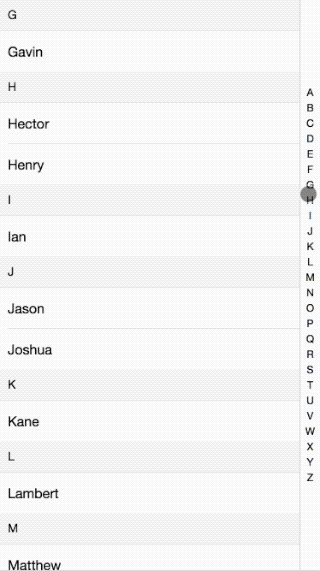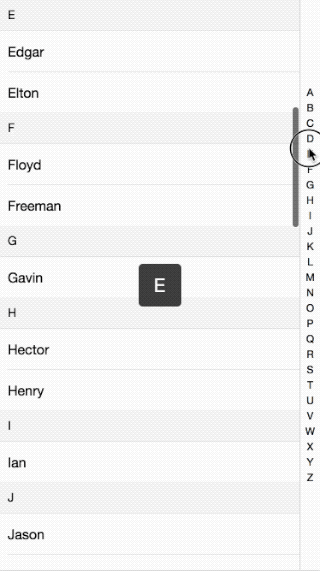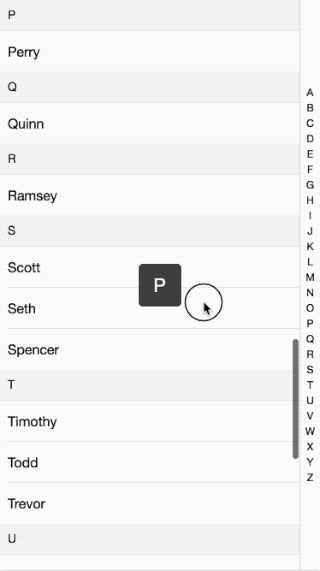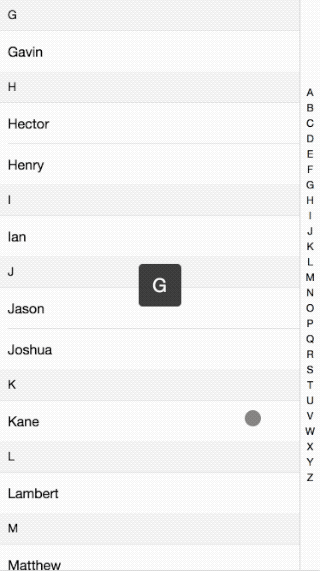
代碼請看這里:github
移動端效果之swiper
移動端效果之picker
移動端效果之cellSwiper
1. 核心解析
總體來說的原理就是當點擊或者滑動右邊的索引條時,通過獲取點擊的索引值來使左邊的內容滑動到相應的位置。其中怎樣滑動到具體的位置,看下面分解:
1.1 基本html代碼
<div class="indexlist"> <ul class="indexlist-content" id="content"> <!-- 需要生成的內容 --> </ul> <div class="indexlist-nav" id="nav"> <ul class="indexlist-navlist" id="navList"> <-- 需要生成的索引條 --> </ul> </div> <div class="indexlist-indicator" id="indicator"></div> </div>
1.2 DOM初始化
由于餓了么組件庫中的indexList是采用vue組件生成DOM,我這里大致使用javascript來模擬生成DOM。
// 內容填充
function initialDOM() {
// D.data 獲取內容數據
var data = D.data;
var contentHtml = '';
var navHtml = '';
// 初始化內容和NAV
data.forEach(function(d) {
var index = d.index;
var items = d.items;
navHtml += '<li class="indexlist-navitem">'+ index +'</li>';
contentHtml += '<li class="indexsection" data-index="'+ index +'"><p class="indexsection-index">'+ index +'</p><ul>';
items.forEach(function(item) {
contentHtml += '<a class="cell"><div class="cell-wrapper"><div class="cell-title"><span class="cell-text">'+ item +'</span></div></div></a>';
});
contentHtml += '</ul></li>';
});
content.innerHTML = contentHtml;
navList.innerHTML = navHtml;
}
// 樣式初始化
if (!currentHeight) {
currentHeight = document.documentElement.clientHeight -content.getBoundingClientRect().top;
}
// 右邊索引欄的寬度
navWidth = nav.clientWidth;
// 左邊內容的初始化高度和右邊距
// 高度為當前頁面的高度與內容top的差值
content.style.marginRight = navWidth + 'px';
content.style.height = currentHeight + 'px';1.3 綁定滑動事件
在右邊的索引欄上加上滑動事件,當點擊或者滑動的時候觸發。在源代碼中在touchstart事件的結尾處,在window上綁定了touchmove與touchend事件,是為了使得滑動得區域更大,只有在開始的時候在索引欄上觸發了touchstart事件時,之后再window上觸發滑動和結束事件,這就意味著我們在滑動的過程中可以在左側的內容區域滑動,同時也能達到index的效果。
function handleTouchstart(e) {
// 如果不是從索引欄開始滑動,則直接return
// 保證了左側內容區域能夠正常滑動
