您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了SpringBoot中怎么使用Redis的相關知識,內容詳細易懂,操作簡單快捷,具有一定借鑒價值,相信大家閱讀完這篇SpringBoot中怎么使用Redis文章都會有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看吧。
maven依賴如下,需要說明的是,spring-boot-starter-data-redis里默認是使用lettuce作為redis客戶端的驅動,但是lettuce其實用的比較少,我們常用的還是jedis作為客戶端的驅動,所以這里排除掉lettuce,引入jedis:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>io.lettuce</groupId> <artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </dependency>
spring data redis中依賴的關系:
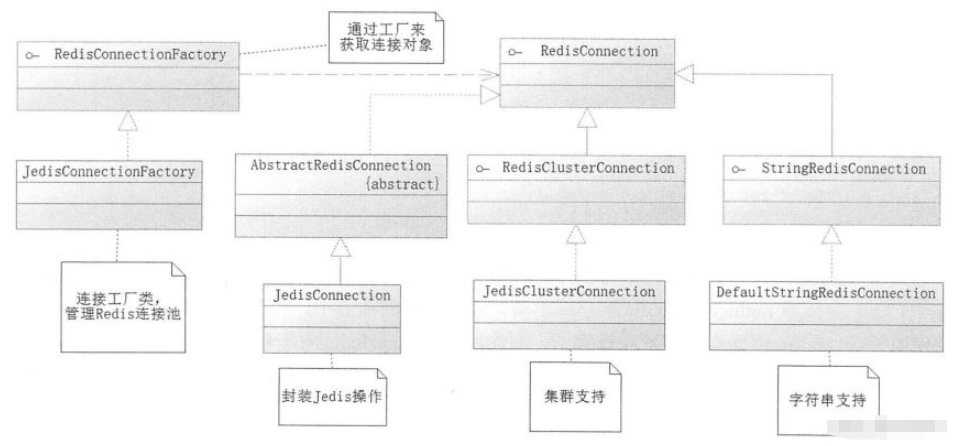
這個依賴關系想表達的是,Spring 是通過 RedisConnection操作Redis的,RedisConnection 則對原生的 Jedis 行封裝。要獲取RedisConnection接口對象是通過RedisConnectionFactory 生成的 。
配置文件進行配置:
# Redis 連接配置 # 單機 Redis spring.redis.host=127.0.0.1 spring.redis.port=6379 # 連接池配置 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=30 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-total=50 spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=2000ms
代碼進行配置:
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
private RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory = null;
@Bean
public RedisConnectionFactory initRedisConnectionFactory(){
if(connectionFactory!=null){
return connectionFactory;
}
JedisPoolConfig poolConfig =new JedisPoolConfig();
//最大空閑數
poolConfig.setMaxIdle(30);
//最大連接數
poolConfig.setMaxTotal(50);
//最大等待毫秒數
poolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(2000);
//創建Jedis連接工廠
JedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory=new JedisConnectionFactory(poolConfig);
//獲取單機的redis配置,如果是集群的話用集群配置類
RedisStandaloneConfiguration rscfg=connectionFactory.getStandaloneConfiguration();
connectionFactory.setHostName("127.0.0.1");
connectionFactory.setPort(6379);
return connectionFactory;
}
}這里要說明的是如果是直接使用RedisConnection來操作redis就需要我們手動去找RedisConnectionFactory拿RedisConnection,并且需要每次手動關閉RedisConnection。所以Spring Data Redis里面提供了RedisTemplate來方便操作,其封裝自jedis,屏蔽了資源獲取和釋放的步驟。
使用RedisTemplate的時候要注意的核心是它的序列化器,RedisTemplate有多種序列化器,不同的序列化器在鍵值寫入、讀出redis的過程中使用的序列化方式會不同,序列化出來的結果也會不同。比如處理字符就需要用字符串專用的序列化器、處理對象需要使用對象專用的序列化器。
目前有的序列化器如下:
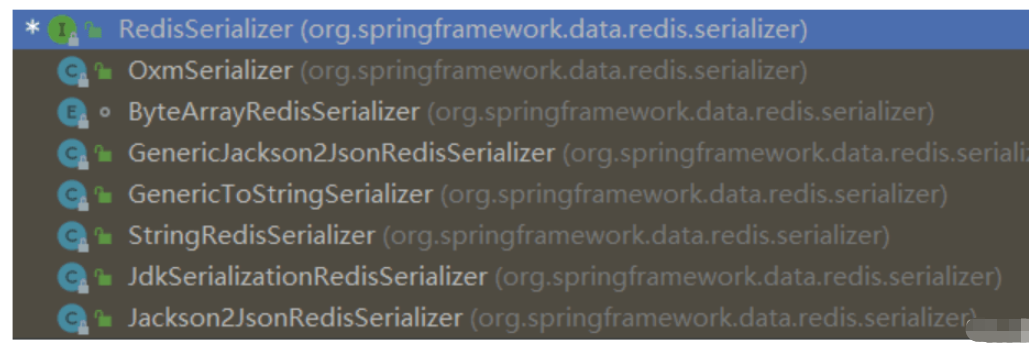
StringRedisSerializer:
StringRedisSerializer 是 RedisTemplate 默認使用的 Key 和 Value 的序列化器,它將字符串序列化為字節數組,使用 UTF-8 編碼。由于 Redis 中 Key 和 Value 都是字符串,因此默認的 StringRedisSerializer 序列化器已經可以滿足大部分情況的需要。
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer:
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 是一個基于 Jackson 的 Redis Key 和 Value 的序列化器,它可以將對象序列化為 JSON 格式的字符串,并存儲到 Redis 中。使用 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer 序列化器需要添加 Jackson 的依賴,可以將對象轉換為 JSON 格式的字符串,也可以將 JSON 格式的字符串轉換為對象。
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer:
JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 是一種基于 Java 自帶的序列化方式的序列化器,它可以將對象序列化為字節數組進行存儲。雖然 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer 簡單易用,但是它的效率比較低,序列化后的字節數組也比較大,不適合存儲大量的數據。
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer:
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer 是一個支持泛型的 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer,它可以序列化任意類型的對象,并將對象序列化為 JSON 格式的字符串。它在序列化和反序列化時都需要指定目標類型。
OxmSerializer:
