您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本文小編為大家詳細介紹“MySQL Count函數如何使用”,內容詳細,步驟清晰,細節處理妥當,希望這篇“MySQL Count函數如何使用”文章能幫助大家解決疑惑,下面跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來學習新知識吧。
COUNT 是一個匯總函數(聚集函數),它接受一個表達式作為參數:
COUNT(expr)
COUNT函數用于統計在符合搜索條件的記錄中,指定的表達式expr不為NULL的行數有多少。這里需要特別注意的是,expr不僅僅可以是列名,其他任意表達式都是可以的。
select COUNT(key1) FROM t;
這個語句是用于統計在 t 表 key1 列 值不為 NULL 的行數是多少。
看下面的這個:
select COUNT('abc') FROM t;這個語句是用于統計在 t 表的所有記錄中,‘abc’ 這個表達式不為 NULL的行數是多少。很顯然,‘abc’ 這個表達式永遠不為 NULL, 所以上述語句其實就是統計 t 表里有多少條記錄。
再看這個:
select COUNT(*) from t;
這個語句就是直接統計 t 表中有多少條記錄。
總結 + 注意:COUNT函數的參數可以是任意表達式, 該函數用于統計在符合搜索條件的記錄中,指定的表達式不為NULL的行數有多少。
mysql> select count(*) from single_table; +----------+ | count(*) | +----------+ | 12610 | +----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) ####### single_table 表結構 ######## CREATE TABLE `single_table` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `key1` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `key2` int DEFAULT NULL, `key3` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `key_part1` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `key_part2` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `key_part3` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, `common_field` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), UNIQUE KEY `idx_key2` (`key2`), KEY `idx_key1` (`key1`), KEY `idx_key3` (`key3`), KEY `idx_key_part` (`key_part1`,`key_part2`,`key_part3`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=20000 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 |
這個語句是要去查詢表 single_table 中共包含多少條記錄。由于聚簇索引和二級索引中的記錄是一一對應的,而二級索引記錄中包含的列是少于聚簇索引記錄的,所以同樣數量的二級索引記錄可以比聚簇索引記錄占用更少的存儲空間。如果我們使用二級索引執行上述查詢,即數一下idx_key2中共有多少條二級索引記錄(存在多個二級索引,為什么選擇idx_key2,下面會具體說明),是比直接數聚簇索引中共有多少聚簇索引記錄可以節省很多I/O成本。所以優化器會決定使用idx_key2執行上述查詢。
mysql> explain select count(*) from single_table; +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key2 | 5 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
在執行上述查詢時,server層會維護一個名叫count的變量,然后:
(1)server層向InnoDB要第一條記錄。
(2)InnoDB找到idx_key1的第一條二級索引記錄,并返回給server層(注意:由于此時只是統計記錄數量,所以并不需要回表)。
(3)由于COUNT函數的參數是*,MySQL會將*當作常數0處理。由于0并不是NULL,server層給count變量加1。
(4)server層向InnoDB要下一條記錄。
(5)InnoDB通過二級索引記錄的next_record屬性找到下一條二級索引記錄,并返回給server層。
(6)server層繼續給count變量加1。
(7)... 重復上述過程,直到InnoDB向server層返回沒記錄可查的消息。
(8)server層將最終的count變量的值發送到客戶端。
下面我們增對 count(*),count(1),count(常數),count(主鍵列),count(普通列(有索引)),count(普通列(無索引))
(1)count(*),count(1),count(常數)
mysql> show create table single_table;
+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Table | Create Table |
+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| single_table | CREATE TABLE `single_table` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`key1` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`key2` int DEFAULT NULL,
`key3` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`key_part1` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`key_part2` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`key_part3` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`common_field` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `idx_key2` (`key2`),
KEY `idx_key1` (`key1`),
KEY `idx_key3` (`key3`),
KEY `idx_key_part` (`key_part1`,`key_part2`,`key_part3`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=20000 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 |
+--------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select count(*) from single_table;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 12610 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
