您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“React首次渲染流程是什么”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
在開始進行源碼分析前,我們先來看幾個題目:
題目一:
渲染下面的組件,打印順序是什么?
import React from 'react'
const channel = new MessageChannel()
// onmessage 是一個宏任務
channel.port1.onmessage = () => {
console.log('1 message channel')
}
export default function App() {
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log('2 use effect')
}, [])
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('3 promise')
})
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
console.log('4 use layout effect')
channel.port2.postMessage('')
}, [])
return <div>App</div>
}答案:4 3 2 1
題目二:
點擊 p 標簽后,下面事件發生的順序
頁面顯示 xingzhi
console.log('useLayoutEffect ayou')
console.log('useLayoutEffect xingzhi')
console.log('useEffect ayou')
console.log('useEffect xingzhi')
import React from 'react'
import {useState} from 'react'
function Name({name}) {
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log(`useEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log(`useEffect destroy ${name}`)
}
}, [name])
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
console.log(`useLayoutEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log(`useLayoutEffect destroy ${name}`)
}
}, [name])
return <span>{name}</span>
}
// 點擊后,下面事件發生的順序
// 1. 頁面顯示 xingzhi
// 2. console.log('useLayoutEffect ayou')
// 3. console.log('useLayoutEffect xingzhi')
// 4. console.log('useEffect ayou')
// 5. console.log('useEffect xingzhi')
export default function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState('ayou')
const onClick = React.useCallback(() => setName('xingzhi'), [])
return (
<div>
<Name name={name} />
<p onClick={onClick}>I am 18</p>
</div>
)
}答案:1 2 3 4 5
你是不是都答對了呢?
我們以下面這個例子來闡述下首次渲染的流程:
function Name({name}) {
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log(`useEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log('useEffect destroy')
}
}, [name])
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
console.log(`useLayoutEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log('useLayoutEffect destroy')
}
}, [name])
return <span>{name}</span>
}
function Gender() {
return <i>Male</i>
}
export default function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState('ayou')
return (
<div>
<Name name={name} />
<p onClick={() => setName('xingzhi')}>I am 18</p>
<Gender />
</div>
)
}
...
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'))首先,我們看看 render,它是從 ReactDOMLegacy 中導出的,并最后調用了 legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer:
function legacyRenderSubtreeIntoContainer(
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
children: ReactNodeList,
container: Container,
forceHydrate: boolean,
callback: ?Function
) {
// TODO: Without `any` type, Flow says "Property cannot be accessed on any
// member of intersection type." Whyyyyyy.
let root: RootType = (container._reactRootContainer: any)
let fiberRoot
if (!root) {
// 首次渲染
root = container._reactRootContainer = legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container,
forceHydrate
)
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback
callback = function () {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot)
originalCallback.call(instance)
}
}
// Initial mount should not be batched.
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback)
})
} else {
// 更新
fiberRoot = root._internalRoot
if (typeof callback === 'function') {
const originalCallback = callback
callback = function () {
const instance = getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot)
originalCallback.call(instance)
}
}
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback)
}
return getPublicRootInstance(fiberRoot)
}首次渲染時,經過下面這一系列的操作,會初始化一些東西:
ReactDOMLegacy.js
function legacyCreateRootFromDOMContainer(
container: Container,
forceHydrate: boolean
): RootType {
...
return createLegacyRoot(
container,
shouldHydrate
? {
hydrate: true,
}
: undefined
)
}
ReactDOMRoot.js
function createLegacyRoot(
container: Container,
options?: RootOptions,
): RootType {
return new ReactDOMBlockingRoot(container, LegacyRoot, options);
}
function ReactDOMBlockingRoot(
container: Container,
tag: RootTag,
options: void | RootOptions,
) {
this._internalRoot = createRootImpl(container, tag, options);
}
function createRootImpl(
container: Container,
tag: RootTag,
options: void | RootOptions,
) {
...
const root = createContainer(container, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks)
...
}
ReactFiberReconciler.old.js
function createContainer(
containerInfo: Container,
tag: RootTag,
hydrate: boolean,
hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
): OpaqueRoot {
return createFiberRoot(containerInfo, tag, hydrate, hydrationCallbacks);
}
ReactFiberRoot.old.js
function createFiberRoot(
containerInfo: any,
tag: RootTag,
hydrate: boolean,
hydrationCallbacks: null | SuspenseHydrationCallbacks,
): FiberRoot {
...
