您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Java數據結構之順序表如何實現”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“Java數據結構之順序表如何實現”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
線性表(linear list)是n個具有相同特性的數據元素的有限序列。 線性表是一種在實際中廣泛使用的數據結構,常見 的線性表:順序表、鏈表、棧、隊列、字符串… 線性表在邏輯上是線性結構,也就說是連續的一條直線。但是在物理結構上并不一定是連續的,線性表在物理上存儲 時,通常以數組和鏈式結構的形式存儲。
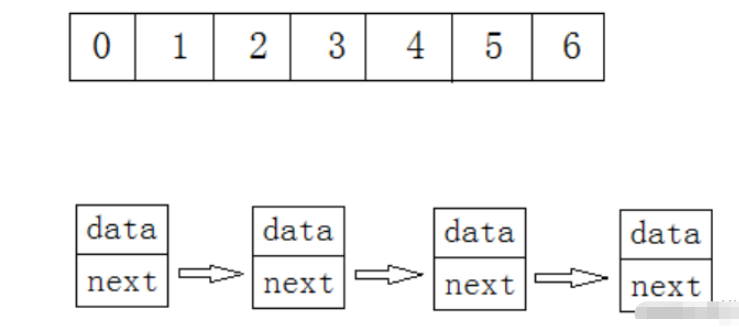
順序表是用一段物理地址連續的存儲單元依次存儲數據元素的線性結構,一般情況下采用數組存儲。在數組上完成數據的增刪查改 。
其實就是一個數組。那為什么還要寫一個順序表,直接用數組不就好了?不一樣的,寫到類里面就可以面向對象。
順序表一般可以分為:
靜態順序表:使用定長數組存儲
動態順序表:使用動態開辟的數組存儲
靜態順序表適用于確定知道需要存多少數據的場景.
靜態順序表的定長數組導致N定大了,空間開多了浪費,開少了不夠用.
相比之下動態順序表更靈活, 根據需要動態的分配空間大小.
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;//數組
public int usedSize;//數據的有效個數
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
}
//打印順序表
public void display(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}//獲取順序表長度
public int size(){
return this.usedSize;
}在順序表里面插入元素的時候所插入的位置的前面一定是存放了元素的

//在 pos 位置新填元素
public void add(int pos,int data){
if(pos < 0 || pos >usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(isfull()) {
Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
for (int i = this.usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//判斷是否滿
public boolean isfull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}//判斷是否包含某個元素
public boolean contains(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}//查找某個元素的對應位置,找不到返回-1
public int search(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}//獲取pos位置的值
public int getPos(int pos){
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//這里說明一下,業務上的處理,不考慮
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
} //給pos位置元素更新value
public void setPos(int pos,int value){
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}//刪除第一次出現的關鍵字key
public void remove(int toRmove){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRmove);
if(index == -1){
System.out.println("沒有你要刪除的數字!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[useSize] = null;如果數組當中是引用數據類型
}//清空順序表
public void clear(){
this.usedSize = 0;
}import java.util.Arrays;
public class MyArrayList {
public int[] elem;
public int usedSize;
public MyArrayList(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
//打印順序表
public void display(){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
//獲取順序表長度
public int size(){
return this.usedSize;
}
//在 pos 位置新填元素
public void add(int pos,int data){
if(pos < 0 || pos >usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法!");
return;
}
if(isfull()) {
Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,2*this.elem.length);
}
for (int i = this.usedSize - 1; i >= pos; i--) {
this.elem[i + 1] = this.elem[i];
}
this.elem[pos] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
//判斷是否滿
public boolean isfull(){
return this.usedSize == this.elem.length;
}
//判斷是否包含某個元素
public boolean contains(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//查找某個元素的對應位置,找不到返回-1
public int search(int toFind){
for (int i = 0; i < this.usedSize; i++) {
if(this.elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//獲取pos位置的值
public int getPos(int pos){
if(pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return -1;//這里說明一下,業務上的處理,不考慮
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return -1;
}
return this.elem[pos];
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.usedSize == 0;
}
//給pos位置元素更新value
public void setPos(int pos,int value){
if (pos < 0 || pos >= this.usedSize){
System.out.println("pos 位置不合法");
return;
}
if(isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return;
}
this.elem[pos] = value;
}
//刪除第一次出現的關鍵字key
public void remove(int toRmove){
if (isEmpty()){
System.out.println("順序表為空!");
return;
}
int index = search(toRmove);
if(index == -1){
System.out.println("沒有你要刪除的數字!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < this.usedSize - 1; i++) {
this.elem[i] = this.elem[i+1];
}
this.usedSize--;
//this.elem[useSize] = null;如果數組當中是引用數據類型
}
//清空順序表
public void clear(){
this.usedSize = 0;
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(0,1);
myArrayList.add(1,2);
myArrayList.add(2,3);
myArrayList.add(3,4);
myArrayList.add(4,5);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.contains(3));
System.out.println(myArrayList.getPos(3));
myArrayList.setPos(0,99);
myArrayList.display();
}
}關于“Java數據結構之順序表如何實現”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。