if (e.target.tagName !== 'LI') {
return;
}
// 記錄開始的clientX值,這個clientX值將在之后的滑動中持續用到,用于定位
navOffsetX = e.changedTouches[0].clientX;
// 內容滑動到指定區域
scrollList(e.changedTouches[0].clientY);
if (indicatorTime) {
clearTimeout(indicatorTime);
}
moving = true;
// 在window區域注冊滑動和結束事件
window.addEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove, { passive: false });
window.addEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);
}這里面用到了e.changedTouches,這個API可以去MDN查一下。
如果不是用到多點觸控,changedTouches和touches的區別并不是特別大,changedTouches在同一點點擊兩次,第二次將不會有touch值。具體可以看這篇文章
下面看一下如何滑動:
function scrollList(y) {
// 通過當前的y值以及之前記錄的clientX值來獲得索引欄中的對應item
var currentItem = document.elementFromPoint(navOffsetX, y);
if (!currentItem || !currentItem.classList.contains('indexlist-navitem')) {
return;
}
// 顯示指示器
currentIndicator = currentItem.innerText;
indicator.innerText = currentIndicator;
indicator.style.display = '';
// 找到左側內容的對應section
var targets = [].slice.call(sections).filter(function(section) {
var index = section.getAttribute('data-index');
return index === currentItem.innerText;
});
var targetDOM;
if (targets.length > 0) {
targetDOM = targets[0];
// 通過對比要滑動到的區域的top值與最開始的一個區域的top值
// 兩者的差值即為要滾動的距離
content.scrollTop = targetDOM.getBoundingClientRect().top - firstSection.getBoundingClientRect().top;
// 或者使用scrollIntoView來達到相同的目的
// 不過存在兼容性的問題
// targetDOM.scrollIntoView();
}
}關于elementFromPoint的API可以看這里
caniuse.com上關于getBoundingClientRect和scrollIntoView的兼容性
getBoundingClientRect
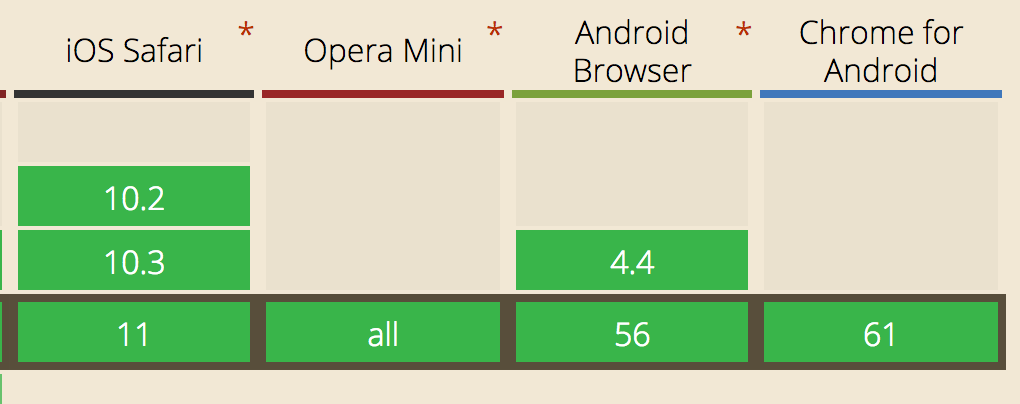
scrollIntoView
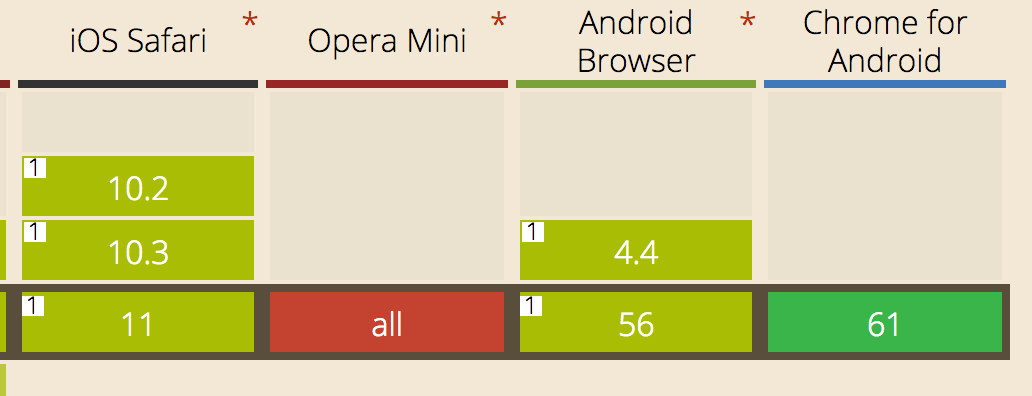
最后需要注銷window上的滑動事件
window.removeEventListener('touchmove', handleTouchMove);
window.removeEventListener('touchend', handleTouchEnd);以上是“移動端效果之IndexList的實現方法”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!希望分享的內容對大家有幫助,更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。