您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“Spring Bean的生命周期是什么”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“Spring Bean的生命周期是什么”文章吧。
我們講 Spring Bean 的生命周期之前先來了解兩個概念:
我們來看下 Spring Framework 的官方文檔:
In Spring, the objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. Otherwise, a bean is simply one of many objects in your application. Beans, and the dependencies among them, are reflected in the configuration metadata used by a container.
簡而言之,bean 是由 Spring IoC 容器實例化、組裝和管理的對象。
對于普通的 Java 對象,當 new 的時候創建對象,然后該對象就能夠使用了。一旦該對象不再被使用,則由 Java 自動進行垃圾回收。
而 Spring 中的對象是 bean,bean 和普通的 Java 對象沒啥大的區別,只不過 Spring 不再自己去 new 對象了,而是由 IoC 容器去幫助我們實例化對象并且管理它,我們需要哪個對象,去問 IoC 容器要即可。IoC 其實就是解決對象之間的耦合問題,Spring Bean 的生命周期完全由容器控制。
這里老周必須要提一下,這里我們說的 Spring Bean 的生命周期主要指的是 singleton bean,對于 prototype 的 bean ,Spring 在創建好交給使用者之后則不會再管理后續的生命周期。
我們也來復習下 Spring 中的 bean 的作用域有哪些?
singleton : 唯一 bean 實例,Spring 中的 bean 默認都是單例的。prototype : 每次請求都會創建一個新的 bean 實例。request : 每一次 HTTP 請求都會產生一個新的 bean,該 bean 僅在當前 HTTP request 內有效。session : 每一次 HTTP 請求都會產生一個新的 bean,該 bean 僅在當前 HTTP session 內有效。global-session: 全局 session 作用域,僅僅在基于 Portlet 的 web 應用中才有意義,Spring5 已經沒有了。Portlet 是能夠生成語義代碼(例如:HTML)片段的小型 Java Web 插件。它們基于 portlet 容器,可以像 servlet 一樣處理 HTTP 請求。但是,與 servlet 不同,每個 portlet 都有不同的會話。
我們知道對于普通的 Java 對象來說,它們的生命周期就是:
實例化
該對象不再被使用時通過垃圾回收機制進行回收
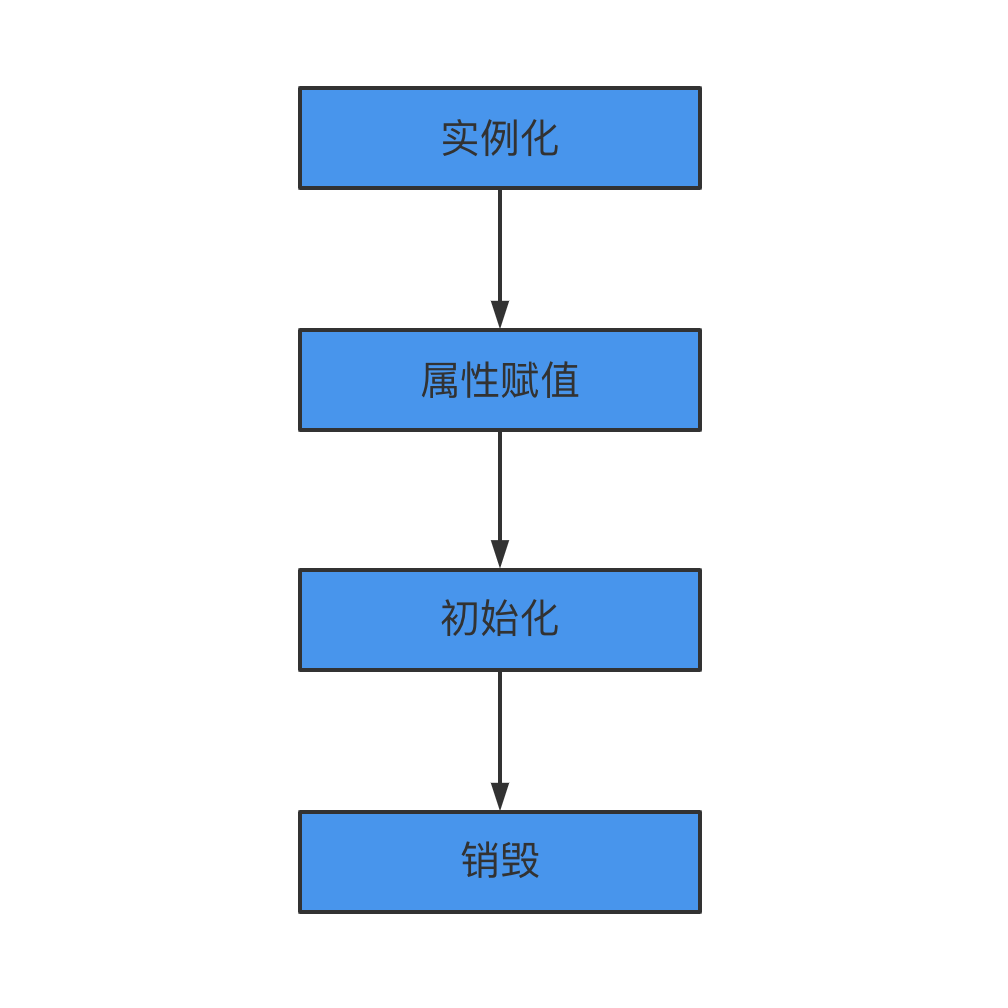
而對于 Spring Bean 的生命周期來說:
實例化 Instantiation
屬性賦值 Populate
初始化 Initialization
銷毀 Destruction
實例化 -> 屬性賦值 -> 初始化 -> 銷毀
只有四個步驟,這樣拆解的話是不是感覺也不難?不像其他人寫的那樣直接一上來就各種 BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor 全部懟進流程里去,別說讀者看著頭大,自己寫的可能短時間內還記得流程,隔個一段時間,你可能都不知道自己寫了個啥。
