您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
使用redis存儲業務信息,同時也可以存儲系統運維信息,比如日志和計數器來收集系統當前的狀態信息,挖掘正在使用系統的顧客信息,以及診斷系統問題,發現潛在的問題。當然,系統日志信息及統計信息也可以存儲在關系型數據庫中,但是存在一個很大的弊端,影響業務性能。
1.使用redis記錄日志
熟悉java的朋友,記錄日志往往采用的是log4j,sl4j,大多記錄載體選擇文本文件。如果使用web集群的話,造成日志分散在各個web服務器,搜集有效日志信息,非常麻煩。如果選擇數據庫保存的話,解決了文件分散情況,但勢必對業務造成影響,日志畢竟是個輔助支撐而已,不應該和業務系統相提并論。這時候,redis是一個不錯的選擇。如果可以的話,可以對log4j擴展,將數據保存到redis中,當然這不是本章的重點。本章重點,主要簡單討論下如何保存日志。
構建一個系統,判斷哪些信息需要被記錄是一件困難的事情,不同的業務有不同的需求。但一般的日志信息往往關注一下方面。
日志時間,日志內容,服務IP,日志級別,日志發生頻率。
1.1redis日志存儲設計
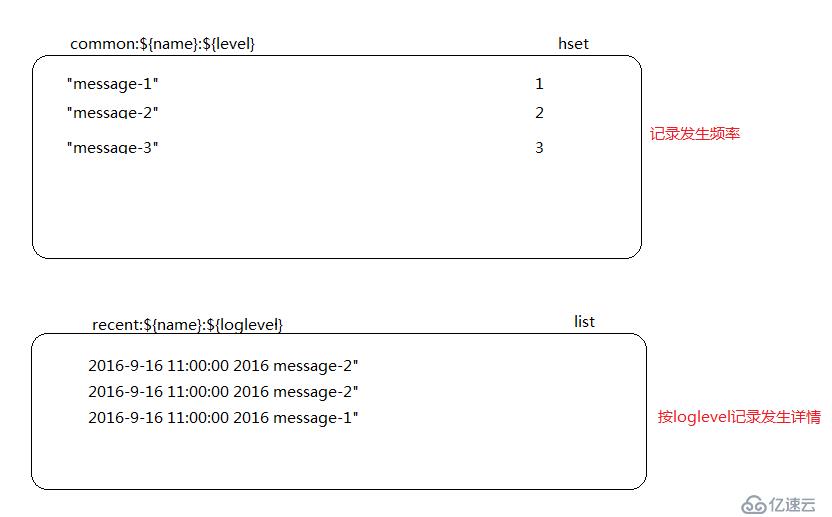
記錄詳情里,可以按要求,增添想要的信息,發生的類名稱,處理IP等。
1.2代碼
public void logCommon(
Jedis conn, String name, String message, String severity, int timeout) {
String commonDest = "common:" + name + ':' + severity;
String startKey = commonDest + ":start";
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + timeout;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < end){
conn.watch(startKey);
//當前所處的小時數
String hourStart = ISO_FORMAT.format(new Date());
String existing = conn.get(startKey);
Transaction trans = conn.multi();
//如果記錄的是上一個小時的日志
if (existing != null && COLLATOR.compare(existing, hourStart) < 0){
trans.rename(commonDest, commonDest + ":last");
trans.rename(startKey, commonDest + ":pstart");
trans.set(startKey, hourStart);
}else{
trans.set(startKey, hourStart);
}
//日志計數器增1
trans.zincrby(commonDest, 1, message);
//記錄最近日志詳情
String recentDest = "recent:" + name + ':' + severity;
trans.lpush(recentDest, TIMESTAMP.format(new Date()) + ' ' + message);
trans.ltrim(recentDest, 0, 99);
List<Object> results = trans.exec();
// null response indicates that the transaction was aborted due to
// the watched key changing.
if (results == null){
continue;
}
return;
}
}2.網站點擊量計數器統計
2.1redis計數器存儲設計
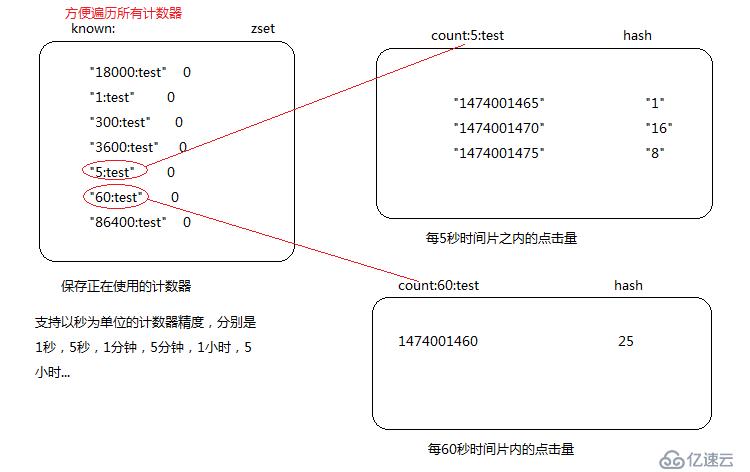
2.2編碼
//以秒為單位的精度
public static final int[] PRECISION = new int[]{1, 5, 60, 300, 3600, 18000, 86400};
public void updateCounter(Jedis conn, String name, int count, long now){
Transaction trans = conn.multi();
//每一次更新,都要更新所有精度的計數器
for (int prec : PRECISION) {
long pnow = (now / prec) * prec;//當前時間片的開始時間
String hash = String.valueOf(prec) + ':' + name;
trans.zadd("known:", 0, hash);
trans.hincrBy("count:" + hash, String.valueOf(pnow), count);
}
trans.exec();
}
public List<Pair<Integer,Integer>> getCounter(
Jedis conn, String name, int precision)
{
String hash = String.valueOf(precision) + ':' + name;
Map<String,String> data = conn.hgetAll("count:" + hash);
ArrayList<Pair<Integer,Integer>> results =
new ArrayList<Pair<Integer,Integer>>();
for (Map.Entry<String,String> entry : data.entrySet()) {
results.add(new Pair<Integer,Integer>(
Integer.parseInt(entry.getKey()),
Integer.parseInt(entry.getValue())));
}
Collections.sort(results);
return results;
}2.3清楚舊數據
流程圖
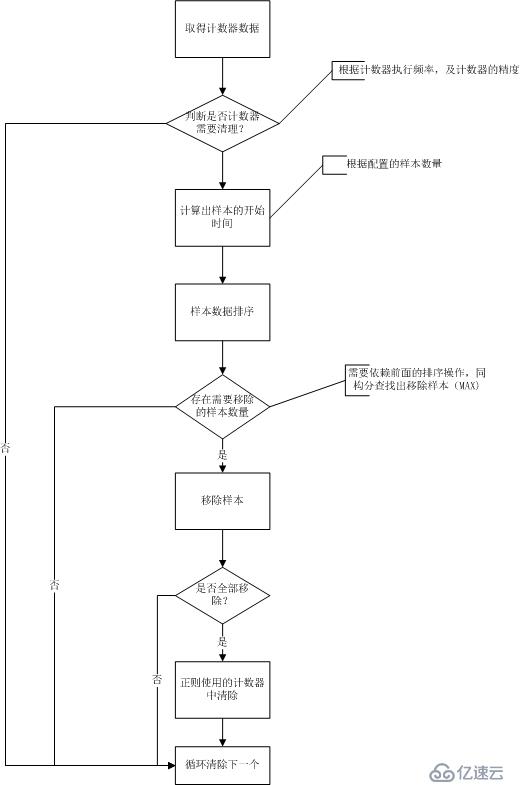
代碼
public class CleanCountersThread
extends Thread
{
private Jedis conn;
private int sampleCount = 100;
private boolean quit;
private long timeOffset; // used to mimic a time in the future.
public CleanCountersThread(int sampleCount, long timeOffset){
this.conn = new Jedis("192.168.163.156");
this.conn.select(15);
this.sampleCount = sampleCount;
