您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下Redisson延遲隊列執行流程是什么的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
在實際分布式項目中延遲任務一般不會使用JDK自帶的延遲隊列,因為它是基于JVM內存存儲,沒有持久化操作,所以當服務重啟后就會丟失任務。在項目中可以使用MQ死信隊列或redisson延遲隊列進行處理延遲任務。
通過腳手架創建一個簡易springboot項目,引入redisson的maven依賴,并簡單配置redisson連接屬性。
<!-- redisson引用 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson</artifactId>
<version>3.16.6</version>
</dependency>
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private String port;
/**
* 獲取redissonClient實例
*
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Bean
public RedissonClient getRedisson() {
Config config = new Config();
String address = "redis://" + host + ":" + port;
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(address);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}定義一個redisson延遲隊列插入和獲取任務處理類RedissonQueueHandle,通過控制spring的bean加載周期開啟獨立線程獲取延遲任務。這里獲取延遲任務使用了三種方法,除了第一種阻塞式獲取任務方法外,其他兩種方法都不是百分比按照延遲參數獲取到任務,因為是時間間隔定時循環獲取延遲任務。
/**
* redisson延遲隊列處理器
*
* @author zrh
*/
@Slf4j
@Component
public class RedissonQueueHandle implements InitializingBean {
private final RBlockingQueue<RedisDataEntity<?>> queue;
private final RDelayedQueue<RedisDataEntity<?>> delayedQueue;
public RedissonQueueHandle (RedissonClient client) {
this.queue = client.getBlockingQueue("redisson:queue");
this.delayedQueue = client.getDelayedQueue(queue);
}
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet () {
// 開一個線程阻塞式獲取任務
thread();
// 使用netty時間輪循環獲取任務
// watchDog(new HashedWheelTimer());
// 使用線程池定時獲取任務
// schedule();
}
private void thread () {
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
try {
RedisDataEntity entity = queue.take();
log.info("本次獲取數據:{},耗時:{}", entity, System.currentTimeMillis() - entity.getTime());
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}, "zrh").start();
}
private void watchDog (final HashedWheelTimer timer) {
timer.newTimeout(timeout -> {
RedisDataEntity entity = queue.poll();
if (null != entity) {
log.info("本次獲取數據:{},耗時:{}", entity, System.currentTimeMillis() - entity.getTime());
}
watchDog(timer);
}, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
private void schedule () {
Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1).scheduleWithFixedDelay(() -> {
RedisDataEntity entity = queue.poll();
if (null != entity) {
log.info("本次獲取數據:{},耗時:{}", entity, System.currentTimeMillis() - entity.getTime());
}
}, 5, 5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 放入redis,定時過期
*
* @param entity
*/
public void offer (RedisDataEntity entity) {
try {
delayedQueue.offer(entity, entity.getExpire(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("放入redis延遲隊列異常", e);
}
}
}放入redisson延遲隊列可以是字符串也可以是對象RedisDataEntity,因為有進行IO磁盤存儲操作,所以必須實現Serializable序列化接口。
/**
* @Author: ZRH
* @Date: 2022/1/10 11:54
*/
@Data
public class RedisDataEntity<T> implements Serializable {
/**
* 數據
*/
private final T data;
/**
* 過期時間(單位:毫秒)
*/
private final Long expire;
/**
* 添加時間
*/
private final Long time;
public RedisDataEntity (T data, Long expire, Long time) {
this.data = data;
this.expire = expire;
this.time = time;
}
}然后開一個插入數據接口:
/**
* @Author: ZRH
* @Date: 2022/1/10 11:45
*/
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class IndexController {
private final RedissonQueueHandle redisHandle;
public IndexController (RedissonQueueHandle redisHandle) {
this.redisHandle = redisHandle;
}
@PostMapping("redissonQueue")