本來小編想通過 Bean 創建流程入口
AbstractApplicationContext#refresh() 方法的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory) 處帶大家跟一下源碼,想了想還是不帶入過多的代碼進來,直接給到最終的主要邏輯。
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) throws BeanCreationException {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = (BeanWrapper)this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
// 實例化階段
instanceWrapper = this.createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
...
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
// 屬性賦值階段
this.populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
// 初始化階段
exposedObject = this.initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
} catch (Throwable var18) {
...
}
...
}至于銷毀,是在容器關閉時調用的,詳見 ConfigurableApplicationContext#close()
是不是很清爽了?至于 BeanPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor 以及其他的類,在老周看來,只不過是對主流程四個步驟的一系列擴展點而已。
Spring Bean 的生命周期的擴展點超級多,老周這里不可能全部列出來,只說核心的擴展點。這也就是為什么 Spring 的擴展性很好的原因,開了很多的口子,盡可能讓某個功能高內聚松耦合,用戶需要哪個功能就用哪個,而不是直接來一個大而全的東西。
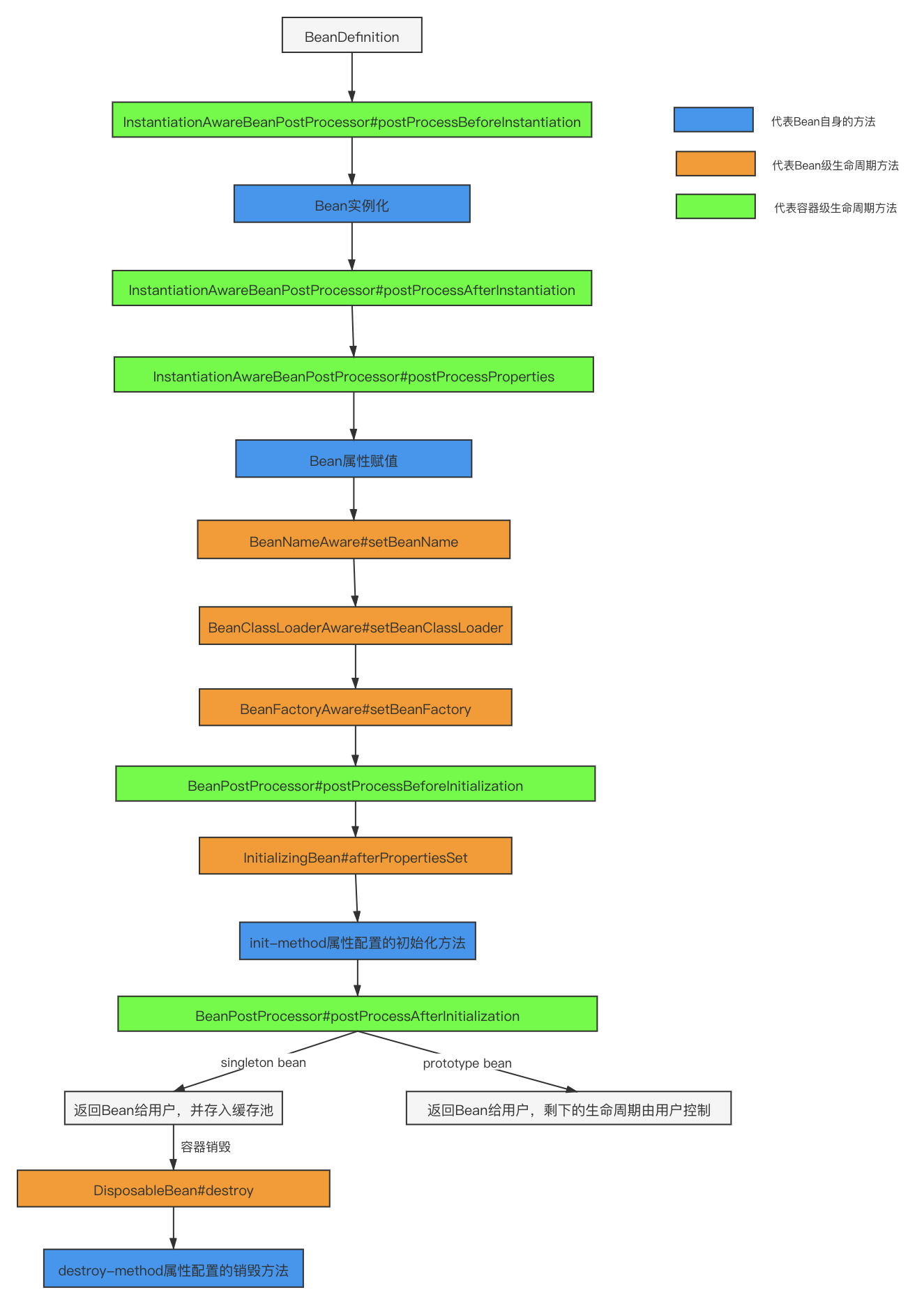
比如構造函數、getter/setter 以及 init-method 和 destory-method 所指定的方法等,也就對應著上文說的實例化 -> 屬性賦值 -> 初始化 -> 銷毀四個階段。
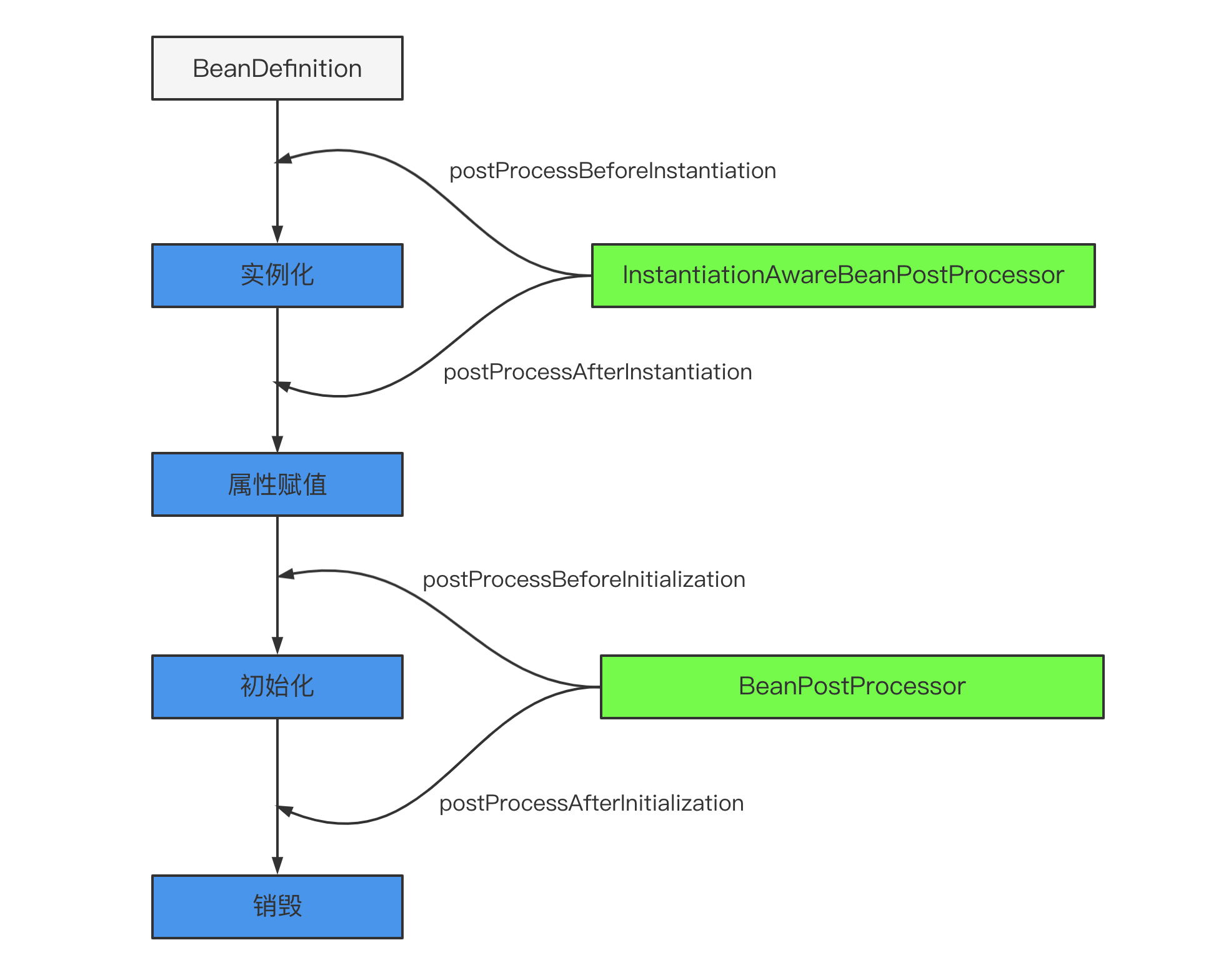
主要是后處理器方法,比如下圖的 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor、BeanPostProcessor 接口方法。這些接口的實現類是獨立于 Bean 的,并且會注冊到 Spring 容器中。在 Spring 容器創建任何 Bean 的時候,這些后處理器都會發生作用。
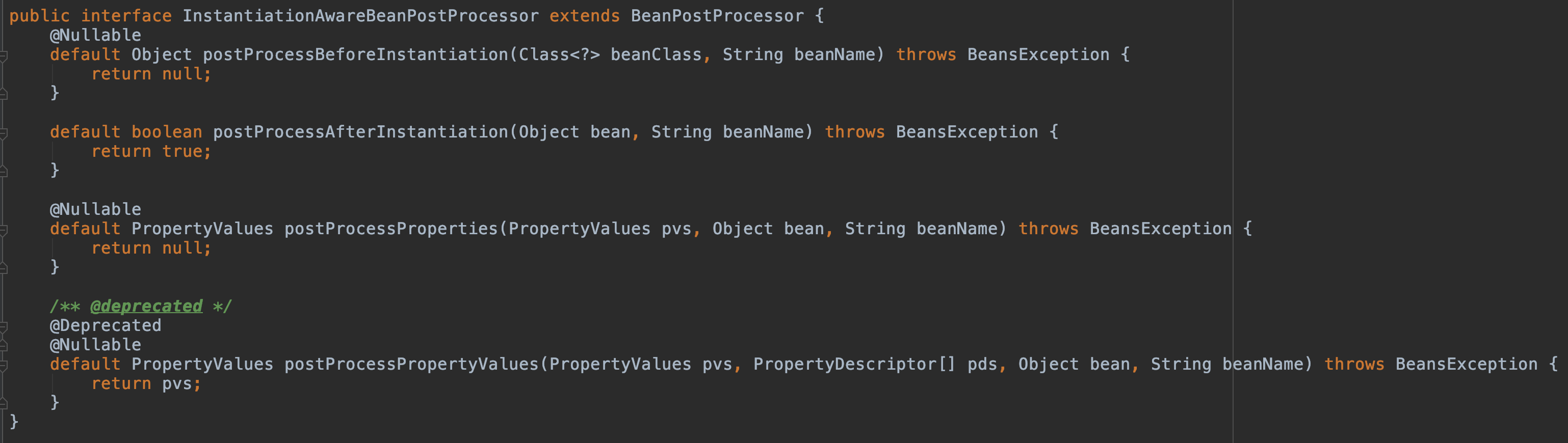
我們翻一下源碼發現 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 是繼承了 BeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInstantiation 調用點
Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
