您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“Python怎么構建一個文檔掃描器”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“Python怎么構建一個文檔掃描器”吧!
首先您應該熟悉Python的基礎知識,還需要了解如何使用NumPy Python庫。
打開任何Python IDE,創建兩個Python文件。將一個命名為main.py,將另一個命名為transform.py。然后在終端上執行以下命令,安裝所需的庫。
pip install OpenCV-Python imutils scikit-image NumPy
您將使用OpenCV-Python獲取圖像輸入并進行一些圖像處理,使用Imutils來調整輸入和輸出圖像的大小,并使用scikit-image對圖像施加閾值。NumPy將幫助您處理數組。
等待安裝完成,并等待IDE更新項目骨干內容。骨干內容更新完成后,您就可以開始編程了。完整的源代碼可以在GitHub代碼庫中找到。
打開main.py文件,導入所安裝的庫。這將使您能夠在必要時調用和使用它們的函數。
import cv2 import imutils from skimage.filters import threshold_local from transform import perspective_transform
忽略perspective_transform方面拋出的錯誤。您完成處理transform.py文件的工作后,錯誤會消失。
為想要掃描的文檔拍攝一張清晰的圖像。確保文檔的四個角及其內容都可見。將圖像復制到存儲程序文件的同一個文件夾中。
將輸入圖像路徑傳遞給OpenCV。制作原始圖像的副本,因為您在透視轉換期間需要它。將原始圖像的高度除以您想要調整到的高度。這將保持縱橫比。最后,輸出調整后的圖像。
# Passing the image path
original_img = cv2.imread('sample.jpg')
copy = original_img.copy()
# The resized height in hundreds
ratio = original_img.shape[0] / 500.0
img_resize = imutils.resize(original_img, height=500)
# Displaying output
cv2.imshow('Resized image', img_resize)
# Waiting for the user to press any key
cv2.waitKey(0)上述代碼的輸出如下:
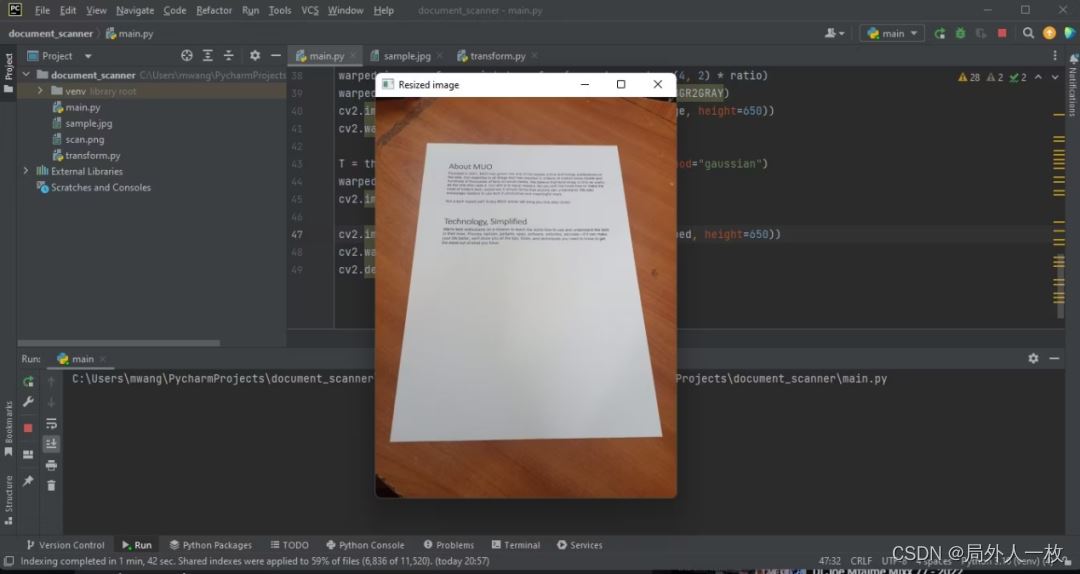
現在您已經將原始圖像的高度調整為500像素。
將調整后的RGB圖像轉換為灰度圖像。大多數圖像處理庫只處理灰度圖像,因為它們更容易處理。
gray_image = cv2.cvtColor(img_resize, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('Grayed Image', gray_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)注意原始圖像和灰度圖像之間的區別。
