您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“C++分支和循環語句怎么使用”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
生活中存在三種語言結構
(1)順序結構
(2)選擇結構<——>分支語句:if switch
(3)循環結構<——>循環語句:while for do while goto
C語言中0表示假,非0表示為真。(比如說-1表示為真)
if 語句
語法結構:
if(表達式)
語句;
if(表達式)
語句1;
else
語句2;
if (表達式1)
語句1;
else if(表達式2)
語句2;
else // 最后一個else語句借以省略,根據需要寫
語句3;
如果if 或者else想要控制多條語句,必須要用大括號括起來,整體形成一個代碼塊。
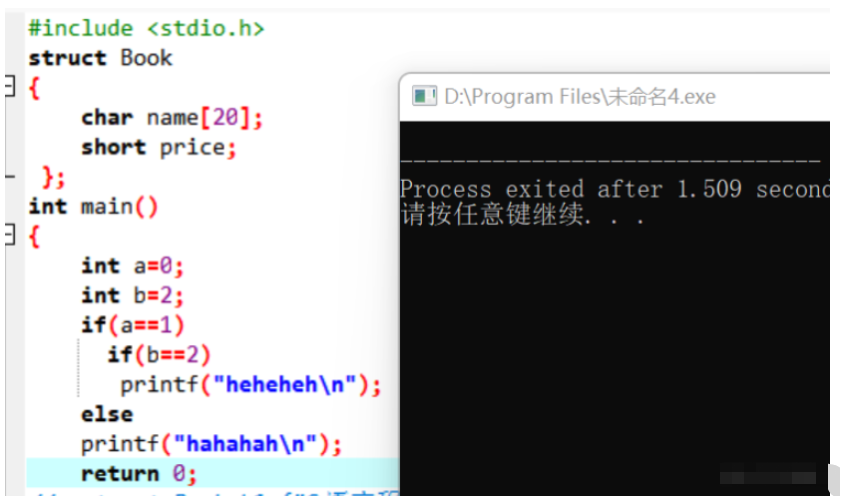
以上程序的輸出結果不是“hahahah”也不是“hehhehe”,結果是什么也不輸出。else是和最近的 if匹配,所以都是屬于第一個if的代碼塊內容。
else是和它離得最近的那個沒有匹配的if 是一對。
如果常量和變量做比較的時候,我們可以把常量寫在前面,這樣能夠避免出現錯誤如:5==num;
練習
1.判斷一個數是否為奇數?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int num=0;
printf("請輸入一個數:\n");
scanf("num=%d\n",&num);
if (num%2==1)
{
printf("該數字為奇數");
}
else
{
printf("該數字為偶數");
}
return 0;
}
2.且輸出1-100之間的奇數。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=1;
while (a<=100)
{
if(a%2==1)
{
printf("%d\n",a);
a++;
}
else
a++;
}
return 0;
}
Switch語句
Switch語句的一般形式:
Switch(語句1)
{
case(語句2):
內容;
break;
case (語句3):
內容;
break;
case(語句4):
內容;
break;
……
default;// 可有可無
內容;
break;
}
Switch語句是從case進入,從break出來,只有當case后面的語句與Switch后面的語句匹配上的時候才會執行。
注意:Switch語句里面必須是整型表達式,case后面必須是整型常量表達式。
while循環
while 語法結構:
while (表達式)
循環語句;
只有在表達式為真的時候,才會執行循環語句,知道發現表達式為假的時候,表達式便不再執行,結束循環。
continue的作用是終止本次循環中,也就是說continue后面的代碼不再執行,直接跳轉到while的判斷部分,判斷是否需要進入下一次循環。
只要循環中遇到break,就停止后期的所有的循環,直接終止循環,所以:while中的break是用于永久終止循環的。
getchar 是輸入字符,putchar() 是輸出字符。putchar(變量名)的含義類似于printf(“%c”,變量名);
EOF——表示的end of file 是文件的結束標志。
int main()
{
int ch=0;
while((ch=getchar()!=EOF)
{
putchar(ch);
}
return 0;
}
當你輸入EOF的時候,循環并不會終止,只有當你輸入Ctrl+z時,才會終止。
getchar與scanf的區別:
