您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“C++紅黑樹應用之set和map怎么使用”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在C++紅黑樹應用之set和map怎么使用問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”C++紅黑樹應用之set和map怎么使用”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
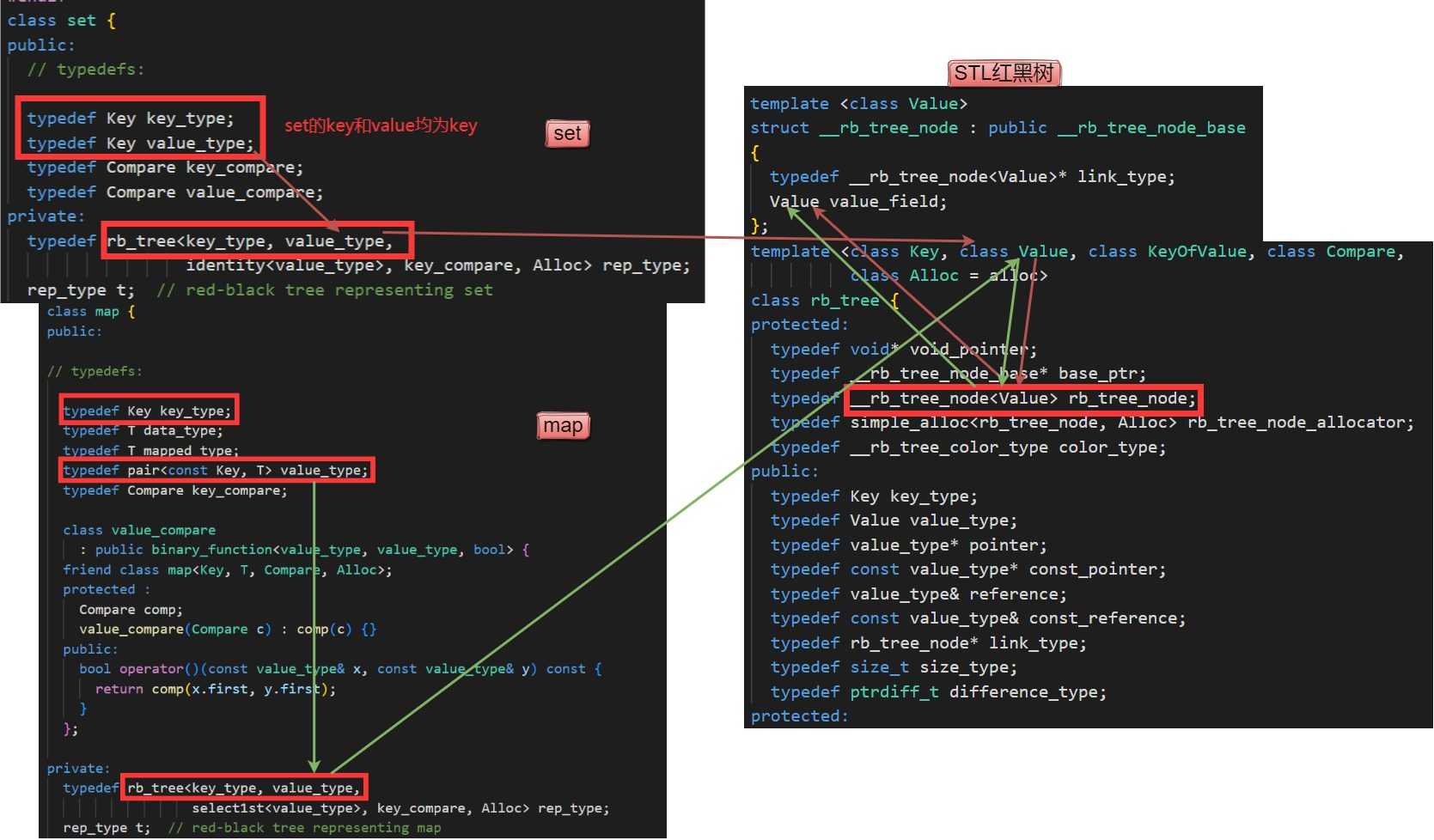
扒一扒STL庫中set和map的底層結構,不難發現,set和map的底層用的都是紅黑樹且均為key/value模型。
只不過set的key/value均為key值填充,而map的key/value使用key和pair<const Key,T>進行填充。因此,set和map中底層雖然都是紅黑樹,但這兩種數據結構中的紅黑樹實例化類型并不相同。
那么使用同一顆紅黑樹的模板,如何實例化出適配set和/map的對象?
