您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Tensorflow如何使用支持向量機擬合線性回歸,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
支持向量機可以用來擬合線性回歸。
相同的最大間隔(maximum margin)的概念應用到線性回歸擬合。代替最大化分割兩類目標是,最大化分割包含大部分的數據點(x,y)。我們將用相同的iris數據集,展示用剛才的概念來進行花萼長度與花瓣寬度之間的線性擬合。
相關的損失函數類似于max(0,|yi-(Axi+b)|-ε)。ε這里,是間隔寬度的一半,這意味著如果一個數據點在該區域,則損失等于0。
# SVM Regression
#----------------------------------
#
# This function shows how to use TensorFlow to
# solve support vector regression. We are going
# to find the line that has the maximum margin
# which INCLUDES as many points as possible
#
# We will use the iris data, specifically:
# y = Sepal Length
# x = Pedal Width
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from sklearn import datasets
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
# Create graph
sess = tf.Session()
# Load the data
# iris.data = [(Sepal Length, Sepal Width, Petal Length, Petal Width)]
iris = datasets.load_iris()
x_vals = np.array([x[3] for x in iris.data])
y_vals = np.array([y[0] for y in iris.data])
# Split data into train/test sets
train_indices = np.random.choice(len(x_vals), round(len(x_vals)*0.8), replace=False)
test_indices = np.array(list(set(range(len(x_vals))) - set(train_indices)))
x_vals_train = x_vals[train_indices]
x_vals_test = x_vals[test_indices]
y_vals_train = y_vals[train_indices]
y_vals_test = y_vals[test_indices]
# Declare batch size
batch_size = 50
# Initialize placeholders
x_data = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
y_target = tf.placeholder(shape=[None, 1], dtype=tf.float32)
# Create variables for linear regression
A = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[1,1]))
# Declare model operations
model_output = tf.add(tf.matmul(x_data, A), b)
# Declare loss function
# = max(0, abs(target - predicted) + epsilon)
# 1/2 margin width parameter = epsilon
epsilon = tf.constant([0.5])
# Margin term in loss
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.maximum(0., tf.subtract(tf.abs(tf.subtract(model_output, y_target)), epsilon)))
# Declare optimizer
my_opt = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.075)
train_step = my_opt.minimize(loss)
# Initialize variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Training loop
train_loss = []
test_loss = []
for i in range(200):
rand_index = np.random.choice(len(x_vals_train), size=batch_size)
rand_x = np.transpose([x_vals_train[rand_index]])
rand_y = np.transpose([y_vals_train[rand_index]])
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x_data: rand_x, y_target: rand_y})
temp_train_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_train]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_train])})
train_loss.append(temp_train_loss)
temp_test_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x_data: np.transpose([x_vals_test]), y_target: np.transpose([y_vals_test])})
test_loss.append(temp_test_loss)
if (i+1)%50==0:
print('-----------')
print('Generation: ' + str(i+1))
print('A = ' + str(sess.run(A)) + ' b = ' + str(sess.run(b)))
print('Train Loss = ' + str(temp_train_loss))
print('Test Loss = ' + str(temp_test_loss))
# Extract Coefficients
[[slope]] = sess.run(A)
[[y_intercept]] = sess.run(b)
[width] = sess.run(epsilon)
# Get best fit line
best_fit = []
best_fit_upper = []
best_fit_lower = []
for i in x_vals:
best_fit.append(slope*i+y_intercept)
best_fit_upper.append(slope*i+y_intercept+width)
best_fit_lower.append(slope*i+y_intercept-width)
# Plot fit with data
plt.plot(x_vals, y_vals, 'o', label='Data Points')
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit, 'r-', label='SVM Regression Line', linewidth=3)
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit_upper, 'r--', linewidth=2)
plt.plot(x_vals, best_fit_lower, 'r--', linewidth=2)
plt.ylim([0, 10])
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.title('Sepal Length vs Pedal Width')
plt.xlabel('Pedal Width')
plt.ylabel('Sepal Length')
plt.show()
# Plot loss over time
plt.plot(train_loss, 'k-', label='Train Set Loss')
plt.plot(test_loss, 'r--', label='Test Set Loss')
plt.title('L2 Loss per Generation')
plt.xlabel('Generation')
plt.ylabel('L2 Loss')
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.show()輸出結果:
----------- Generation: 50 A = [[ 2.91328382]] b = [[ 1.18453276]] Train Loss = 1.17104 Test Loss = 1.1143 ----------- Generation: 100 A = [[ 2.42788291]] b = [[ 2.3755331]] Train Loss = 0.703519 Test Loss = 0.715295 ----------- Generation: 150 A = [[ 1.84078252]] b = [[ 3.40453291]] Train Loss = 0.338596 Test Loss = 0.365562 ----------- Generation: 200 A = [[ 1.35343242]] b = [[ 4.14853334]] Train Loss = 0.125198 Test Loss = 0.16121
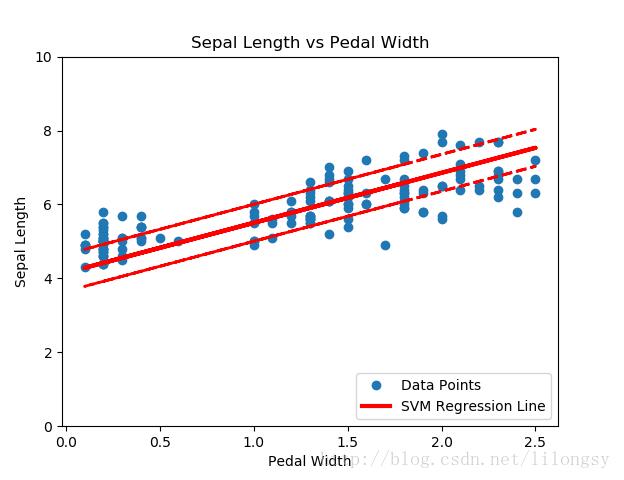
基于iris數據集(花萼長度和花瓣寬度)的支持向量機回歸,間隔寬度為0.5
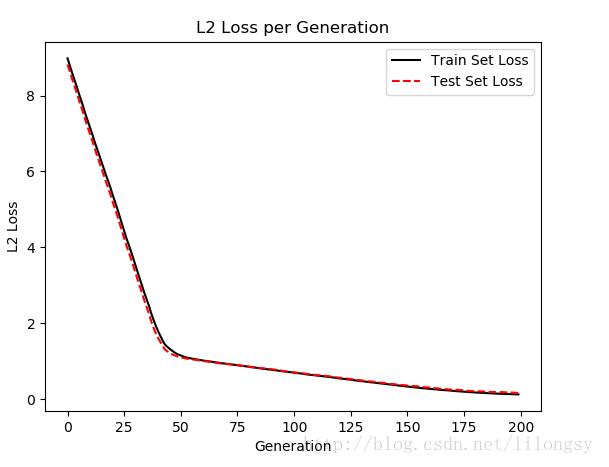
每次迭代的支持向量機回歸的損失值(訓練集和測試集)
直觀地講,我們認為SVM回歸算法試圖把更多的數據點擬合到直線兩邊2ε寬度的間隔內。這時擬合的直線對于ε參數更有意義。如果選擇太小的ε值,SVM回歸算法在間隔寬度內不能擬合更多的數據點;如果選擇太大的ε值,將有許多條直線能夠在間隔寬度內擬合所有的數據點。作者更傾向于選取更小的ε值,因為在間隔寬度附近的數據點比遠處的數據點貢獻更少的損失。
感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Tensorflow如何使用支持向量機擬合線性回歸”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。