返回值:如果返回的不為null,那么后續的Bean的創建流程【實例化、初始化afterProperties】都不會執行,而是直接使用返回的快捷Bean,此時的正常執行順序如下:
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口中的postProcessBeforeInstantiation,在實例化之前調用。
BeanPostProcessor接口中的postProcessAfterInitialization,在實例化之后調用。
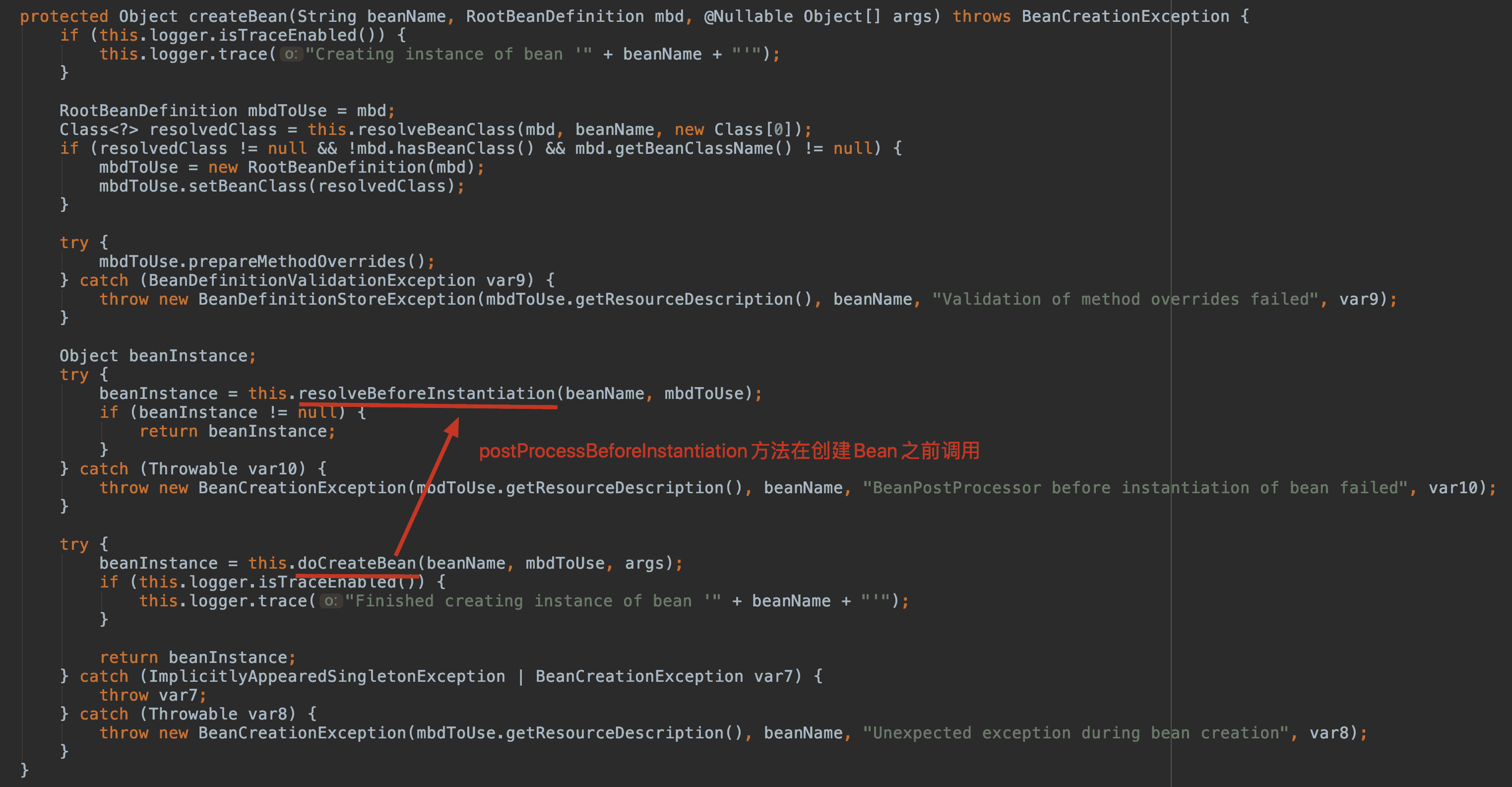
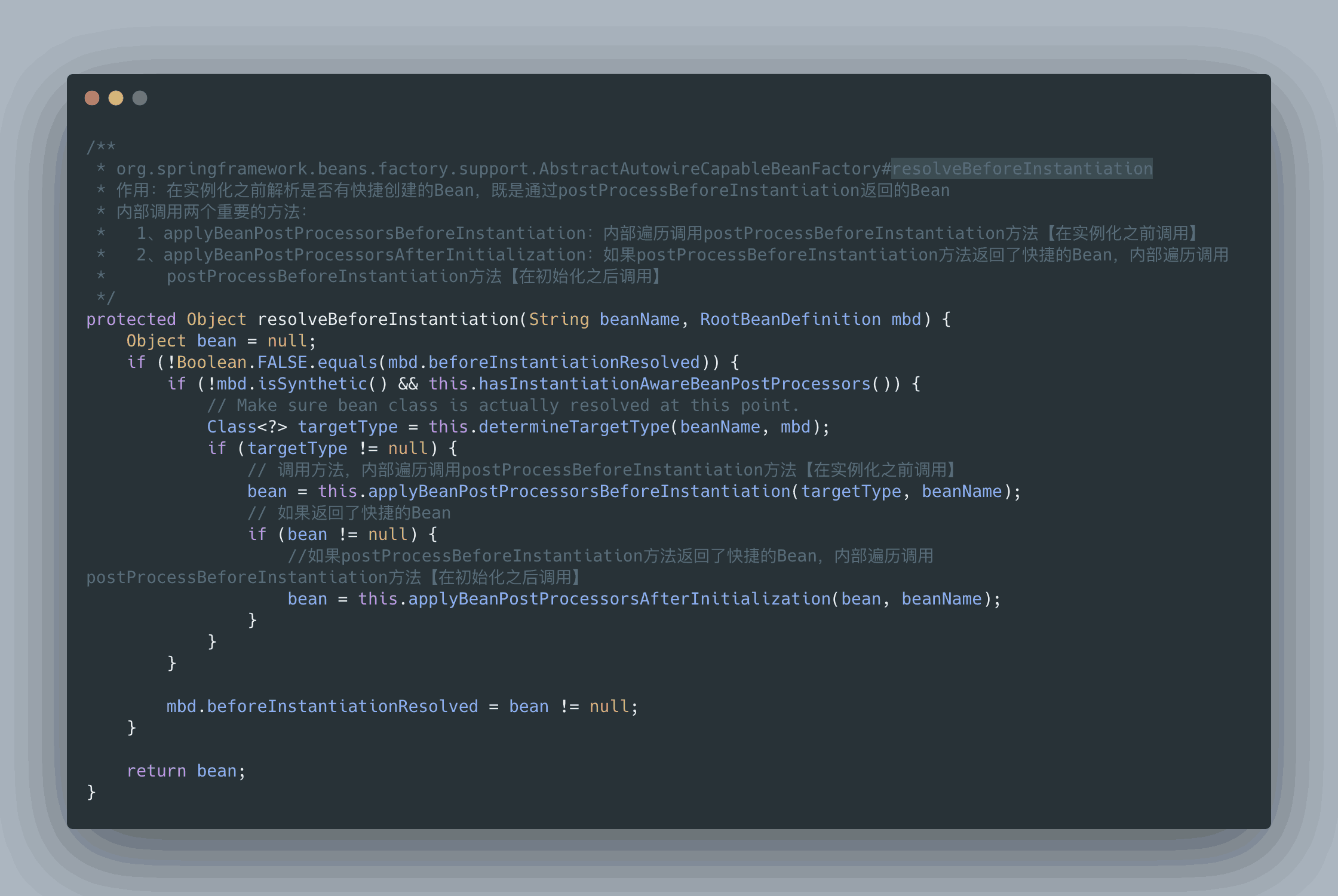
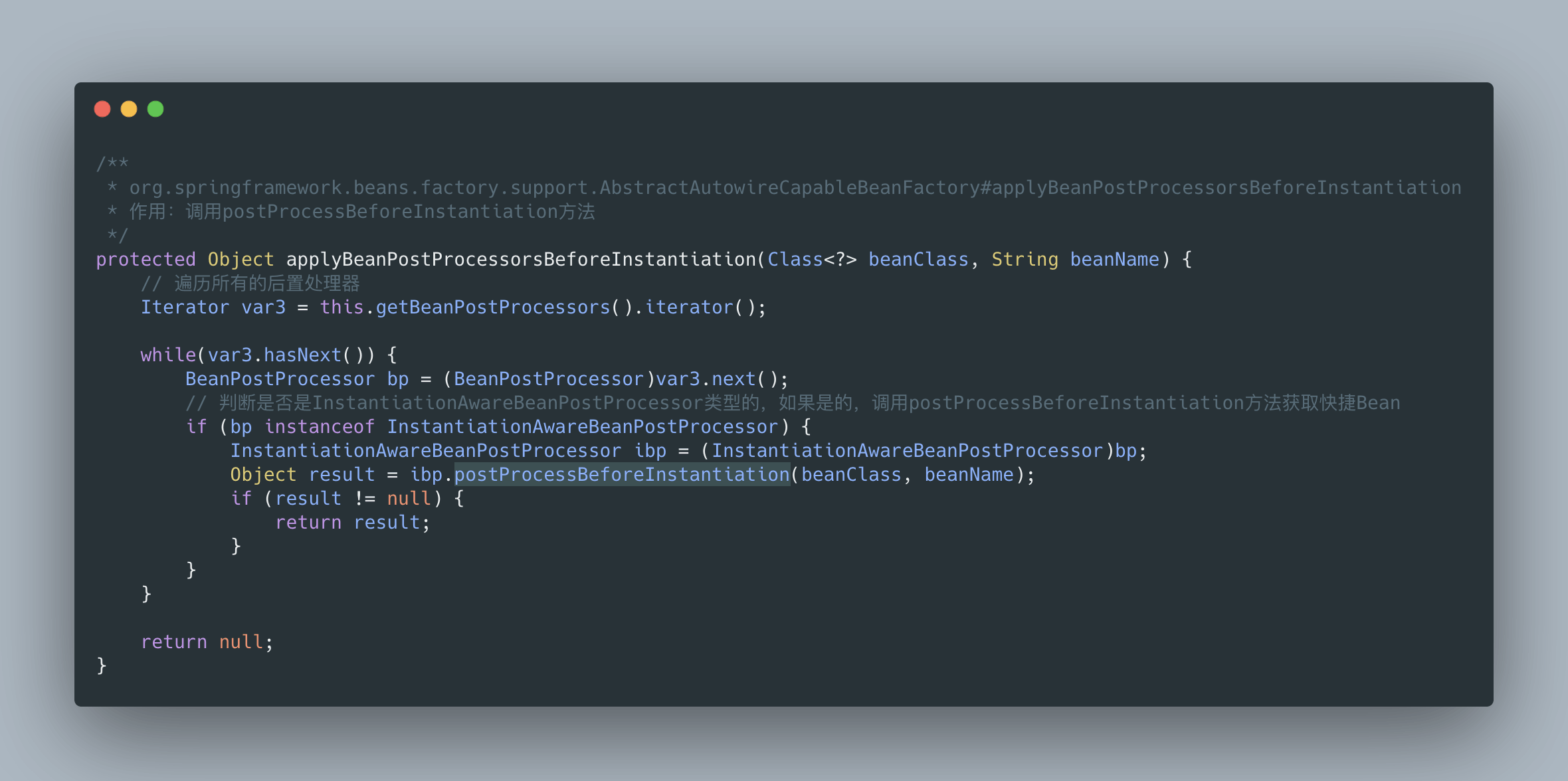
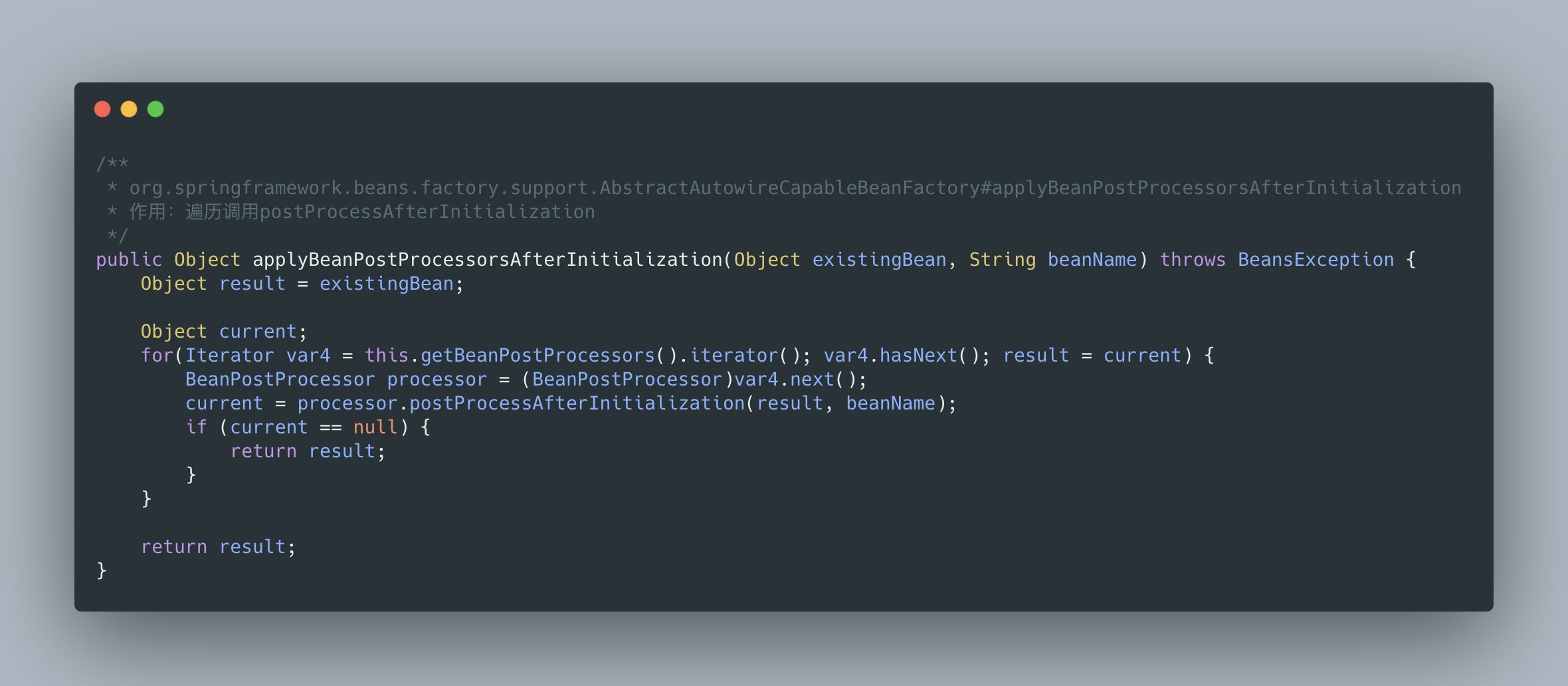
總之,postProcessBeforeInstantiation 在 doCreateBean 之前調用,也就是在 bean 實例化之前調用的,英文源碼注釋解釋道該方法的返回值會替換原本的 Bean 作為代理,這也是 AOP 等功能實現的關鍵點。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInstantiation 調用點
boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException
正常情況下在實例化之后在執行populateBean之前調用
返回值:如果有指定的bean的時候返回false,那么后續的屬性填充和屬性依賴注入【populateBean】將不會執行,同時后續的postProcessPropertyValues將不會執行,但是初始化和BeanPostProcessor的仍然會執行。
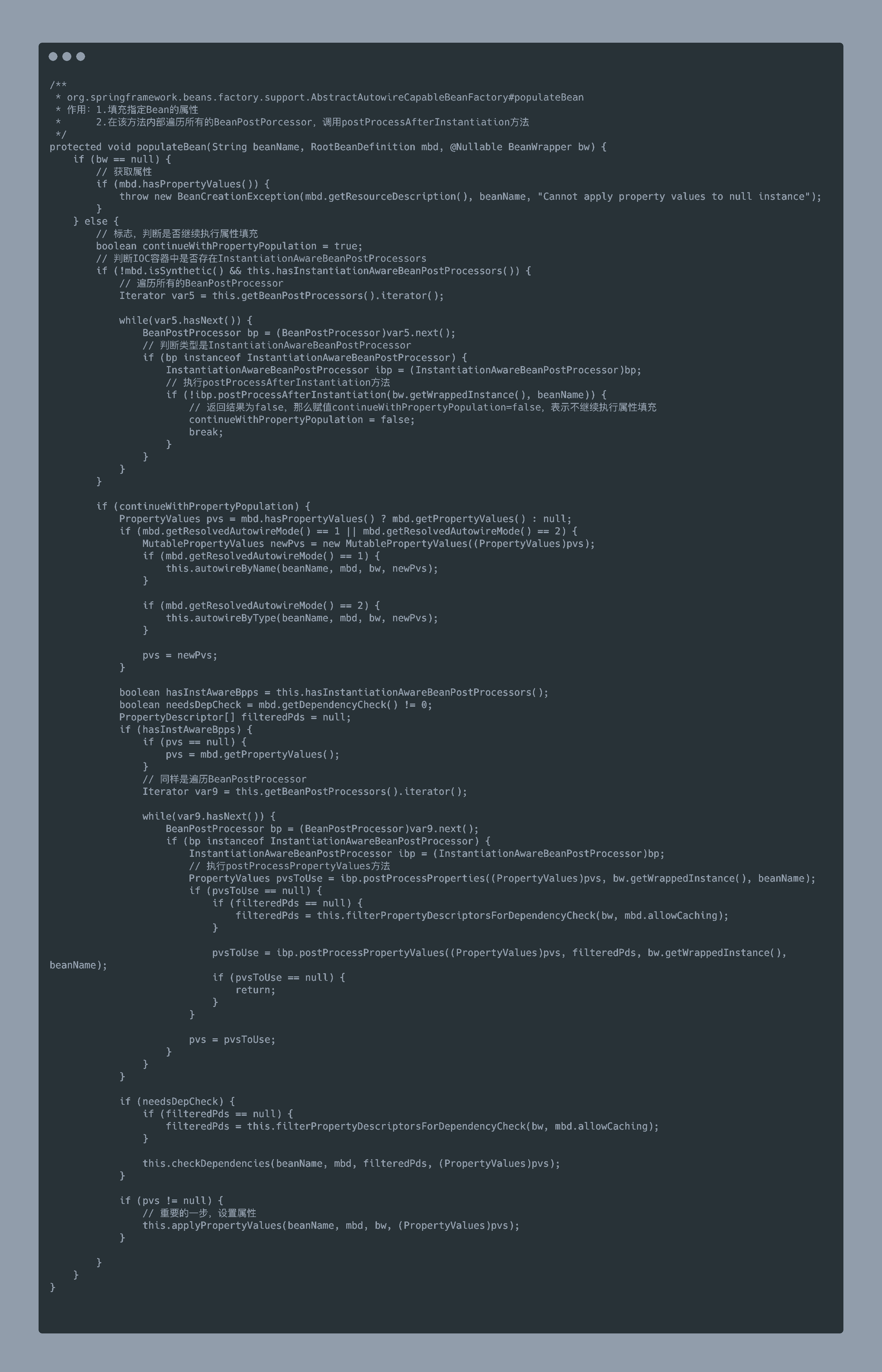
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName)
實例化之后調用,在方法applyPropertyValues【屬性填充】之前
返回值:如果返回null,那么將不會進行后續的屬性填充,比如依賴注入等,如果返回的pvs額外的添加了屬性,那么后續會填充到該類對應的屬性中。
pvs:PropertyValues對象,用于封裝指定類的對象,簡單來說就是PropertyValue的集合,里面相當于以key-value形式存放類的屬性和值。
pds:PropertyDescriptor對象數組,PropertyDescriptor相當于存儲類的屬性,不過可以調用set,get方法設置和獲取對應屬性的值。
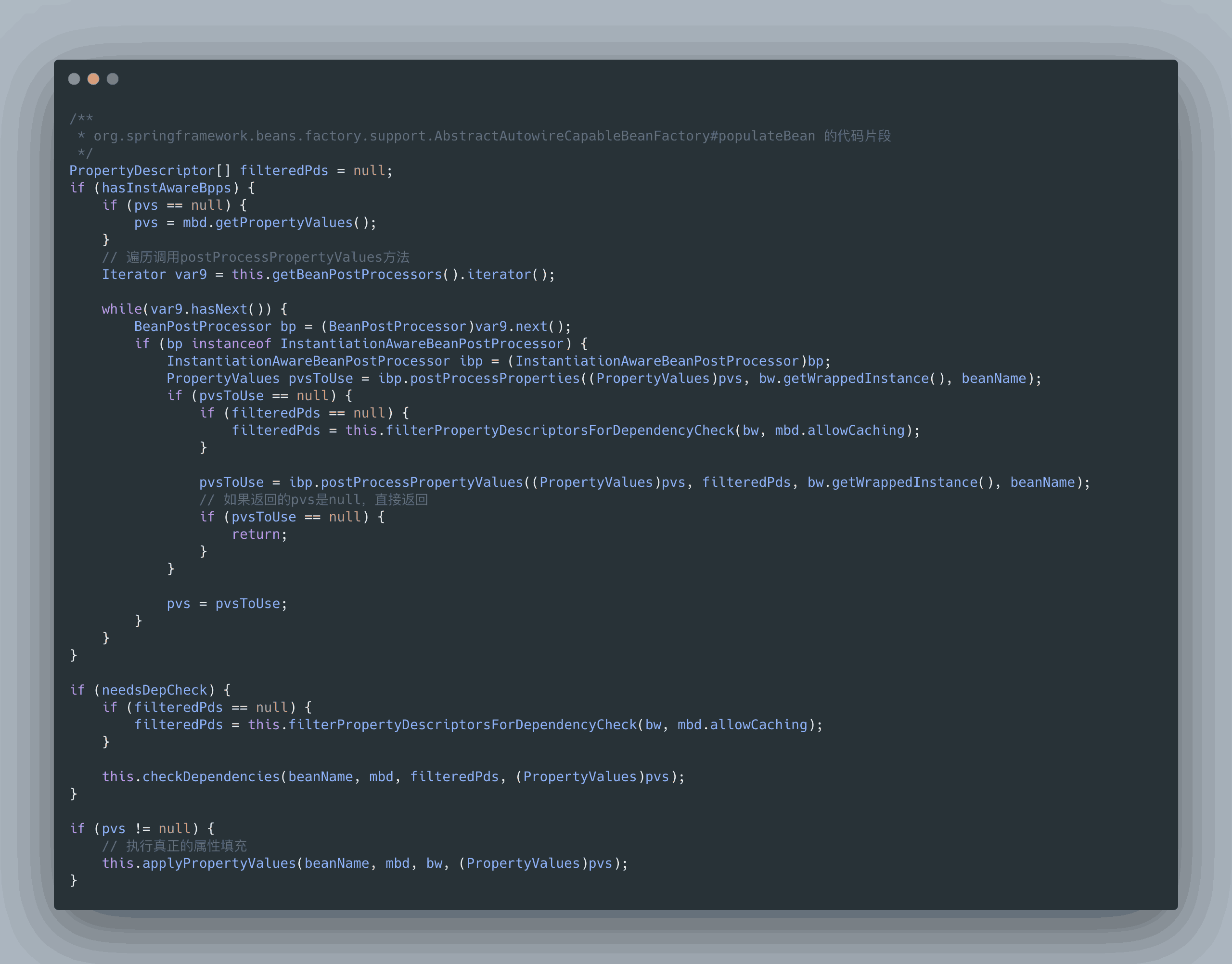
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean
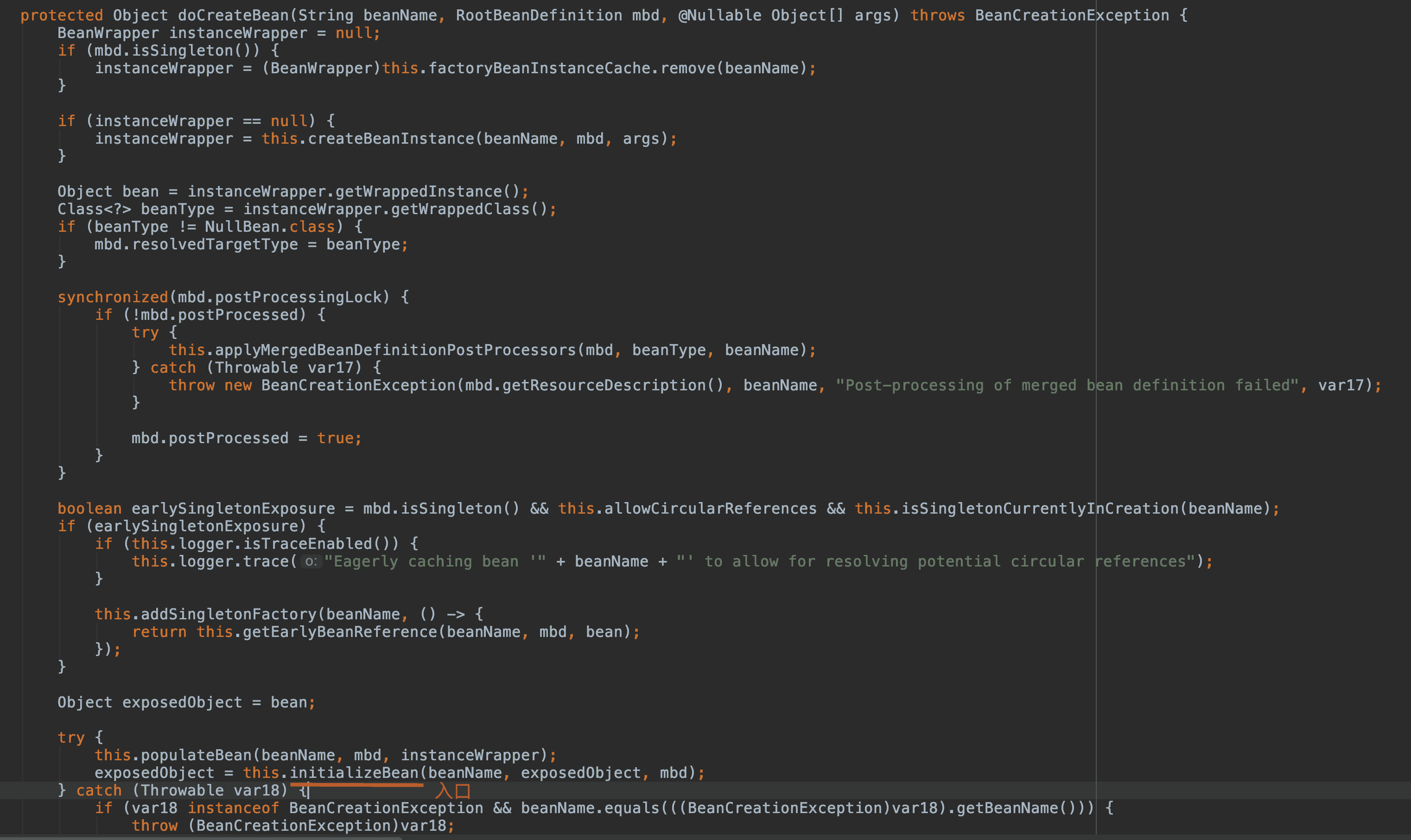
進入初始化接口:

我們先來看
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
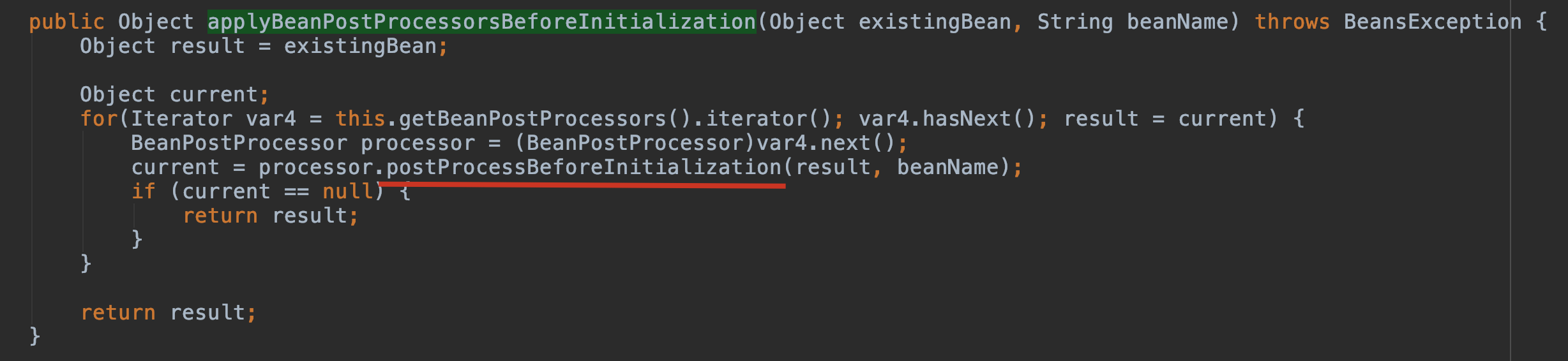
首先獲取到所有的后置處理器 getBeanPostProcessors()
在 for 循環中依次調用后置處理器的方法 processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
進入 postProcessBeforeInitialization 方法
