您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Java源碼之ArrayQueue內部是怎么實現的”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Java源碼之ArrayQueue內部是怎么實現的”吧!
在談ArrayQueue的內部實現之前我們先來看一個ArrayQueue的使用例子:
public void testQueue() {
ArrayQueue<Integer> queue = new ArrayQueue<>(10);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
queue.add(4);
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0); // 這個參數只能為0 表示刪除隊列當中第一個元素,也就是隊頭元素
System.out.println(queue);
queue.remove(0);
System.out.println(queue);
}// 輸出結果
[1, 2, 3, 4]
[2, 3, 4]
[3, 4]
首先ArrayQueue內部是由循環數組實現的,可能保證增加和刪除數據的時間復雜度都是 O ( 1 ) O(1) O(1),不像ArrayList刪除數據的時間復雜度為 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。在ArrayQueue內部有兩個整型數據head和tail,這兩個的作用主要是指向隊列的頭部和尾部,它的初始狀態在內存當中的布局如下圖所示:

因為是初始狀態head和tail的值都等于0,指向數組當中第一個數據。現在我們向ArrayQueue內部加入5個數據,那么他的內存布局將如下圖所示:
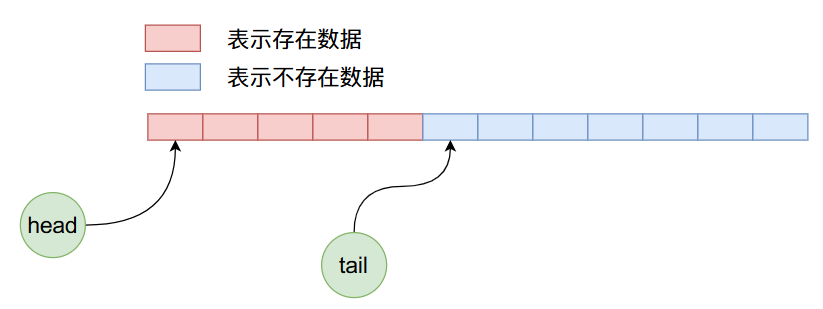
現在我們刪除4個數據,那么上圖經過4次刪除操作之后,ArrayQueue內部數據布局如下:
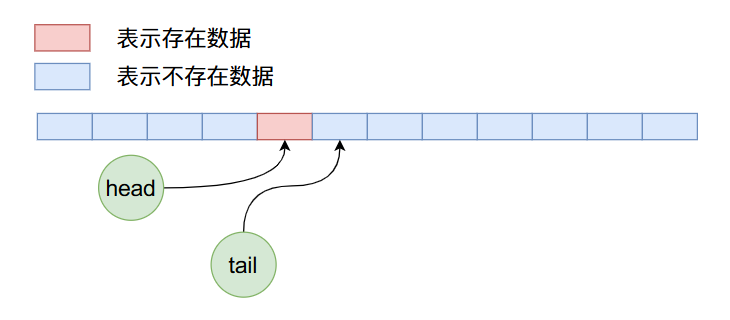
在上面的狀態下,我們繼續加入8個數據,那么布局情況如下:
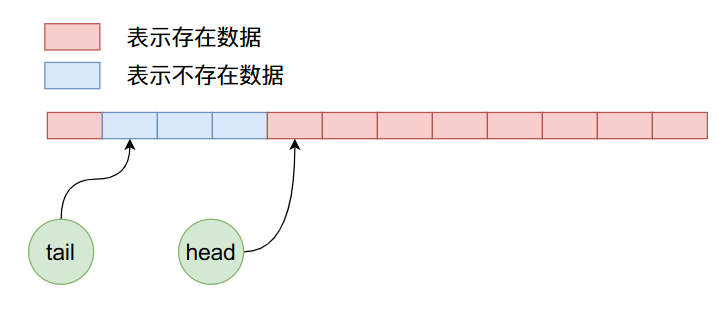
我們知道上圖在加入數據的時候不僅將數組后半部分的空間使用完了,而且可以繼續使用前半部分沒有使用過的空間,也就是說在ArrayQueue內部實現了一個循環使用的過程。
構造函數
public ArrayQueue(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity + 1;
this.queue = newArray(capacity + 1);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private T[] newArray(int size) {
return (T[]) new Object[size];
}上面的構造函數的代碼比較容易理解,主要就是根據用戶輸入的數組空間長度去申請數組,不過他具體在申請數組的時候會多申請一個空間。
add函數
public boolean add(T o) {
queue[tail] = o;
// 循環使用數組
int newtail = (tail + 1) % capacity;
if (newtail == head)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue full");
tail = newtail;
return true; // we did add something