public String redissonQueue (@RequestParam String data, @RequestParam Long expire) {
RedisDataEntity entity = new RedisDataEntity(data, expire, System.currentTimeMillis());
log.info("本次添加數據:{}", entity);
redisHandle.offer(entity);
return "ok";
}
}
訪問接口設置延遲30秒:http://localhost:8802/redissonQueue?data=a&expire=30000,打印結果如下
2022-01-14 14:21:52.140 INFO 10808 --- [nio-8802-exec-1] c.r.web.controller.IndexController : 本次添加數據:RedisDataEntity(data=a, expire=30000, time=1642141312135)
2022-01-14 14:21:52.887 INFO 10808 --- [nio-8802-exec-2] c.r.web.controller.IndexController : 本次添加數據:RedisDataEntity(data=a, expire=30000, time=1642141312887)
2022-01-14 14:22:22.240 INFO 10808 --- [ zrh] c.r.web.redis.RedissonQueueHandle : 本次獲取數據:RedisDataEntity(data=a, expire=30000, time=1642141312135),耗時:30105
2022-01-14 14:22:22.914 INFO 10808 --- [ zrh] c.r.web.redis.RedissonQueueHandle : 本次獲取數據:RedisDataEntity(data=a, expire=30000, time=1642141312887),耗時:30027初始執行流程源碼解析 redisson延遲隊列最終都是和redis服務進行交互的,那可以使用monitor命令查看redis中執行了哪些命令,這樣對了解其執行流程有很大幫助。
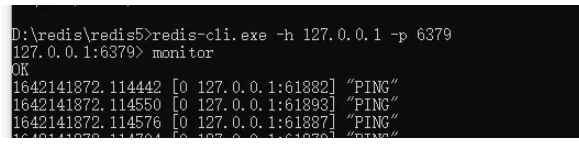
上圖是項目啟動時,對redis發送的幾個指令
"SUBSCRIBE":訂閱隊列"redisson_delay_queue_channel:{redisson:queue}",里面有個定時任務通過該隊列獲取數據
"zrangebyscore":獲取"redisson_delay_queue_timeout:{redisson:queue}"集合中排序score值在0到1642148406748(當前時間戳)內的前100元素
"zrange":獲取"redisson_delay_queue_timeout:{redisson:queue}"集合中第一個元素,用于獲取下一個元素的到期時間
"BLPOP":取出并移除"redisson:queue"列表里的第一個元素,如果沒有元素就一直等待阻塞。所以這里會阻塞著
"rpush":如果指令"zrangebyscore"獲取到了元素,那就將元素推送到隊列redisson:queue內
"lrem":如果指令"zrangebyscore"獲取到了元素,那就刪除隊列"redisson_delay_queue:{redisson:queue}內元素為v的第一個元素
進入RedissonDelayedQueue延遲隊列的構造函數,里面就有上述執行指令的lua腳本命令(為了不影響篇幅刪了一部分代碼,下同):
......
protected RedissonDelayedQueue(QueueTransferService queueTransferService, Codec codec, final CommandAsyncExecutor commandExecutor, String name) {
super(codec, commandExecutor, name);
// list結構,用于延遲隊列的訂閱發布
channelName = prefixName("redisson_delay_queue_channel", getRawName());
// list結構,存放元素原始順序
queueName = prefixName("redisson_delay_queue", getRawName());
// zset結構,存放未到期元素,并按照過期時間進行排好序
timeoutSetName = prefixName("redisson_delay_queue_timeout", getRawName());
QueueTransferTask task = new QueueTransferTask(commandExecutor.getConnectionManager()) {
@Override
protected RFuture<Long> pushTaskAsync() {
return commandExecutor.evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG,
"local expiredValues = redis.call('zrangebyscore', KEYS[2], 0, ARGV[1], 'limit', 0, ARGV[2]); "
+ "if #expiredValues > 0 then "
+ "for i, v in ipairs(expiredValues) do "
+ "local randomId, value = struct.unpack('dLc0', v);"
+ "redis.call('rpush', KEYS[1], value);"
+ "redis.call('lrem', KEYS[3], 1, v);"
+ "end; "
+ "redis.call('zrem', KEYS[2], unpack(expiredValues));"
+ "end; "
// get startTime from scheduler queue head task
+ "local v = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[2], 0, 0, 'WITHSCORES'); "
+ "if v[1] ~= nil then "
+ "return v[2]; "
+ "end "
+ "return nil;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getRawName(), timeoutSetName, queueName),
System.currentTimeMillis(), 100);
}
@Override
protected RTopic getTopic() {
return RedissonTopic.createRaw(LongCodec.INSTANCE, commandExecutor, channelName);
}
};
queueTransferService.schedule(queueName, task);
this.queueTransferService = queueTransferService;
}繼續跟進queueTransferService.schedule(queueName, task)方法,因為第一次進入tasks集合,所以最后執行start()方法:
......