const root: FiberRoot = (new FiberRootNode(containerInfo, tag, hydrate): any)
const uninitializedFiber = createHostRootFiber(tag)
root.current = uninitializedFiber
uninitializedFiber.stateNode = root
initializeUpdateQueue(uninitializedFiber)
return root
}經過這一系列的操作以后,會形成如下的數據結構:
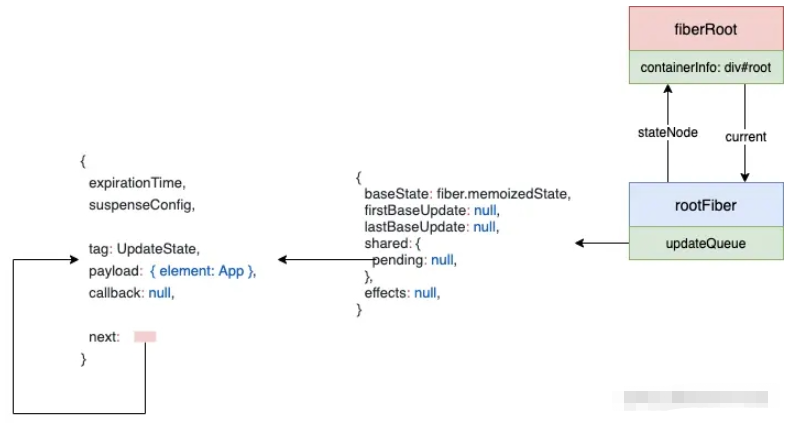
然后,會來到:
unbatchedUpdates(() => {
// 這里的 children 是 App 對應的這個 ReactElement
updateContainer(children, fiberRoot, parentComponent, callback)
})這里 unbatchedUpdates 會設置當前的 executionContext:
export function unbatchedUpdates<A, R>(fn: (a: A) => R, a: A): R {
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext
// 去掉 BatchedContext
executionContext &= ~BatchedContext
// 加上 LegacyUnbatchedContext
executionContext |= LegacyUnbatchedContext
try {
return fn(a)
} finally {
executionContext = prevExecutionContext
if (executionContext === NoContext) {
// Flush the immediate callbacks that were scheduled during this batch
flushSyncCallbackQueue()
}
}
}然后執行 updateContainer:
export function updateContainer(
element: ReactNodeList,
container: OpaqueRoot,
parentComponent: ?React$Component<any, any>,
callback: ?Function
): ExpirationTime {
const current = container.current
const currentTime = requestCurrentTimeForUpdate()
const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig()
const expirationTime = computeExpirationForFiber(
currentTime,
current,
suspenseConfig
)
const context = getContextForSubtree(parentComponent)
if (container.context === null) {
container.context = context
} else {
container.pendingContext = context
}
const update = createUpdate(expirationTime, suspenseConfig)
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
update.payload = {element}
callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback
if (callback !== null) {
update.callback = callback
}
enqueueUpdate(current, update)
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(current, expirationTime)
return expirationTime
}這里,會創建一個 update,然后入隊,我們的數據結構會變成這樣:
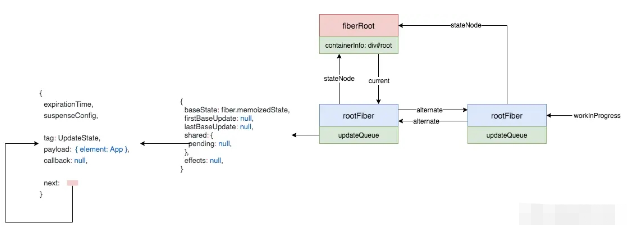
接下來就到了 scheduleUpdateOnFiber:
export function scheduleUpdateOnFiber(
fiber: Fiber,
expirationTime: ExpirationTime
) {
checkForNestedUpdates()
warnAboutRenderPhaseUpdatesInDEV(fiber)
const root = markUpdateTimeFromFiberToRoot(fiber, expirationTime)
if (root === null) {
warnAboutUpdateOnUnmountedFiberInDEV(fiber)
return
}
// TODO: computeExpirationForFiber also reads the priority. Pass the
// priority as an argument to that function and this one.
const priorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel()
if (expirationTime === Sync) {
if (
// Check if we're inside unbatchedUpdates
(executionContext & LegacyUnbatchedContext) !== NoContext &&
// Check if we're not already rendering
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext
) {
// Register pending interactions on the root to avoid losing traced interaction data.
schedulePendingInteractions(root, expirationTime)
// This is a legacy edge case. The initial mount of a ReactDOM.render-ed
// root inside of batchedUpdates should be synchronous, but layout updates
// should be deferred until the end of the batch.
performSyncWorkOnRoot(root)
} else {
// 暫時不看
}
} else {
// 暫時不看
}
}最后走到了 performSyncWorkOnRoot:
function performSyncWorkOnRoot(root) {
invariant(
(executionContext & (RenderContext | CommitContext)) === NoContext,
'Should not already be working.'
)
flushPassiveEffects()
const lastExpiredTime = root.lastExpiredTime
let expirationTime
if (lastExpiredTime !== NoWork) {
...
