溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
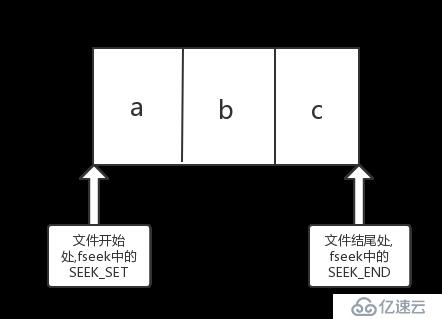
c語言中文件的結尾指的是文件的最后一個字符的下一個字符
例如:文件a.txt中有三個字符abc,即文件大小為3
那么文件的實際內容如下圖.
echo -n abc > a.txt
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
FILE* fp = fopen("a.txt","r");
if(NULL==fp){
perror("fopen"),exit(-1);
}
int c;
while(!feof(fp)){ //當文件指針第一次到達文件結尾處時,feof函數返回的是0.
c = getc(fp);
printf("c=%d\n",c);
if(ferror(fp)){
perror("ferror"),exit(-1);
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}c=97
c=98
c=99
c=-1
所以正確做法應該是
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void){
FILE* fp = fopen("a.txt","r");
if(NULL==fp){
perror("fopen"),exit(-1);
}
int c;
while((c=getc(fp))!=EOF){
printf("c=%d\n",c);
if(ferror(fp)){
perror("ferror"),exit(-1);
}
}
return 0;
}c=97
c=98
c=99
如何讀出文件最后一個字符c,如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(void){
FILE* fp = fopen("a.txt","r");
fseek(fp,-1,SEEK_END);
char c;
c = getc(fp);
printf("c=%d\n",c);
fseek(fp,0,SEEK_END);
printf("feof(fp)=%d\n",feof(fp));//此時在文件結尾處
//即文件最后一個字符(即c字符)的下一個字符處
//結果為0
c = getc(fp);
printf("c=%d\n",c); //c=-1
printf("feof(fp)=%d\n",feof(fp));//結果為1
return 0;
}c=99
feof(fp)=0
c=-1
feof(fp)=1
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。