template <class T>//T類型代表value
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_parent(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _col(RED)
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
T _data;
Color _col;
};map和set的區別在于value的不同,紅黑樹模板參數T,代表value用以區分set和map。
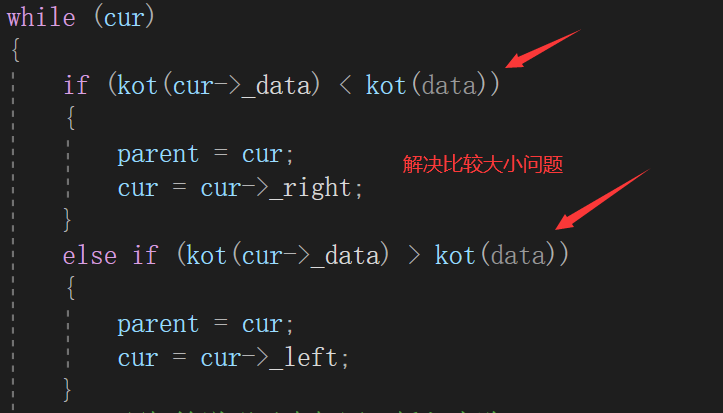
我們會發現紅黑樹的插入等接口會對key值進行比較大小,像set直接對key進行比較,這沒問題,但是map中的節點裝的是pair<K,V>,pair的比較規則是first比完之后可能會再去比較second(而我們僅僅想要比較first,該比較規則不適用)。
通過源碼啟發,我們可以對紅黑樹新增一個模板參數:仿函數KeyOfT,在set和map類中完善該仿函數的比較對象,用于區分set和map的比較:
template <class K>
class set
{
//仿函數用于比較大小
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)//傳入節點的值
{
return key;//返回key
}
};
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)//傳入節點的值
{
return kv.first;//返回kv.first
}
};
private:
RBTree<const K, pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
//利用模板確定傳入對象是set還是map
template <class K, class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree//紅黑樹
{};利用仿函數,傳入節點的值,set將會返回key值,map將會的返回pair的first。這樣就解決了比較大小的規則問題。
因為紅黑樹的中序遍歷是有序的,可以根據中序遍歷作為迭代器++--的依據。
STL源碼采用下圖結構,多搞了一個頭結點。迭代器begin()可以指向header的左,迭代器end()指向header。
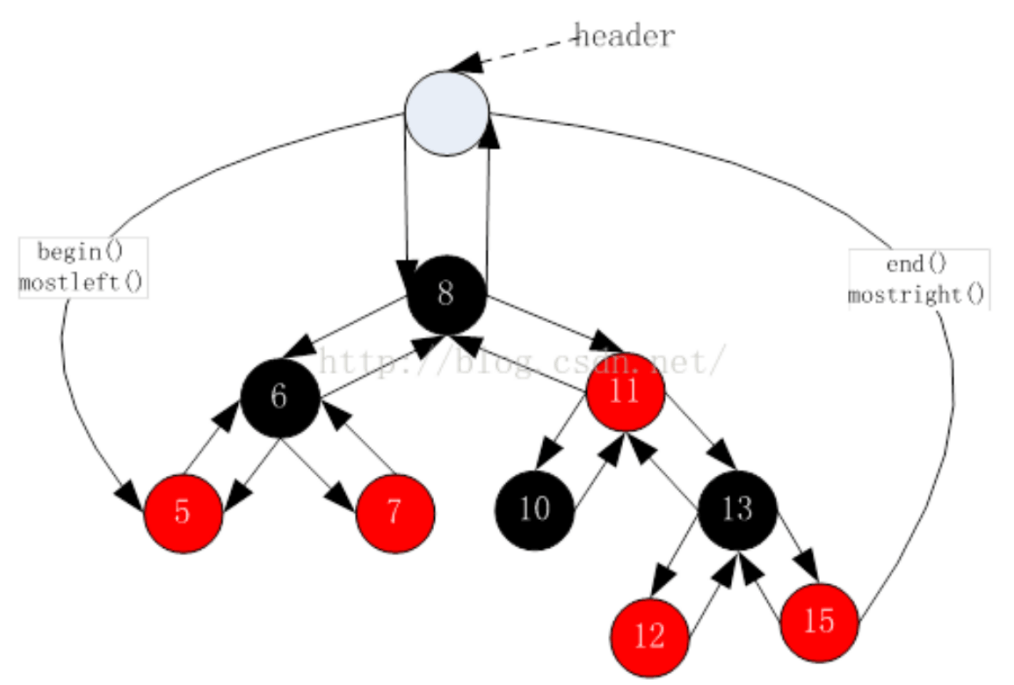
不過本文采用無頭結點的常規紅黑樹仿寫紅黑樹的迭代器。
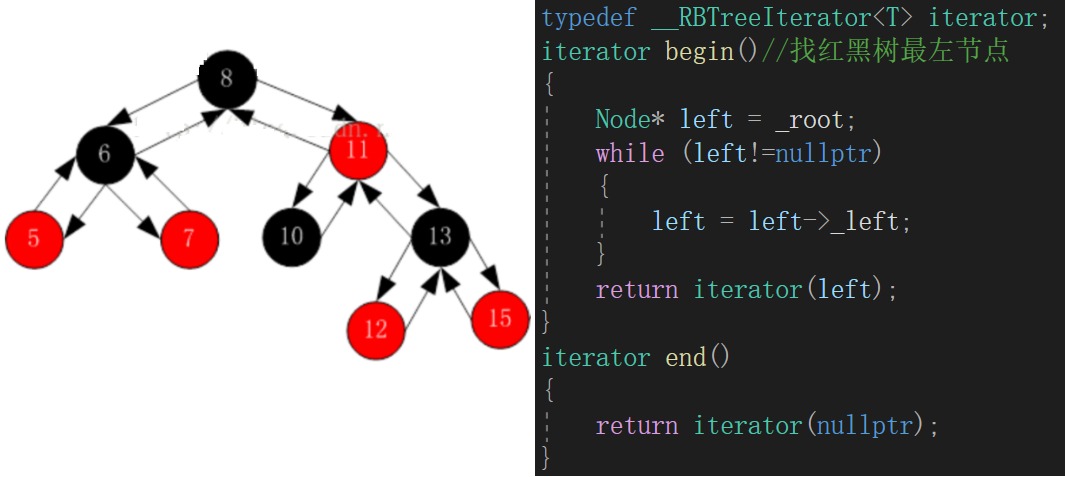
1、如果當前節點的右不為空,迭代器++返回右子樹的最左節點
2、如果當前節點的右為空,迭代器++返回祖先(當前節點是父親的左)(end()-1迭代器++返回nullptr即end())
template <class T>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//1、右不為空,下一個節點是右樹的最小節點
//2、右為空,去找右是父親左的最近祖先
Self& operator++()//找中序的下一個節點,即根的右樹的最左節點,返回值是一個迭代器的對象
{
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left != nullptr)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};1、如果當前節點的左不為空,迭代器--返回左子樹的最右節點
2、如果當前節點的左為空,迭代器--返回祖先(當前節點是父親的右)
template <class T>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T> Self;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left!=nullptr)
{
Node* max = _node;
while (max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
};對于set和map,它們的key都是不能改的。set的value不能修改,map的value可以修改。
因為set的value是不能改的,所以它的底層將普通迭代器和const迭代器全部封裝成const迭代器來“解決”:
//自己實現的,不代表STL typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator; typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
封裝之后又會出現新問題,set使用迭代器其實都是在使用const迭代器,但是自己實現的紅黑樹的迭代器接口返回普通類型的迭代器,在Set.h中對this加上const“解決”:
iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}這時使用迭代器調用上方函數會發現紅黑樹返回了普通迭代器類型的迭代器,類型不匹配。在紅黑樹中補齊const版本的迭代器函數解決:
const_iterator begin()const//找紅黑樹最左節點
{
Node* left = _root;
while (left != nullptr && left->_left != nullptr)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return const_iterator(left);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}map的value是可以改的,所以要分別設計普通迭代器和const迭代器。
typedef typename RBTree<const K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<const K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}STL庫中的普通迭代器都可以轉換為const迭代器,這是迭代器類的拷貝構造所支持的。
這個拷貝構造有點特殊:
//紅黑樹的迭代器
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>//key/value、T&、T*
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
__RBTreeIterator(const iterator& it)//const iterator本質還是普通迭代器
:_node(it._node)
