您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“MySQL中的聚合查詢和聯合查詢怎么實現”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“MySQL中的聚合查詢和聯合查詢怎么實現”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
函數 | 說明 |
count | 查詢到的數據的數量 |
sum | 查詢到的數據的總和(針對數值,否則無意義) |
avg | 查詢到的數據的平均值(針對數值,否則無意義) |
max | 查詢到的數據的最大值(針對數值,否則無意義) |
min | 查詢到的數據的最小值(針對數值,否則無意義) |
Select count(*) from student(統計行數) Select count(1) from student(統計第一列數據的行數,如果有null則不算行數) Select sum(math) from student(數學成績總分) Select sum(math) from student where math > 60(數學大于60的總分) Select avg(math+chinese+english) from student(統計平均總分) Select max(math) from student(數學最高分) Select min(math) from student where math >60(數學大于60的最低分)
select 中使用 group by 子句可以對指定列進行分組查詢。使用 group by 進行分組查詢時,select 指定的字段必須是“分組依據字段”,其他字段若想出現在select 中則必須包含在聚合函數中。
select column1, sum(column2), .. from table group by column1,column3; //示例:查詢每個角色的最高工資、最低工資和平均工資 Select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary) from emp group by role;
group by 子句進行分組以后,需要對分組結果再進行條件過濾時,不能使用 WHERE 語句,而需要用Having
//示例:顯示平均工資低于1500的角色和它的平均工資 select role,avg(salary) from emp group by role having avg(salary)<1500;
關于分組查詢指定條件有三種情況:
1.分組之前,指定條件(先篩選,再分組)用where
2.分組之后,指定條件(先分組,再篩選)用having
3.分組之前和分組之后都指定條件(先where后having)
關于執行順序:
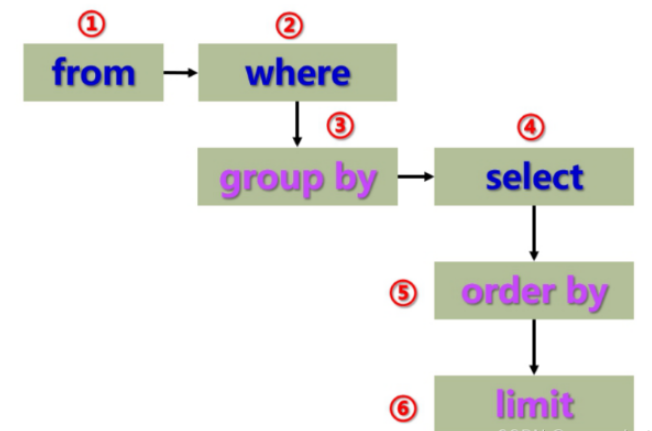
多表查詢是對多張表的數據取笛卡爾積,笛卡爾積是通過排列組合算出來的,因此包含了很多無效數據,因此需要加上連接條件,用來篩選有效的數據。
1.首先計算笛卡爾積
2.引入連接條件(如:where student.id = score.student_id)
3.再根據需求,加入必要的條件(where where student.id = score.student_id and student.name=’xxx’)
4.去掉多余的列,只保留需要關注的列(select student.name,score.score from student,score where where student.id = score.student_id and student.name=’xxx’)
語法:
select 字段 from 表1 (as)別名1 [inner] join 表2 (as)別名2 on 連接條件 and 其他條件;
select 字段 from 表1 (as)別名1,表2 (as)別名2 where 連接條件 and 其他條件;
示例:查詢“張三”同學的成績
select sco.score from student as stu inner join score as sco on stu.id=sco.student_id and stu.name='張三';
或者
select sco.score from student as stu, score as sco where stu.id=sco.student_id and stu.name='張三';
外連接分為左外連接和右外連接。如果聯合查詢,左側的表完全顯示我們就說是左外連接;右側的表完全顯示我們就說是右外連接。
語法:
左外連接,表1完全顯示
select 字段名 from 表名1 left join 表名2 on 連接條件;
右外連接,表2完全顯示
select 字段 from 表名1 right join 表名2 on 連接條件;
自連接是指在同一張表中連接自身進行查詢。
示例:顯示所有“數學”成績比“語文”成績高的學生成績信息
先查詢“數學”和“語文”課程的id
select id,name from course where name='數學' or name='語文';
數學id=1;
語文id=2;
再查詢成績表中,“數學”成績比“語文”成績 好的信息
select s1.* from score s1,score s2 where s1.student_id = s2.student_id and s1.score > s2.score and s1.course_id = 1 and s2.course_id = 2;
子查詢是指嵌入在其他sql語句中的select語句,也叫嵌套查詢。
單行子查詢:返回一行記錄的子查詢
select * from student where classes_id=(select classes_id from student where name='張三');
多行子查詢:返回多行記錄的子查詢
1.使用(not) in 關鍵字
使用 in
select * from score where course_id in (select id from course where
name='語文' or name='英文');
使用not in
select * from score where course_id not in (select id from course where
name!='語文' and name!='英文');
1.使用(not) exists 關鍵字
使用 exists
select * from score sco where exists (select sco.id from course cou
where (name='語文' or name='英文') and cou.id = sco.course_id);
使用 not exists
select * from score sco where not exists (select sco.id from course cou
where (name!='語文' and name!='英文') and cou.id = sco.course_id);
在from子句中使用子查詢,把一個子查詢當做一個臨時表使用。(not)in是放在內存中的,如果查詢的數據太大,內存中放不下,此時就需要使用(not)exists。exists本質上就是讓數據庫執行多個查詢操作,并把結果放在磁盤中,因此對于exists來說,執行效率大大低于in,而且可讀性也不是很好,這種比較適合處理一些特殊的場景。
合并查詢本質上就是把兩個查詢結果集合并成一個,但是要求這兩個結果集的列一樣,才能合并。即:
為了合并多個select的執行結果,可以使用集合操作符 union,union all。使用union和union all時,前后查詢的結果集中,字段需要一致。
1.union關鍵字
用于取得兩個結果集的并集。當使用該操作符時,會自動去掉結果集中的重復行。
示例:
select * from course where id<3 union select * from course where name='英文';
或者使用or來實現
select * from course where id<3 or name='英文';
2.union all關鍵字
用于取得兩個結果集的并集。當使用該操作符時,不會去掉結果集中的重復行。
示例:
可以看到結果集中出現重復數據
select * from course where id<3 union all select * from course where name='英文';
關于“MySQL中的聚合查詢和聯合查詢怎么實現”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。