OxmSerializer 是一種基于 Spring 的 O/X 映射框架的序列化器,它支持將對象序列化為 XML 格式的字符串。雖然 OxmSerializer 靈活性較高,但是序列化和反序列化的性能比較低,不適合存儲大量的數據。
總之,在選擇序列化器時需要根據實際情況進行選擇,根據數據類型和性能要求選擇合適的序列化器。
使用的時候直接set進去即可,set的時候給了很多生效粒度選擇,是對所有redis類型的數據結構都生效,還是對某一類redis的數據結構類型生效:
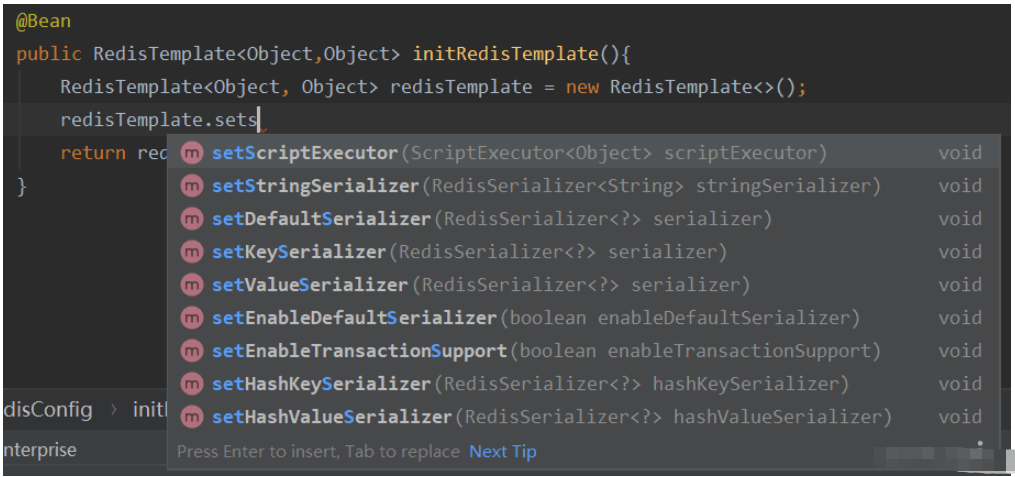
比如我想使用String序列化器,在全局都生效:
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> initRedisTemplate(){
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
redisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
return redisTemplate;
}以下是使用RedisTemplate操作redis基本數據類型的代碼示例:
要注意的是@Bean定義RedisTemplate的時候泛型要和使用時的泛型對齊。
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.HashOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ListOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.SetOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ZSetOperations;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class RedisService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public void setString(String key, String value) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
}
public String getString(String key) {
return stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
public void setHash(String key, String hashKey, Object value) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> hashOps = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hashOps.put(key, hashKey, value);
}
public Object getHash(String key, String hashKey) {
HashOperations<String, String, Object> hashOps = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
return hashOps.get(key, hashKey);
}
public void setList(String key, Object value) {
ListOperations<String, Object> listOps = redisTemplate.opsForList();
listOps.rightPush(key, value);
}
public Object getList(String key, long index) {
ListOperations<String, Object> listOps = redisTemplate.opsForList();
return listOps.index(key, index);
}
public void setSet(String key, Object value) {
SetOperations<String, Object> setOps = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
setOps.add(key, value);
}
public Object getSet(String key) {
SetOperations<String, Object> setOps = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
return setOps.members(key);
}
public void setZSet(String key, Object value, double score) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> zsetOps = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
zsetOps.add(key, value, score);
}
public Object getZSet(String key, long start, long end) {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> zsetOps = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
return zsetOps.range(key, start, end);
}
}以下是使用事務的代碼示例:
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
public void transactionalOperation() {
// 開啟 Redis 事務
redisTemplate.multi();
try {
// 執行多個 Redis 命令
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key1", "value1");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key2", "value2");
// 提交事務
redisTemplate.exec();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 回滾事務
redisTemplate.discard();
}
}關于“SpringBoot中怎么使用Redis”這篇文章的內容就介紹到這里,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家對“SpringBoot中怎么使用Redis”知識都有一定的了解,大家如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。