org.springframework.context.support.ApplicationContextAwareProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization
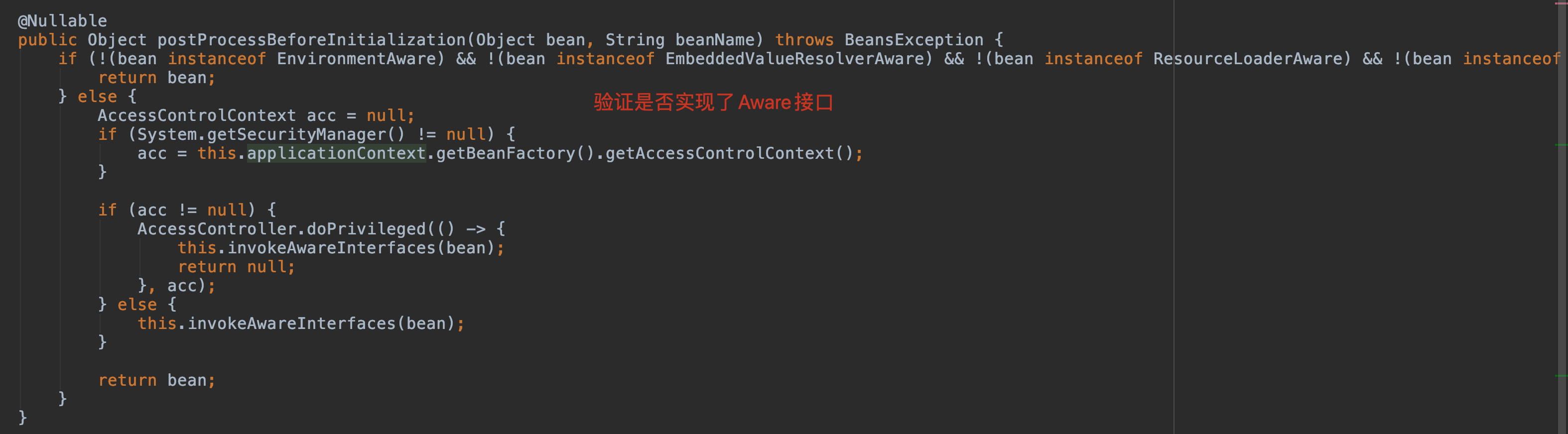
進入 invokeAwareInterfaces(bean); 方法,當前 bean 實現了 ApplicationContextAware 接口。
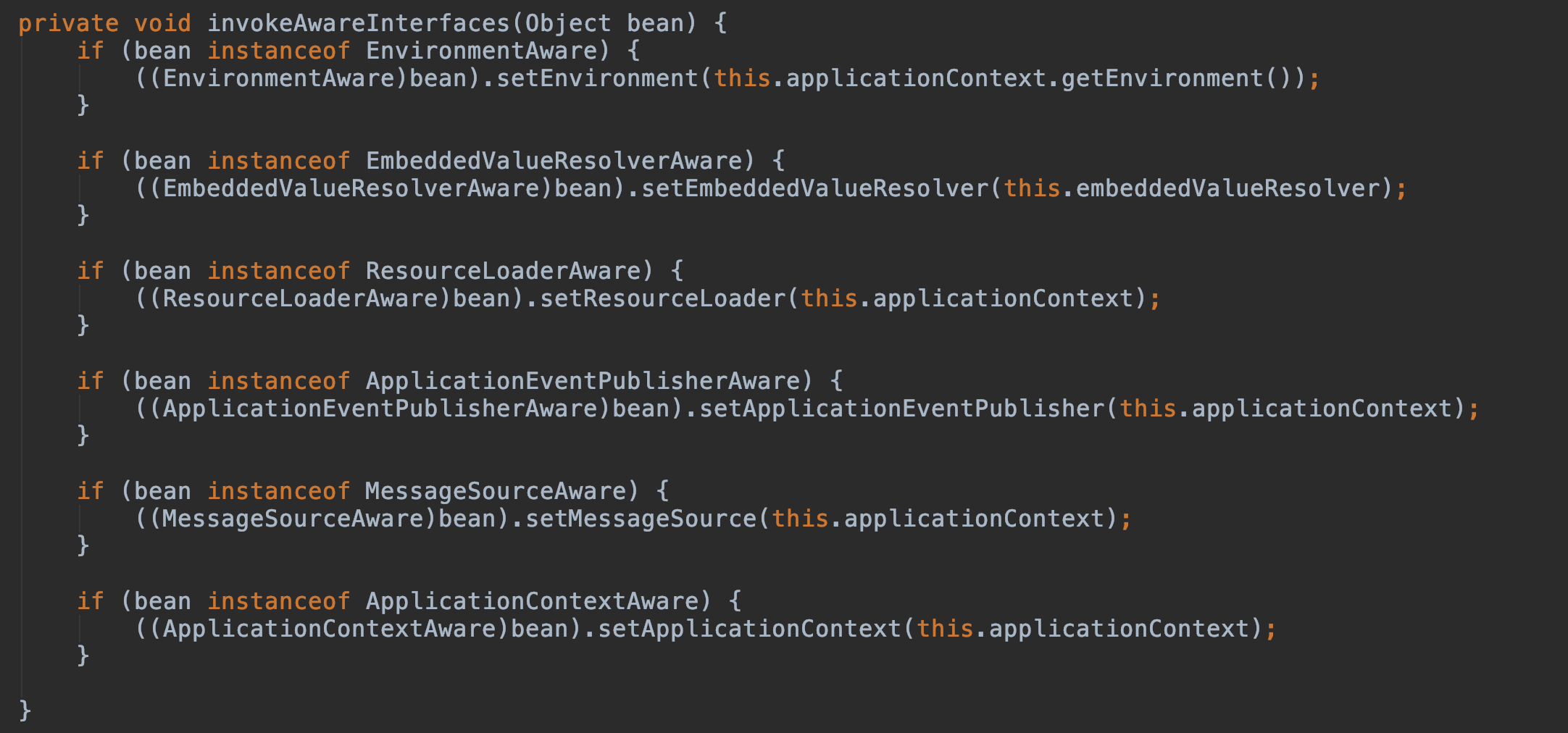
ApplicationContextAwareProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization 首先判斷此 bean 是不是各種的Aware,如果是它列舉的那幾個 Aware 就獲取 Bean 工廠的權限,可以向容器中導入相關的上下文環境,目的是為了 Bean 實例能夠獲取到相關的上下文,如果不是它列舉的幾個 Aware,那就調用 invokeAwareInterfaces(bean),向容器中添加相關接口的上下文環境。
包括 AspectJWeavingEnabler、CustomAutowireConfigurer、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 等。這些都是 Spring 框架中已經實現好的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,用來實現某些特定的功能。
我們知道 Spring IoC 容器初始化的關鍵環節就在 org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 方法中 ,容器創建的主體流程都在這個方法里面,這個方法是真的重要!!!
對于工廠后處理器方法老周這里直接帶你看 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); 方法,這個方法處理的是 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 Bean。調用方法如下:
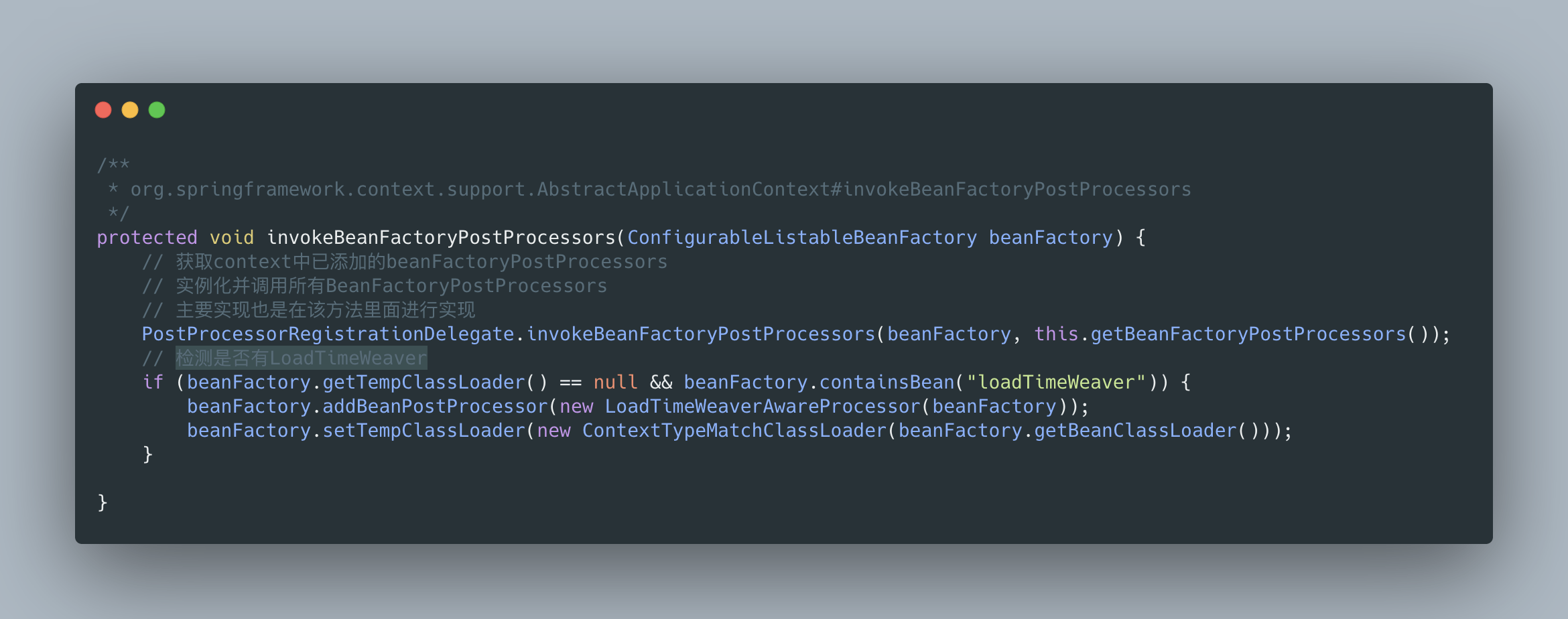
跟到最重要的方法里去,代碼雖長,但邏輯中規中矩。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor:一切處理 BeanFactory 的父接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor:實現了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的接口
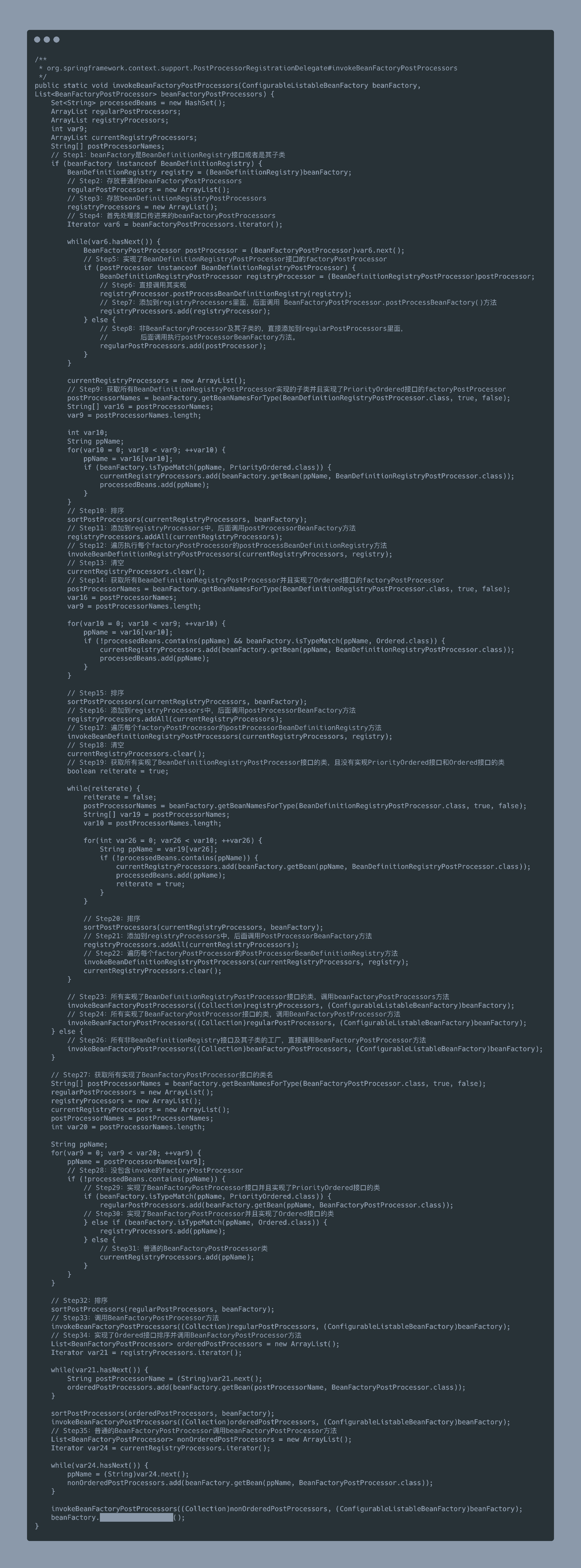
流程說明:
調用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry) 方法。參數 beanFactoryPostProcessors 傳入的優先處理掉。然后獲取容器注冊的,對于這些 Bean 按照 PriorityOrdered 接口、Ordered、沒有排序接口的實例分別進行處理。
