您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天小編給大家分享一下前端進階JS數組高級使用方法實例分析的相關知識點,內容詳細,邏輯清晰,相信大部分人都還太了解這方面的知識,所以分享這篇文章給大家參考一下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后有所收獲,下面我們一起來了解一下吧。
一、創建新數組使用 for 循環批量 push 數據
function createData() {
const data = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
data.push({
name: `name${i + 1}`,
});
}
return data;
}
const data = createData();
console.log(data);二、創建空數組,填充full,然后map
function createData() {
// 如果不 fill 循環默認會跳過空值
return new Array(1000).fill(null).map((v, i) => ({ name: `name${i + 1}` }));
}
const data = createData();
console.log(data);三、Array.from 第二個初始化函數返回數據
function createData() {
return Array.from({ length: 1000 }, (v, i) => ({ name: `name${i + 1}` }));
}
const data = createData();
console.log(data);一、Set去重
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3]; const arr2 = [3, 4, 5]; console.log(new Set([...arr1, ...arr2]));
二、for循環,indexOf判斷是否存在
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
function mergeArray(arr1, arr2) {
// 克隆
const cloneArr1 = arr1.slice(0);
let v;
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
v = arr2[i];
// 按位非,反轉操作數的位,表象是對后面數字取負減一
// 當數組中不存在此項 indexOf 返回 -1 按位非得 0 不走 if 邏輯
// 如果兩個數組都包含NaN,想要去重可使用includes
if (~cloneArr1.indexOf(v)) {
continue;
}
cloneArr1.push(v);
}
return cloneArr1;
}
console.log(mergeArray(arr1, arr2));去重對象?
const arr1 = [{ id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 3 }];
const arr2 = [{ id: 3 }, { id: 4 }, { id: 5 }];
console.log(Array.from(new Set([...arr1, ...arr2])));
// [ { id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 3 }, { id: 3 }, { id: 4 }, { id: 5 } ]
// 這樣對象都是獨立的引用,肯定無法去除屬性相同的數據啦如果是相同引用呢?
const obj3 = { id: 3 };
const arr1 = [{ id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, obj3];
const arr2 = [obj3, { id: 4 }, { id: 5 }];
console.log(Array.from(new Set([...arr1, ...arr2]))); // 確實可以,但是你開發這樣做?我們可以這樣做
const arr1 = [{ id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 3 }];
const arr2 = [{ id: 3 }, { id: 4 }, { id: 5 }];
function mergeArray(arr1, arr2) {
// 克隆
const cloneArr1 = arr1.slice(0);
let v;
for (let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
v = arr2[i];
// 能找到相同 id 屬性值的數據則進入判斷
if (~cloneArr1.findIndex((el) => el.id === v.id)) {
continue;
}
cloneArr1.push(v);
}
return cloneArr1;
}
console.log(mergeArray(arr1, arr2)); // [ { id: 1 }, { id: 2 }, { id: 3 }, { id: 4 }, { id: 5 } ]字面量
// 字面量 const arr1 = [1, 2, 3, ...[4, 5, 6]]; // 1,2,3,4,5,6 const arr2 = [, , , , ,]; // [empty × 5]
new Array(當參數只有一個且是數字時,new Array()表示數組的長度,其余參數則是數組的內容)
const arr3 = new Array(5); // [empty × 5]
const arr4 = new Array(1, 2, 3); // 1,2,3
const arr5 = new Array("a"); // ["a"]Array.of(參數只用來作為數組中的內容)
const arr6 = Array.of(5); // [5] const arr7 = Array.of(1, 'abc', true); // [1, "abc", true]
Array.from 可傳入類數組和可遍歷對象轉換為真數組
(第一個參數傳入對應類數組和可遍歷對象,第二個函數參數則相當于對生成的數組做一次map)
可遍歷和類數組 ==> 數組、字符串、Set、Map、NodeList、HTMLCollection、arguments以及擁有 length 屬性的任意對象
const arr8 = Array.from([1, 2, 3]); // [1,2,3]
const arr9 = Array.from({ length: 3 }, (value, index) => {
return index + 1;
}); // [1,2,3]
const arr10 = Array.from({ 0: "a", 1: "b", 2: "c", length: 3 }); // ["a", "b", "c"]其他的很多可以返回數組的方法都算
// Array.prototype.slice
const arr11 = Array.prototype.slice.call(document.querySelectorAll("div")); // [div, div, div....]
