您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
小編這次要給大家分享的是怎么實現Python列表去重復項,文章內容豐富,感興趣的小伙伴可以來了解一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后能夠有所收獲。
說明
Python語言中列表(List)與其他語言的數組(Array)類似,是一種有序的集合數據結構,Python List可支持各種數據類型,長度也可動態調整,與JS中的數組或Java ArrayList很接近。在實際編程中,經常會遇到數組或列表去掉重復項,保持成員唯一性。實現方式有多種,比如新建列表來存儲非重復項,或者在原有基礎上刪除掉重復的項,也可以利用數據結構來達到去重復。具體哪一種方法更好呢?以下約20種方式都可以實現,我們可以通過這些來交流和學習。

方式
## 1. 新建列表,如果新列表中不存在,則添加到新列表。
def unique(data):
new_list = []
for item in data:
if item not in new_list:
new_list.append(item)
return new_list
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("new_list + not in data:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
# result
$ python -V
Python 2.7.16
$ python unique.py
('for list + not in. data:', ['a', 1, 2, 'b'])
time:0.0441074371338 ms
## 2. 新建列表。根據下標判斷是否存在新列表中,如果新列表中不存在則添加到新列表。
def unique(data):
new_list = []
for i in range(len(data)):
if data[i] not in new_list:
new_list.append(data[i])
return new_list
## 2.1 新建列表,使用列表推導來去重。是前一種的簡寫。
def unique(data):
new_list = []
[new_list.append(i) for i in data if not i in new_list]
return new_list
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("for range + not in. data:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 3. 通過index找不到該項,則追加到新列表中。index找不到會報錯,因此放在異常處理里。
def unique(data):
new_list = []
for i in range(len(data)):
item = data[i]
try:
if (new_list.index(item) < 0):
print('new_list:', new_list)
except ValueError:
new_list.append(item)
return new_list
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("list index + except:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 4. 新建列表,兩個循環。如果內循環與外循環項相同,且下標相同就添加到新列表,其余忽略
def unique(data):
new_list = []
for i in range(len(data)):
j = 0
while j <= i:
if data[i] == data[j]:
if i == j:
new_list.append(data[i])
break
j += 1
return new_list
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("new list + for. new_list:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
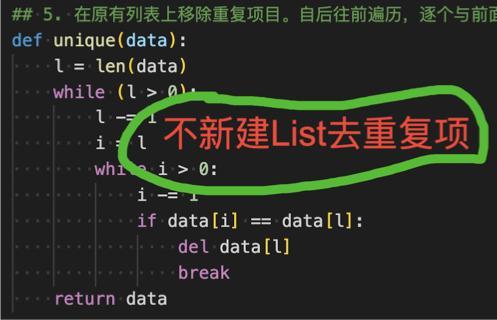
## 5. 在原有列表上移除重復項目。自后往前遍歷,逐個與前面項比較,如果值相同且下標相同,則移除當前項。
def unique(data):
l = len(data)
while (l > 0):
l -= 1
i = l
while i > 0:
i -= 1
if data[i] == data[l]:
del data[l]
break
return data
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("one list while. last -> first result. data:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 6. 在原有列表上移除重復項目。自前往后遍歷,逐個與后面項比較,如果值相同且下標相同,則移除當前項。
def unique(data):
l = len(data)
i = 0
while i < l:
j = i + 1
while j < l:
if data[i] == data[j]:
del data[j]
l -= 1
i -= 1
break
j += 1
i += 1
return data
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("one list while. first -> last result. data:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 7. 新建列表。遍歷列表,利用index比較出現的位置,如果出現在第一次的位置則追加到新數組。
def unique(data):
new_list = []
for i in range(len(data)):
if i == data.index(data[i]):
new_list.append(data[i])
return new_list
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("for range + index. data:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 8. 利用字典屬性唯一性來實現去重復。
def unique(data):
obj = {}
for item in data:
obj[item] = item
return obj.values()
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("list + dict:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 或者直接通過dict.fromkeys來實現
print("dict fromkeys:", dict.fromkeys(data).keys())
## 9. 利用filter函數,即把不符合條件的過濾掉。這里filter不支持下標,因此需要借助外部列表存儲不重復項
def uniq(item):
i = data.index(item)
if (item not in new_list):
new_list.append(item)
return True
return False
def unique(item):
if obj.get(item) == None:
obj[item] = item
return True
return False
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
new_list = []