調用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory) 方法。備注:BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 屬于 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 子接口。先處理屬于 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口實例的 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory) 方法,然后獲取容器注冊的。對于這些 Bean 按照 PriorityOrdered 接口、Ordered、沒有排序接口的實例分別進行處理。
可以理解為 Bean 類直接實現接口的方法,比如 BeanNameAware、BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware、InitializingBean、DisposableBean 等方法,這些方法只對當前 Bean 生效。
Aware 類型的接口的作用就是讓我們能夠拿到 Spring 容器中的一些資源。基本都能夠見名知意,Aware 之前的名字就是可以拿到什么資源,例如 BeanNameAware 可以拿到 BeanName,以此類推。調用時機需要注意:所有的 Aware 方法都是在初始化階段之前調用的。
Aware 接口眾多,這里同樣通過分類的方式幫助大家記憶。Aware 接口具體可以分為兩組,至于為什么這么分,詳見下面的源碼分析。如下排列順序同樣也是 Aware 接口的執行順序,能夠見名知意的接口不再解釋。
Aware Group1
BeanNameAware
BeanClassLoaderAware
BeanFactoryAware
Aware Group2
EnvironmentAware
EmbeddedValueResolverAware
這個知道的人可能不多,實現該接口能夠獲取 Spring EL 解析器,用戶的自定義注解需要支持 SPEL 表達式的時候可以使用,非常方便。
ApplicationContextAware(ResourceLoaderAware/ApplicationEventPublisherAware/MessageSourceAware)
這幾個接口可能讓人有點懵,實際上這幾個接口可以一起記,其返回值實質上都是當前ApplicationContext 對象,因為 ApplicationContext 是一個復合接口,如下:
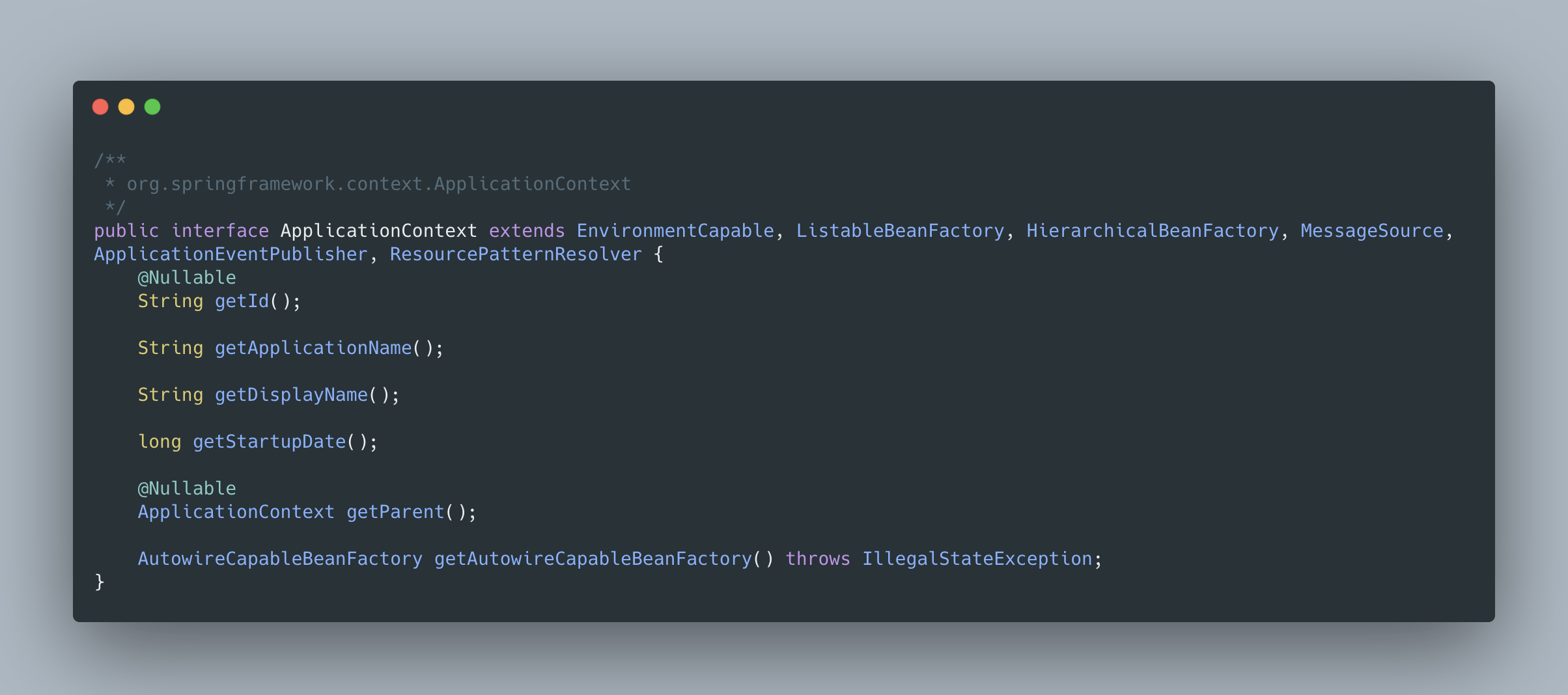
Aware 調用時機源碼分析
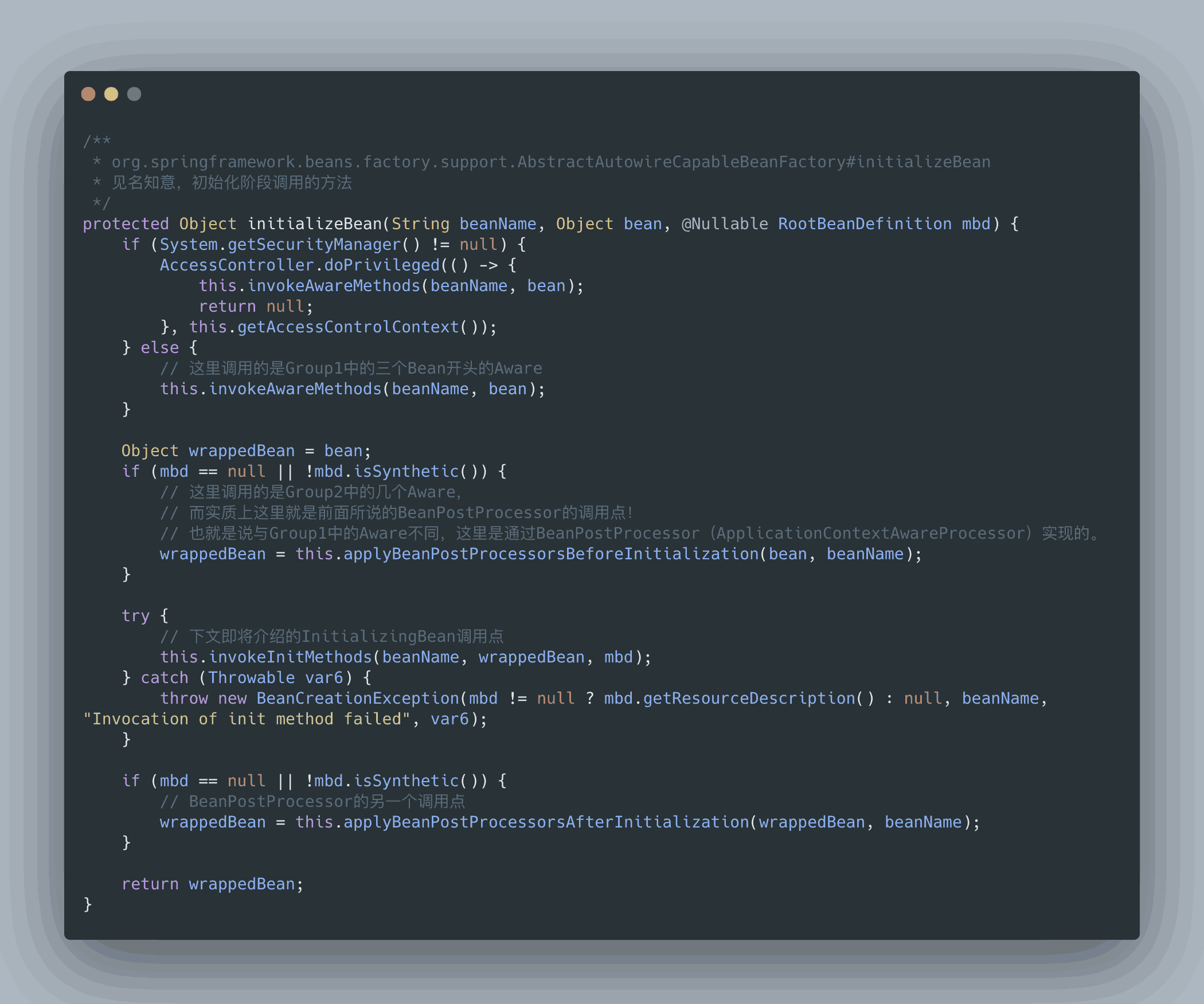
可以看到并不是所有的 Aware 接口都使用同樣的方式調用。Bean××Aware 都是在代碼中直接調用的,而 ApplicationContext 相關的 Aware 都是通過 BeanPostProcessor#postProcessBeforeInitialization() 實現的。感興趣的可以自己看一下 ApplicationContextAwareProcessor 這個類的源碼,就是判斷當前創建的 Bean 是否實現了相關的 Aware 方法,如果實現了會調用回調方法將資源傳遞給 Bean。
BeanPostProcessor 的調用時機也能在這里體現,包圍住 invokeInitMethods 方法,也就說明了在初始化階段的前后執行。
關于 Aware 接口的執行順序,其實只需要記住第一組在第二組執行之前就行了。
至于剩下的兩個生命周期接口就很簡單了,實例化和屬性賦值都是 Spring 幫助我們做的,能夠自己實現的有初始化和銷毀兩個生命周期階段。
InitializingBean 對應生命周期的初始化階段,在上面源碼的 invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);方法中調用。