// Array.prototype.concat
const arr12 = Array.prototype.concat.call([], [1, 2, 3]); // [1, 2, 3]是一個普通對象,不具備數組自帶豐富的內建方法
key是以數字或者字符串數字組成
必須有length屬性
const arrayLike = {
0: "a",
1: "b",
2: "c",
name: "test",
length: 3,
push: Array.prototype.push, //自己實現
splice: Array.prototype.splice,
};
//由于類數組對象length屬性聲明了對象有多少個屬性,所以可以使用for遍歷對象屬性:
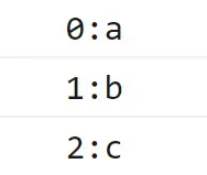
for (let i = 0; i < arrayLike.length; i++) {
console.log(i + ":" + arrayLike[i]);
}
arguments
function person(name, age, sex) {
console.log("person arguments:", arguments);
console.log("person type:", Object.prototype.toString.call(arguments));
}
person("name", "age", "sex");打印結果如下:

NodeList、HTMLCollection、DOMTokenList等
const nodeList = document.querySelectorAll("box");
console.log("querySelectorAll type:", Object.prototype.toString.call(nodeList));
const htmlCollection = document.getElementsByTagName("div");
console.log("getElementsByTagName type:", Object.prototype.toString.call(htmlCollection));
const DOMTokenList = document.querySelector("div").classList;
console.log("classList:", DOMTokenList);
奇特:字符串(具備類數組的特性,但一般類數組指對象)
const str = "abc"; console.log(Object.keys(str)); // ['0', '1', '2'] console.log(Array.from(str)); // ['a', 'b', 'c']
function isArrayLikeObject(arr) {
// 不是對象直接返回
if (arr == null || typeof arr !== "object") return false;
const lengthMaxValue = Math.pow(2, 53) - 1;
// 是否有 length 屬性
if (!Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(arr, "length")) return false;
// length 屬性是否是number類型
if (typeof arr.length != "number") return false;
//使用 isFinite() 判斷是否在正常數字范圍
if (!isFinite(arr.length)) return false;
// 構造函數等于Array
if (Array === arr.constructor) return false;
// 長度有效值
if (arr.length >= 0 && arr.length < lengthMaxValue) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
console.log(isArrayLikeObject(null)); // false
console.log(isArrayLikeObject({ 0: "a", 1: "b", length: 2 })); // true
console.log(isArrayLikeObject({ 0: 1, 2: 3, length: "" })); // false
console.log(isArrayLikeObject({ 0: 1, 2: 3 })); // false
console.log(isArrayLikeObject([1, 2])); // false復制遍歷
const arr = [];
const arrayLike = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
length: 2,
};
for (let i = 0; i < arrayLike.length; i++) {
arr[i] = arrayLike[i];
}
console.log(arr); // [1, 2]slice, concat等
const arrayLike = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
length: 2,
};
const array1 = Array.prototype.slice.call(arrayLike);
console.log(array1); // [ 1, 2 ]
const array2 = Array.prototype.concat.apply([], arrayLike);
console.log(array2); // [ 1, 2 ]Array.from
const arrayLike = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
length: 2,
};
console.log(Array.from(arrayLike)); // [ 1, 2 ]Array.apply
const arrayLike = {
0: 1,
1: 2,
length: 2,
};
console.log(Array.apply(null, arrayLike)); // [ 1, 2 ]擴展運算符
console.log([...document.body.childNodes]); // [div, script, script...]
// arguments
function argumentsTest() {
console.log([...arguments]); // [ 1, 2, 3 ]
}
argumentsTest(1, 2, 3);在類數組對象上直接定義數組原型的方法
運用call或者apply顯示綁定this的指向
例如我想通過 filter 方法過濾出類數組中元素包含 "i" 這個字符的所有元素。
const arrayLike = {
0: "i love",
1: "you",
length: 1,
};
console.log([].filter.call(arrayLike, (item) => item.includes("i"))); // [ 'i love' ]為什么會這樣?其實可以想想 filter 是如何實現的。
[].__proto__.myfilter = function (callback) {
let newArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (callback(this[i])) {
newArr.push(this[i]);
}
}
return newArr;
};可以看出因為 filter 實現是通過 this 進行綁定的,哪個數組調用了這個filter,filter中的 this 就指向哪個數組
| 方法/特征 | 數組 | 類數組 |
|---|---|---|
| 自帶方法 | 多個方法 | 無 |
| length屬性 | 有 | 有 |
| toString返回 | [object Array] | [object Object] |
| instanceof | Array | Object |
| constructor | [Function: Array] | [Function: Object] |
| Array.isArray | true | false |
const arr1 = [1];
const arr2 = [1, ,];
const arr3 = new Array("10");
const arr4 = new Array(10);
console.log("arr1 length: " + arr1.length); // arr1 length: 1
console.log("arr2 length: " + arr2.length); // arr2 length: 2
console.log("arr3 length: " + arr3.length); // arr3 length: 1
