您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
6.倒排索引和正排索引(doc value)
GET /_search
{
"took": 6,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 6,
"successful": 6,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 10,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": ".kibana",
"_type": "config",
"_id": "5.2.0",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"buildNum": 14695
}
}
]
}
}took:整個搜索請求花費了多少毫秒
hits.total:本次搜索,返回了幾條結果
hits.max_score:本次搜索的所有結果中,最大的相關度分數是多少,每一條document對于search的相關度,越相關,_score分數越大,排位越靠前
hits.hits:默認查詢前10條數據,完整數據,_score降序排序
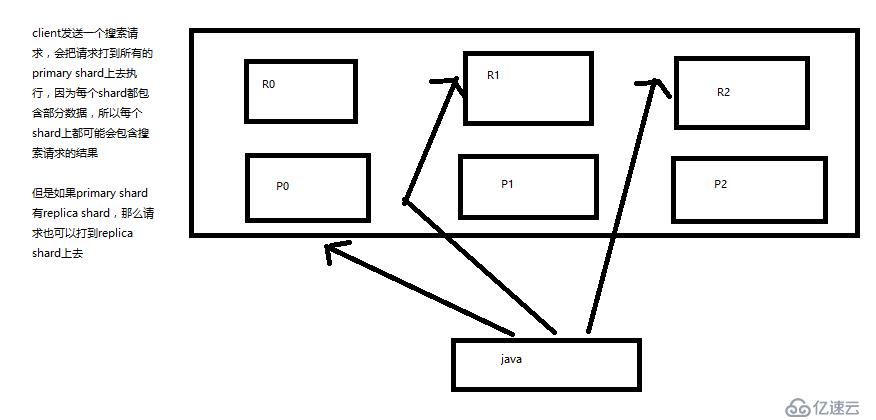
shards:shards fail的條件(primary和replica全部掛掉),不影響其他shard。默認情況下來說,一個搜索請求,會打到一個index的所有primary shard上去,當然了,每個primary shard都可能會有一個或多個replic shard,所以請求也可以到primary shard的其中一個replica shard上去。
timeout:默認無timeout,latency平衡completeness,手動指定timeout,timeout查詢執行機制
格式:timeout=10ms,timeout=1s,timeout=1m
GET /_search?timeout=10m
2.1、multi-index和multi-type搜索模式
如何一次性搜索多個index和多個type下的數據
/_search:所有索引,所有type下的所有數據都搜索出來
/index1/_search:指定一個index,搜索其下所有type的數據
/index1,index2/_search:同時搜索兩個index下的數據
/*1,*2/_search:按照通配符去匹配多個索引
/index1/type1/_search:搜索一個index下指定的type的數據
/index1/type1,type2/_search:可以搜索一個index下多個type的數據
/index1,index2/type1,type2/_search:搜索多個index下的多個type的數據
/_all/type1,type2/_search:_all,可以代表搜索所有index下的指定type的數據
2.2、初步圖解簡單的搜索原理
3.1、使用es進行分頁搜索的語法
size,from
GET /_search?size=10
GET /_search?size=10&from=0
GET /_search?size=10&from=20
//分頁的上機實驗
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
"hits": {
"total": 9,
"max_score": 1,
//我們假設將這9條數據分成3頁,每一頁是3條數據,來實驗一下這個分頁搜索的效果
GET /test_index/test_type/_search?from=0&size=3
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 9,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "test_type",
"_id": "8",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"test_field": "test client 2"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "test_type",
"_id": "6",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"test_field": "tes test"
}
},
{
"_index": "test_index",
"_type": "test_type",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"test_field": "test4"
}
}
]
}
}3.2、deep paging問題?為什么會產生這個問題,它的底層原理是什么?