} else {
// There's no expired work. This must be a new, synchronous render.
expirationTime = Sync
}
let exitStatus = renderRootSync(root, expirationTime)
...
const finishedWork: Fiber = (root.current.alternate: any);
root.finishedWork = finishedWork;
root.finishedExpirationTime = expirationTime;
root.nextKnownPendingLevel = getRemainingExpirationTime(finishedWork);
commitRoot(root);
return null
}這里,可以分為兩個大的步驟:
render
commit
首先看看 renderRootSync:
function renderRootSync(root, expirationTime) {
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext
executionContext |= RenderContext
const prevDispatcher = pushDispatcher(root)
// If the root or expiration time have changed, throw out the existing stack
// and prepare a fresh one. Otherwise we'll continue where we left off.
if (root !== workInProgressRoot || expirationTime !== renderExpirationTime) {
// 主要是給 workInProgress 賦值
prepareFreshStack(root, expirationTime)
startWorkOnPendingInteractions(root, expirationTime)
}
const prevInteractions = pushInteractions(root)
do {
try {
workLoopSync()
break
} catch (thrownValue) {
handleError(root, thrownValue)
}
} while (true)
resetContextDependencies()
if (enableSchedulerTracing) {
popInteractions(((prevInteractions: any): Set<Interaction>))
}
executionContext = prevExecutionContext
popDispatcher(prevDispatcher)
if (workInProgress !== null) {
// This is a sync render, so we should have finished the whole tree.
invariant(
false,
'Cannot commit an incomplete root. This error is likely caused by a ' +
'bug in React. Please file an issue.'
)
}
// Set this to null to indicate there's no in-progress render.
workInProgressRoot = null
return workInProgressRootExitStatus
}這里首先調用 prepareFreshStack(root, expirationTime),這一句主要是通過 root.current 來創建 workInProgress。調用后,數據結構成了這樣:
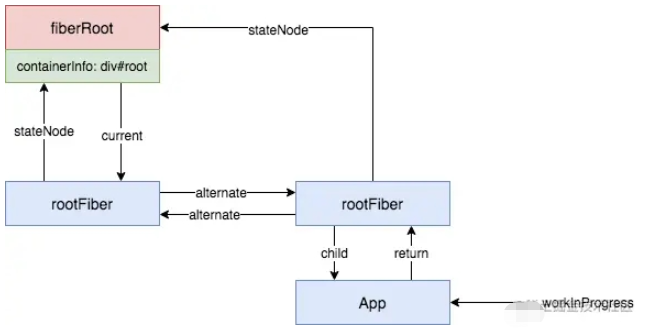
跳過中間的一些語句,我們來到 workLoopSync:
function workLoopSync() {
// Already timed out, so perform work without checking if we need to yield.
while (workInProgress !== null) {
performUnitOfWork(workInProgress)
}
}function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally
// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't
// need an additional field on the work in progress.
const current = unitOfWork.alternate
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(unitOfWork)
let next
if (enableProfilerTimer && (unitOfWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode) {
startProfilerTimer(unitOfWork)
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, renderExpirationTime)
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(unitOfWork, true)
} else {
next = beginWork(current, unitOfWork, renderExpirationTime)
}
resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV()
unitOfWork.memoizedProps = unitOfWork.pendingProps
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork)
} else {
workInProgress = next
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null
}這里又分為兩個步驟:
beginWork,傳入當前 Fiber 節點,創建子 Fiber 節點。
completeUnitOfWork,通過 Fiber 節點創建真實 DOM 節點。
這兩個步驟會交替的執行,其目標是:
構建出新的 Fiber 樹
與舊 Fiber 比較得到 effect 鏈表(插入、更新、刪除、useEffect 等都會產生 effect)
function beginWork(
current: Fiber | null,
workInProgress: Fiber,
renderExpirationTime: ExpirationTime
): Fiber | null {
const updateExpirationTime = workInProgress.expirationTime
if (current !== null) {
const oldProps = current.memoizedProps
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps
if (
oldProps !== newProps ||
hasLegacyContextChanged() ||
// Force a re-render if the implementation changed due to hot reload:
(__DEV__ ? workInProgress.type !== current.type : false)
) {
// 略
} else if (updateExpirationTime < renderExpirationTime) {
// 略
} else {
// An update was scheduled on this fiber, but there are no new props
// nor legacy context. Set this to false. If an update queue or context
// consumer produces a changed value, it will set this to true. Otherwise,
// the component will assume the children have not changed and bail out.
didReceiveUpdate = false
}
} else {
didReceiveUpdate = false
}
// Before entering the begin phase, clear pending update priority.
// TODO: This assumes that we're about to evaluate the component and process
// the update queue. However, there's an exception: SimpleMemoComponent
// sometimes bails out later in the begin phase. This indicates that we should
// move this assignment out of the common path and into each branch.
workInProgress.expirationTime = NoWork
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case IndeterminateComponent:
// ...省略
case LazyComponent:
// ...省略
case FunctionComponent:
// ...省略
case ClassComponent:
// ...省略
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime)
case HostComponent:
// ...省略
case HostText:
// ...省略
// ...省略其他類型
}
}這里因為是 rootFiber,所以會走到 updateHostRoot:
function updateHostRoot(current, workInProgress, renderExpirationTime) {
// 暫時不看
pushHostRootContext(workInProgress)
const updateQueue = workInProgress.updateQueue
const nextProps = workInProgress.pendingProps
const prevState = workInProgress.memoizedState
const prevChildren = prevState !== null ? prevState.element : null
cloneUpdateQueue(current, workInProgress)
processUpdateQueue(workInProgress, nextProps, null, renderExpirationTime)
const nextState = workInProgress.memoizedState
// Caution: React DevTools currently depends on this property
// being called "element".
