您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“spring初始化源碼分析”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“spring初始化源碼分析”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
通過ClassPathXmlApplicationContext構造方法進入 refresh方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//容器刷新前做一些準備工作
prepareRefresh();
// 創建DefaultListableBeanFactory對象,解析出所有BeanDefinition信息,
//注冊緩存在DefaultListableBeanFactory的beanDefinitionMap屬性中,供后面創建bean對象時使用
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 為beanFactory提供一些標準配置,如:類加載器、環境變量等
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 為beanFactory提供一些個性配置,通過在子上下文中復寫該方法來實現
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//創建實現BeanFactoryPostProcessor的實現類,并執行接口的方法。
//該方法執行完后會輸出實例中的1-7步的日志
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//創建BeanPostProcessor的實現類,并注冊到BeanFactoryPostProcessor的beanPostProcessors列表中,
//在后面創建普通非lazy對象時會遍歷該列表回調前置和后置方法
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//跟國際化消息相關,沒去研究過
initMessageSource();
//初始化該上下文的事件廣播
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//模板方法,在不同的容器刷新的時候可以自定義邏輯
onRefresh();
//創建ApplicationListener的實現類,并注冊到該上下文中
registerListeners();
//完成所有剩余的非lazy的bean的創建
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//上下文的創建完成的一些設置和緩存清理,并發布創建完成事件
finishRefresh();
}catch (BeansException ex) {
……
}finally {
//Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
//might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}先看《spring初始化源碼淺析之關鍵類和擴展接口》文中代碼執行結果:

首先找到beanFactory的入口方法,如下
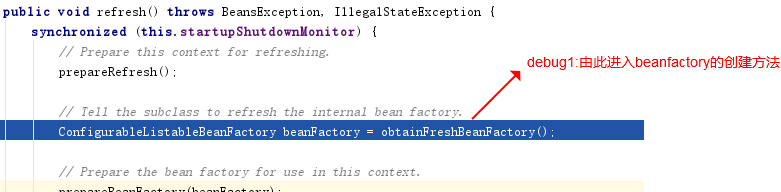
繼續debug進入refreshBeanFactory方法,如下

從下圖中可以看到,XmlBeanDefinitionReader為加載BeanDefinition的關鍵類,而將beanFactoy作為構造參數主要是為了將創建好的BeanDefinition對象注冊到beanFactory中,后面會貼出相應的代碼,如下
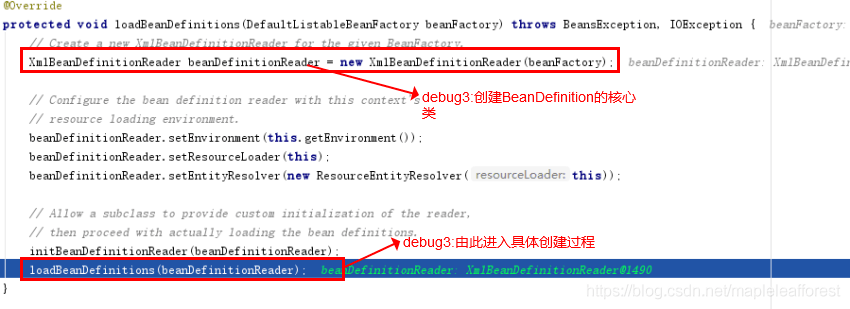
繼續斷點進入XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions方法,可見入參為main方法中的指定配置文件的名稱,如下
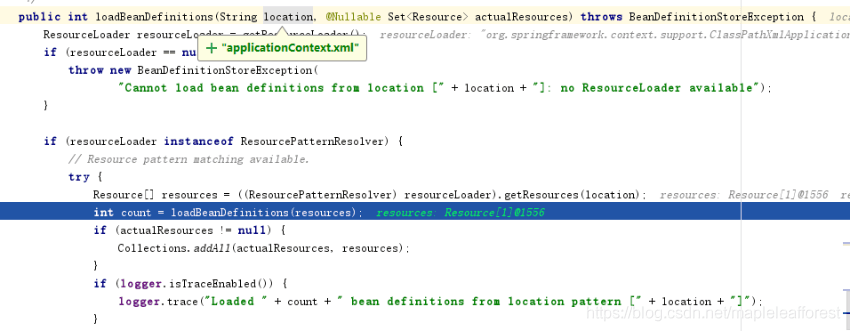
斷點繼續走,跳過將applicationContext.xml文件解析成Document的過程,進入registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource)方法,入參為applicationContext.xml對應的Document對象,該方法構造一個BeanDefinitionDocumentReader對象來具體的負責從doc對象創建BeanDefinition對象,并注冊到beanFactory中,如下

