您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
一、HTML DOM 節點
在 HTML DOM 中,所有事物都是節點。DOM 是被視為節點樹的 HTML。
DOM 節點
根據 W3C 的 HTML DOM 標準,HTML 文檔中的所有內容都是節點:
整個文檔是一個文檔節點
每個 HTML 元素是元素節點
HTML 元素內的文本是文本節點
每個 HTML 屬性是屬性節點
注釋是注釋節點
HTML DOM 將 HTML 文檔視作樹結構。這種結構被稱為節點樹:

通過 HTML DOM,樹中的所有節點均可通過 JavaScript 進行訪問。所有 HTML 元素(節點)均可被修改,也可以創建或刪除節點。
節點樹中的節點彼此擁有層級關系。
父(parent)、子(child)和同胞(sibling)等術語用于描述這些關系。父節點擁有子節點。同級的子節點被稱為同胞(兄弟或姐妹)。
在節點樹中,頂端節點被稱為根(root)
每個節點都有父節點、除了根(它沒有父節點)
一個節點可擁有任意數量的子
同胞是擁有相同父節點的節點
下面的圖片展示了節點樹的一部分,以及節點之間的關系:
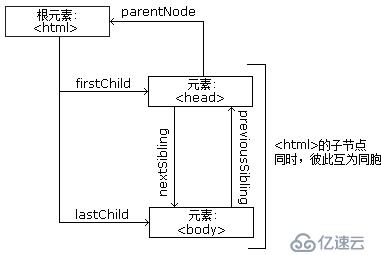
<html> <head> <title>DOM 教程</title> </head> <body> <h2>DOM 第一課</h2> <p>Hello world!</p> </body> </html>
從上面的 HTML 中:
<html> 節點沒有父節點;它是根節點
<head> 和 <body> 的父節點是 <html> 節點
文本節點 "Hello world!" 的父節點是 <p> 節點
并且:
<html> 節點擁有兩個子節點:<head> 和 <body>
<head> 節點擁有一個子節點:<title> 節點
<title> 節點也擁有一個子節點:文本節點 "DOM 教程"
<h2> 和 <p> 節點是同胞節點,同時也是 <body> 的子節點
并且:
<head> 元素是 <html> 元素的首個子節點
<body> 元素是 <html> 元素的最后一個子節點
<h2> 元素是 <body> 元素的首個子節點
<p> 元素是 <body> 元素的最后一個子節點
DOM 處理中的常見錯誤是希望元素節點包含文本。
在本例中:<title>DOM 教程</title>,元素節點 <title>,包含值為 "DOM 教程" 的文本節點。
可通過節點的 innerHTML 屬性來訪問文本節點的值。
您將在稍后的章節中學習更多有關 innerHTML 屬性的知識。
三、HTML DOM 方法
方法是我們可以在節點(HTML 元素)上執行的動作。
可通過 JavaScript (以及其他編程語言)對 HTML DOM 進行訪問。
所有 HTML 元素被定義為對象,而編程接口則是對象方法和對象屬性。
方法是您能夠執行的動作(比如添加或修改元素)。
屬性是您能夠獲取或設置的值(比如節點的名稱或內容)。
getElementById() 方法返回帶有指定 ID 的元素:
var element=document.getElementById("intro");<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>getElementById</b> 方法!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("intro");
document.write("<p>來自 intro 段落的文本:" + x.innerHTML + "</p>");
</script>
</body>
</html>一些常用的 HTML DOM 方法:
getElementById(id) - 獲取帶有指定 id 的節點(元素)
appendChild(node) - 插入新的子節點(元素)
removeChild(node) - 刪除子節點(元素)
一些常用的 HTML DOM 屬性:
innerHTML - 節點(元素)的文本值
parentNode - 節點(元素)的父節點
childNodes - 節點(元素)的子節點
attributes - 節點(元素)的屬性節點
您將在本教程的下一章中學到更多有關屬性的知識。
某個人是一個對象。
人的方法可能是 eat(), sleep(), work(), play() 等等。
所有人都有這些方法,但會在不同時間執行它們。
一個人的屬性包括姓名、身高、體重、年齡、性別等等。
所有人都有這些屬性,但它們的值因人而異。
這里提供一些您將在本教程中學到的常用方法:
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| getElementById() | 返回帶有指定 ID 的元素。 |
| getElementsByTagName() | 返回包含帶有指定標簽名稱的所有元素的節點列表(集合/節點數組)。 |
| getElementsByClassName() | 返回包含帶有指定類名的所有元素的節點列表。 |
| appendChild() | 把新的子節點添加到指定節點。 |
| removeChild() | 刪除子節點。 |
| replaceChild() | 替換子節點。 |
| insertBefore() | 在指定的子節點前面插入新的子節點。 |
| createAttribute() | 創建屬性節點。 |
| createElement() | 創建元素節點。 |
| createTextNode() | 創建文本節點。 |
| getAttribute() | 返回指定的屬性值。 |
| setAttribute() | 把指定屬性設置或修改為指定的值。 |
屬性是節點(HTML 元素)的值,您能夠獲取或設置。
可通過 JavaScript (以及其他編程語言)對 HTML DOM 進行訪問。
所有 HTML 元素被定義為對象,而編程接口則是對象方法和對象屬性。
方法是您能夠執行的動作(比如添加或修改元素)。
屬性是您能夠獲取或設置的值(比如節點的名稱或內容)。
獲取元素內容的最簡單方法是使用 innerHTML 屬性。
innerHTML 屬性對于獲取或替換 HTML 元素的內容很有用。
下面的代碼獲取 id="intro" 的 <p> 元素的 innerHTML:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
var txt=document.getElementById("intro").innerHTML;
document.write(txt);
</script>
</body>
</html>在上面的例子中,getElementById 是一個方法,而 innerHTML 是屬性。
innerHTML 屬性可用于獲取或改變任意 HTML 元素,包括 <html> 和 <body>。
nodeName 屬性規定節點的名稱。
nodeName 是只讀的
元素節點的 nodeName 與標簽名相同
屬性節點的 nodeName 與屬性名相同
文本節點的 nodeName 始終是 #text
文檔節點的 nodeName 始終是 #document
注釋:nodeName 始終包含 HTML 元素的大寫字母標簽名。
nodeValue 屬性規定節點的值。
元素節點的 nodeValue 是 undefined 或 null
文本節點的 nodeValue 是文本本身
屬性節點的 nodeValue 是屬性值
下面的例子會取回 <p id="intro"> 標簽的文本節點值:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("intro");