有一點需要注意,因為 Aware 方法都是執行在初始化方法之前,所以可以在初始化方法中放心大膽的使用 Aware 接口獲取的資源,這也是我們自定義擴展 Spring 的常用方式。
除了實現 InitializingBean 接口之外還能通過注解或者 xml 配置的方式指定初始化方法,至于這幾種定義方式的調用順序其實沒有必要記。因為這幾個方法對應的都是同一個生命周期,只是實現方式不同,我們一般只采用其中一種方式。
DisposableBean 類似于 InitializingBean,對應生命周期的銷毀階段,以ConfigurableApplicationContext#close()方法作為入口,實現是通過循環取所有實現了 DisposableBean 接口的 Bean 然后調用其 destroy() 方法,感興趣的可以自行跟一下源碼。
該接口只有一個方法 setBeanName(String name),用來獲取 bean 的id 或者 name。
該接口只有一個方法 setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory),用來獲取當前環境中的 BeanFactory。
該接口只有一個方法 setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext),用來獲取當前環境中的 ApplicationContext。
該接口只有一個方法 afterPropertiesSet(),在屬性注入完成后調用。
該接口只有一個方法 destroy(),在容器銷毀的時候調用,在用戶指定的 destroy-method 之前調用。
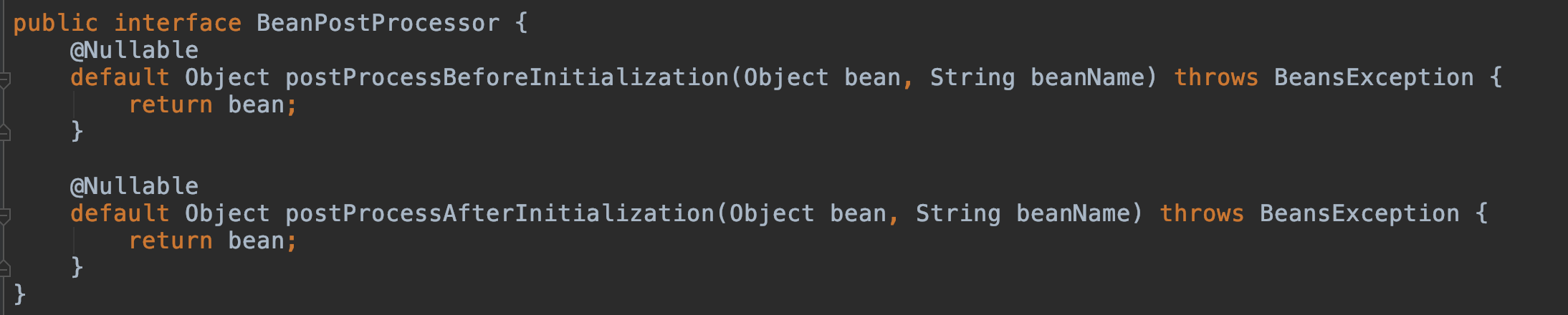
該接口有兩個方法:
postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName):在初始化之前調用此方法
postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName):在初始化之后調用此方法
通過方法簽名我們可以知道,我們可以通過 beanName 來篩選出我們需要進行個性化定制的 bean。
該類是 BeanPostProcessor 的子接口,常用的有如下三個方法:
postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName):在bean實例化之前調用
postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName):在bean實例化之后、設置屬性前調用
postProcessAfterInstantiation(Class beanClass, String beanName):在bean實例化之后調用
思路:創建一個類 UserBean ,讓其實現幾個特殊的接口,并分別在接口實現的構造器、接口方法中斷點,觀察線程調用棧,分析出 Bean 對象創建和管理關鍵點的觸發時機。
@Component
public class UserBean implements InitializingBean, BeanNameAware, DisposableBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private int id;
private String name;
public UserBean(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
System.out.println("2. 調用構造函數");