this.timeOffset = timeOffset;
}
public void quit(){
quit = true;
}
public void run(){
int passes = 0;
while (!quit){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis() + timeOffset;
int index = 0;
while (index < conn.zcard("known:")){
Set<String> hashSet = conn.zrange("known:", index, index);
index++;
if (hashSet.size() == 0) {
break;
}
String hash = hashSet.iterator().next();
int prec = Integer.parseInt(hash.substring(0, hash.indexOf(':')));
int bprec = (int)Math.floor(prec / 60);
if (bprec == 0){
bprec = 1;
}
if ((passes % bprec) != 0){
continue;
}
String hkey = "count:" + hash;
String cutoff = String.valueOf(
((System.currentTimeMillis() + timeOffset) / 1000) - sampleCount * prec);
ArrayList<String> samples = new ArrayList<String>(conn.hkeys(hkey));
Collections.sort(samples);
int remove = bisectRight(samples, cutoff);
if (remove != 0){
conn.hdel(hkey, samples.subList(0, remove).toArray(new String[0]));
if (remove == samples.size()){
conn.watch(hkey);
if (conn.hlen(hkey) == 0) {
Transaction trans = conn.multi();
trans.zrem("known:", hash);
trans.exec();
index--;
}else{
conn.unwatch();
}
}
}
}
passes++;
long duration = Math.min(
(System.currentTimeMillis() + timeOffset) - start + 1000, 60000);
try {
sleep(Math.max(60000 - duration, 1000));
}catch(InterruptedException ie){
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
// mimic python's bisect.bisect_right
public int bisectRight(List<String> values, String key) {
int index = Collections.binarySearch(values, key);
return index < 0 ? Math.abs(index) - 1 : index + 1;
}
}3.使用redis統計數據
上面提到的計數器,是最簡單的統計數據。除了計數器(count(*)),還是最大值(max),最小值(min).
設計

stats:模塊(頁面)名稱:指標名稱
public List<Object> updateStats(Jedis conn, String context, String type, double value){
int timeout = 5000;
String destination = "stats:" + context + ':' + type;
String startKey = destination + ":start";
long end = System.currentTimeMillis() + timeout;
while (System.currentTimeMillis() < end){
conn.watch(startKey);
String hourStart = ISO_FORMAT.format(new Date());
String existing = conn.get(startKey);
Transaction trans = conn.multi();
if (existing != null && COLLATOR.compare(existing, hourStart) < 0){
trans.rename(destination, destination + ":last");
trans.rename(startKey, destination + ":pstart");
trans.set(startKey, hourStart);
}
//借助redis提供的最大值,最小值計算
String tkey1 = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
String tkey2 = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
trans.zadd(tkey1, value, "min");
trans.zadd(tkey2, value, "max");
trans.zunionstore(
destination,
new ZParams().aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.MIN),
destination, tkey1);
trans.zunionstore(
destination,
new ZParams().aggregate(ZParams.Aggregate.MAX),
destination, tkey2);
trans.del(tkey1, tkey2);
trans.zincrby(destination, 1, "count");
trans.zincrby(destination, value, "sum");
trans.zincrby(destination, value * value, "sumsq");
List<Object> results = trans.exec();
if (results == null){
continue;
}
return results.subList(results.size() - 3, results.size());
}
return null;
}需要注意的使用redis自帶的最大值最小值,計算,所以創建了2個臨時有序集合。其他的邏輯參照日志相關部分。
參考內容
《redis in action》
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。