document.write(x.firstChild.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>nodeType 屬性返回節點的類型。nodeType 是只讀的。
比較重要的節點類型有:
| 元素類型 | NodeType |
|---|---|
| 元 素 | 1 |
| 屬性 | 2 |
| 文本 | 3 |
| 注釋 | 8 |
| 文 檔 | 9 |
訪問 HTML DOM - 查找 HTML 元素。
訪問 HTML 元素等同于訪問節點
您能夠以不同的方式來訪問 HTML 元素:
通過使用 getElementById() 方法
通過使用 getElementsByTagName() 方法
通過使用 getElementsByClassName() 方法
getElementById() 方法返回帶有指定 ID 的元素:
node.getElementById("id");下面的例子獲取 id="intro" 的元素:
document.getElementById("intro");<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>getElementById</b> 方法!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("intro");
document.write("<p>來自 intro 段落的文本:" + x.innerHTML + "</p>");
</script>
</body>
</html>getElementsByTagName() 返回帶有指定標簽名的所有元素。
node.getElementsByTagName("tagname");下面的例子返回包含文檔中所有 <p> 元素的列表:
document.getElementsByTagName("p");<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>getElementsByTagName</b> 方法。</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");
document.write("第一段的文本: " + x[0].innerHTML);
</script>
</body>
</html>下面的例子返回包含文檔中所有 <p> 元素的列表,并且這些 <p> 元素應該是 id="main" 的元素的后代(子、孫等等):
document.getElementById("main").getElementsByTagName("p");<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<div id="main">
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>getElementsByTagName</b> 方法。</p>
</div>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("main").getElementsByTagName("p");
document.write("div 中的第一段的文本: " + x[0].innerHTML);
</script>
</body>
</html>如果您希望查找帶有相同類名的所有 HTML 元素,請使用這個方法:
document.getElementsByClassName("intro");上面的例子返回包含 class="intro" 的所有元素的一個列表:
注釋:getElementsByClassName() 在 Internet Explorer 5,6,7,8 中無效。
六、HTML DOM - 修改
修改 HTML = 改變元素、屬性、樣式和事件。
修改 HTML DOM 意味著許多不同的方面:
改變 HTML 內容
改變 CSS 樣式
改變 HTML 屬性
創建新的 HTML 元素
刪除已有的 HTML 元素
改變事件(處理程序)
在接下來的章節,我們會深入學習修改 HTML DOM 的常用方法。
改變元素內容的最簡答的方法是使用 innerHTML 屬性。
下面的例子改變一個 <p> 元素的 HTML 內容:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello World!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="New text!";
</script>
<p>上面的段落被一段腳本改變了。</p>
</body>
</html>提示:我們將在下面的章節為您解釋例子中的細節。
通過 HTML DOM,您能夠訪問 HTML 元素的樣式對象。
下面的例子改變一個段落的 HTML 樣式:
<html>
<body>
<p id="p2">Hello world!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p2").style.color="blue";
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello world!</p>
<p id="p2">Hello world!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p2").style.color="blue";
document.getElementById("p2").style.fontFamily="Arial";
document.getElementById("p2").style.fontSize="larger";
</script>
</body>
</html>如需向 HTML DOM 添加新元素,您首先必須創建該元素(元素節點),然后把它追加到已有的元素上。
<div id="d1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var element=document.getElementById("d1");
element.appendChild(para);
</script><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var element=document.getElementById("div1");
element.appendChild(para);
</script>
</body>
</html>通過 HTML DOM,JavaScript 能夠訪問 HTML 文檔中的每個元素。
改變元素內容的最簡答的方法是使用 innerHTML 屬性。
下面的例子更改 <p> 元素的 HTML 內容:
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello World!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="New text!";
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello World!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="New text!";
</script>
<p>上面的段落被一段腳本改變了。</p>
</body>
</html>通過 HTML DOM,您能夠訪問 HTML 對象的樣式對象。
下面的例子更改段落的 HTML 樣式:
<html>
<body>
