溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“Python中set的基本使用方法有哪些”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“Python中set的基本使用方法有哪些”文章吧。
(1) 無序性
(2) 確定性
(3) 不重復性
內部進行 可迭代性的 for 循環
例子:

2.1.1 增
add(self, *args, **kwargs) copy(self, *args, **kwargs)
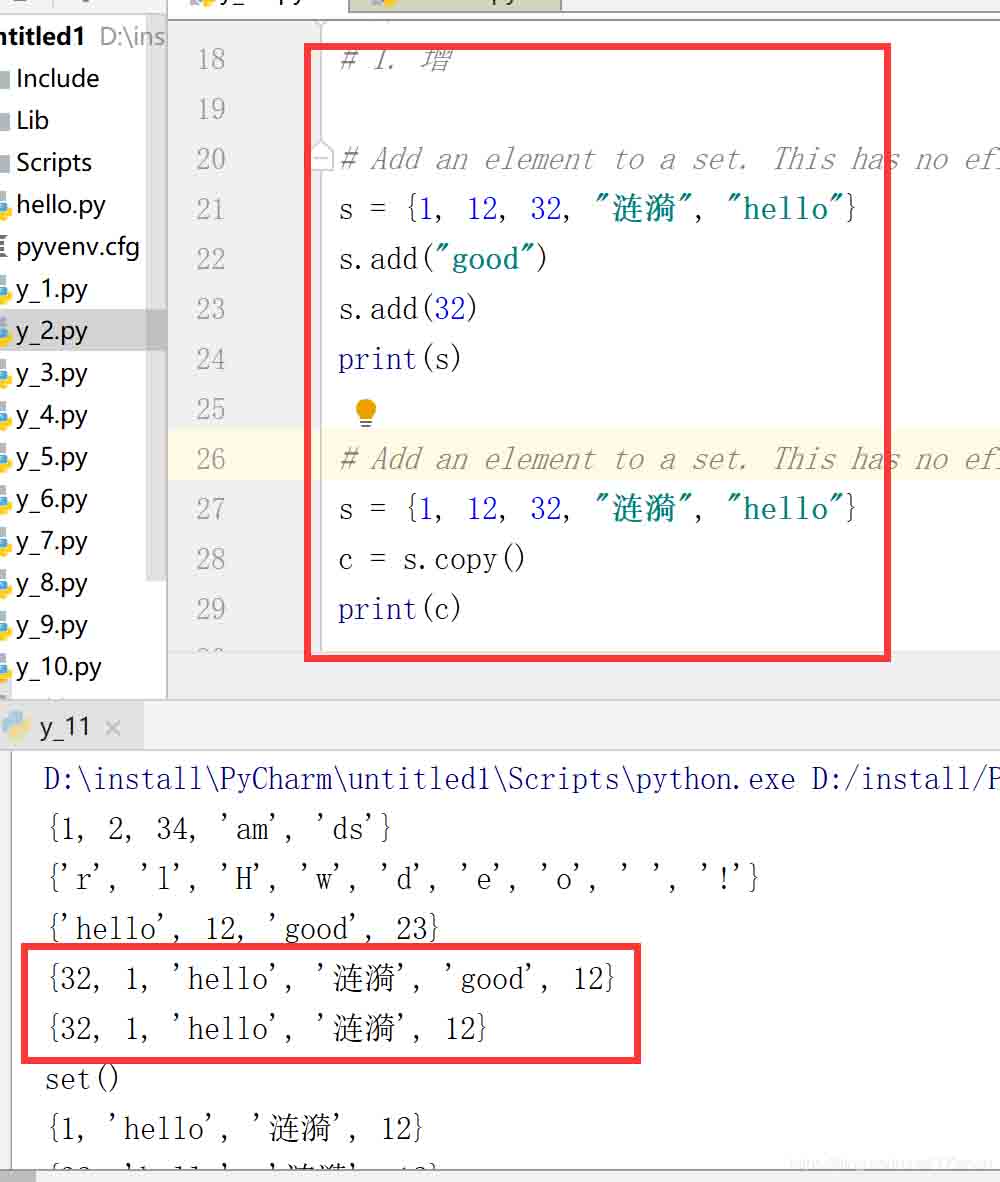
# 1. 增
# Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
s.add("good")
s.add(32)
print(s)
# Add an element to a set. This has no effect if the element is already present.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
c = s.copy()
print(c)結果:
2.1.1 刪
clear(self, *args, **kwargs) pop(self, *args, **kwargs) remove(self, *args, **kwargs) discard(self, *args, **kwargs)
# 2. 刪
# Remove all elements from this set.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
s.clear()
print(s)
# Remove and return an arbitrary set element. Raises KeyError if the set is empty.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
s.pop()
print(s)
# Remove an element from a set; it must be a member. If the element is not a member, raise a KeyError.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
s.remove(1)
# s.remove("good")
print(s)