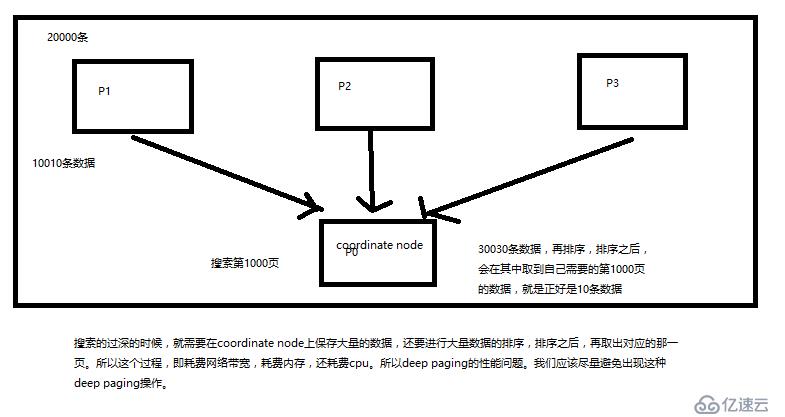
搜索過深的時候,就需要在coordinate node上保存大量的數據,還要進行大量數據的排序,排序之后,再取出對應的那一頁。所以這個過程,既消耗網絡帶寬,消耗內存,消耗CPU。所以應盡量避免。
4.1query string search語法和_all metedata
1、query string基礎語法
GET /test_index/test_type/_search?q=test_field:test
GET /test_index/test_type/_search?q=+test_field:test(必須包含)
GET /test_index/test_type/_search?q=-test_field:test(不包含)
一個是掌握q=field:search content的語法,還有一個是掌握+和-的含義
2、_all metadata的原理和作用
GET /test_index/test_type/_search?q=test
直接可以搜索所有的field,任意一個field包含指定的關鍵字就可以搜索出來。我們在進行中搜索的時候,難道是對document中的每一個field都進行一次搜索嗎?不是的
es中的_all元數據,在建立索引的時候,我們插入一條document,它里面包含了多個field,此時,es會自動將多個field的值,全部用字符串的方式串聯起來,變成一個長的字符串,作為_all field的值,同時建立索引
后面如果在搜索的時候,沒有對某個field指定搜索,就默認搜索_all field,其中是包含了所有field的值的
4.2query DSL
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2、Query DSL的基本語法
{
QUERY_NAME: {
ARGUMENT: VALUE,
ARGUMENT: VALUE,...
}
}
{
QUERY_NAME: {
FIELD_NAME: {
ARGUMENT: VALUE,
ARGUMENT: VALUE,...
}
}
}
示例:
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"test_field": "test"
}
}
}4.2.1如何組合多個搜索條件
搜索需求:title必須包含elasticsearch,content可以包含elasticsearch也可以不包含,author_id必須不為111
GET /website/article/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"title": "elasticsearch"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"content": "elasticsearch"
}
}
],
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"author_id": 111
}
}
]
}
}
}
GET /test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "name": "tom" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "hired": true }},
{ "bool": {
"must": { "match": { "personality": "good" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "rude": true }}
}}
],
"minimum_should_match": 1
}
}
}filter,僅僅只是按照搜索條件過濾出需要的數據而已,不計算任何相關度分數,對相關度沒有任何影響
query,會去計算每個document相對于搜索條件的相關度,并按照相關度進行排序
一般來說,如果你是在進行搜索,需要將最匹配搜索條件的數據先返回,那么用query;如果你只是要根據一些條件篩選出一部分數據,不關注其排序,那么用filter
除非是你的這些搜索條件,你希望越符合這些搜索條件的document越排在前面返回,那么這些搜索條件要放在query中;如果你不希望一些搜索條件來影響你的document排序,那么就放在filter中即可
filter,不需要計算相關度分數,不需要按照相關度分數進行排序,同時還有內置的自動cache最常使用filter的數據
query,相反,要計算相關度分數,按照分數進行排序,而且無法cache結果
1、match all
GET /_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
2、match
GET /_search
{
"query": { "match": { "title": "my elasticsearch article" }}
}
3、multi match
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "test",
"fields": ["test_field", "test_field1"]
}
}
}
4、range query
GET /company/employee/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30
}
}
}
}
5、term query
GET /test_index/test_type/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"test_field": "test hello"
}
}
}
6、terms query
GET /_search
{
"query": { "terms": { "tag": [ "search", "full_text", "nosql" ] }}
}