}上面的代碼也相對比較容易看懂,在上文當中我們已經提到了ArrayQueue可以循環將數據加入到數組當中去,這一點在上面的代碼當中也有所體現。
remove函數
public T remove(int i) {
if (i != 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Can only remove head of queue");
if (head == tail)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Queue empty");
T removed = queue[head];
queue[head] = null;
head = (head + 1) % capacity;
return removed;
}從上面的代碼當中可以看出,在remove函數當中我們必須傳遞參數0,否則會拋出異常。而在這個函數當中我們只會刪除當前head下標所在位置的數據,然后將head的值進行循環加1操作。
get函數
public T get(int i) {
int size = size();
if (i < 0 || i >= size) {
final String msg = "Index " + i + ", queue size " + size;
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(msg);
}
int index = (head + i) % capacity;
return queue[index];
}get函數的參數表示得到第i個數據,這個第i個數據并不是數組位置的第i個數據,而是距離head位置為i的位置的數據,了解這一點,上面的代碼是很容易理解的。
resize函數
public void resize(int newcapacity) {
int size = size();
if (newcapacity < size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Resizing would lose data");
newcapacity++;
if (newcapacity == this.capacity)
return;
T[] newqueue = newArray(newcapacity);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
newqueue[i] = get(i);
this.capacity = newcapacity;
this.queue = newqueue;
this.head = 0;
this.tail = size;
}在resize函數當中首先申請新長度的數組空間,然后將原數組的數據一個一個的拷貝到新的數組當中,注意在這個拷貝的過程當中,重新更新了head與tail,而且并不是簡單的數組拷貝,因為在之前的操作當中head可能已經不是了0,因此新的拷貝需要我們一個一個的從就數組拿出來,讓后放到新數組當中。下圖可以很直觀的看出這個過程:
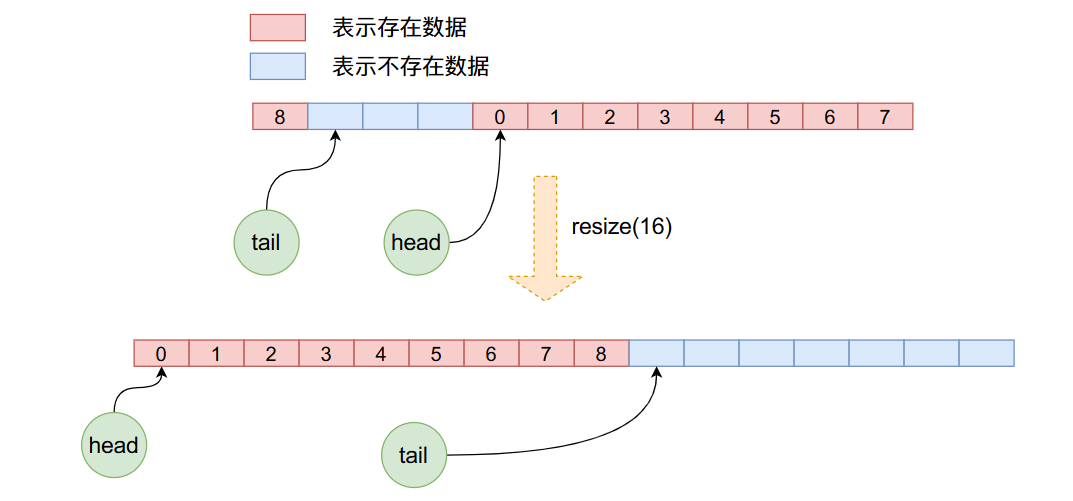
感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Java源碼之ArrayQueue內部是怎么實現的”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Java源碼之ArrayQueue內部是怎么實現的這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。