private final ConcurrentMap<String, QueueTransferTask> tasks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public synchronized void schedule(String name, QueueTransferTask task) {
QueueTransferTask oldTask = tasks.putIfAbsent(name, task);
if (oldTask == null) {
task.start();
} else {
oldTask.incUsage();
}
}進入QueueTransferTask,繼續跟進schedulerTopic.addListener(...)方法:
......
private int messageListenerId;
private int statusListenerId;
public void start() {
RTopic schedulerTopic = getTopic();
statusListenerId = schedulerTopic.addListener(new BaseStatusListener() {
@Override
public void onSubscribe(String channel) {
pushTask();
}
});
messageListenerId = schedulerTopic.addListener(Long.class, new MessageListener<Long>() {
@Override
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, Long startTime) {
scheduleTask(startTime);
}
});
}然后會進入PublishSubscribeService.subscribe(...)方法:
注意:這里繼續調用重載方法subscribe(...)時設置了參數:PubSubType.SUBSCRIBE
......
public RFuture<PubSubConnectionEntry> subscribe(Codec codec, ChannelName channelName, RedisPubSubListener<?>... listeners) {
return subscribe(PubSubType.SUBSCRIBE, codec, channelName, getEntry(channelName), listeners);
}
private RFuture<PubSubConnectionEntry> subscribe(PubSubType type, Codec codec, ChannelName channelName, MasterSlaveEntry entry, RedisPubSubListener<?>... listeners) {
RPromise<PubSubConnectionEntry> promise = new RedissonPromise<>();
AsyncSemaphore lock = getSemaphore(channelName);
// 創建一個線程任務放入lock對象
lock.acquire(() -> {
if (promise.isDone()) {
lock.release();
return;
}
subscribe(codec, channelName, entry, promise, type, lock, listeners);
});
return promise;
}AsyncSemaphore對象的acquire(...)方法會把線程任務放入自身隊列listeners里,然后依次讀取執行線程任務;
public class AsyncSemaphore {
private final AtomicInteger counter;
private final Queue<Runnable> listeners = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
public void acquire(Runnable listener) {
listeners.add(listener);
tryRun();
}
private void tryRun() {
if (counter.decrementAndGet() >= 0) {
Runnable listener = listeners.poll();
if (listener == null) {
counter.incrementAndGet();
return;
}
listener.run();
} else {
if (counter.incrementAndGet() > 0) {
tryRun();
}
}
}
}然后繼續跟進方法subscribe(codec, channelName, entry, promise, type, lock, listeners):
.....
private void subscribe(Codec codec, ChannelName channelName, MasterSlaveEntry entry,
RPromise<PubSubConnectionEntry> promise, PubSubType type,
AsyncSemaphore lock, RedisPubSubListener<?>... listeners) {
PubSubConnectionEntry connEntry = name2PubSubConnection.get(new PubSubKey(channelName, entry));
if (connEntry != null) {
addListeners(channelName, promise, type, lock, connEntry, listeners);
return;
}
freePubSubLock.acquire(() -> {
if (promise.isDone()) {
lock.release();
freePubSubLock.release();
return;
}
MasterSlaveEntry msEntry = Optional.ofNullable(connectionManager.getEntry(entry.getClient())).orElse(entry);
// 第一次進入entry2PubSubConnection集合為null,所以使用默認值,最后 freeEntry == null
PubSubEntry freePubSubConnections = entry2PubSubConnection.getOrDefault(msEntry, new PubSubEntry());
PubSubConnectionEntry freeEntry = freePubSubConnections.getEntries().peek();
if (freeEntry == null) {
freePubSubLock.release();
connect(codec, channelName, msEntry, promise, type, lock, listeners);
return;
}
......
