您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“JavaScript中如何利用Object()函數創建對象”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“JavaScript中如何利用Object()函數創建對象”文章能幫助大家解決問題。

JavaScript 原生提供Object對象(注意起首的O是大寫),所有其他對象都繼承自這個對象。Object本身也是一個構造函數,可以直接通過它來生成新對象。
Object()函數可以將給定的值包裝為一個新對象。
語法:
new Object() new Object(value)
參數 value 是任意類型的可選參數。
如果value值是null或undefined或不傳時,則會創建并返回一個空對象;
如果value值是一個基本類型,則會構造其包裝類的對象,返回一個和給定的值相對應的類型的對象。;
如果value值是引用類型,則仍然返回這個值。
如果給定值是一個已經存在的對象,則會返回這個已經存在的值(相同地址)。
var obj = new Object(); //創建了一個空的對象
obj.uname = 'zhangsanfeng';
obj.name = 18; //字面量方式創建對象不同,這里需要用 = 賦值添加屬性和方法
obj.sex = 'nan'; //屬性和方法后面以;結束
obj.sayHi = function() {
console.log('hi');
}
console.log(obj.uname);
console.log(obj['age']);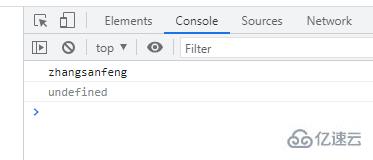
說明:通過new Object()的寫法生成新對象,與字面量的寫法o = {}是等價的。
var o1 = {a: 1};
var o2 = new Object(o1);
o1 === o2 // true
new Object(123) instanceof Number
// true與其他構造函數一樣,如果要在Object對象上面部署一個方法,有兩種做法。
(1)部署在Object對象本身
比如,在Object對象上面定義一個print方法,顯示其他對象的內容。
Object.print = function(o){ console.log(o) };
var o = new Object();
Object.print(o)
// Object(2)部署在Object.prototype對象
所有構造函數都有一個prototype屬性,指向一個原型對象。凡是定義在Object.prototype對象上面的屬性和方法,將被所有實例對象共享。(關于prototype屬性的詳細解釋,參見《面向對象編程》一章。)
Object.prototype.print = function(){ console.log(this)};
var o = new Object();
o.print() // Object上面代碼在Object.prototype定義了一個print方法,然后生成一個Object的實例o。o直接繼承了Object.prototype的屬性和方法,可以在自身調用它們,也就是說,o對象的print方法實質上是調用Object.prototype.print方法。。
可以看到,盡管上面兩種寫法的print方法功能相同,但是用法是不一樣的,因此必須區分“構造函數的方法”和“實例對象的方法”。
Object()
Object本身就是一個函數,本身當作工具方法使用時,可以將任意值轉為對象。這個方法常用于保證某個值一定是對象。
如果參數是原始類型的值,Object方法返回對應的包裝對象的實例
Object() // 返回一個空對象
Object() instanceof Object // true
Object(undefined) // 返回一個空對象
Object(undefined) instanceof Object // true
Object(null) // 返回一個空對象
Object(null) instanceof Object // true
Object(1) // 等同于 new Number(1)
Object(1) instanceof Object // true
Object(1) instanceof Number // true
Object('foo') // 等同于 new String('foo')
Object('foo') instanceof Object // true
Object('foo') instanceof String // true
Object(true) // 等同于 new Boolean(true)
Object(true) instanceof Object // true
Object(true) instanceof Boolean // true上面代碼表示Object函數可以將各種值轉為對應的構造函數生成的對象。
如果Object方法的參數是一個對象,它總是返回原對象。
var arr = [];
Object(arr) // 返回原數組
Object(arr) === arr // true
var obj = {};
Object(obj) // 返回原對象
Object(obj) === obj // true
var fn = function () {};
Object(fn) // 返回原函數
Object(fn) === fn // true利用這一點,可以寫一個判斷變量是否為對象的函數。
function isObject(value) {
return value === Object(value);
}
isObject([]) // true
isObject(true) // false1. 對象字面量{…}
對象字面量的方式是最常用的方式之一,它用內含屬性的花括號{...}快速創建對象。
var obj1 = {};
obj1.name = "Tom";
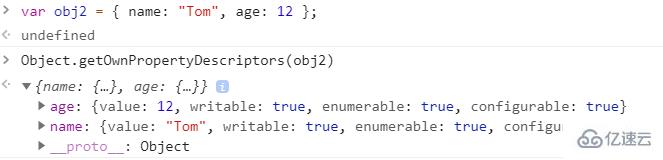
var obj2 = { name: "Tom", age: 12 };
var name = "Tom", age = 12;
var obj3 = { name: name, age: age };
// ES2015中,屬性名和變量名相同時可簡寫為:
var obj3 = { name, age };
// 擴展屬性,ES2018新特性,可用于克隆或合并對象,淺拷貝,不包括原型
var obj4 = { ...obj3 };以字面量方式創建的對象屬性默認是可寫,可枚舉和可配置的
對象的原型默認為Object.prototype。通過定義屬性__proto__(只能使用冒號標記的屬性定義)的值來變更原型。只有給出的值是對象或null,對象的原型才會被設置為給出的值,否則原型不會改變。
var obj1 = {};
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj1) === Object.prototype; // true
var obj2 = { __proto__: null };
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj2) === null; // true
var __proto__= {};
var obj3 = { "__proto__": __proto__ };
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj3) === __proto__; // true
// 不使用冒號標記的屬性定義,不會變更對象的原型,只是名字為__proto__的普通屬性