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
System.out.println("5. 屬性注入 id");
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("5. 屬性注入 name");
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String name) {
System.out.println("6. 調用 BeanNameAware.setBeanName() 方法");
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
UserBean userBean = (UserBean) applicationContext.getBean("userBean");
System.out.println(userBean);
System.out.println("7. 調用 BeanNameAware.setBeanName() 方法");
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("9. 調用 InitializingBean.afterPropertiesSet() 方法");
}
public void myInit() {
System.out.println("10. 調用 init-method 方法");
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("12. 調用 DisposableBean.destroy() 方法");
}
public void myDestroy() {
System.out.println("13. 調用 destroy-method 方法");
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "UserBean{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}@Component
public class MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userBean".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("1. 調用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInstantiation() 方法");
}
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userBean".equals(beanName)) {
UserBean userBean = (UserBean) bean;
System.out.println("3. 調用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInstantiation() 方法");
System.out.println(userBean);
}
return true;
}
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userBean".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("4. 調用 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.postProcessProperties() 方法");
}
return null;
}
}@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userBean".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("8. 調用 BeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization() 方法");
}
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if ("userBean".equals(beanName)) {
System.out.println("11. 調用 BeanPostProcessor.postProcessAfterInitialization() 方法");
}
return bean;
}
}@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("0. 調用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory() 方法");
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd "> <bean class="com.riemann.test.MyInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor" /> <bean id="userBean" class="com.riemann.test.UserBean" init-method="myInit" destroy-method="myDestroy"> <!-- 構造函數注入 --> <constructor-arg index="0" type="int"> <value>1</value> </constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" type="java.lang.String"> <value>微信公眾號【老周聊架構】</value> </constructor-arg> <!-- setter方法注入 --> <property name="id" value="2"/> <property name="name" value="riemann"/> </bean> <bean class="com.riemann.test.MyBeanPostProcessor" /> <bean class="com.riemann.test.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor" /> </beans>
public class BeanLifeCycleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:applicationContext.xml");
UserBean user = (UserBean) applicationContext.getBean("userBean");
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).close();
}
}
以上就是關于“Spring Bean的生命周期是什么”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。