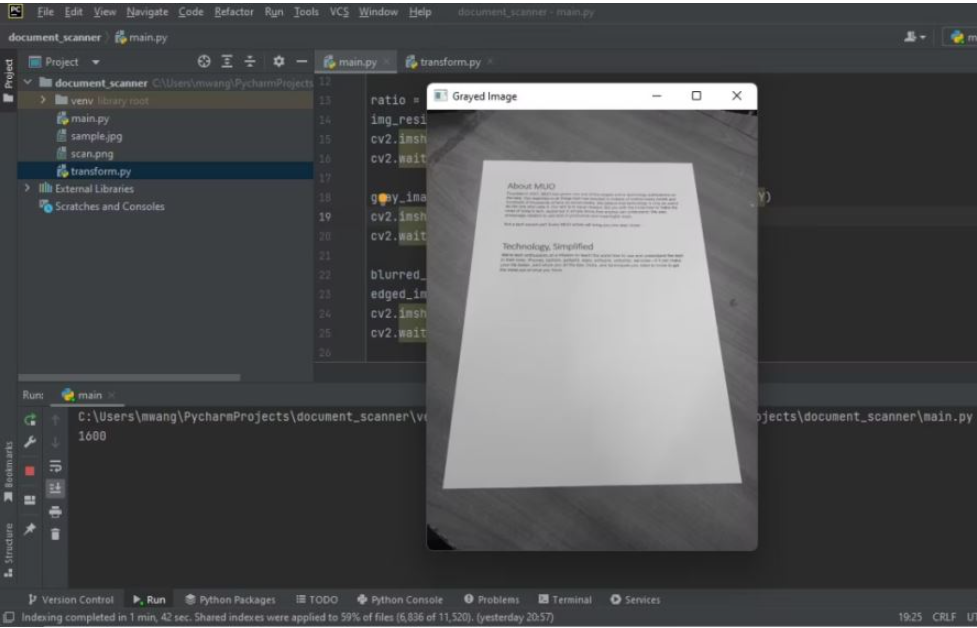
彩色桌變成了黑白桌。
對灰度圖像運用高斯模糊濾鏡以去除噪聲。然后調用OpenCV canny函數來檢測圖像中存在的邊緣。
blurred_image = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray_image, (5, 5), 0)
edged_img = cv2.Canny(blurred_image, 75, 200)
cv2.imshow('Image edges', edged_img)
cv2.waitKey(0)邊緣在輸出上是可見的。
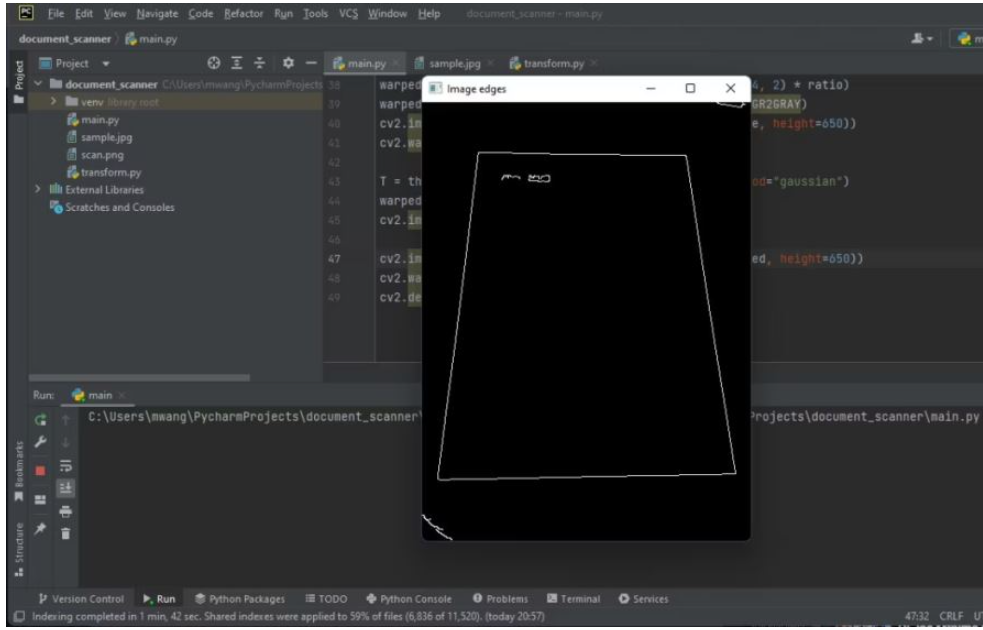
您將處理的邊緣是文檔的邊緣。
檢測邊緣圖像中的輪廓。按降序排序,只保留五個最大的輪廓。通過循環排序后的輪廓,近似獲取最大的四邊輪廓。
cnts, _ = cv2.findContours(edged_img, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE) cnts = sorted(cnts, key=cv2.contourArea, reverse=True)[:5] for c in cnts: peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True) approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True) if len(approx) == 4: doc = approx break
有四個邊的輪廓很可能含有文檔。
圈出檢測到的文檔輪廓的幾個角。這將幫助您確定您的程序是否能夠檢測圖像中的文檔。
p = []
for d in doc:
tuple_point = tuple(d[0])
cv2.circle(img_resize, tuple_point, 3, (0, 0, 255), 4)
p.append(tuple_point)
cv2.imshow('Circled corner points', img_resize)
cv2.waitKey(0)對調整后的RGB圖像圈出幾個角。
檢測到文檔之后,現在需要從圖像中提取文檔。
扭曲透視(warp perspective)是一種計算機視覺技術,用于轉換圖像以糾正失真。它將圖像轉換成不同的平面,讓您可以從不同的角度查看圖像。
warped_image = perspective_transform(copy, doc.reshape(4, 2) * ratio)
warped_image = cv2.cvtColor(warped_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow("Warped Image", imutils.resize(warped_image, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)為了獲得扭曲后的圖像,您需要創建一個簡單的模塊來執行透視轉換。
該模塊將對文檔角的點進行排序。它還會將文檔圖像轉換成不同的平面,并將相機角度更改為俯拍。
打開之前創建的那個transform.py文件,導入OpenCV庫和NumPy庫。