const nextChildren = nextState.element
if (nextChildren === prevChildren) {
// 省略
}
const root: FiberRoot = workInProgress.stateNode
if (root.hydrate && enterHydrationState(workInProgress)) {
// 省略
} else {
// 給 rootFiber 生成子 fiber
reconcileChildren(
current,
workInProgress,
nextChildren,
renderExpirationTime
)
resetHydrationState()
}
return workInProgress.child
}經過 updateHostRoot 后,會返回 workInProgress.child 作為下一個 workInProgress,最后的數據結構如下(這里先忽略 reconcileChildren 這個比較復雜的函數):
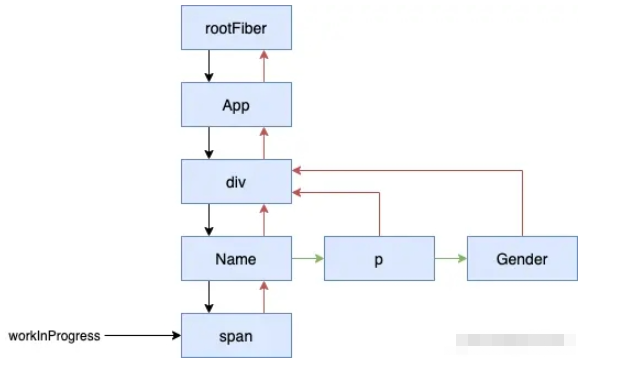
接著會繼續進行 beginWork,這次會來到 mountIndeterminateComponent (暫時忽略)。總之,經過不斷的 beginWork 后,我們會得到如下的一個結構:
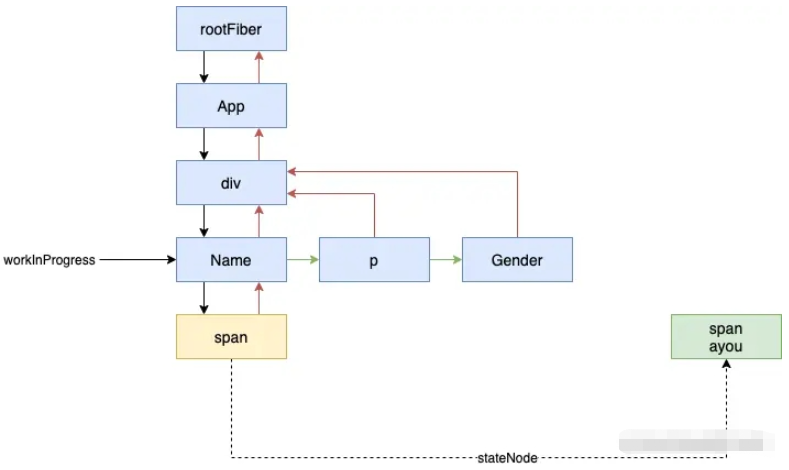
此時 next 為空,我們會走到:
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork)
} else {
...
}function completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
// Attempt to complete the current unit of work, then move to the next
// sibling. If there are no more siblings, return to the parent fiber.
let completedWork = unitOfWork
do {
// The current, flushed, state of this fiber is the alternate. Ideally
// nothing should rely on this, but relying on it here means that we don't
// need an additional field on the work in progress.
const current = completedWork.alternate
const returnFiber = completedWork.return
// Check if the work completed or if something threw.
if ((completedWork.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect) {
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(completedWork)
let next
if (
!enableProfilerTimer ||
(completedWork.mode & ProfileMode) === NoMode
) {
next = completeWork(current, completedWork, renderExpirationTime)
} else {
startProfilerTimer(completedWork)
next = completeWork(current, completedWork, renderExpirationTime)
// Update render duration assuming we didn't error.
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(completedWork, false)
}
resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV()
resetChildExpirationTime(completedWork)
if (next !== null) {
// Completing this fiber spawned new work. Work on that next.
workInProgress = next
return
}
if (
returnFiber !== null &&
// Do not append effects to parents if a sibling failed to complete
(returnFiber.effectTag & Incomplete) === NoEffect
) {
// Append all the effects of the subtree and this fiber onto the effect
// list of the parent. The completion order of the children affects the
// side-effect order.
if (returnFiber.firstEffect === null) {
returnFiber.firstEffect = completedWork.firstEffect
}
if (completedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = completedWork.firstEffect
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = completedWork.lastEffect
}
// If this fiber had side-effects, we append it AFTER the children's
// side-effects. We can perform certain side-effects earlier if needed,
// by doing multiple passes over the effect list. We don't want to
// schedule our own side-effect on our own list because if end up
// reusing children we'll schedule this effect onto itself since we're
// at the end.
const effectTag = completedWork.effectTag
// Skip both NoWork and PerformedWork tags when creating the effect
// list. PerformedWork effect is read by React DevTools but shouldn't be
// committed.
if (effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (returnFiber.lastEffect !== null) {
returnFiber.lastEffect.nextEffect = completedWork
} else {
returnFiber.firstEffect = completedWork
}
returnFiber.lastEffect = completedWork
}
}
} else {
// This fiber did not complete because something threw. Pop values off
// the stack without entering the complete phase. If this is a boundary,
// capture values if possible.
const next = unwindWork(completedWork, renderExpirationTime)
// Because this fiber did not complete, don't reset its expiration time.
