您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“Python怎么用CNN實現對時序數據進行分類”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“Python怎么用CNN實現對時序數據進行分類”文章吧。
數據集利用的是CPSC2020數據集。
訓練數據包括從心律失常患者收集的10個單導聯心電圖記錄,每個記錄持續約24小時。

下載完成后的TrainingSet數據集包括兩個文件夾,分別是data和ref。data和ref文件夾內分別有10個mat文件。
data文件夾存儲數據文件,每個文件以mat格式存儲,n ∗ 1 n*1n∗1數組表示;
ref文件夾為標簽文件夾,每個文件以mat文件存儲,結構體存儲,包括S_ref,V_ref兩個n*1數組,分別存儲對應標簽(S,V)的位置;
采樣率為 400。
S:室上早搏(SPB);
V:心室早搏(PVC);
查看一下前1000個心電圖數據:
datafile = 'E:/Wendy/Desktop/TrainingSet/data/A04.mat'# 采樣率400 data = scio.loadmat(datafile) #rint(data) # dict sig = data['ecg']# (x,1) #print(sig) sig = np.reshape(sig,(-1)) # (x,)轉換為一維向量 print(sig) sigPlot = sig[1:5*200]# # 獲取前1000個信號 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10),dpi=400) plt.plot(sigPlot) plt.show()
運行結果:
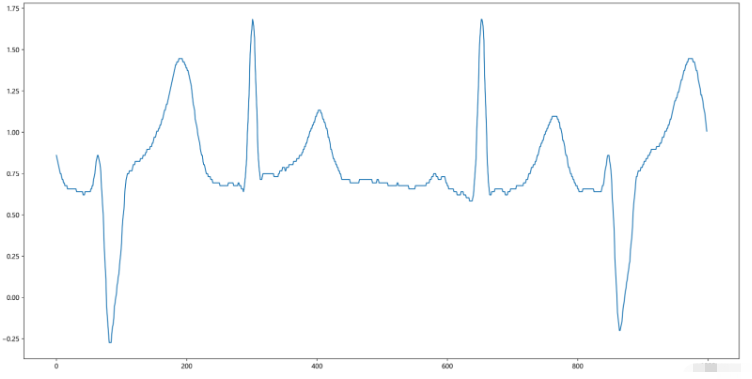
將標簽數據轉化為一維向量
datafile = 'E:/Wendy/Desktop/TrainingSet/ref/R04.mat'# 采樣率400 data = scio.loadmat(datafile) #print(data) label = data['ref'][0][0] S_ref = label[0]; S_ref = np.reshape(S_ref,(-1)) # 轉換為一維向量 V_ref = label[1]; V_ref = np.reshape(V_ref,(-1)) # 轉換為一維向量
數據分割為5s一個片段
思路:房早室早心拍和前后兩個心拍均有關系,按照平均心率72計算,平均每個心拍的時間為60/72,因此5個心拍的時間為60/725=4.1667 4.1667s不好計算,故選擇5s 5 ( 秒 ) s a m p r = 5 ∗ 400 = 2000 個 s a m p l e 5(秒)sampr = 5*400=2000個sample5(秒)sampr=5∗400=2000個sample
定義標簽:0:其他;1:V_ref; 2:S_ref;
a = len(sig) Fs = 400 # 采樣率為400 segLen = 5*Fs # 2000 num = int(a/segLen) print(num)
運行結果:
17650
其中Fs為采樣率,segLen為片段長度,num為片段數量。
接下來需要整合數據和標簽:
all_data=[] all_label = []; i=1 while i<num+1: all_data.append(np.array(sig[(i-1)*segLen:i*segLen])) # 標簽 if set(S_ref) & set(range((i-1)*segLen,i*segLen)): all_label.append(2) elif set(V_ref) & set(range((i-1)*segLen,i*segLen)): all_label.append(1) else: all_label.append(0) i=i+1 type(all_data)# list類型 type(all_label)# list類型 print((np.array(all_data)).shape) # 17650為數據長度,2000為數據個數 print((np.array(all_label)).shape) #print(all_data)
運行結果:
(17650, 2000)
(17650,)
17650為數據長度,2000為數據個數。
將數據保存為字典類型:
import pickle
res = {'data':all_data, 'label':all_label} # 字典類型dict
with open('./cpsc2020.pkl', 'wb') as fout: # #將結果保存為cpsc2020.pkl
pickle.dump(res, fout)將數據歸一化并進行標簽編碼,劃分訓練集和測試集,訓練集為90%,測試集為10%,打亂數據并將其擴展為二維:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import scipy.io
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import pickle
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from collections import Counter
from tqdm import tqdm
def read_data_physionet():
"""
only N V, S
"""
# read pkl
with open('./cpsc2020.pkl', 'rb') as fin:
res = pickle.load(fin) # 加載數據集
## 數據歸一化
all_data = res['data']
for i in range(len(all_data)):
tmp_data = all_data[i]
tmp_std = np.std(tmp_data) # 獲取數據標準差
tmp_mean = np.mean(tmp_data) # 獲取數據均值
if(tmp_std==0): # i=1239-1271均為0
tmp_std = 1
all_data[i] = (tmp_data - tmp_mean) / tmp_std # 歸一化
all_data = []
## 標簽編碼
all_label = []
for i in range(len(res['label'])):
if res['label'][i] == 1:
all_label.append(1)
all_data.append(res['data'][i])
elif res['label'][i] == 2:
all_label.append(2)
all_data.append(res['data'][i])
else:
all_label.append(0)