{}
};1、當這個模板的的Ref和PTR被實例化為T&和T*時,__RBTreeIterator(const iterator& it)就是一個拷貝構造(沒啥意義)
2、當這個模板的的Ref和PTR被實例化為const T&和const T*時,__RBTreeIterator(const iterator& it)就是一個構造函數,支持用普通迭代器去構造const迭代器。此時const迭代器的拷貝構造函數則由編譯器自動生成,剛好滿足迭代器值拷貝的特點。
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK,
};
template <class T>//T類型代表value
struct RBTreeNode
{
RBTreeNode(const T& data)
:_parent(nullptr)
, _left(nullptr)
, _right(nullptr)
, _data(data)
, _col(RED)
{}
RBTreeNode<T>* _parent;
RBTreeNode<T>* _left;
RBTreeNode<T>* _right;
T _data;
Color _col;
};
//紅黑樹的迭代器
// key/value T& T*
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct __RBTreeIterator
{
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
Node* _node;
__RBTreeIterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
__RBTreeIterator(const iterator& it)
:_node(it._node)
{}
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_data;
}
Ptr operator->()//返回類型的地址
{
return &_node->_data;
}
//1、右不為空,下一個節點是右樹的最小節點
//2、右為空,去找右是父親左的最近祖先
Self& operator++()//找中序的下一個節點,即根的右樹的最左節點,返回值是一個迭代器的對象
{
if (_node->_right != nullptr)
{
Node* min = _node->_right;
while (min->_left != nullptr)
{
min = min->_left;
}
_node = min;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && cur == parent->_right)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
Self& operator--()
{
if (_node->_left!=nullptr)
{
Node* max = _node;
while (max->_right)
{
max = max->_right;
}
_node = max;
}
else
{
Node* cur = _node;
Node* parent = cur->_parent;
while (parent != nullptr && cur == parent->_left)
{
cur = cur->_parent;
parent = parent->_parent;
}
_node = parent;
}
return *this;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)const
{
return _node != s._node;
}
bool operator==(const Self& s)const
{
return _node == s._node;
}
};
//pair的比較是如果first小還要比second,我們只要比first,所以加了仿函數KeyOfT,用以取出first進行比較
//set->RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>
//map->RBTree<const K, pair<K,V>, MapKeyOfT>
template <class K, class T,class KeyOfT>
class RBTree
{
public:
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef __RBTreeIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
iterator begin()//找紅黑樹最左節點
{
Node* left = _root;
while (left!=nullptr&&left->_left!=nullptr)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return iterator(left);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(nullptr);
}
const_iterator begin()const//找紅黑樹最左節點
{
Node* left = _root;
while (left != nullptr && left->_left != nullptr)
{
left = left->_left;
}
return const_iterator(left);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_iterator(nullptr);
}
typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
pair<iterator,bool> Insert(const T& data)//對于map來說data是pair
{
if (_root == nullptr)
{
_root = new Node(data);
_root->_col = BLACK;//根節點給黑色
return make_pair(iterator(_root), true);//返回插入的節點
}
KeyOfT kot;//搞一個仿函數對象
//_root不為空
Node* parent = nullptr;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data))
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else//相等說明元素相同,插入失敗
