您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
決策樹也是有監督機器學習方法。 電影《無恥混蛋》里有一幕游戲,在德軍小酒館里有幾個人在玩20問題游戲,游戲規則是一個設迷者在紙牌中抽出一個目標(可以是人,也可以是物),而猜謎者可以提問題,設迷者只能回答是或者不是,在幾個問題(最多二十個問題)之后,猜謎者通過逐步縮小范圍就準確的找到了答案。這就類似于決策樹的工作原理。(圖一)是一個判斷郵件類別的工作方式,可以看出判別方法很簡單,基本都是閾值判斷,關鍵是如何構建決策樹,也就是如何訓練一個決策樹。
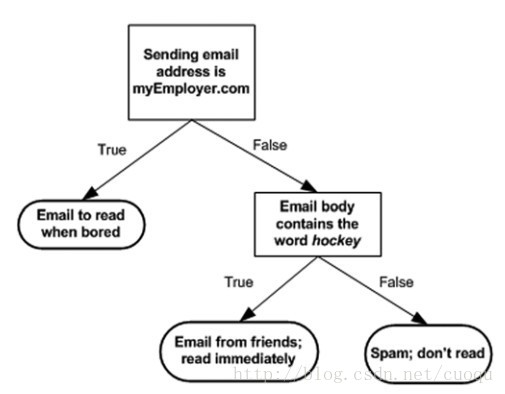
(圖一)
構建決策樹的偽代碼如下:
Check if every item in the dataset is in the same class:
If so return the class label
Else
find the best feature to split the data
split the dataset
create a branch node
for each split
call create Branch and add the result to the branch node
return branch node
原則只有一個,盡量使得每個節點的樣本標簽盡可能少,注意上面偽代碼中一句說:find the best feature to split the data,那么如何find thebest feature?一般有個準則就是盡量使得分支之后節點的類別純一些,也就是分的準確一些。如(圖二)中所示,從海洋中撈取的5個動物,我們要判斷他們是否是魚,先用哪個特征?

(圖二)
為了提高識別精度,我們是先用“離開陸地能否存活”還是“是否有蹼”來判斷?我們必須要有一個衡量準則,常用的有信息論、基尼純度等,這里使用前者。我們的目標就是選擇使得分割后數據集的標簽信息增益最大的那個特征,信息增益就是原始數據集標簽基熵減去分割后的數據集標簽熵,換句話說,信息增益大就是熵變小,使得數據集更有序。熵的計算如(公式一)所示:
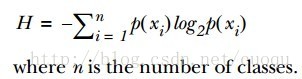
有了指導原則,那就進入代碼實戰階段,先來看看熵的計算代碼:
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet):
numEntries = len(dataSet)
labelCounts = {}
for featVec in dataSet: #the the number of unique elements and their occurance
currentLabel = featVec[-1]
if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel] = 0
labelCounts[currentLabel] += 1 #收集所有類別的數目,創建字典
shannonEnt = 0.0
for key in labelCounts:
prob = float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries
shannonEnt -= prob * log(prob,2) #log base 2 計算熵
return shannonEnt
有了熵的計算代碼,接下來看依照信息增益變大的原則選擇特征的代碼:
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value):
retDataSet = []
for featVec in dataSet:
if featVec[axis] == value:
reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting
reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:])
retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec)
return retDataSet
def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet):
numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels
baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet)
bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1
for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features
featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature
uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values
newEntropy = 0.0
for value in uniqueVals:
subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value)
prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet))
newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet)
infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy
if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far #選擇信息增益最大的代碼在此
bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best
bestFeature = i
return bestFeature #returns an integer
從最后一個if可以看出,選擇使得信息增益最大的特征作為分割特征,現在有了特征分割準則,繼續進入一下個環節,如何構建決策樹,其實就是依照最上面的偽代碼寫下去,采用遞歸的思想依次分割下去,直到執行完成就構建了決策樹。代碼如下:
def majorityCnt(classList):
classCount={}
for vote in classList:
if vote not in classCount.keys(): classCount[vote] = 0
classCount[vote] += 1
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.iteritems(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]
def createTree(dataSet,labels):
classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet]
if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList):
return classList[0]#stop splitting when all of the classes are equal
if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet
return majorityCnt(classList)
bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet)
bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat]
myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}}
del(labels[bestFeat])
featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet]
uniqueVals = set(featValues)
for value in uniqueVals:
subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don't mess up existing labels
myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels)
return myTree
用圖二的樣本構建的決策樹如(圖三)所示:
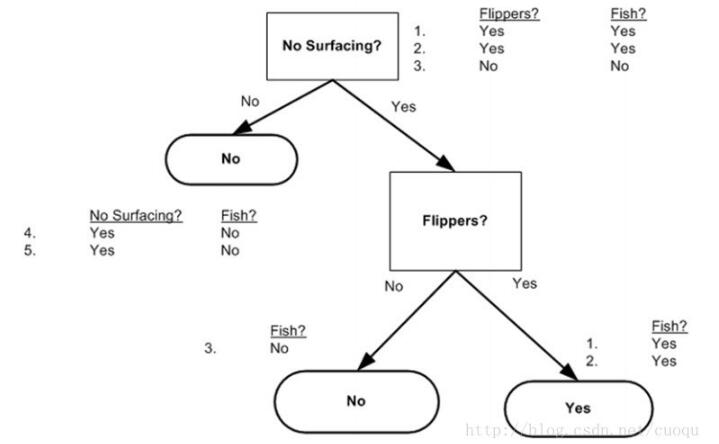
(圖三)
有了決策樹,就可以用它做分類咯,分類代碼如下:
def classify(inputTree,featLabels,testVec):
firstStr = inputTree.keys()[0]
secondDict = inputTree[firstStr]
featIndex = featLabels.index(firstStr)
key = testVec[featIndex]
valueOfFeat = secondDict[key]
if isinstance(valueOfFeat, dict):
classLabel = classify(valueOfFeat, featLabels, testVec)
else: classLabel = valueOfFeat
return classLabel
最后給出序列化決策樹(把決策樹模型保存在硬盤上)的代碼:
def storeTree(inputTree,filename): import pickle fw = open(filename,'w') pickle.dump(inputTree,fw) fw.close() def grabTree(filename): import pickle fr = open(filename) return pickle.load(fr)
優點:檢測速度快
缺點:容易過擬合,可以采用修剪的方式來盡量避免
參考文獻:machine learning in action
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持億速云。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。