7、exist query(2.x中的查詢,現在已經不提供了)4.2.5、多搜索條件組合查詢
bool
must,must_not,should,filter
每個子查詢都會計算一個document針對它的相關度分數,然后bool綜合所有分數,合并為一個分數,當然filter是不會計算分數的
{
"bool": {
"must": { "match": { "title": "how to make millions" }},
"must_not": { "match": { "tag": "spam" }},
"should": [
{ "match": { "tag": "starred" }}
],
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "range": { "date": { "gte": "2014-01-01" }}},
{ "range": { "price": { "lte": 29.99 }}}
],
"must_not": [
{ "term": { "category": "ebooks" }}
]
}
}
}
}(1)往es里面直接插入數據,es會自動建立索引,同時建立type以及對應的mapping
(2)mapping中就自動定義了每個field的數據類型
(3)不同的數據類型(比如說text和date),可能有的是exact value,有的是full text
(4)exact value,在建立倒排索引的時候,分詞的時候,是將整個值一起作為一個關鍵詞建立到倒排索引中的;full text,會經歷各種各樣的處理,分詞,normaliztion(時態轉換,同義詞轉換,大小寫轉換),才會建立到倒排索引中
(5)同時呢,exact value和full text類型的field就決定了,在一個搜索過來的時候,對exact value field或者是full text field進行搜索的行為也是不一樣的,會跟建立倒排索引的行為保持一致;比如說exact value搜索的時候,就是直接按照整個值進行匹配,full text query string,也會進行分詞和normalization再去倒排索引中去搜索
(6)可以用es的dynamic mapping,讓其自動建立mapping,包括自動設置數據類型;也可以提前手動創建index和type的mapping,自己對各個field進行設置,包括數據類型,包括索引行為,包括分詞器,等等
mapping,就是index的type的元數據,每個type都有一個自己的mapping,決定了數據類型,建立倒排索引的行為,還有進行搜索的行為
插入幾條數據,讓es自動建立一個索引
PUT /website/article/1
{
"post_date": "2017-01-01",
"title": "my first article",
"content": "this is my first article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}
PUT /website/article/2
{
"post_date": "2017-01-02",
"title": "my second article",
"content": "this is my second article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}
PUT /website/article/3
{
"post_date": "2017-01-03",
"title": "my third article",
"content": "this is my third article in this website",
"author_id": 11400
}
嘗試各種搜索
GET /website/article/_search?q=2017 3條結果
GET /website/article/_search?q=2017-01-01 3條結果
GET /website/article/_search?q=post_date:2017-01-01 1條結果
GET /website/article/_search?q=post_date:2017 1條結果搜索結果為什么不一致,因為es自動建立mapping的時候,設置了不同的field不同的data type。不同的data type的分詞、搜索等行為是不一樣的。所以出現了_all field和post_date field的搜索表現完全不一樣。
下面解釋
GET /_search?q=2017 搜索的是_all field,document所有的field都會拼接成一個大串,進行分詞 2017-01-02 my second article this is my second article in this website 11400 doc1 doc2 doc3 2017 * * * 01 * 02 * 03 * _all,2017,自然會搜索到3個docuemnt ------------------------------------------------------------- GET /_search?q=2017-01-01 _all,2017-01-01,query string會用跟建立倒排索引一樣的分詞器去進行分詞 2017 01 01 ---------------------------------------------------------------- GET /_search?q=post_date:2017-01-01 date,會作為exact value去建立索引 doc1 doc2 doc3 2017-01-01 * 2017-01-02 * 2017-01-03 * post_date:2017-01-01,2017-01-01,doc1一條document ----------------------------------------------------------- GET /_search?q=post_date:2017,這個在這里不說,因為是es 5.2以后做的一個優化