注意 BeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions方法一個入參為XmlReaderContext對象,該對象的reader即為前面創建XmlBeanDefinitionReader對象。
繼續斷點進入以下方法:
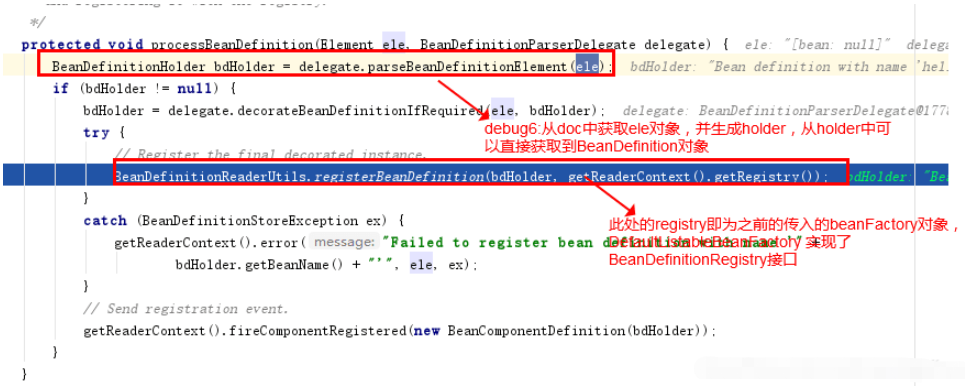
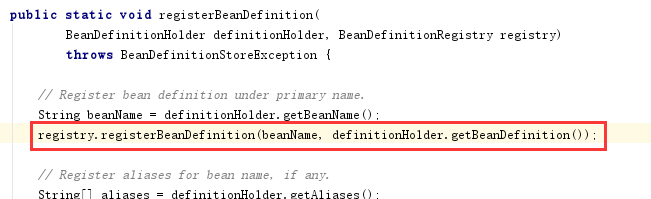
最后進入DefaultListableBeanFactory的registerBeanDefinition方法,最后將創建好的BeanDefinition對象緩存到DefaultListableBeanFactory的一個ConcurrentHashMap中

最終將配置文件中所有的bean配置轉成BeanDefinition對象緩存起來,供后面創建具體的bean對象使用。
進入方法發現邏輯都交給PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate類來處理:
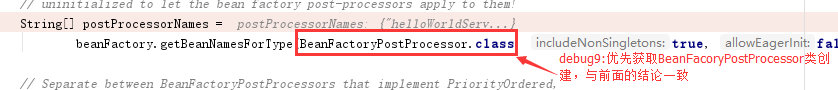
斷點一直走到下面方法,先嘗試從單利的緩存中去找,找不到再通過單例工廠類創建對象:
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
………………
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
…………
if (newSingleton) {
//添加到單例緩存中
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
//由于緩存單例對象的 hashmap沒有hellword對象,進入singletonFactory.getObject()方法 ,
//繼續斷點到 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory的doCreateBean放法
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//創建bean對象的包裝器,beanName=hellowordService,
//該方法執行完成后輸出第一步日志:1->HelloWorldService constructor
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();//創建bean對象
…………
try {
//從RootBeanDefinition 獲取屬性信息并填充到instanceWrapper對象
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//進入初始化bean對象的操作
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
}
…………
//將創建好的bean對象注冊到緩存起來
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
…………
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
// 開始調用各種ware接口的方法,會輸出2、3、4步的日志
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//執行BeanPostProcessor的前置方法postProcessBeforeInitialization,由于
//ApplicationContextAwareProcessor實現該接口,該類中會執行很多*Aware的類,而hellwordService
//實現ApplicationContextAware類,所在會輸出:4->ApplicationContextAware.setApplicationContext:
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//init bean對象
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//執行BeanPostProcessor的后置方法postProcessAfterInitialization,
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
//日志輸出 2->BeanNameAware.setBeanName:helloWorldService
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
ClassLoader bcl = getBeanClassLoader();
if (bcl != null) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(bcl);
}
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
//日志輸出 3->BeanFactoryAware.setBeanFactory:
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
…………
protected void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd)
throws Throwable {
boolean isInitializingBean = (bean instanceof InitializingBean);
if (isInitializingBean && (mbd == null || !mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod("afterPropertiesSet"))) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking afterPropertiesSet() on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
try {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
catch (PrivilegedActionException pae) {
throw pae.getException();
}
}
else {
//日志輸出:5->InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
}
if (mbd != null && bean.getClass() != NullBean.class) {
String initMethodName = mbd.getInitMethodName();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(initMethodName) &&
!(isInitializingBean && "afterPropertiesSet".equals(initMethodName)) &&
!mbd.isExternallyManagedInitMethod(initMethodName)) {
//執行自定義init method方法,輸出日志 :6->init method
invokeCustomInitMethod(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
}
}
}最后回到getSingleton方法:
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
……
//添加到單例緩存中
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}hellwordService對象創建完畢后,便執行 下一步的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,輸出第7步日志:
7->BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory 將peopleService的content屬性修改為i am ok
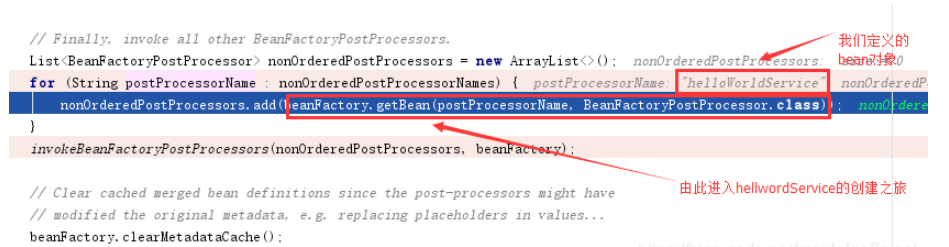
到此為止,invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);執行完畢
可以看到代碼和invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)的代碼模式幾乎一樣,在本方法中會創建所有實現BeanPostProcessor接口類并注冊到beanFactory中供后面對象創建時回調,代碼不再做分析
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}protected void registerListeners() {
// Register statically specified listeners first.
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {
//hellowordService便在此處注冊
getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);
}
…………
}斷點直接進入一下代碼:
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Boolean>)
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
//所有非lazy對象便在此處創建,如實例中的peopleServcie,對象創建過程前面已分析
//peopleServcie的創建過程回掉beanpostProcessors的前置和后置方法,輸出日志:
//8->BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization->peopleService
//9->BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization->peopleService
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
…………
}protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
//發布ContextRefreshedEvent事件,輸入日志
//10->ApplicationListener.onApplicationEvent:
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}關于“spring初始化源碼分析”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。