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
(completedWork.mode & ProfileMode) !== NoMode
) {
// Record the render duration for the fiber that errored.
stopProfilerTimerIfRunningAndRecordDelta(completedWork, false)
// Include the time spent working on failed children before continuing.
let actualDuration = completedWork.actualDuration
let child = completedWork.child
while (child !== null) {
actualDuration += child.actualDuration
child = child.sibling
}
completedWork.actualDuration = actualDuration
}
if (next !== null) {
// If completing this work spawned new work, do that next. We'll come
// back here again.
// Since we're restarting, remove anything that is not a host effect
// from the effect tag.
next.effectTag &= HostEffectMask
workInProgress = next
return
}
if (returnFiber !== null) {
// Mark the parent fiber as incomplete and clear its effect list.
returnFiber.firstEffect = returnFiber.lastEffect = null
returnFiber.effectTag |= Incomplete
}
}
const siblingFiber = completedWork.sibling
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
workInProgress = siblingFiber
return
}
// Otherwise, return to the parent
completedWork = returnFiber
// Update the next thing we're working on in case something throws.
workInProgress = completedWork
} while (completedWork !== null)
// We've reached the root.
if (workInProgressRootExitStatus === RootIncomplete) {
workInProgressRootExitStatus = RootCompleted
}
}此時這里的 unitOfWork 是 span 對應的 fiber。從函數頭部的注釋我們可以大致知道該函數的功能:
// Attempt to complete the current unit of work, then move to the next // sibling. If there are no more siblings, return to the parent fiber. // 嘗試去完成當前的工作單元,然后處理下一個 sibling。如果沒有 sibling 了,就返回去完成父 fiber
這里一路走下去最后會來到 completeWork 這里 :
case HostComponent: ... // 會調用 ReactDOMComponent.js 中的 createELement 方法創建 span 標簽 const instance = createInstance( type, newProps, rootContainerInstance, currentHostContext, workInProgress ) // 將子元素 append 到 instance 中 appendAllChildren(instance, workInProgress, false, false) workInProgress.stateNode = instance;
執行完后,我們的結構如下所示(我們用綠色的圓來表示真實 dom):
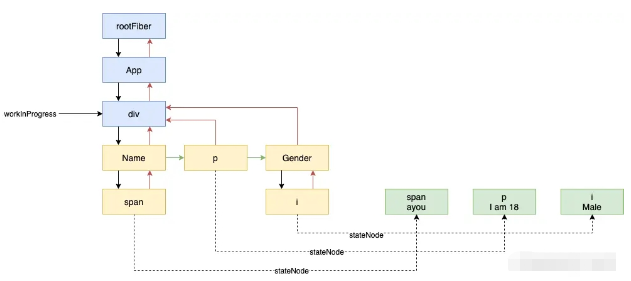
此時 next 將會是 null,我們需要往上找到下一個 completedWork,即 Name,因為 Name 是一個 FunctionComponent,所以在 completeWork 中直接返回了 null。又因為它有 sibling,所以會將它的 sibling 賦值給 workInProgress,并返回對其進行 beginWork。
const siblingFiber = completedWork.sibling
if (siblingFiber !== null) {
// If there is more work to do in this returnFiber, do that next.
// workInProgress 更新為 sibling
workInProgress = siblingFiber
// 直接返回,回到了 performUnitOfWork
return
}function performUnitOfWork(unitOfWork: Fiber): void {
...
if (next === null) {
// If this doesn't spawn new work, complete the current work.
// 上面的代碼回到了這里
completeUnitOfWork(unitOfWork)
} else {
workInProgress = next
}
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null
}這樣 beginWork 和 completeWork 不斷交替的執行,當我們執行到 div 的時候,我們的結構如下所示:
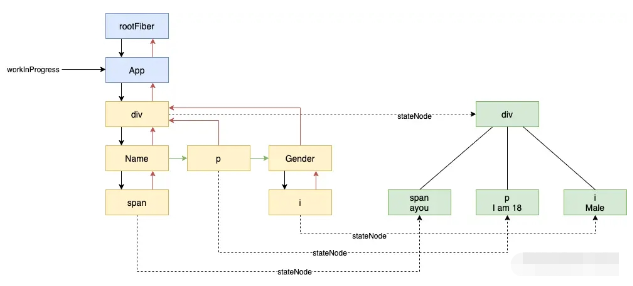
之所以要額外的分析 div 的 complete 過程,是因為這個例子方便我們分析 appendAllChildren:
appendAllChildren = function (
parent: Instance,
workInProgress: Fiber,
needsVisibilityToggle: boolean,
isHidden: boolean
) {
// We only have the top Fiber that was created but we need recurse down its
// children to find all the terminal nodes.
let node = workInProgress.child
while (node !== null) {
if (node.tag === HostComponent || node.tag === HostText) {
appendInitialChild(parent, node.stateNode)
} else if (enableFundamentalAPI && node.tag === FundamentalComponent) {
appendInitialChild(parent, node.stateNode.instance)
} else if (node.tag === HostPortal) {
// If we have a portal child, then we don't want to traverse
// down its children. Instead, we'll get insertions from each child in
// the portal directly.
