您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Laravel路由與MVC怎么應用”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Laravel路由與MVC怎么應用”吧!
路由的作用就是將用戶的不同url請求轉發給相應的程序進行處理,laravel的路由定義在routes文件夾中,默認提供了四個路由文件,其中web.php文件定義基本頁面請求。
最基本的路由請求是get與post請求,laravel通過Route對象來定義不同的請求方式。例如定義一個url為'req'的get請求,返回字符串‘get response':
Route::get('req',function (){
return 'get response';
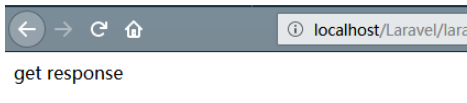
});當我以get的方式請求http://localhost/Laravel/laravel52/public/req時,返回如下:
同理,當定義post請求時,使用Route::post(url,function(){});
如果希望對多種請求方式采用相同的處理,可以使用match或any:
使用match來匹配對應的請求方式,例如當以get或post請求req2時,都返回match response:
Route::match(['get','post'],'req2',function (){
return 'match response';
});any會匹配任意請求方式,例如以任意方式請求req3,返回any response:
Route::any('req3',function (){
return 'any response';
});必選參數:當以帶參數的形式發送請求時,可以在路由中進行接收,用大括號將參數括起,用/分割,例如:
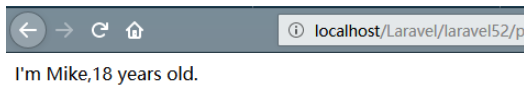
Route::get('req4/{name}/{age}', function ($name, $age) {
return "I'm {$name},{$age} years old.";
});以get請求時將參數傳遞,結果如下:
可選參數:以上的參數是必須的,如果缺少某一個參數就會報錯,如果希望某個參數是可選的,可以為它加一個?,并設置默認值,默認參數必須為最后一個參數,否則放中間沒法識別:
Route::get('req4/{name}/{age?}', function ($name, $age=0) {
return "I'm {$name},{$age} years old.";
});正則校驗:可以通過where對請求中的參數進行校驗
Route::get('req4/{name}/{age?}', function ($name, $age=0) {
return "I'm {$name},{$age} years old.";
})->where(['name'=>'[A-Za-z]+','age'=>'[0-9]+']);有時我們的路由可能有多個層級,例如定義一級路由home,其下有二級路由article,comment等,這就需要將article與comment放到home這個群組中。通過數組鍵prefix為路由article添加前綴home:
Route::group(['prefix' => 'home'], function () {
Route::get('article', function () {
return 'home/article';
});
});這樣通過home/article就可以訪問到該路由了。
有時需要給路由起個名字,需要在定義路由時使用as數組鍵來指定路由名稱。例如將路由home/comment命名為comment,在生成url與重定向時就可以使用路由的名字comment:
Route::get('home/comment',['as'=>'comment',function(){
return route('comment'); //通過route函數生成comment對應的url
}]);輸出為http://localhost/Laravel/laravel52/public/home/comment
route路由只對請求進行分配跳轉,具體的業務邏輯則需要由控制器來處理,控制器一般封裝成為一個php類。控制器的文件一般放在app/Http/Controlers文件夾下。例如新建一個LoginController類繼承自Controller,定義checkLog方法回應登錄請求,
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
class LoginController extends Controller
{
public function checkLog($name){
return $name.'登錄成功';
}
}在route.php中將login請求分配到checkLog方法:
Route::get('login/{name}','LoginController@checkLog');同樣的,可以為控制器路由起個名字,比如將其命名為login:
Route::get('login/{name}',['uses'=>'LoginController@checkLog','as'=>'login']);controller負責處理應用的邏輯,應用的顯示則由視圖View負責,這體現了MVC中不同的邏輯之間的分離。視圖一般位于/resource/views目錄下,一般一個controller文件對應一個視圖文件夾,因此我創建的視圖為:views/Login/login.blade.php。blade文件是laravel的一個模板引擎,它編譯為PHP儲存起來。它包含HTML語言,可以在其中直接使用PHP,例如login.blade.php:
<!DOCTYPE Html>
<html>
<head>
<title>登錄界面</title>
</head>
<body>
{{$name}}登錄成功
</body>
</html>在controller的checkLog方法中調用視圖并傳入參數:
public function checkLog($name){
return View('Login/login',[
"name"=>$name
]);
}在mvc中通過Models與數據庫中的表進行交互,每個數據庫對應一個Model模板。laravel并沒有定義models目錄,一般可以在app目錄下新建一個models文件夾存放模板文件。例如定義一個Student模板并指定表名與主鍵:
namespace App\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Student extends Model
{
protected $table='student';
protected $primaryKey='id';
}在controller中通過Student模板查詢所有:
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\Student;
class Login
{
public static function showDB(){
$table=Student::all();
dd($table);
}
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Laravel路由與MVC怎么應用”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Laravel路由與MVC怎么應用這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。