您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
Tessellation is the process of breaking a high-order primitive (which is known as a patch in OpenGL) into many smaller(Tessellation就是把很多高階的圖元變成很多小圖元的過程), simpler primitives such as triangles for rendering(比如說三角形這種簡單的圖元). OpenGL includes a fixed-function, configurable tessellation engine that is able to break up quadrilaterals, triangles, and lines into a potentially large number of smaller points, lines, or triangles that can be directly consumed by the normal rasterization hardware further down the pipeline(OpenGL的固定功能部分,可以通過配置tessellation引擎,能夠將一些四邊形、三角形、線變成大量的硬件光柵化時可以支持處理的小的點、線和三角形). Logically, the tessellation phase sits directly after the vertex shading stage in the OpenGL pipeline(邏輯上來說,tessellation階段是緊接著vertex shader階段的) and is made up of three parts: the tessellation control shader, the fixed-function tessellation engine, and the tessellation evaluation shader( 并且tessellation階段由三個部分組成:the tessellation control shader, the fixed-function tessellation engine, and the tessellation evaluation shader)
Tessellation Control Shaders
The first of the three tessellation phases is the tessellation control shader (TCS;sometimes known as simply the control shader). (tessellation shader的第一部分叫tessellation control shader) This shader takes its input from the vertex shader and is primarily responsible for two things(它的輸入數據是由vertex shader給的,它主要干兩件事): the determination of the level of tessellation that will be sent to the tessellation engine(第一件是確定發送給tessellation引擎的tessellation的級別), and the generation of data that will be sent to the tessellation evaluation shader that is run after tessellation has occurred(以及生成將會被在tessellation發生后,tessellation evaluation shader使用的數據)
Tessellation in OpenGL works by breaking down high-order surfaces known as patches into points, lines, or triangles.(在OpenGL中,Tessellation主要是把高階的patch圖形變成點、線、三角形) Each patch is formed from a number of control points.(每一個patch的數據是從一堆控制點鐘獲取的) The number of control points per patch is configurable and set by calling glPatchParameteri() with pname set to GL_PATCH_VERTICES and value set to the number of control points that will be used to construct each patch(控制點的數量是可以通過glPatchParameteri來設置的,pname參數傳GL_PATCH_VERTICES,value參數設置每個patch的控制點個數). The prototype of glPatchParameteri() is(這個API的定義如下)
void glPatchParameteri(GLenum pname,GLint value);
By default, the number of control points per patch is three(缺省情況下,每個patch的控制點數量是3). Thus, if this is what you want(as in our example application), you don’t need to call it at all(如果你的 patch就是由三個點組成的話,你就不用調用這個API). The maximum number of control points that can be used to form a single patch is implementation defined(每個patch的控制點的上線個數會因為硬件不一樣而不一樣), but is guaranteed to be at least 32(但至少這個數目會有32個)
When tessellation is active, the vertex shader runs once per control point(當激活tessellation的時候,vertex shader是每個點會執行一次), while the tessellation control shader runs in batches on groups of control points where the size of each batch is the same as the number of vertices per patch(而tessellation control shader是按照patch執行的,每個patch中點數數目是用API去設置好的). That is, vertices are used as control points (也就是說,點是被當做控制點來使用的)and the result of the vertex shader is passed in batches to the tessellation control shader as its input(并且vertex shader的執行結果就是tessellation control shader的輸入). The number of control points per patch can be changed such that the number of control points that is output by the tessellation control shader can differ from the number of control points that it consumes(控制點的個數是可以被修改的,意味著輸入tessellation control shader的點的個數不一定和該shader的輸出點的個數相等). The number of control points produced by the control shader is set using an output layout qualifier in the control shader’s source code(tessellation control shader產生的點的個數是在tessellation control shader里使用output layout修飾符修飾的). Such a layout qualifier looks like this(舉個例子):
layout (vertices = N) out;
Here, N is the number of control points per patch(這里的N就是每個patch輸出的點的個數). The control shader is responsible for calculating the values of the output control points(control shader需要計算輸出的控制點的值) and for setting the tessellation factors for the resulting patch that will be sent to the fixed-function tessellation engine(這些值將會被tessellation引擎使用,并成為最終進行曲面細分時的決定因素). The output tessellation factors are written to the gl_TessLevelInner and gl_TessLevelOuter built-in output variables(曲面細分的影響因素要寫在兩個內置輸出變量上,一個是gl_TessLevelInner一個是gl_TessLevelOuter), whereas any other data that is passed down the pipeline is written to user-defined output variables(這倆變量就跟你自己寫的輸出變量一樣) (those declared using the out keyword, or the special built-in gl_out array) as normal
Listing 3.7 shows a simple tessellation control shader(Listing3.7顯示了一個簡單的tessellation control shader). It sets the number of output control points to three (它使用layout (vertices = 3) out設置了輸出的數據個數是3)(the same as the default number of input control points(就跟缺省的control shader的輸入數據個數一樣)) using the layout (vertices = 3) out; layout qualifier, copies its input to its output (using the built-in variables gl_in and gl_out) (layout修飾符會使用內置的gl_in和gl_out,拷貝它的輸入到它的輸出里去), and sets the inner and outer tessellation level to 5(并且設置inner和outer的tessellation級別為5). Higher numbers would produce a more densely tessellated output(細分級別越高,產生的曲面的小面片就越多), and lower numbers would yield a more coarsely tessellated output(細分級別越小,產生的結果的面片數就越少). Setting the tessellation factor to 0 will cause the whole patch to be thrown away(設置tessellation因子為0將會使得整個patch被丟棄)
The built-in input variable gl_InvocationID is used as an index into the gl_in and gl_out arrays. This variable contains the zero-based index of the control point within the patch being processed by the current invocation of the tessellation control shader
#version 450 core
layout (vertices = 3) out;
void main(void)
{
// Only if I am invocation 0 ...