scanf是把你所輸入的內容放到一個緩沖區中,最后的回車鍵作為結束標志,在最終顯示的時候不會顯示出\n。但是getchar首先是去輸入緩沖區中看是否有內容,不管里面的內容是否是自己所需要的,都會被讀走。所以,一般我們在使用getchar()輸入的時候,前面一般加上一句getchar();不用給他賦予返回值,因為我們此時的目的就是清空數據緩沖區中的內容,讓getchar獲取我們想要的內容。
getchar函數是一位一位的讀取字符的。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
while ((ch=getchar())!=EOF)
{
if(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
continue;
putchar(ch);
}
return 0;
}
以上代碼的意思是只有在輸入字符0-9之間的字符,包含0和9,才會有輸出,否則就不輸出。
for循環
語法:for (表達式1;表達式2;表達式3)
{
循環語句;
}
表達式 1為初始化部分,用于初始化循環變量的。表達式2 為條件判斷部分,用于判斷循環時候終止。表達式3位調整部分,用于循環條件的調整。
break和continue的用法和在while語句中的用法一致。
有一個小區別:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=0;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
if (i==5)
continue;
printf("%d",i);
}
return 0;
}
此結果的輸出是1 2 3 4 6 7 8 9 10 因為在i=5的時候遇到了continue之后直接跳轉到了變量調整部分i++那里,所以,這個時候變量的值變為了6,繼續輸出。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=1;
while (i<=10)
{
if(i==5)
continue;
printf("%d",i);
i++;
}
}
此代碼的結果是1 2 3 4 最后是一個死循環,因為當i=5的時候,遇到了continue,后面的部分不再執行,直接跳過了變量調整部分,一直在判斷i=5。
for語句循環控制變量的一些建議:
不可在for循環體內修改循環變量,防止for循環失去控制。
建議for語句的循環控制變量的取值采用“前閉后開區間”寫法。
當for循環的表達式2,即判斷語句不寫的時候,就意味著這個判斷條件恒為真,那么就進入了死循環。
請問一下代碼循環了多少次?
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=0;
int k=0;
for (i=0,k=0;k=0;i++,k++)
k++;
return 0;
}
答案是循環了0次,就是根本就沒有進入循環,因為判斷語句處是一個賦值語句,賦值表達式的結果是0,為假,那么就不進入循環。
do while 循環
語法:do
{
循環;
}
while()
練習題
1. 從鍵盤輸入一個數n,并且求n!
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n=0;
int i=1;
int sum=1;
printf("請輸入n:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
while (i<=n)
{
sum=sum*i;
i++;
}
printf("sum=%d\n",sum);
return 0;
}
2.求1!+2!+3!+4!+……n!