});
}繼續跟進方法connect(codec, channelName, msEntry, promise, type, lock, listeners):
......
private void connect(Codec codec, ChannelName channelName,
MasterSlaveEntry msEntry, RPromise<PubSubConnectionEntry> promise, PubSubType type, AsyncSemaphore lock, RedisPubSubListener<?>... listeners) {
RFuture<RedisPubSubConnection> connFuture = nextPubSubConnection(msEntry, channelName);
promise.onComplete((res, e) -> {...});
connFuture.onComplete((conn, ex) -> {
if (ex != null) {...}
freePubSubLock.acquire(() -> {
PubSubConnectionEntry entry = new PubSubConnectionEntry(conn, config.getSubscriptionsPerConnection());
int remainFreeAmount = entry.tryAcquire();
PubSubKey key = new PubSubKey(channelName, msEntry);
PubSubConnectionEntry oldEntry = name2PubSubConnection.putIfAbsent(key, entry);
if (oldEntry != null) {...}
if (remainFreeAmount > 0) {
addFreeConnectionEntry(channelName, entry);
}
freePubSubLock.release();
RFuture<Void> subscribeFuture = addListeners(channelName, promise, type, lock, entry, listeners);
ChannelFuture future;
// 這里通過上述重載方法傳遞的參數可知,最后走else邏輯
if (PubSubType.PSUBSCRIBE == type) {
future = entry.psubscribe(codec, channelName);
} else {
future = entry.subscribe(codec, channelName);
}
future.addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future1 -> {
if (!future1.isSuccess()) {...}
connectionManager.newTimeout(timeout ->
subscribeFuture.cancel(false),
config.getTimeout(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
});
});
});
}該方法中支線內容不表述,主要看方法 entry.subscribe(codec, channelName),最后進入RedisPubSubConnection.async(...)方法,就是發送SUBSCRIBE指令的流程:
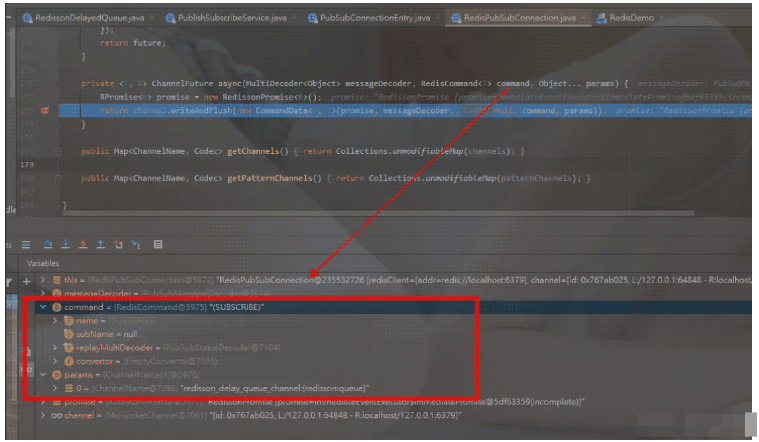
訂閱指令SUBSCRIBE發出后,在QueueTransferTask.start()方法里添加的監聽器觸發了,就會執行pushTask()
pushTaskAsync()方法執行完(lua腳本執行完),就會開啟一個定時任務scheduleTask()
......
protected abstract RTopic getTopic();
protected abstract RFuture<Long> pushTaskAsync();
private void pushTask() {
// 這個抽象方法在之前構建RedissonDelayedQueue對象的構造函數里有實現,最后返回元素過期時間
RFuture<Long> startTimeFuture = pushTaskAsync();
startTimeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof RedissonShutdownException) {
return;
}
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
scheduleTask(System.currentTimeMillis() + 5 * 1000L);
return;
}
if (res != null) {
scheduleTask(res);
}
});
}當RedissonDelayedQueue延遲隊列構造完成后,會調用延遲隊列的take()方法獲取延遲任務,然后會進入RedissonBlockingQueue.takeAsync()方法:
......