# Remove an element from a set if it is a member. If the element is not a member, do nothing.
s = {1, 12, 32, "漣漪", "hello"}
s.discard(1)
s.discard("good")
print(s)結果:
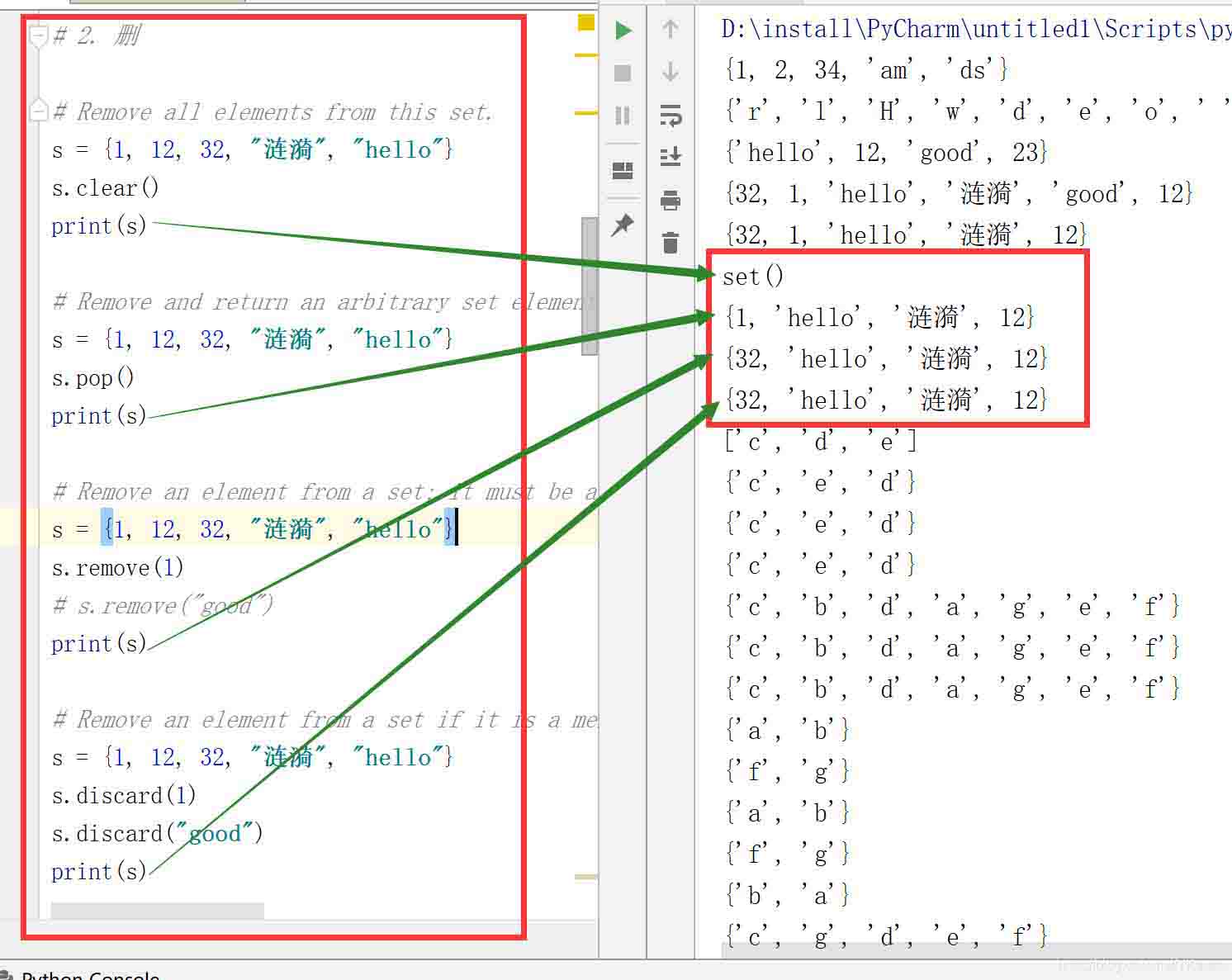
pop() 是隨機刪除。
remove() 和 discard() 指定刪除,但是指定不存在的元素時,remove() 會報錯,而 discard() 不會報錯
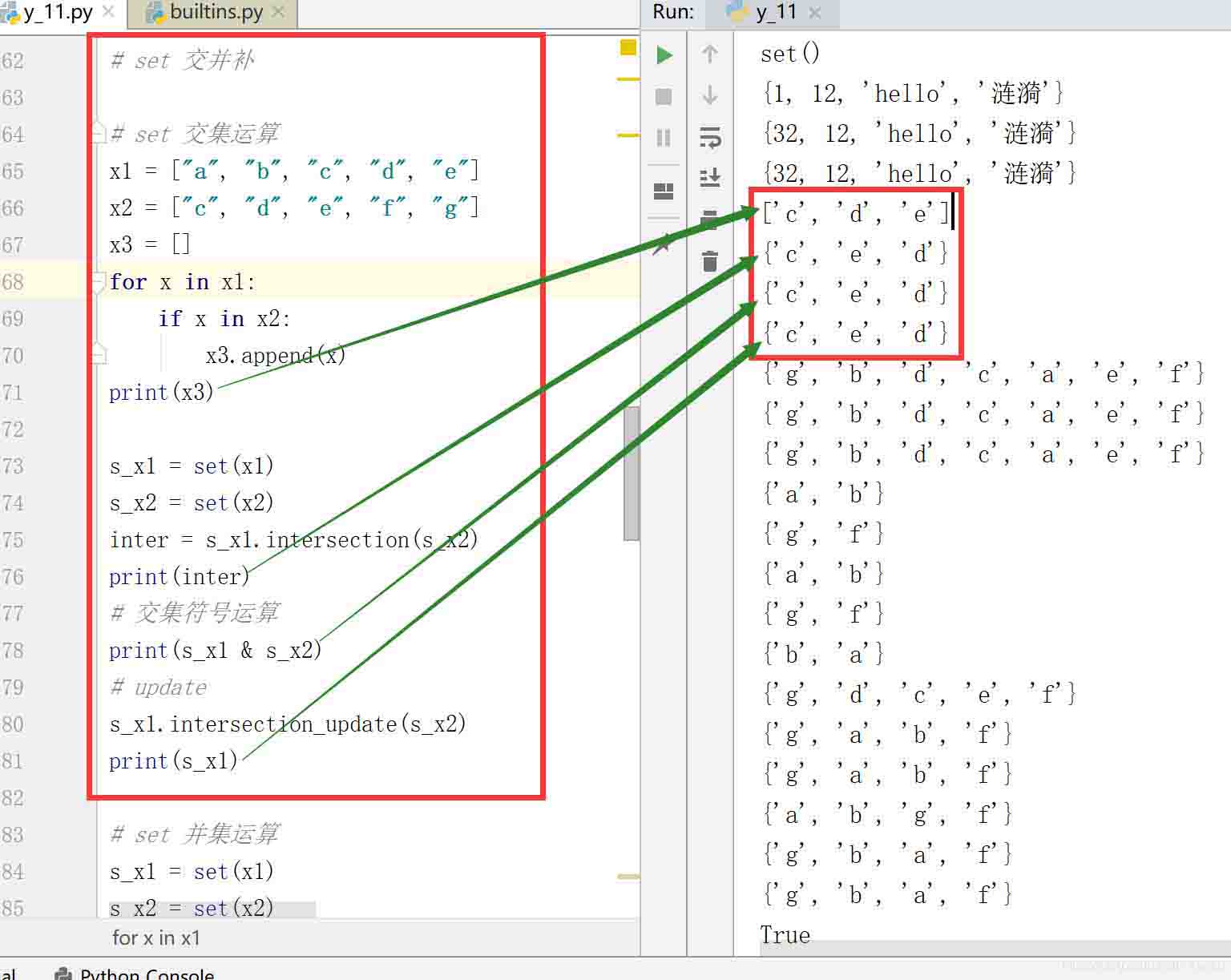
2.2.1 set 交集運算
# set 交集運算 x1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"] x2 = ["c", "d", "e", "f", "g"] x3 = [] for x in x1: if x in