[x]
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n=0;
int i=1;
int sum=1;
int get=0;
printf("請輸入n:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for (n=1;n<=10;n++)
{
sum=1;
while (i<=n)
{
sum=sum*i;
i++;
}
get=get+sum;
}
printf("get=%d\n",get);
return 0;
}
[x]
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n=0;
int i=1;
int sum=1;
int get=0;
printf("請輸入n:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
for (n=1;n<=10;n++)
{
sum=sum*n;
get=get+sum;
}
printf("get=%d\n",get);
return 0;
}
3.在一個有序數組中查找具體的某個數字n,編寫int binsearch(intx, int v[],int n);功能:在v[0]<=v[1]<=v[2]<=……v[n-1]的數組中查找x。
[x]
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=1;
int k=7;
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int lgth=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]) ;
for(i=0;i<lgth;i++)
{
if(k==arr[i])
{
printf("找到了,下標為%d\n",i);
break;
}
}
if (i==lgth)
printf("沒有找到");
return 0;
}
[x]二分查找法
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int k=7;
int arr[]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int i=0;
int legth=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int right=legth-1;
int left=0;
while(left<=right)
{
int mide=(right+left)/2;
if(k>arr[mide])
{
left=mide+1;
}
else if(k<arr[mide])
{
right=mide-1;
}
else
{
printf("找到了,下標為%d\n",mide);
break;
}
}
if(left>right)
{
printf("找不到");
}
return 0;
}
4.編寫代碼,演示多個字符從兩端移動,向中間匯聚。
#include <stdio.h>//這個是printf所在的庫函數
#include <string.h>//這個是 strlen所在的庫函數
#include<windows.h>//這個是sleep所在的庫函數
#include<stdlib.h> //這個是system所在的庫函數
int main()
{
char arr1[]="Welcome to DongHua!!!!";
char arr2[]="######################";
int left =0;
int right=strlen(arr1)-1;
while (left<right)
{
arr2[left]=arr1[left];
arr2[right]=arr1[right];
printf("%s\n",arr2);
Sleep(1000);//表示在輸出的時候停留1000毫秒
system("cls");//表示在輸出一次結果后清屏
left++;
right--;
}
return 0;
}
5.編寫代碼實現,模擬用戶登錄情景,并且只能登錄三次。(只允許輸入三次密碼,如果密碼正確就提示登錄成功,如果三次均輸入錯誤,則退出程序)
strcmp(A,B)是比較字符串A和字符串B,如果字符串A>B,那么會返回一個大于0的數字,如果A<B,那么會返回一個個小于0的數字
#include <stdio.h>//這個是printf所在的庫函數
#include <string.h>//這個是 strlen所在的庫函數
int main()
{
int i=0;
char password[20]={0};//不能寫成password[]={0},這樣定義的話,就不知道數組的長度是多少結果就會出錯
for (i=0;i<3;i++)
{
printf("請輸入密碼:\n");
scanf("%s",password);
if(strcmp(password,"123456")==0)//在比較兩個字符串是否相等的時候,不能直接用==來判斷,要用strcmp函數,它在string.h函數庫中
{
printf("密碼正確,登陸成功\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("密碼錯誤\n");
}
}
if (i==3)
{
printf("三次密碼錯誤,退出程序\n");
}
return 0;
}
goto 語句
在一般編寫程序的時候很少使用goto語句,因為它會破壞程序的邏輯性,它所使用的場景是跳出多層循環嵌套。
分支和循環的作業和練習
1.輸入三個數,按照從大到小的順序輸出。
#include <stdio.h>//這個是printf所在的庫函數
int main()
{
int a=0;
int b=0;
int c=0;
printf("請輸入三個數:\n");
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
if (a<b)
{
int temp=a;//在此注意,不能直接將b賦值給a,因為這樣a的值容易丟失
a=b;
b=temp;
}
if(a<c)
{
int temp=a;
a=c;
c=temp;
}
if(b<c)
{
int temp=b;
b=c;
c=temp;
}
printf("由大到小的順序為:%d %d %d\n",a,b,c);
return 0;
}
2.寫一個代碼打印1-100之間的所有的3的倍數的數字
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i=0;
for (i=0;i<100;i++)
{
if (i%3==0)
{
printf("%d",i);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.給定兩個數,求這兩個數的最大公倍數.