print('filter + list + not in: ', filter(uniq, data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 10. 利用字典結合過濾來實現去重復。
def unique(item):
if obj.get(item) == None:
obj[item] = item
return True
return False
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
obj = {}
print("filter + dict + get:", filter(unique, data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 11. 利用map來實現去重復。與map與filter類似,是一個高階函數。可以針對其中項逐個修改操作。
## 與filter不同map會保留原有項目,并不會刪除,因此值可以改為None,然后再過濾掉。
def unique(item):
if item not in new_list:
new_list.append(item)
return item
return None
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
new_list = []
start_time = time.time()
print("list from Map:", filter(lambda item: item != None, map(unique, data)))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 12. 利用set數據結構里key的唯一性來去重復
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
print("from Set:", list(set(data)))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 13. 提前排序,從后向前遍歷,將當前項與前一項對比,如果重復則移除當前項
def unique(data):
data.sort()
l = len(data)
while (l > 0):
l -= 1
if (data[l] == data[l - 1]):
data.remove(data[l])
return data
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("sort + remove:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 14. 提前排序,自前往后遍歷,將當前項與后一項對比,如果重復則移除當前項
def unique(data):
"""
in python 3: TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of 'int' and 'str'
need to keep the same Type of member in List
"""
data.sort()
l = len(data) - 1
i = 0
while i < l:
if (data[i] == data[i + 1]):
del data[i]
i -= 1
l -= 1
i += 1
return data
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("sort+del ASE:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 15. 利用reduce函數來去重復。reduce具有累計的作用,判斷如果不在累計結果中出現,則追加到結果中。
import functools
def unique(data):
new_list = []
def foo(result, item):
if isinstance(result, list) == False:
result = [result]
return result if item in result else result + [item]
return functools.reduce(foo, data)
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("functools.reduce:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 16. 利用遞歸調用來去重復。遞歸自后往前逐個調用,當長度為1時終止。
## 當后一項與前任一項相同說明有重復,則刪除當前項。相當于利用自我調用來替換循環
def recursion_unique(data, len):
if (len <= 1):
return data
l = len
last = l - 1
is_repeat = False
while (l > 1):
l -= 1
if (data[last] == data[l - 1]):
is_repeat = True
break
if (is_repeat):
del data[last]
return recursion_unique(data, len - 1)
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("recursion_unique:", recursion_unique(data, len(data)))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 17. 利用遞歸調用來去重復的另外一種方式。遞歸自后往前逐個調用,當長度為1時終止。
## 與上一個遞歸不同,這里將不重復的項目作為結果拼接起來
def recursion_unique_new(data, len):
if (len <= 1):
return data
l = len
last = l - 1
is_repeat = False
while (l > 1):
l -= 1
if (data[last] == data[l - 1]):
is_repeat = True
break
if (is_repeat):
del data[last:]
result = []
else:
result = [data[last]]
return recursion_unique_new(data, len - 1) + result
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("recursion_unique_new:", recursion_unique_new(data, len(data)))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms")
## 18. 利用numpy lib庫. 需提前安裝 `pip install numpy`
import numpy as np
def unique(data):
res = np.array(data)
return list(np.unique(res))
# test
data = ['a', 'a', 1, 1, 2, 2, 'b', 'b', 2, 1]
start_time = time.time()
print("import numpy as np.unique:", unique(data))
print("time:" + str((time.time() - start_time) * 1000) + " ms") 
討論
從以上例子上可以看出,相對來講,Python比起其它語言要靈活得多,與JS并列最流行的腳本類語言,這也就是為何Python如此流行的原因吧。
哪一種方式更適合呢?你常用那種方式來實現去重復項?新建數組、非新建、借助Dict或Set等結構,亦或是其它方式?
看完這篇關于怎么實現Python列表去重復項的文章,如果覺得文章內容寫得不錯的話,可以把它分享出去給更多人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。