} else if (node.child !== null) {
node.child.return = node
node = node.child
continue
}
if (node === workInProgress) {
return
}
while (node.sibling === null) {
if (node.return === null || node.return === workInProgress) {
return
}
node = node.return
}
node.sibling.return = node.return
node = node.sibling
}
}由于 workInProgress 指向 div 這個 fiber,他的 child 是 Name,會進入 else if (node.child !== null) 這個條件分支。然后繼續下一個循環,此時 node 為 span 這個 fiber,會進入第一個分支,將 span 對應的 dom 元素插入到 parent 之中。
這樣不停的循環,最后會執行到 if (node === workInProgress) 退出,此時所有的子元素都 append 到了 parent 之中:
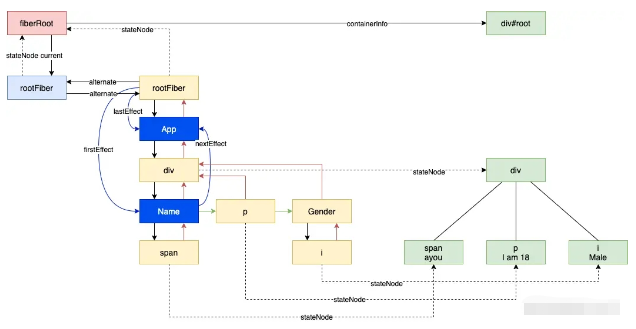
然后繼續 beginWork 和 completeWork,最后會來到 rootFiber。不同的是,該節點的 alternate 并不為空,且該節點 tag 為 HootRoot,所以 completeWork 時會來到這里:
case HostRoot: {
...
updateHostContainer(workInProgress);
return null;
}updateHostContainer = function (workInProgress: Fiber) {
// Noop
}看來幾乎沒有做什么事情,到這我們的 render 階段就結束了,最后的結構如下所示:

其中藍色表示是有 effect 的 Fiber 節點,他們組成了一個鏈表,方便 commit 過程進行遍歷。
可以查看 render 過程動畫。
commit 大致可分為以下過程:
準備階段
before mutation 階段(執行 DOM 操作前)
mutation 階段(執行 DOM 操作)
切換 Fiber Tree
layout 階段(執行 DOM 操作后)
收尾階段
do {
// 觸發useEffect回調與其他同步任務。由于這些任務可能觸發新的渲染,所以這里要一直遍歷執行直到沒有任務
flushPassiveEffects()
// 暫時沒有復現出 rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null 的情景
// 首次渲染 rootWithPendingPassiveEffects 為 null
} while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null)
// finishedWork 就是正在工作的 rootFiber
const finishedWork = root.
// 優先級相關暫時不看
const expirationTime = root.finishedExpirationTime
if (finishedWork === null) {
return null
}
root.finishedWork = null
root.finishedExpirationTime = NoWork
root.callbackNode = null
root.callbackExpirationTime = NoWork
root.callbackPriority_old = NoPriority
const remainingExpirationTimeBeforeCommit = getRemainingExpirationTime(
finishedWork
)
markRootFinishedAtTime(
root,
expirationTime,
remainingExpirationTimeBeforeCommit
)
if (rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates !== null) {
const lastDiscreteTime = rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates.get(root)
if (
lastDiscreteTime !== undefined &&
remainingExpirationTimeBeforeCommit < lastDiscreteTime
) {
rootsWithPendingDiscreteUpdates.delete(root)
}
}
if (root === workInProgressRoot) {
workInProgressRoot = null
workInProgress = null
renderExpirationTime = NoWork
} else {
}
// 將effectList賦值給firstEffect
// 由于每個fiber的effectList只包含他的子孫節點
// 所以根節點如果有effectTag則不會被包含進來
// 所以這里將有effectTag的根節點插入到effectList尾部
// 這樣才能保證有effect的fiber都在effectList中
let firstEffect
if (finishedWork.effectTag > PerformedWork) {
if (finishedWork.lastEffect !== null) {
finishedWork.lastEffect.nextEffect = finishedWork
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect
} else {
firstEffect = finishedWork
}
} else {
firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect
}準備階段主要是確定 firstEffect,我們的例子中就是 Name 這個 fiber。
const prevExecutionContext = executionContext
executionContext |= CommitContext
const prevInteractions = pushInteractions(root)
// Reset this to null before calling lifecycles
ReactCurrentOwner.current = null
// The commit phase is broken into several sub-phases. We do a separate pass
// of the effect list for each phase: all mutation effects come before all
// layout effects, and so on.