## count(*) 采用了 idx_key2 索引
mysql> explain select count(*) from single_table;
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key2 | 5 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
## count(1) 采用了 idx_key2 索引
mysql> explain select count(1) from single_table;
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key2 | 5 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
## count('abc') 采用了 idx_key2 索引
mysql> explain select count('abc') from single_table;
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key2 | 5 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)通過上述查詢結果可以看出:
count(*)、count(1)、count('abc') 均采用了 idx_key2,而索引idx_key2 對應的索引列為 key2,字段類型為 int,占用空間為最小的索引列。
結論:
對于 COUNT(*)、COUNT(1) 或者任意的 COUNT(常數) 來說,讀取哪個索引的記錄其實并不重要,因為server層只關心存儲引擎是否讀到了記錄,而并不需要從記錄中提取指定的字段來判斷是否為NULL。所以優化器會使用占用存儲空間最小的那個索引來執行查詢。
(2)count(主鍵列)
## count(id) 采用了 idx_key2 索引 mysql> explain select count(id) from single_table; +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key2 | 5 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index | +----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
通過上述查詢結果可以看出:
count(id)采用了 idx_key2,而索引idx_key2 對應的索引列為 key2,字段類型為 int,占用空間為最小的索引列。
結論:
對于 COUNT(id) 來說,由于id是主鍵,不論是聚簇索引記錄,還是任意一個二級索引記錄中都會包含主鍵字段,所以其實讀取任意一個索引中的記錄都可以獲取到id字段,此時優化器也會選擇占用空間最小的那個索引來執行查詢。
(3)count(普通列(有索引))
## count('key1') 采用了 idx_key1 索引
mysql> explain select count(key1) from single_table;
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | index | NULL | idx_key1 | 303 | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+-------+---------------+----------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
## count(common_field) 未采用任何索引
mysql> explain select count(common_field) from single_table;
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | single_table | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 12590 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+--------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+-------+----------+-------+
1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)通過上述查詢結果可以看出:
count(key1)采用了 idx_key1,索引idx_key1對應的索引列即為key1。count(common_field)未采用任何索引,common_field也不存在任何索引。
結論:
對于COUNT(非主鍵列)來說,我們指定的列可能并不會包含在每一個索引中。這樣優化器只能選擇包含我們指定的列的索引去執行查詢,這就可能導致優化器選擇的索引并不是最小的那個。
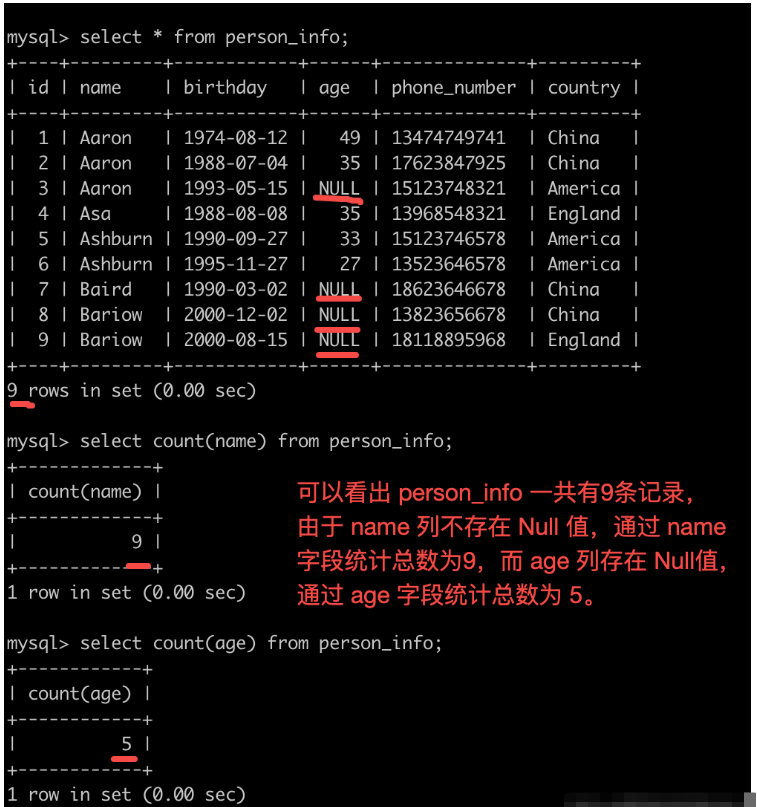
對于count(非空普通列)來說,使用索引情況會怎么樣?會不會直接采用最小占用空間索引呢?
mysql> show create table person_info; +-------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Table | Create Table | +-------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | person_info | CREATE TABLE `person_info` ( `id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `name` varchar(100) NOT NULL, `birthday` date NOT NULL, `age` int DEFAULT NULL, `phone_number` char(11) NOT NULL, `country` varchar(100) NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`), KEY `idx_name` (`name`), KEY `idx_age` (`age`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=10 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb3 | +-------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec) mysql> explain select count(phone_number) from person_info; +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | person_info | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 9 | 100.00 | NULL | +----+-------------+-------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
通過上述查詢結果可以看出:
雖然 phone_number 字段為 not null,count(phone_number) 和 count(*) 結果一致,但是 phone_number 仍然并有選擇走索引。
讀到這里,這篇“MySQL Count函數如何使用”文章已經介紹完畢,想要掌握這篇文章的知識點還需要大家自己動手實踐使用過才能領會,如果想了解更多相關內容的文章,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。