<p id="p2">Hello world!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p2").style.color="blue";
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello world!</p>
<p id="p2">Hello world!</p>
<script>
document.getElementById("p2").style.color="blue";
document.getElementById("p2").style.fontFamily="Arial";
document.getElementById("p2").style.fontSize="larger";
</script>
</body>
</html>HTML DOM 允許您在事件發生時執行代碼。
當 HTML 元素”有事情發生“時,瀏覽器就會生成事件:
在元素上點擊
加載頁面
改變輸入字段
你可以在下一章學習更多有關事件的內容。
下面兩個例子在按鈕被點擊時改變 <body> 元素的背景色:
<html> <body> <input type="button" onclick="document.body.style.backgroundColor='lavender';" value="Change background color" /> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <input type="button" onclick="document.body.style.backgroundColor='lavender';" value="改變背景色"> </body> </html>
在本例中,由函數執行相同的代碼:
<html>
<body>
<script>
function ChangeBackground()
{
document.body.style.backgroundColor="lavender";
}
</script>
<input type="button" onclick="ChangeBackground()"
value="Change background color" />
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<script>
function ChangeBackground()
{
document.body.style.backgroundColor="lavender";
}
</script>
<input type="button" onclick="ChangeBackground()" value="改變背景色" />
</body>
</html>下面的例子在按鈕被點擊時改變 <p> 元素的文本:
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello world!</p>
<script>
function ChangeText()
{
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="New text!";
}
</script>
<input type="button" onclick="ChangeText()" value="Change text">
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1">Hello world!</p>
<script>
function ChangeText()
{
document.getElementById("p1").innerHTML="New text!";
}
</script>
<input type="button" onclick="ChangeText()" value="改變文本" />
</body>
</html>八、HTML DOM - 元素
添加、刪除和替換 HTML 元素。
如需向 HTML DOM 添加新元素,您首先必須創建該元素,然后把它追加到已有的元素上。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var element=document.getElementById("div1");
element.appendChild(para);
</script>
</body>
</html>這段代碼創建了一個新的 <p> 元素:
var para=document.createElement("p");如需向 <p> 元素添加文本,您首先必須創建文本節點。這段代碼創建文本節點:
var node=document.createTextNode("This is a new paragraph.");然后您必須向 <p> 元素追加文本節點:
para.appendChild(node);
最后,您必須向已有元素追加這個新元素。
這段代碼查找到一個已有的元素:
var element=document.getElementById("div1");這段代碼向這個已存在的元素追加新元素:
element.appendChild(para);
上一個例子中的 appendChild() 方法,將新元素作為父元素的最后一個子元素進行添加。
如果不希望如此,您可以使用 insertBefore() 方法:
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var element=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
element.insertBefore(para,child);
</script>編寫代碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var element=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
element.insertBefore(para,child);
</script>
</body>
</html>如需刪除 HTML 元素,您必須清楚該元素的父元素:
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var parent=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
parent.removeChild(child);
</script>編寫代碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var parent=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
parent.removeChild(child);
</script>
</body>
</html>這個 HTML 文檔包含一個帶有兩個子節點(兩個 <p> 元素)的 <div> 元素:
<div id="div1"> <p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p> <p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p> </div>
查找 id="div1" 的元素:
var parent=document.getElementById("div1");查找 id="p1" 的 <p> 元素:
var child=document.getElementById("p1");從父元素中刪除子元素:
parent.removeChild(child);
提示:能否在不引用父元素的情況下刪除某個元素?