import numpy as np import cv2
這個模塊將含有兩個函數。創建一個對文檔角點的坐標進行排序的函數。第一個坐標將是左上角的坐標,第二個將是右上角的坐標,第三個將是右下角的坐標,第四個將是左下角的坐標。
def order_points(pts): # initializing the list of coordinates to be ordered rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = "float32") s = pts.sum(axis = 1) # top-left point will have the smallest sum rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)] # bottom-right point will have the largest sum rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)] '''computing the difference between the points, the top-right point will have the smallest difference, whereas the bottom-left will have the largest difference''' diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1) rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)] rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)] # returns ordered coordinates return rect
創建將計算新圖像的角坐標,并獲得俯拍的第二個函數。然后,它將計算透視變換矩陣,并返回扭曲的圖像。
def perspective_transform(image, pts): # unpack the ordered coordinates individually rect = order_points(pts) (tl, tr, br, bl) = rect '''compute the width of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between bottom-right and bottom-left x-coordinates or the top-right and top-left x-coordinates''' widthA = np.sqrt(((br[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) widthB = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - tl[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)) maxWidth = max(int(widthA), int(widthB)) '''compute the height of the new image, which will be the maximum distance between the top-left and bottom-left y-coordinates''' heightA = np.sqrt(((tr[0] - br[0]) ** 2) + ((tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2)) heightB = np.sqrt(((tl[0] - bl[0]) ** 2) + ((tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)) maxHeight = max(int(heightA), int(heightB)) '''construct the set of destination points to obtain an overhead shot''' dst = np.array([ [0, 0], [maxWidth - 1, 0], [maxWidth - 1, maxHeight - 1], [0, maxHeight - 1]], dtype = "float32") # compute the perspective transform matrix transform_matrix = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) # Apply the transform matrix warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, transform_matrix, (maxWidth, maxHeight)) # return the warped image return warped
現在您已創建了轉換模塊。perspective_transform導入方面的錯誤現在將消失。
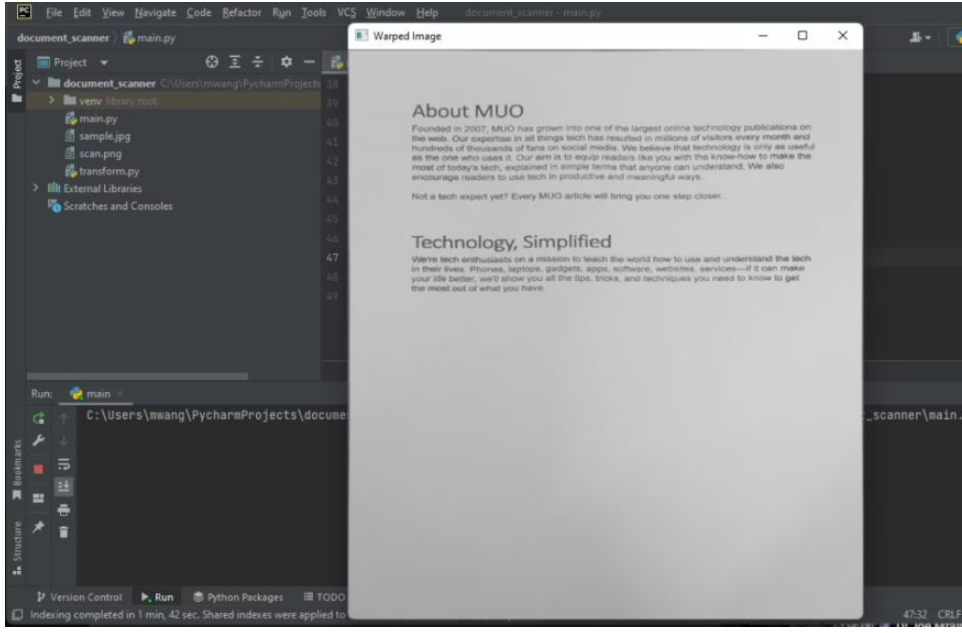
注意,顯示的圖像有俯拍。
在main.py文件中,對扭曲的圖像運用高斯閾值。這將給扭曲的圖像一個掃描后的外觀。將掃描后的圖像輸出保存到含有程序文件的文件夾中。
T = threshold_local(warped_image, 11, offset=10, method="gaussian")
warped = (warped_image > T).astype("uint8") * 255
cv2.imwrite('./'+'scan'+'.png',warped)以jpg格式保存掃描件可以保持文檔質量。
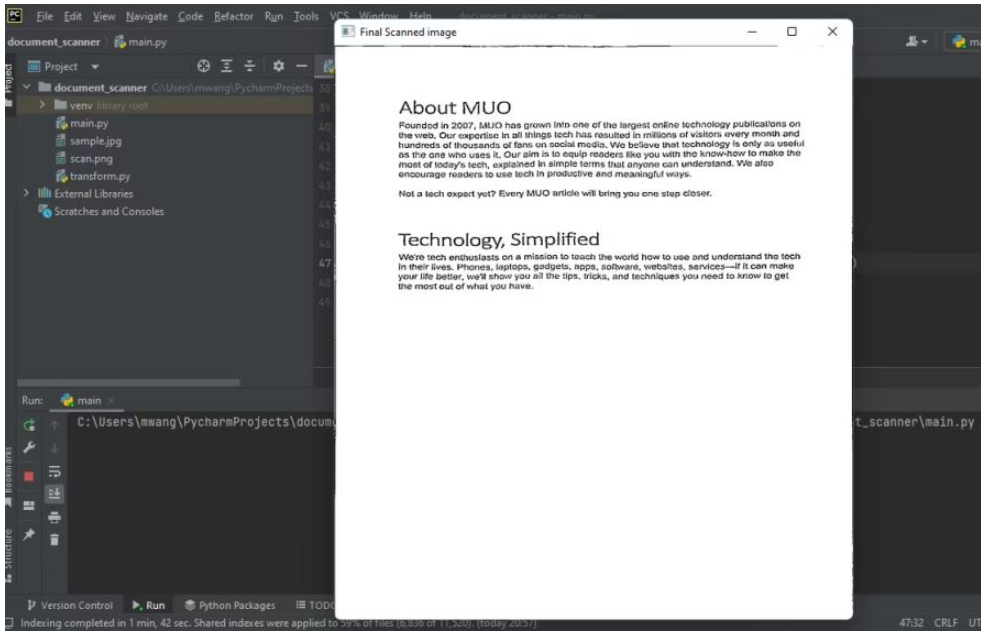
輸出掃描后文檔的圖像:
cv2.imshow("Final Scanned image", imutils.resize(warped, height=650))
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()下圖顯示了程序的輸出,即掃描后文檔的俯拍。
到此,相信大家對“Python怎么構建一個文檔掃描器”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。