return make_pair(iterator(cur),false);//插入失敗,說明找到了,返回被查找節點的迭代器
}
//開始插入
cur = new Node(data);
Node* newNode = cur;//記錄cur的地址,make_pair返回插入節點的地址
cur->_col = RED;//新插入節點給紅色,可能違反規則。如果給黑色會導致其他路徑的黑色節點數量不相同,必定違反規則。
if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data))
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;//維護cur的父指針
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
//調整
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;//找到祖父
if (grandfather->_left == parent)//如果父親是祖父的左孩子
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;//找到叔叔
//情況一:叔叔存在且為紅
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
//變色
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else//情況二或情況三
{
if (cur == parent->_left)//情況二,直線
{
RotateRight(grandfather);//右單旋
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//情況三,折線
{
RotateLeft(parent);//左單旋
RotateRight(grandfather);//右單旋
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
else//如果父親是祖父的右孩子
{
Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;
if (uncle != nullptr && uncle->_col == RED)
{
parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
cur = grandfather;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else
{
if (cur == parent->_right)//情況二,直線
{
//g
// p
// c
RotateLeft(grandfather);//左單旋
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
else//情況三,折線
{
//g
// p
//c
RotateRight(parent);//右單旋
RotateLeft(grandfather);//左單旋
cur->_col = BLACK;
grandfather->_col = RED;
}
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(iterator(newNode), true);//返回插入的節點
}
void Inorder()
{
_Inorder(_root);
}
bool IsBalance()
{
return _IsBalance();
}
private:
void _Inorder(Node* root)
{
if (root == nullptr)
return;
_Inorder(root->_left);
cout << kot(root->_data) << ":" << root->_data.second << endl;
_Inorder(root->_right);
}
bool Check(Node* root, int blackNum, const int ref)//檢查有沒有連續紅節點
{
if (root == nullptr)
{
if (blackNum != ref)
{
cout << "路徑上黑節點數量不一致" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
{
++blackNum;
}
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
{
cout << "違反規則,父子均為紅" << endl;
return false;
}
return Check(root->_left, blackNum, ref) && Check(root->_right, blackNum, ref);
}
bool _IsBalance()
{
if (_root == nullptr)
return true;
if (_root->_col != BLACK)
{
return false;
}
//數一下一條路徑黑色節點數量
int ref = 0;//統計一條路上黑色節點的數量
Node* left = _root;
while (left != nullptr)
{
if (left->_col == BLACK)
{
++ref;
}
left = left->_left;
}
return Check(_root, 0, ref);
}
void RotateLeft(Node* parent)//左單旋
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* cur = parent->_right;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (grandfather->_left == parent)//需要判定parent原來屬于grandfather的哪一邊
grandfather->_left = cur;
else
grandfather->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = grandfather;
}
parent->_right = cur->_left;
if (cur->_left != nullptr)
cur->_left->_parent = parent;
cur->_left = parent;
parent->_parent = cur;
}
void RotateRight(Node* parent)//右單旋
{
Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;