@Override
public RFuture<V> takeAsync() {
return commandExecutor.writeAsync(getRawName(), codec, RedisCommands.BLPOP_VALUE, getRawName(), 0);
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
* @see java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue#take()
*/
@Override
public V take() throws InterruptedException {
return commandExecutor.getInterrupted(takeAsync());
}
......注意這里的參數其值為 BLPOP,很明顯這里就是和我們要找的BLPOP指令有關,所以這里其實就是客戶端通過BLPOP指令阻塞式獲取值。在客戶端開個線程一直循環阻塞獲取元素即可;
看下源碼繼續向下進入CommandAsyncService.writeAsync(...)方法,然后繼續向下進入RedisExecutor.execute()方法:
......
public void execute() {
if (mainPromise.isCancelled()) {...}
if (!connectionManager.getShutdownLatch().acquire()) {...}
codec = getCodec(codec);
// 獲取連接
RFuture<RedisConnection> connectionFuture = getConnection();
RPromise<R> attemptPromise = new RedissonPromise<>();
mainPromiseListener = (r, e) -> {...};
if (attempt == 0) {...}
scheduleRetryTimeout(connectionFuture, attemptPromise);
connectionFuture.onComplete((connection, e) -> {
if (connectionFuture.isCancelled()) {...}
if (!connectionFuture.isSuccess()) {...}
// 連接獲取成功就執行當前方法
sendCommand(attemptPromise, connection);
writeFuture.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
checkWriteFuture(writeFuture, attemptPromise, connection);
}
});
});
attemptPromise.onComplete((r, e) -> {...});
}該方法里一些支線方法按下不表。中間有個超時重試機制,使用netty的時間輪,不是重點也就不表述了。
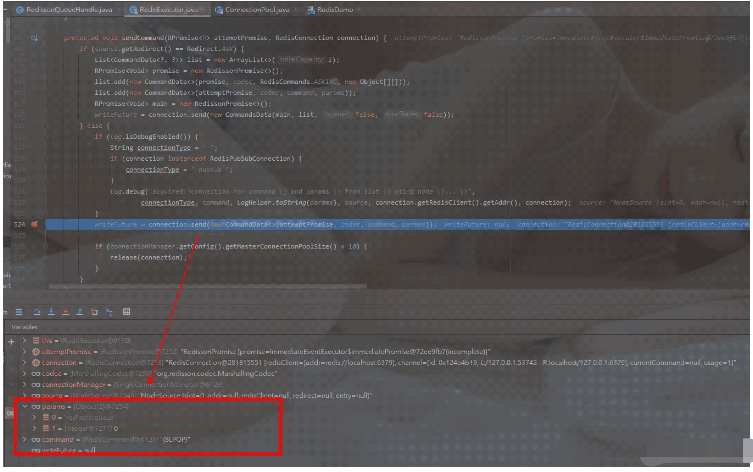
先獲取寫入操作連接對象任務,然后進入方法sendCommand(attemptPromise, connection)發送
指令指令:"BLPOP",參數:"redisson:queue" "0"
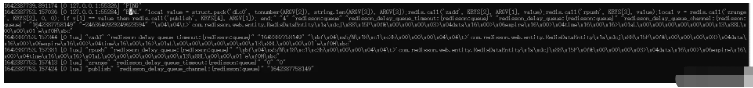
offer添加任務流程源碼解析 項目啟動完成后,添加一個延遲任務到redis中,查看redis中所執行的指令:
然后跟進插入元素offer方法,進入RedissonDelayedQueue.offerAsync()方法內,如下所示:
......