x2: x3.append(x) print(x3) s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) inter = s_x1.intersection(s_x2) print(inter) # 交集符號運算 print(s_x1 & s_x2) # update s_x1.intersection_update(s_x2) print(s_x1)
結果:
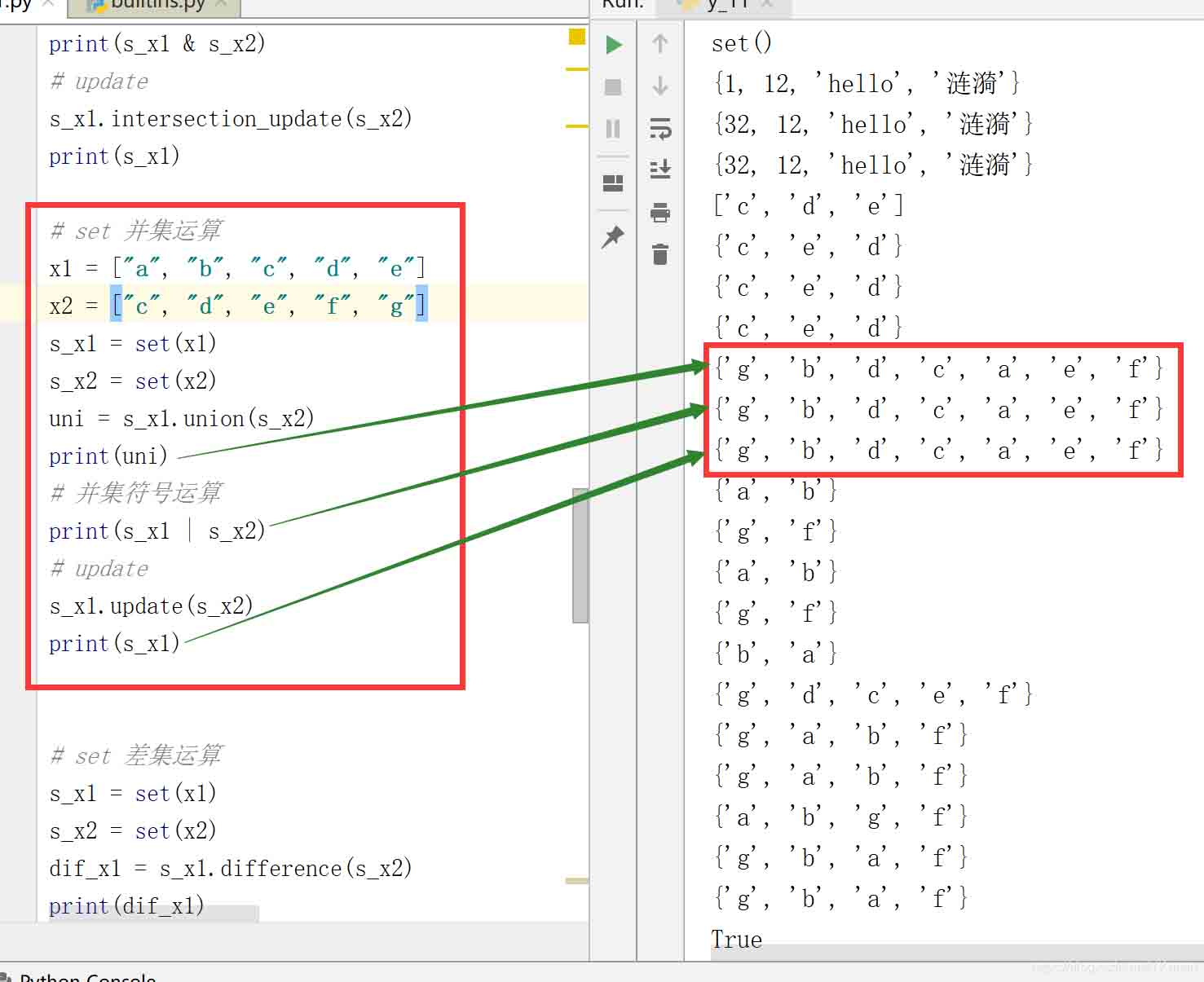
2.2.2 set 并集運算
# set 并集運算 x1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"] x2 = ["c", "d", "e", "f", "g"] s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) uni = s_x1.union(s_x2) print(uni) # 并集符號運算 print(s_x1 | s_x2) # update s_x1.update(s_x2) print(s_x1)
結果:
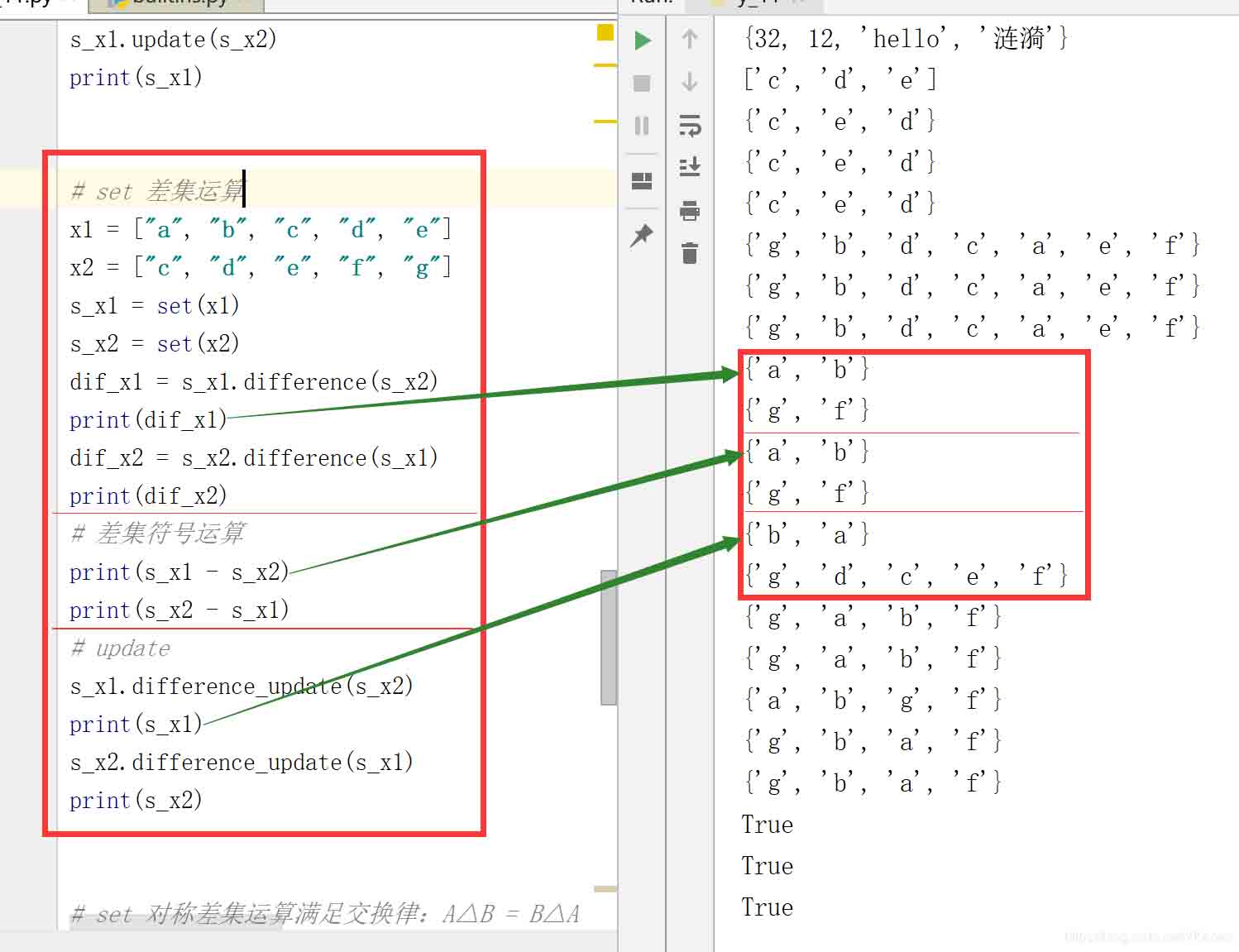
2.2.3 set 差集運算
# set 差集運算 x1 = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e"] x2 = ["c", "d", "e", "f", "g"] s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) dif_x1 = s_x1.difference(s_x2) print(dif_x1) dif_x2 = s_x2.difference(s_x1) print(dif_x2) # 差集符號運算 print(s_x1 - s_x2) print(s_x2 - s_x1) # update s_x1.difference_update(s_x2) print(s_x1) s_x2.difference_update(s_x1) print(s_x2)
結果:
2.2.4 set 對稱差集運算
# set 對稱差集運算滿足交換律:A△B = B△A s_x1 = set(x1) s_x2 = set(x2) sym = s_x1.symmetric_difference(s_x2) print(sym) # 對稱差集符號運算 print(s_x1 ^ s_x2) print(s_x1 - s_x2 | s_x2 - s_x1) print((s_x1 | s_x2) - (s_x2 & s_x1)) # update s_x1.symmetric_difference_update(s_x2) print(s_x1)
結果:

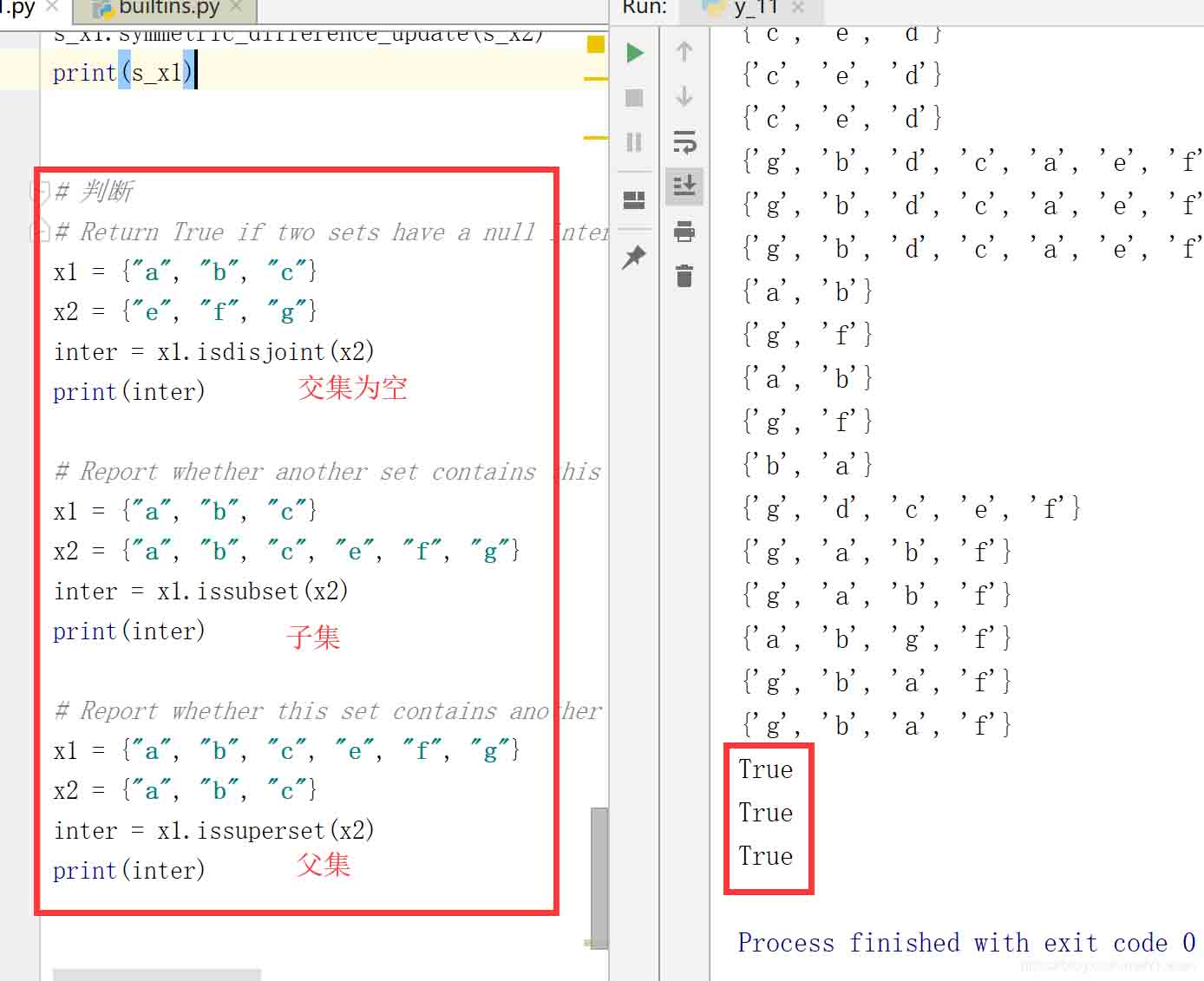
2.2.5 set 邏輯判斷運算
# 判斷
# Return True if two sets have a null intersection.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c"}
x2 = {"e", "f", "g"}
inter = x1.isdisjoint(x2)
print(inter)
# Report whether another set contains this set.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c"}
x2 = {"a", "b", "c", "e", "f", "g"}
inter = x1.issubset(x2)
print(inter)
# Report whether this set contains another set.
x1 = {"a", "b", "c", "e", "f", "g"}
x2 = {"a", "b", "c"}
inter = x1.issuperset(x2)
print(inter)結果:
以上就是關于“Python中set的基本使用方法有哪些”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。