輾轉相除法比如說24和18,首先看24%18余數是否為0,如果不為0的話,再用除數與余數相除,直到余數為0為止,此時最后的除數就是公倍數。
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int temp = 0;
printf("請輸入兩個數字:\n");
scanf_s("%d %d", &a, &b);
while(temp = a % b)//只要結果為非0,就進入循環。
{
a = b;
b = temp;
}
printf("公倍數為:%d", b);
return 0;
}
4.打印1000年到2000年之間的閏年
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int year = 0;
for (year = 0; year <= 2000; year++)
{
//判斷year是否為閏年
//1.能被4整除并且不能被100整除
//2.能被400整除是閏年
if (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)
{
printf("閏年為:%d\n", year);
}
else if(year%400==0)
{
printf("閏年為:%d\n", year);
}
}
return 0;
}
5.打印100-200之間的素數
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = 100; i <= 200; i++)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 2; j < i ; j++)
{
if (i%j == 0)
VPsx9aha"> {
break;
}
}
if (j == i)
{
count++;
printf("%d\n", i);
}
}
printf("count=%d\n", count);
return 0;
}
優化程序:首先偶數肯定不是素數,所以先產生100-200之間的奇數。根據c=a*b,那么a或者b中必有一個小于c開平方
#include <stdio.h>
# include<math.h>//sqrt函數在此函數庫中
int main()
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = 101; i <= 200; i+2)
{
int j = 0;
for (j = 2; j <= sqrt(i) ; j++)
{
if (i%j == 0)
{
break;
}
}
if (j >sqrt(i))
{
count++;
printf("%d\n", i);
}
}
printf("count=%d\n", count);
return 0;
}
6.編寫程序數一下1-100之間所有的整數中出現了多少個數字9
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
if (i % 10 == 9)
{
count++;
}
if (i / 10 == 9)
{
count++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", count);
return 0;
}
7.計算1/1-1/2+1/3+1/4+1/5+……+1/99+1/100的值,打印出結果
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
double sum = 0.0;
int flag = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= 100; i++)
{
sum += flag*(1.0 / i);//此處必須是1.0,否則結果都是不對的
flag = (-flag);
}
printf("%lf\n", sum);
return 0;
}
8.求10個整數中的最大值
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
int sz = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int max = arr[0];
for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++)
{
if(max<arr[i])
max = arr[i];
}
printf("%d\n", max);
return 0;
}
輸入10個數字,并且找出其中的最大值
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int arr[10] = { 0 };
printf("請輸入數字:");
for (i = 0; i < ; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);//切勿忘記加上取地址運算符
}
int max = arr[0];
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
if (arr[i]>max)
{
max = arr[i];
}
}
printf("max=%d\n", max);
return 0;
}
9.輸出乘法口訣表
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
for (i = 1; i < 10; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j < i+1; j++)
{
printf("%d*%d=%2d ", i, j, i*j);//輸出為%2d表示的是輸出為兩個字符,不夠兩個字符的,自動補一個空格。%-2d是輸出左對齊
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
10.設計一個猜數字游戲
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS//scanf所在的頭文件
#include<stdio.h>//srand函數所在的頭文件
#include<time.h>//time函數所在的頭文件
#include<stdlib.h>//rand函數所在的頭文件
void menu()
{
printf("********************************************\n");
printf("*** 1.play 0.exit ***\n");
printf("********************************************\n");
}
void game()
{
//時間戳:當前時間-1970年1.1 0:0:0 時間差換算成秒后的數字。
int ret = 0;
int guess = 0;
printf("猜數字\n");
ret = rand()%100+1;//生成隨機數,生成隨機數的范圍是0-0x7fff,即轉換為十進制是32767,對100取余,使其輸出1-100以內的隨機數
while (1)
{
scanf("%d", &guess);
if (guess < ret)
{
printf("猜小了\n");
}
else if (guess > ret)
{
printf("猜大了\n");
}
else if (guess == ret)
{
printf("恭喜你,猜對了\n");
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
//猜數字游戲
//1.電腦會生成一個隨機數
//2.猜數字
int input = 0;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));//設置時間起點
do
{
menu();
printf("請選擇:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
printf("開始游戲\n");
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("退出游戲\n");
break;
default:
printf("您輸錯了,請重新輸入\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
11.一個關機程序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>//system 函數所在的頭文件
#include <string.h>//strcmp函數所在的頭文件
int main()
{
char input[20] = { 0 };
system("shutdown -s -t 60");//此處一定要注意,命令的格式,空格鍵不能敲錯
again:
printf("提示!!!您的電腦將在1分鐘后關機,如果您輸入“我是豬”可以取消關機\n");
scanf("%s", input);
if (strcmp(input, "我是豬") == 0)
{
system("shutdown -a");
}
else
{
goto again;
}
return 0;
}
“C++分支和循環語句怎么使用”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。