@Override
public void offer(V e, long delay, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
get(offerAsync(e, delay, timeUnit));
}
@Override
public RFuture<Void> offerAsync(V e, long delay, TimeUnit timeUnit) {
if (delay < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Delay can't be negative");
}
long delayInMs = timeUnit.toMillis(delay);
long timeout = System.currentTimeMillis() + delayInMs;
long randomId = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextLong();
return commandExecutor.evalWriteNoRetryAsync(getRawName(), codec, RedisCommands.EVAL_VOID,
"local value = struct.pack('dLc0', tonumber(ARGV[2]), string.len(ARGV[3]), ARGV[3]);"
+ "redis.call('zadd', KEYS[2], ARGV[1], value);"
+ "redis.call('rpush', KEYS[3], value);"
// if new object added to queue head when publish its startTime
// to all scheduler workers
+ "local v = redis.call('zrange', KEYS[2], 0, 0); "
+ "if v[1] == value then "
+ "redis.call('publish', KEYS[4], ARGV[1]); "
+ "end;",
Arrays.<Object>asList(getRawName(), timeoutSetName, queueName, channelName),
timeout, randomId, encode(e));
}其中很明顯一長串的腳本命令就是在redis中執行的指令,基本流程比較簡單:
"zadd":這是向zset集合"redisson_delay_queue_timeout:{redisson:queue}"里添加元素數據(此數據被處理過,不用管其結構),排序值為當前時間戳+延遲時間
"rpush":把元素數據推送到list隊列"redisson:queue"
"zrange":獲取zset集合"redisson_delay_queue_timeout:{redisson:queue}"中排好序的第一個元素
"publish":如果上述獲取的元素是本次插入的元素,那就發布通知隊列"redisson_delay_queue_channel:{redisson:queue}",內容為當前元素的過期時間,這樣做是為了減少本次元素到期的時間差。
定時器任務主要是通過監聽器監聽到了有新的客戶端訂閱或元素通知發布出來時,就會執行pushTask()和scheduleTask(...)方法:
......
private int messageListenerId;
private int statusListenerId;
public void start() {
RTopic schedulerTopic = getTopic();
// 當有新的客戶端訂閱schedulerTopic,就是觸發執行pushTask()方法
statusListenerId = schedulerTopic.addListener(new BaseStatusListener() {
@Override
public void onSubscribe(String channel) {
pushTask();
}
});
// 當redis有新的消息通知,就會觸發scheduleTask(...)方法,startTime為上述中publish通知的元素過期時間
messageListenerId = schedulerTopic.addListener(Long.class, new MessageListener<Long>() {
@Override
public void onMessage(CharSequence channel, Long startTime) {
scheduleTask(startTime);
}
});
}pushTask()方法是對redis延遲隊列進行操作的方法,scheduleTask(...)是netty時間輪來控制調用pushTask()方法,所以pushTask()和scheduleTask()互相調用。
......
private void scheduleTask(final Long startTime) {
TimeoutTask oldTimeout = lastTimeout.get();
if (startTime == null) {...}
if (oldTimeout != null) {...}
long delay = startTime - System.currentTimeMillis();
if (delay > 10) {
Timeout timeout = connectionManager.newTimeout(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {
pushTask();
TimeoutTask currentTimeout = lastTimeout.get();
if (currentTimeout.getTask() == timeout) {
lastTimeout.compareAndSet(currentTimeout, null);
}
}
}, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!lastTimeout.compareAndSet(oldTimeout, new TimeoutTask(startTime, timeout))) {
timeout.cancel();
}
} else {
pushTask();
}
}
protected abstract RTopic getTopic();
protected abstract RFuture<Long> pushTaskAsync();
private void pushTask() {
RFuture<Long> startTimeFuture = pushTaskAsync();
startTimeFuture.onComplete((res, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
if (e instanceof RedissonShutdownException) {
return;
}
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
scheduleTask(System.currentTimeMillis() + 5 * 1000L);
return;
}
if (res != null) {
scheduleTask(res);
}
});
}以上就是“Redisson延遲隊列執行流程是什么”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。