Node* cur = parent->_left;
if (parent == _root)
{
_root = cur;
cur->_parent = nullptr;
}
else
{
if (grandfather->_left == parent)
{
grandfather->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = grandfather;
}
else
{
grandfather->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = grandfather;
}
}
parent->_parent = cur;
parent->_left = cur->_right;
if (cur->_right != nullptr)
cur->_right->_parent = parent;
cur->_right = parent;
}
private:
Node* _root = nullptr;
};迭代器的begin(),end()接口放在紅黑樹這個類中,而operator++--放在迭代器這個類中,自己寫一下循環遍歷紅黑樹的代碼就知道為什么這樣設計了。
#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace jly
{
template <class K>
class set
{
struct SetKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const K& key)//傳入value
{
return key;
}
};
public:
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{
pair<typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator,bool> ret= _t.Insert(key);
return pair<iterator, bool>(ret.first, ret.second);
}
iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
private:
RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test2()
{
//int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
//int a[] = { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
set<int> s;
for (auto e : a)
{
s.insert(e);
}
set<int>::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
}
}#pragma once
#include "RBTree.h"
namespace jly
{
template <class K,class V>
class map
{
struct MapKeyOfT
{
const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv)//傳入value
{
return kv.first;
}
};
public:
//typename是C++中用于指定一個類的類型的關鍵字。
//通常用于表示某個類型是一個類類型,而不是其他類型,如int等。
//這里不加typedef編譯器無法區分iterator是一個類型還是一個靜態變量。因為他倆都可以這么寫。。
//所以從類模板取出內嵌類型就需要加typedef
typedef typename RBTree<const K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;
typedef typename RBTree<const K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;
pair<iterator,bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
return _t.Insert(kv);
}
iterator begin()
{
return _t.begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return _t.end();
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return _t.begin();
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return _t.end();
}
V& operator[](const K& key)//傳入key值
{
pair<iterator,bool> ret= _t.Insert(key,V());
return ret.first->second;//找到ret(make_pair<iterator,bool>)的first,解引用找到節點value
}
private:
RBTree<const K, pair<const K,V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;
};
void test1()
{
int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };
//int a[] = { 16, 3, 7, 11, 9, 26, 18, 14, 15 };
//int a[] = { 4, 2, 6, 1, 3, 5, 15, 7, 16, 14 };
//int a[] = { 9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1};
map<int,int> m;
for (auto e : a)
{
m.insert(make_pair(e,e));
}
map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while (it != m.end())
{
cout << (* it).first << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto& e : m)
{
cout << e.first<<" ";
}
}
}到此,關于“C++紅黑樹應用之set和map怎么使用”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。