很抱歉。DOM 需要了解您需要刪除的元素,以及它的父元素。
這里提供一個常用的解決方法:找到您需要刪除的子元素,然后使用 parentNode 屬性來查找其父元素:
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
child.parentNode.removeChild(child);如需替換 HTML DOM 中的元素,請使用 replaceChild() 方法:
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
var parent=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
parent.replaceChild(para,child);
</script>編寫代碼:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div id="div1">
<p id="p1">This is a paragraph.</p>
<p id="p2">This is another paragraph.</p>
</div>
<script>
var parent=document.getElementById("div1");
var child=document.getElementById("p1");
var para=document.createElement("p");
var node=document.createTextNode("This is new.");
para.appendChild(node);
parent.replaceChild(para,child);
</script>
</body>
</html>九、HTML DOM - 事件
HTML DOM 允許 JavaScript 對 HTML 事件作出反應。。
當事件發生時,可以執行 JavaScript,比如當用戶點擊一個 HTML 元素時。
如需在用戶點擊某個元素時執行代碼,請把 JavaScript 代碼添加到 HTML 事件屬性中:
onclick=JavaScript
HTML 事件的例子:
當用戶點擊鼠標時
當網頁已加載時
當圖片已加載時
當鼠標移動到元素上時
當輸入字段被改變時
當 HTML 表單被提交時
當用戶觸發按鍵時
在本例中,當用戶點擊時,會改變 <h2> 元素的內容:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h2 onclick="this.innerHTML='hello!'">請點擊這段文本!</h2> </body> </html>
代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <h2 onclick="this.innerHTML='hello!'">請點擊這段文本!</h2> </body> </html>
在本例中,會從事件處理程序中調用函數:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function changetext(id)
{
id.innerHTML="hello!";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2 onclick="changetext(this)">請點擊這段文本!</h2>
</body>
</html>代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function changetext(id)
{
id.innerHTML="hello!";
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h2 onclick="changetext(this)">請點擊這段文本!</h2>
</body>
</html>如需向 HTML 元素分配事件,您可以使用事件屬性。
向 button 元素分配一個 onclick 事件:
<button onclick="displayDate()">試一試</button>
代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>點擊按鈕來執行 <b>displayDate()</b> 函數。</p>
<button onclick="displayDate()">試一試</button>
<script>
function displayDate()
{
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=Date();
}
</script>
<p id="demo"></p>
</body>
</html>在上面的例子中,當點擊按鈕時,會執行名為 displayDate 的函數。
HTML DOM 允許您使用 JavaScript 向 HTML 元素分配事件:
為 button 元素分配 onclick 事件:
<script>
document.getElementById("myBtn").onclick=function(){displayDate()};
</script>代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<p>點擊按鈕來執行 <b>displayDate()</b> 函數。</p>
<button id="myBtn">試一試</button>
<script>
document.getElementById("myBtn").onclick=function(){displayDate()};
function displayDate()
{
document.getElementById("demo").innerHTML=Date();
}
</script>
<p id="demo"></p>
</body>
</html>在上面的例子中,名為 displayDate 的函數被分配給了 id=myButn" 的 HTML 元素。
當按鈕被點擊時,將執行函數。
當用戶進入或離開頁面時,會觸發 onload 和 onunload 事件。
onload 事件可用于檢查訪客的瀏覽器類型和版本,以便基于這些信息來加載不同版本的網頁。
onload 和 onunload 事件可用于處理 cookies。
<body onload="checkCookies()">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body onload="checkCookies()">
<script>
function checkCookies()
{
if (navigator.cookieEnabled==true)
{
alert("Cookies are enabled")
}
else
{
alert("Cookies are not enabled")
}
}
</script>
<p>彈出的提示框會告訴你瀏覽器是否已啟用 cookie。</p>
</body>
</html>onchange 事件常用于輸入字段的驗證。
下面的例子展示了如何使用 onchange。當用戶改變輸入字段的內容時,將調用 upperCase() 函數。
<input type="text" id="fname" onchange="upperCase()">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<script>
function myFunction()
{
var x=document.getElementById("fname");
x.value=x.value.toUpperCase();
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
請輸入你的英文名:<input type="text" id="fname" onchange="myFunction()">