var obj4 = { __proto__ };
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj4) === __proto__; // false
obj4.hasOwnProperty("__proto__"); // true
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj4) === Object.prototype; // true
var obj5 = { __proto__: "not an object or null" };
obj5.hasOwnProperty("__proto__"); // false
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj5) === Object.prototype; // true2. Object.create()
Object.create()方法創建一個新對象,使用現有的對象來提供新創建的對象的__proto__。
/**
* 創建一個具有指定原型的對象,并且包含指定的屬性。
* @param o 新創建對象的原型對象。可能為空
* @param properties 包含一個或多個屬性描述符的 JavaScript 對象。
*/
create(o: object | null, properties?: PropertyDescriptorMap): any;
interface PropertyDescriptorMap {
[s: string]: PropertyDescriptor;
}
interface PropertyDescriptor {
configurable?: boolean;
enumerable?: boolean;
value?: any;
writable?: boolean;
get?(): any;
set?(v: any): void;
}var obj1 = Object.create(null);
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj1) === null; // true
var proto= {};
var obj2 = Object.create(proto);
Object.getPrototypeOf(obj2) === proto; // true
var obj3 = Object.create({}, { p: { value: 42 } });
// 屬性描述對象中省略了的屬性默認為false,所以p是不可寫,不可枚舉,不可配置的
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj3); // p: {value: 42, writable: false, enumerable: false, configurable: false}
//創建一個可寫的,可枚舉的,可配置的屬性p
var obj4 = Object.create({}, {
p: { value: 42, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true }
});
//不能同時指定訪問器(get和set)和 值或可寫屬性
var obj4 = Object.create({}, {
p: {
// value: 42, // 不能和get set同時存在
// writable: true, // 不能和get set同時存在
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function() { return 10 },
set: function(value) { console.log("Setting `p` to", value); }
}
});3. Object.assign()
Object.assign()方法并不是直接用來創建對象的,但它可以達到創建對象的效果,所以這里把它也作為一種創建對象的方式。
Object.assign() 方法用于將所有自身的可枚舉屬性的值從一個或多個源對象復制到目標對象。返回目標對象。
Object.assign(target, …sources)
如果目標對象或源對象中具有相同的屬性,后面的對象的屬性將覆蓋前面的對象的屬性。
只會拷貝源對象自身的可枚舉屬性到目標對象。對源對象原型上的對象不做處理。
該方法使用源對象的Get和目標對象的Set來獲取和設置值。
var o1 = { name: "Tom" };
var o2 = { name: "Jerry" };
var o3 = Object.create(o2, { // o2是o3的原型,name: "Jerry"是原型上的屬性
a: { value: 42 }, // 不可枚舉
b: { value: 42, writable: false, enumerable: true, configurable: false },
c: { enumerable: true, get: function() { return 10; } }
});
var obj1 = Object.assign(o1, o2);
obj1 === o1; // true
obj1; // {name: "Tom", b: 42, c: 10}
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj1); // 不會拷貝屬性的
/* b: {value: 42, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
c: {value: 10, writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true}
name: {value: "Tom", writable: true, enumerable: true, configurable: true} */
var o4 = { a: "a", b: { name: "Tom", age: 18 } };
var obj2 = Object.assign({}, o4);
obj2.b === o4.b; // true, 淺拷貝,如果源值是一個對象的引用,它僅僅會復制其引用值。
// 合并對象,后面屬性覆蓋前面屬性
var o1 = { a: 1, b: 1 };
var o2 = { b: 2, c: 2 };
var o3 = { a: 3 };
var obj3 = Object.assign({}, o1, o2, o3);
obj3; // {a: 3, b: 2, c: 2}
// 基本類型會被轉為包裝對象,只有字符串的包裝對象有自身可枚舉屬性。
var obj4 = Object.assign({}, "abc", null, true, undefined, 10, Symbol("foo"));
obj4; // {0: "a", 1: "b", 2: "c"}
// 拷貝過程中發生異常,會終止后續拷貝任務,已拷貝的數據保留
var t = Object.create( {}, { b: { value: 42, writable: false } }); // b是只讀屬性
Object.assign(t, {a: 1}, {a: 2, b: 2, c: 3}, {c: 4}); // Cannot assign to read only property 'b' of object '#<Object>'
t; // {a: 2, b: 42}關于“JavaScript中如何利用Object()函數創建對象”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。