if (gl_InvocationID == 0)
{
gl_TessLevelInner[0] = 5.0;
gl_TessLevelOuter[0] = 5.0;
gl_TessLevelOuter[1] = 5.0;
gl_TessLevelOuter[2] = 5.0;
}/
/ Everybody copies their input to their output
gl_out[gl_InvocationID].gl_Position =
gl_in[gl_InvocationID].gl_Position;
}
Listing 3.7: Our first tessellation control shader
By using the shader of Listing 2.8, we can assign a different position to each of the vertices based on its value of gl_VertexID(我們可以根據gl_VertexID給每個頂點賦值一個位置). The points in the array vertices form a triangle(那些點是以三角形的方式進行組織的), and if we modify our rendering function to pass GL_TRIANGLES to glDrawArrays() instead of GL_POINTS(并且我們修改glDrawArrays的參數,從GL_POINTS變成GL_TRIANGLES,如Listing2.9所示), as shown in Listing 2.9, then we obtain the image shown in Figure 2.4(這樣一來,我們應該會得到如圖2.4的運行結果).
// Our rendering function
void render(double currentTime)
{
const GLfloat color[] = { 0.0f, 0.2f, 0.0f, 1.0f };glClearBufferfv(GL_COLOR, 0, color);
// Use the program object we created earlier for rendering
glUseProgram(rendering_program);
// Draw one triangle
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
}
Listing 2.9: Rendering a single triangle
The Tessellation Engine
The tessellation engine is a fixed-function part of the OpenGL pipeline that takes highorder surfaces represented as patches and breaks them down into simpler primitives such as points, lines, or triangles(Tessellation引擎是OpenGL固定功能的一部分,它會把高階的patch打碎成點、線、三角形). Before the tessellation engine receives a patch, the tessellation control shader processes the incoming control points and sets tessellation factors that are used to break down the patch(在tessellation引擎收到patch之前,tessellation control shader會處理輸入的控制點,并且設置一些用于打碎patch的一些參數). After the tessellation engine produces the output primitives, the vertices representing them are picked up by the tessellation evaluation shader(當tessellation引擎輸出了圖元之后,這些點會被tessellation evaluation shader處理). The tessellation engine is responsible for producing the parameters that are fed to the invocations of the tessellation evaluation shader (tessellation引擎負責設置在調用tessellation evaluation shader時需要的參數), which it then uses to transform the resulting primitives and get them ready for rasterization(evaluation shader處理完畢之后,得到的結果就可以被用于進行光柵化處理了)
Tessellation Evaluation Shaders
Once the fixed-function tessellation engine has run(當tessellation引擎運行之后,它會產生很多輸出的點), it produces a number of output vertices representing the primitives it has generated. These are passed to the tessellation evaluation shader(這些點會被傳遞給tessellation evaluation shader). The tessellation evaluation shader (TES; also called simply the evaluation shader) runs an invocation for each vertex produced by the tessellator (tessellation evaluation shader會每個點運行一次). When the tessellation levels are high, the tessellation evaluation shader could run an extremely large number of times(當細分的數目很多時,TES會運行很多次). For this reason, you should be careful with complex evaluation shaders and high tessellation levels(因此,你需要小心的處理那些細分很多,而TES很復雜的情況)
Listing 3.8 shows a tessellation evaluation shader that accepts input vertices produced by the tessellator as a result of running the control shader shown in Listing 3.7. (Listing3.8顯示了接收來自Listing3.7的TCS所產生的點的TES代碼) At the beginning of the shader is a layout qualifier that sets the tessellation mode(在一開始的時候設置tessellation的模式). In this case,we selected the mode to be triangles(這里我們設置成了三角形). Other qualifiers, equal_spacing and cw,(其他的一些設置,比如equal_spacing,cw) indicate that new vertices should be generated equally spaced along the tessellated polygon edges and that a clockwise vertex winding order should be used for the generated triangles(這些參數的意思是,在細分曲面的時候,在邊線上的分界點之間的間隔要相等,然后再產生圖元的時候,需要用順時針方向去組織三角形). We will cover the other possible choices in the “Tessellation” section in Chapter 8(我們將在第8章的時候,來講解其他的關于Tessellation的一些內容).