5.1、query string分詞
query string必須以和index建立時相同的analyzer進行分詞
query string對exact value和full text的區別對待
date:exact value
_all:full text
比如我們有一個document,其中有一個field,包含的value是:hello you and me,建立倒排索引
我們要搜索這個document對應的index,搜索文本是hell me,這個搜索文本就是query string
query string,默認情況下,es會使用它對應的field建立倒排索引時相同的分詞器去進行分詞,分詞和normalization,只有這樣,才能實現正確的搜索
我們建立倒排索引的時候,將dogs --> dog,結果你搜索的時候,還是一個dogs,那不就搜索不到了嗎?所以搜索的時候,那個dogs也必須變成dog才行。才能搜索到。
知識點:不同類型的field,可能有的就是full text,有的就是exact value
post_date,date:exact value
_all:full text,分詞,normalization
1、核心的數據類型
string
byte,short,integer,long
float,double
boolean
date
2、dynamic mapping
true or false --> boolean
123 --> long
123.45 --> double
2017-01-01 --> date
"hello world" --> string/text
3、查看mapping
GET /index/_mapping/type
1、multivalue field
{ "tags": [ "tag1", "tag2" ]}
建立索引時與string是一樣的,數據類型不能混
2、empty field
null,[],[null]
3、object field
PUT /company/employee/1
{
"address": {
"country": "china",
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
},
"name": "jack",
"age": 27,
"join_date": "2017-01-01"
}
address:object類型
{
"company": {
"mappings": {
"employee": {
"properties": {
"address": {
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"country": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"province": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"join_date": {
"type": "date"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}6.倒排索引和正排索引(doc value)
搜索的時候,要依靠倒排索引;排序的時候,需要依靠正排索引,看到每個document的每個field,然后進行排序,所謂的正排索引,其實就是doc values
在建立索引的時候,一方面會建立倒排索引,以供搜索用;一方面會建立正排索引,也就是doc values,以供排序,聚合,過濾等操作使用
doc values是被保存在磁盤上的,此時如果內存足夠,os會自動將其緩存在內存中,性能還是會很高;如果內存不足夠,os會將其寫入磁盤上
倒排索引
doc1: hello world you and me doc2: hi, world, how are you
word doc1 doc2
hello * world * * you * * and * me * hi * how * are * |
正排索引
oc1: { "name": "jack", "age": 27 } doc2: { "name": "tom", "age": 30 } document name age doc1 jack 27 doc2 tom 30 |
什么是分詞器:切分詞語,normalization(提升recall召回率)
給你一段句子,然后將這段句子拆分成一個一個的單個的單詞,同時對每個單詞進行normalization(時態轉換,單復數轉換),分詞器
recall,召回率:搜索的時候,增加能夠搜索到的結果的數量
character filter:在一段文本進行分詞之前,先進行預處理,比如說最常見的就是,過濾html標簽(<span>hello<span> --> hello),& --> and(I&you --> I and you)
tokenizer:分詞,hello you and me --> hello, you, and, me
token filter:lowercase,stop word,synonymom,dogs --> dog,liked --> like,Tom --> tom,a/the/an --> 干掉,mother --> mom,small --> little
一個分詞器,很重要,將一段文本進行各種處理,最后處理好的結果才會拿去建立倒排索引
1、exact value
2017-01-01,exact value,搜索的時候,必須輸入2017-01-01,才能搜索出來
如果你輸入一個01,是搜索不出來的
2、full text
(1)縮寫 vs. 全程:cn vs. china
(2)格式轉化:like liked likes
(3)大小寫:Tom vs tom
(4)同義詞:like vs love
1、如何建立索引
analyzed:進行分詞
not_analyzed:不進行分詞
no:不建立索引,不被查詢
2、修改mapping
只能創建index時手動建立mapping,或者新增field mapping,但是不能update field mapping