<p>當你離開輸入框時,被觸發的函數會把你輸入的文本轉換為大寫字母。</p>
</body>
</html>onmouseover 和 onmouseout 事件可用于在鼠標指針移動到或離開元素時觸發函數。
一個簡單的 onmouseover-onmouseout 例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div
onmouseover="mOver(this)"
onmouseout="mOut(this)"
style="background-color:#D94A38;width:200px;height:50px;padding-top:25px;text-align:center;">
Mouse Over Me
</div>
<script>
function mOver(obj)
{
obj.innerHTML="謝謝你"
}
function mOut(obj)
{
obj.innerHTML="把鼠標指針移動到上面"
}
</script>
</body>
</html>onmousedown、onmouseup 以及 onclick 事件是鼠標點擊的全部過程。首先當某個鼠標按鈕被點擊時,觸發 onmousedown 事件,然后,當鼠標按鈕被松開時,會觸發 onmouseup 事件,最后,當鼠標點擊完成時,觸發 onclick 事件。
一個簡單的 onmousedown-onmouseup 實例:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<div
onmousedown="mDown(this)"
onmouseup="mUp(this)"
style="background-color:#D94A38;width:200px;height:50px;padding-top:25px;text-align:center;">
點擊這里
</div>
<script>
function mDown(obj)
{
obj.style.backgroundColor="#1ec5e5";
obj.innerHTML="松開鼠標"
}
function mUp(obj)
{
obj.style.backgroundColor="#D94A38";
obj.innerHTML="謝謝你"
}
</script>
</body>
</html>通過 HTML DOM,您能夠使用節點關系在節點樹中導航。
getElementsByTagName() 方法返回節點列表。節點列表是一個節點數組。
下面的代碼選取文檔中的所有 <p> 節點:
var x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");可以通過下標號訪問這些節點。如需訪問第二個 <p>,您可以這么寫:
y=x[1];
代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");
document.write("第二段的 innerHTML 是: " + x[1].innerHTML);
</script>
</body>
</html>注釋:下標號從 0 開始。
length 屬性定義節點列表中節點的數量。
您可以使用 length 屬性來循環節點列表:
x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");
for (i=0;i<x.length;i++)
{
document.write(x[i].innerHTML);
document.write("<br />");
}代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p>DOM 很有用!</p>
<p>本例演示 <b>length</b> 屬性。</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementsByTagName("p");
for (i=0;i<x.length;i++)
{
document.write(x[i].innerHTML);
document.write("<br>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>獲取所有 <p> 元素節點
輸出每個 <p> 元素的文本節點的值
您能夠使用三個節點屬性:parentNode、firstChild 以及 lastChild ,在文檔結構中進行導航。
請看下面的 HTML 片段:
<html> <body> <p>Hello World!</p> <div> <p>DOM 很有用!</p> <p>本例演示節點關系。</p> </div> </body> </html>
首個 <p> 元素是 <body> 元素的首個子元素(firstChild)
<div> 元素是 <body> 元素的最后一個子元素(lastChild)
<body> 元素是首個 <p> 元素和 <div> 元素的父節點(parentNode)
firstChild 屬性可用于訪問元素的文本:
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("intro");
document.write(x.firstChild.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
x=document.getElementById("intro");
document.write(x.firstChild.nodeValue);
</script>
</body>
</html>這里有兩個特殊的屬性,可以訪問全部文檔:
document.documentElement - 全部文檔
document.body - 文檔的主體
<html> <body> <p>Hello World!</p> <div> <p>DOM 很有用!</p> <p>本例演示 <b>document.body</b> 屬性。</p> </div> <script> alert(document.body.innerHTML); </script> </body> </html>
代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <body> <p>Hello World!</p> <div> <p>DOM 很有用!</p> <p>本例演示 <b>document.body</b> 屬性。</p> </div> <script> alert(document.body.innerHTML); </script> </body> </html>
除了 innerHTML 屬性,您也可以使用 childNodes 和 nodeValue 屬性來獲取元素的內容。
下面的代碼獲取 id="intro" 的 <p> 元素的值:
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
var txt=document.getElementById("intro").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.write(txt);
</script>
</body>
</html>代碼實現:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="intro">Hello World!</p>
<script>
txt=document.getElementById("intro").childNodes[0].nodeValue;
document.write(txt);
</script>
</body>
</html>在上面的例子中,getElementById 是一個方法,而 childNodes 和 nodeValue 是屬性。
在本教程中,我們將使用 innerHTML 屬性。不過,學習上面的方法有助于對 DOM 樹結構和導航的理解。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。