The remainder of the shader assigns a value to gl_Position just like a vertex shader does(剩余的代碼也就是給gl_Position賦值,就如同vertex shader). It calculates this using the contents of two more built-in variables(同時它使用到了另外的兩個內置變量). The first is gl_TessCoord, which is the barycentric coordinate of the vertex generated by the tessellator(其中一個是gl_TessCoord,它是由tessellator產生的重心坐標). The second is the gl_Position member of the gl_in[] array of structures(第二個是gl_in數組,里面放著的是一堆gl_Position). This matches the gl_out structure written to in the tessellation control shader given in Listing 3.7(對應的gl_out的結構體和Listing3.7中的對應). This shader essentially implements pass-through tessellation(這個shader就是一個基本的簡單的傳輸數據的tessellation). That is, the tessellated output patch is exactly the same shape as the original, incoming triangular patch(也就是最終輸出的圖形跟原來的patch代表的圖元一模一樣,沒什么改變)
#version 450 core
layout (triangles, equal_spacing, cw) in;
void main(void)
{
gl_Position = (gl_TessCoord.x gl_in[0].gl_Position +
gl_TessCoord.y gl_in[1].gl_Position +
gl_TessCoord.z * gl_in[2].gl_Position);
}
Listing 3.8: Our first tessellation evaluation shader
To see the results of the tessellator, we need to tell OpenGL to draw only the outlines of the resulting triangles(為了顯示tessellation的結果,我們需要告訴OpenGL采用線框模式去繪制). To do this, we call glPolygonMode(), whose prototype is(這時候,我們需要使用glPolygonMode函數,它的定義如下:)
void glPolygonMode(GLenum face, GLenum mode);
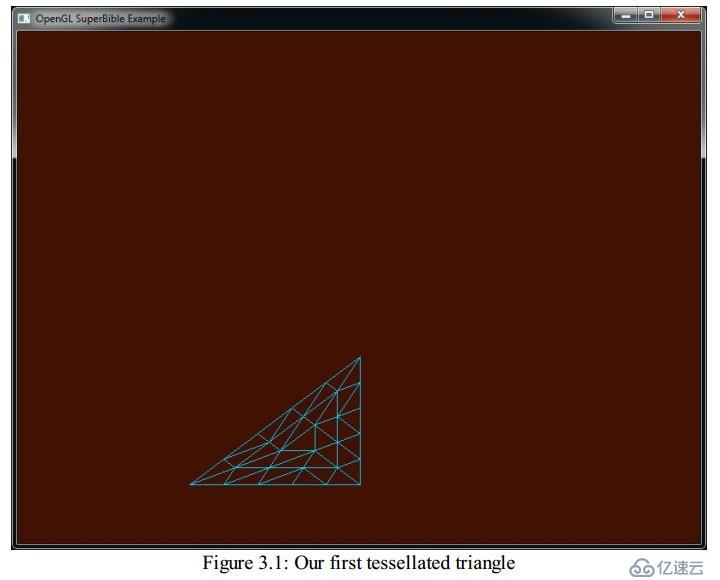
The face parameter specifies which type of polygons we want to affect(face參數需要設置我們希望哪個面被影響). Because we want to affect everything, we set it to GL_FRONT_AND_BACK(因為我們希望影響到所有東西,所以我們設置成GL_FRONT_AND_BACK). The other modes will be explained shortly(其他的模式稍后再解釋). mode says how we want our polygons to be rendered(模式設置的是你希望你的多邊形如何被渲染). As we want to render in wireframe mode (i.e., lines)(由于我們希望它被渲染成線框模式,我們設置這個參數為GL_LINE), we set this to GL_LINE. The result of rendering our one triangle example with tessellation enabled and the two shaders of Listing 3.7 and Listing 3.8 is shown in Figure 3.1(完事之后,剛才的Listing3.7和Listing3.8的代碼所渲染出來的結果就如同圖3.1所示)
本日的翻譯就到這里,明天見,拜拜~~
第一時間獲取最新橋段,請關注東漢書院以及圖形之心公眾號
東漢書院,等你來玩哦
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。