PUT /website
{
"mappings": {
"article": {
"properties": {
"author_id": {
"type": "long"
},
"title": {
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "english"
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"post_date": {
"type": "date"
},
"publisher_id": {
"type": "text",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}GET /search
{}
GET /index1,index2/type1,type2/search
{}
GET /_search
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10
}HTTP協議,一般不允許get請求帶上request body,但是因為get更加適合描述查詢數據的操作,因此還是這么用了
GET /_search?from=0&size=10
POST /_search
{
"from":0,
"size":10
}
碰巧,很多瀏覽器,或者是服務器,也都支持GET+request body模式
如果遇到不支持的場景,也可以用POST /_search
relevance score算法,簡單來說,就是計算出,一個索引中的文本,與搜索文本,他們之間的關聯匹配程度
Elasticsearch使用的是 term frequency/inverse document frequency算法,簡稱為TF/IDF算法
Term frequency:搜索文本中的各個詞條在field文本中出現了多少次,出現次數越多,就越相關
搜索請求:hello world
doc1:hello you, and world is very good
doc2:hello, how are you
Inverse document frequency:搜索文本中的各個詞條在整個索引的所有文檔中出現了多少次,出現的次數越多,就越不相關
搜索請求:hello world
doc1:hello, today is very good
doc2:hi world, how are you
比如說,在index中有1萬條document,hello這個單詞在所有的document中,一共出現了1000次;world這個單詞在所有的document中,一共出現了100次
doc2更相關
Field-length norm:field長度,field越長,相關度越弱
搜索請求:hello world
doc1:{ "title": "hello article", "content": "babaaba 1萬個單詞" }
doc2:{ "title": "my article", "content": "blablabala 1萬個單詞,hi world" }
hello world在整個index中出現的次數是一樣多的
doc1更相關,title field更短
1、preference
決定了哪些shard會被用來執行搜索操作
_primary, _primary_first, _local, _only_node:xyz, _prefer_node:xyz, _shards:2,3
bouncing results問題,兩個document排序,field值相同;不同的shard上,可能排序不同;每次請求輪詢打到不同的replica shard上;每次頁面上看到的搜索結果的排序都不一樣。這就是bouncing result,也就是跳躍的結果。
搜索的時候,是輪詢將搜索請求發送到每一個replica shard(primary shard),但是在不同的shard上,可能document的排序不同
解決方案就是將preference設置為一個字符串,比如說user_id,讓每個user每次搜索的時候,都使用同一個replica shard去執行,就不會看到bouncing results了
2、timeout,已經講解過原理了,主要就是限定在一定時間內,將部分獲取到的數據直接返回,避免查詢耗時過長
3、routing,document文檔路由,_id路由,routing=user_id,這樣的話可以讓同一個user對應的數據到一個shard上去
4、search_type
default:query_then_fetch
dfs_query_then_fetch,可以提升revelance sort精準度
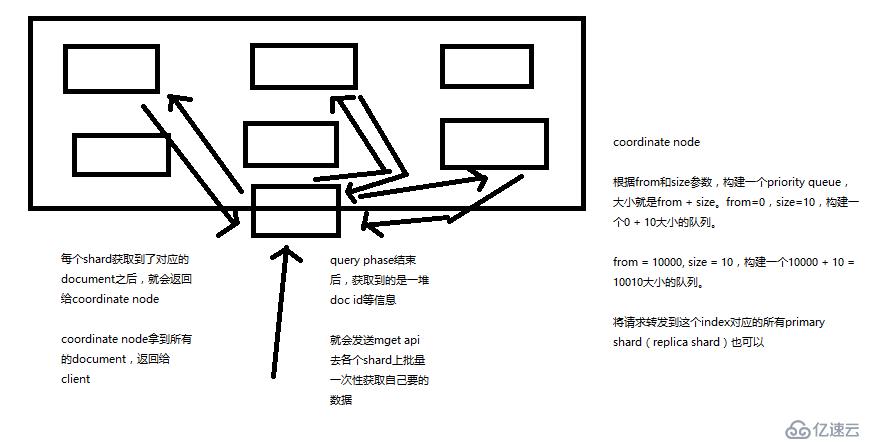
1、query phase
(1)搜索請求發送到某一個coordinate node,構構建一個priority queue,長度以paging操作from和size為準,默認為10
(2)coordinate node將請求轉發到所有shard,每個shard本地搜索,并構建一個本地的priority queue
(3)各個shard將自己的priority queue返回給coordinate node,并構建一個全局的priority queue
2、replica shard如何提升搜索吞吐量
一次請求要打到所有shard的一個replica/primary上去,如果每個shard都有多個replica,那么同時并發過來的搜索請求可以同時打到其他的replica上去

1、fetch phbase工作流程
(1)coordinate node構建完priority queue之后,就發送mget請求去所有shard上獲取對應的document
(2)各個shard將document返回給coordinate node
(3)coordinate node將合并后的document結果返回給client客戶端
2、一般搜索,如果不加from和size,就默認搜索前10條,按照_score排序
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。