// The first phase a "before mutation" phase. We use this phase to read the
// state of the host tree right before we mutate it. This is where
// getSnapshotBeforeUpdate is called.
focusedInstanceHandle = prepareForCommit(root.containerInfo)
shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = false
nextEffect = firstEffect
do {
if (__DEV__) {
...
} else {
try {
commitBeforeMutationEffects()
} catch (error) {
invariant(nextEffect !== null, 'Should be working on an effect.')
captureCommitPhaseError(nextEffect, error)
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect
}
}
} while (nextEffect !== null)
// We no longer need to track the active instance fiber
focusedInstanceHandle = null
if (enableProfilerTimer) {
// Mark the current commit time to be shared by all Profilers in this
// batch. This enables them to be grouped later.
recordCommitTime()
}before mutation 階段主要是調用了 commitBeforeMutationEffects 方法:
function commitBeforeMutationEffects() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
if (
!shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur &&
focusedInstanceHandle !== null &&
isFiberHiddenOrDeletedAndContains(nextEffect, focusedInstanceHandle)
) {
shouldFireAfterActiveInstanceBlur = true
beforeActiveInstanceBlur()
}
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag
if ((effectTag & Snapshot) !== NoEffect) {
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(nextEffect)
const current = nextEffect.alternate
// 調用getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber(current, nextEffect)
resetCurrentDebugFiberInDEV()
}
if ((effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
// If there are passive effects, schedule a callback to flush at
// the earliest opportunity.
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true
scheduleCallback(NormalPriority, () => {
flushPassiveEffects()
return null
})
}
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect
}
}因為 Name 中 effectTag 包括了 Passive,所以這里會執行:
scheduleCallback(NormalPriority, () => {
flushPassiveEffects()
return null
})這里主要是對 useEffect 中的任務進行異步調用,最終會在下個事件循環中執行 commitPassiveHookEffects:
export function commitPassiveHookEffects(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
if ((finishedWork.effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case FunctionComponent:
case ForwardRef:
case SimpleMemoComponent:
case Block: {
if (
enableProfilerTimer &&
enableProfilerCommitHooks &&
finishedWork.mode & ProfileMode
) {
try {
startPassiveEffectTimer();
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
);
commitHookEffectListMount(
HookPassive | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
);
} finally {
recordPassiveEffectDuration(finishedWork);
}
} else {
commitHookEffectListUnmount(
HookPassive | HookHasEffect,
finishedWork,
);
commitHookEffectListMount(HookPassive | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
function commitHookEffectListUnmount(tag: number, finishedWork: Fiber) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & tag) === tag) {
// Unmount
const destroy = effect.destroy;
effect.destroy = undefined;
if (destroy !== undefined) {
destroy();
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}
function commitHookEffectListMount(tag: number, finishedWork: Fiber) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & tag) === tag) {
// Mount
const create = effect.create;
effect.destroy = create();
...
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}其中,commitHookEffectListUnmount 會執行 useEffect 上次渲染返回的 destroy 方法,commitHookEffectListMount 會執行 useEffect 本次渲染的 create 方法。具體到我們的例子:
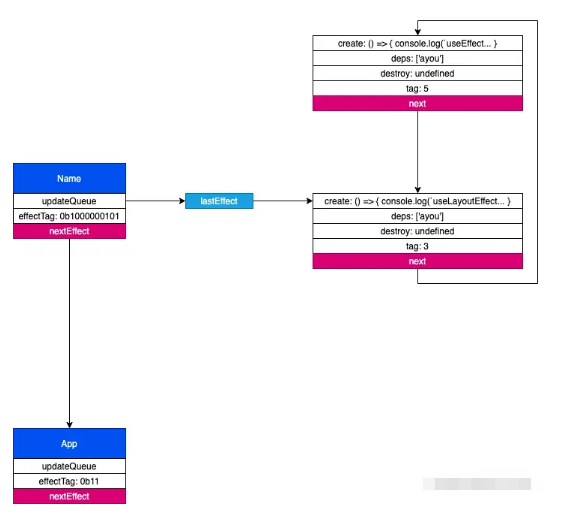
因為是首次渲染,所以 destroy 都是 undefined,所以只會打印 useEffect ayou。
mutation 階段主要是執行了 commitMutationEffects 這個方法:
function commitMutationEffects(root: FiberRoot, renderPriorityLevel) {
// TODO: Should probably move the bulk of this function to commitWork.
while (nextEffect !== null) {
setCurrentDebugFiberInDEV(nextEffect)
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag
...
// The following switch statement is only concerned about placement,
// updates, and deletions. To avoid needing to add a case for every possible
// bitmap value, we remove the secondary effects from the effect tag and
// switch on that value.
const primaryEffectTag =
effectTag & (Placement | Update | Deletion | Hydrating)
switch (primaryEffectTag) {
case Placement: {
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is
// inserted, before any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.