all_data.append(res['data'][i])
all_label = np.array(all_label)
all_data = np.array(all_data)
# 劃分訓練集和測試集,訓練集90%,測試集10%
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(all_data, all_label, test_size=0.1, random_state=15)
print('訓練集和測試集中 其他類別(0);室早(1);房早(2)的數量: ')
print(Counter(Y_train), Counter(Y_test))
# 打亂訓練集
shuffle_pid = np.random.permutation(Y_train.shape[0])
X_train = X_train[shuffle_pid]
Y_train = Y_train[shuffle_pid]
# 擴展為二維(x,1)
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, 1)
X_test = np.expand_dims(X_test, 1)
return X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = read_data_physionet()運行結果:
訓練集和測試集中 其他類別(0);室早(1);房早(2)的數量:
Counter({1: 8741, 0: 4605, 2: 2539}) Counter({1: 1012, 0: 478, 2: 275})
自行構建數據集:
# 構建數據結構 MyDataset # 單條數據信號的形狀為:1*2000 import numpy as np from collections import Counter from tqdm import tqdm from matplotlib import pyplot as plt from sklearn.metrics import classification_report import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.optim as optim import torch.nn.functional as F from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader class MyDataset(Dataset): def __init__(self, data, label): self.data = data self.label = label #把numpy轉換為Tensor def __getitem__(self, index): return (torch.tensor(self.data[index], dtype=torch.float), torch.tensor(self.label[index], dtype=torch.long)) def __len__(self): return len(self.data)
搭建CNN網絡結構:
# 搭建神經網絡 class CNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(CNN, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (1, 1, 2000) nn.Conv1d( in_channels=1, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2, ), # output shape (16, 1, 2000) nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=5), # choose max value in 1x5 area, output shape (16, 1, 400)2000/5 ) self.conv2 = nn.Sequential( # input shape (16, 1, 400) nn.Conv1d(16, 32, 5, 1, 2), # output shape (32, 1, 400) nn.Dropout(0.2), nn.ReLU(), nn.MaxPool1d(kernel_size=5), # output shape (32, 1, 400/5=80) ) self.out = nn.Linear(32 * 80, 3) # fully connected layer, output 3 classes def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) x = self.conv2(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) output = self.out(x) #output.Softmax() return output, x cnn = CNN() print(cnn)
運行結果:
CNN(
(conv1): Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(1, 16, kernel_size=(5,), stride=(1,), padding=(2,))
(1): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False)
(2): ReLU()
(3): MaxPool1d(kernel_size=5, stride=5, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(conv2): Sequential(
(0): Conv1d(16, 32, kernel_size=(5,), stride=(1,), padding=(2,))
(1): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False)
(2): ReLU()
(3): MaxPool1d(kernel_size=5, stride=5, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(out): Linear(in_features=2560, out_features=3, bias=True)
)
優化器利用的是Adam優化器,損失函數使用crossEntropy函數。
代碼略
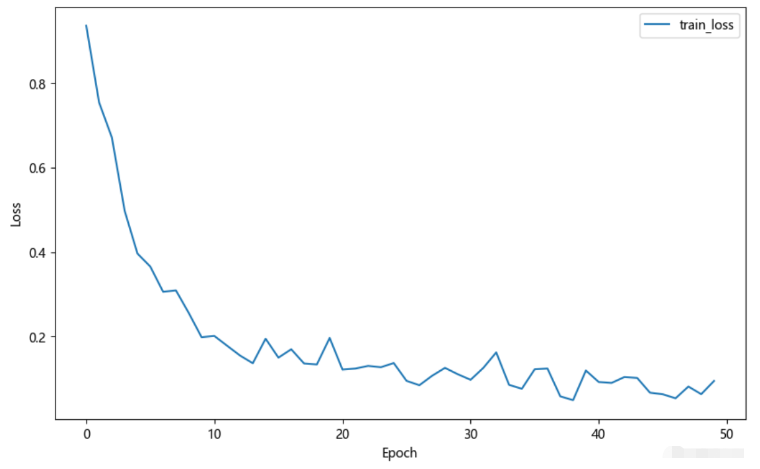
50個epoch的運行效果如下:
以上就是關于“Python怎么用CNN實現對時序數據進行分類”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。