// TODO: findDOMNode doesn't rely on this any more but isMounted does
// and isMounted is deprecated anyway so we should be able to kill this.
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;
break;
}
case PlacementAndUpdate: {
// Placement
commitPlacement(nextEffect);
// Clear the "placement" from effect tag so that we know that this is
// inserted, before any life-cycles like componentDidMount gets called.
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement;
// Update
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
case Hydrating: {
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;
break;
}
case HydratingAndUpdate: {
nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Hydrating;
// Update
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
case Update: {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitWork(current, nextEffect);
break;
}
case Deletion: {
commitDeletion(root, nextEffect, renderPriorityLevel);
break;
}
}
}
}其中,Name 會走 Update 這個分支,執行 commitWork,最終會執行到 commitHookEffectListUnmount:
function commitHookEffectListUnmount(tag: number, finishedWork: Fiber) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
if ((effect.tag & tag) === tag) {
// Unmount
const destroy = effect.destroy;
effect.destroy = undefined;
if (destroy !== undefined) {
destroy();
}
}
effect = effect.next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}這里會同步執行 useLayoutEffect 上次渲染返回的 destroy 方法,我們的例子里是 undefined。
而 App 會走到 Placement 這個分支,執行 commitPlacement,這里的主要工作是把整棵 dom 樹插入到了 <div id='root'></div> 之中。
mutation 階段完成后,會執行:
root.current = finishedWork
完成后, fiberRoot 會指向 current Fiber 樹。
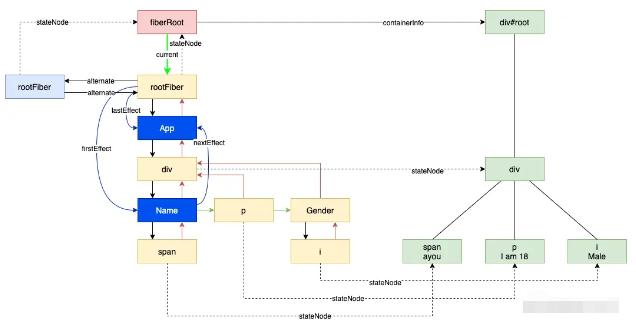
對應到我們的例子,layout 階段主要是同步執行 useLayoutEffect 中的 create 函數,所以這里會打印 useLayoutEffect ayou。
現在,我們來分析下文章開始的兩個題目:
題目一:
渲染下面的組件,打印順序是什么?
import React from 'react'
const channel = new MessageChannel()
// onmessage 是一個宏任務
channel.port1.onmessage = () => {
console.log('1 message channel')
}
export default function App() {
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log('2 use effect')
}, [])
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.log('3 promise')
})
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
console.log('4 use layout effect')
channel.port2.postMessage('')
}, [])
return <div>App</div>
}解析:
useLayoutEffect 中的任務會跟隨渲染過程同步執行,所以先打印 4
Promise 對象 then 中的任務是一個微任務,所以在 4 后面執行,打印 3
console.log('1 message channel') 和 console.log('2 use effect') 都會在宏任務中執行,執行順序就看誰先生成,這里 2 比 1 先,所以先打印 2,再打印 1。
題目二:
點擊 p 標簽后,下面事件發生的順序
頁面顯示 xingzhi
console.log('useLayoutEffect ayou')
console.log('useLayoutEffect xingzhi')
console.log('useEffect ayou')
console.log('useEffect xingzhi')
import React from 'react'
import {useState} from 'react'
function Name({name}) {
React.useEffect(() => {
console.log(`useEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log(`useEffect destroy ${name}`)
}
}, [name])
React.useLayoutEffect(() => {
console.log(`useLayoutEffect ${name}`)
return () => {
console.log(`useLayoutEffect destroy ${name}`)
}
}, [name])
return <span>{name}</span>
}
// 點擊后,下面事件發生的順序
// 1. 頁面顯示 xingzhi
// 2. console.log('useLayoutEffect destroy ayou')
// 3. console.log(`useLayoutEffect xingzhi`)
// 4. console.log('useEffect destroy ayou')
// 5. console.log(`useEffect xingzhi`)
export default function App() {
const [name, setName] = useState('ayou')
const onClick = React.useCallback(() => setName('xingzhi'), [])
return (
<div>
<Name name={name} />
<p onClick={onClick}>I am 18</p>
</div>
)
}解析:
span 這個 Fiber 位于 effect 鏈表的首部,在 commitMutations 中會先處理,所以頁面先顯示 xingzhi。
Name 這個 Fiber 位于 span 之后,所以 useLayoutEffect 中上一次的 destroy 緊接著其執行。打印 useLayoutEffect ayou。
commitLayoutEffects 中執行 useLayoutEffect 這一次的 create。打印 useLayoutEffect xingzhi。
useEffect 在下一個宏任務中執行,先執行上一次的 destroy,再執行這一次的 create。所以先打印 useEffect ayou,再打印 useEffect xingzhi。
“React首次渲染流程是什么”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。