console.log("arr4 length: " + arr4.length); // arr4 length: 10empty:數組的空位,指數組的某一位置沒有任何值,有空位的數組也叫稀疏數組
稀疏數組性能會較差,可以避免創建
Array.apply(null,Array(3))
[...new Array(3)]
Array.from(Array(3))
一般遍歷如forEach、map、reduce 會自動跳過空位
const arr = [1, ,];
arr.forEach((item) => console.log(item)); // 1
console.log("arr", arr);// arr [ 1, <1 empty item> ]find,findIndex,includes等, indexOf除外
當被作為迭代的時候,參與Object.entries、擴展運算符、for of 等
視為空字符串
toString 內部其實會調用 join 方法
(,[, + , -,/,其作為一行代碼的開頭,很可能產生意外的情況,所以,沒事代碼最后寫個分號,保準沒錯
const objA = { a: 1 }
["a"];
console.log(objA); // 1
const objB = ["a"]
["a"];
console.log(objB); // undefined
const a = [[1, 2], 2, 3];
console.log(a)
[0, 2, 3].map((v) => console.log(v * v)); // 報錯
console.log(a);| 方法 | 返回值 | 是否能查找NaN | [, ,]空位 | undefined |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| indexOf | number | × | × | √ |
| includes | boolean | √ | √ | √ |
const array1 = [NaN];
console.log("array.includes NaN:", array1.includes(NaN)); // true
console.log("array.indexOf NaN:", array1.indexOf(NaN) > -1); // false
const array2 = [1, ,];
console.log("array.includes ,,:", array2.includes(undefined)); // true
console.log("array.indexOf ,,:", array2.indexOf(undefined) > -1); // false
const array3 = [undefined];
console.log("array.includes undefined:", array3.includes(undefined)); // true
console.log("array.indexOf undefined:", array3.indexOf(undefined) > -1); // true
console.log(Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(array2, 1)); // 區分空位和undefined,判斷此位上是否有值length 代表數組中元素個數,數組額外附加屬性不計算在內
length 可寫,可以通過修改length改變數組的長度
數組操作不存在越界,找不到下標,返回undefined
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6];
array[10] = 10; // 盡量不要這樣破壞數組默認線性存儲的結構
console.log("array.length:", array.length); // 11
array["test"] = "test";
console.log("array.length:", array.length); // 11
array.length = 3;
console.log("array.length:", array.length); // 3
console.log("array value:", array[Number.MAX_VALUE + 1000]); // undefined| 方法 | 返回結果類型 | 是否能短路操作 | 是否需要全部滿足條件 | 遍歷空元素 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| some | boolean | √ | × | × |
| find | undefined | object | √ | × | √ |
| findelndex | number | √ | × | √ |
| every | boolean | √ | √ | × |
| filter | array | × | × | × |
push、pop、unshift、shift
sort、splice、reverse
ES6: copyWithin、fill
let array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
array.push("push");
console.log("array push:", array);
array.pop();
console.log("array pop:", array);
array.unshift("unshift");
console.log("array unshift:", array);
array.shift();
console.log("array shift:", array);
array.reverse();
console.log("array reverse:", array);
array.sort();
console.log("array sort:", array);
array.splice(2, 1);
console.log("array splice:", array);
array.copyWithin(2, 0);
console.log("array copyWithin:", array);
array.fill("fill", 3);
console.log("array fill:", array);delete刪除數組元素,后面元素不會補齊,delete刪除引用
const array = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
delete array[2];
console.log("delete array:", array); // delete array: [ 1, 2, <1 empty item>, 4, 5 ]大量數據操作的時候 push 性能會比 concat 性能高很多
const count = 10000;
const array1 = [1, 2, 4, 5, 6];
let newArray = [];
console.time("push");
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
newArray.push(array1[0], array1[1], array1[2], array1[3], array1[4]);
}
console.timeEnd("push");
console.time("concat");
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
newArray = newArray.concat(array1[0], array1[1], array1[2], array1[3], array1[4]);
}
console.timeEnd("concat");const createValues = (creator, length = 10) => Array.from({ length }, creator);
// 第一個參數控制隨機數生成,第二個控制其數組長度
const createRandomValues = (len) => createValues(Math.random, len);
const values = createRandomValues();
console.log("values:", values.length, values);const createValues = (creator, length = 10) => Array.from({ length }, creator);
const createRange = (start, stop, step) =>
createValues((_, i) => start + i * step, (stop - start) / step + 1);
// 生成數組,里面元素是 1 ~ 100 以內每次從 1 開始每次遞增 3 的數字
const values = createRange(1, 100, 3);
console.log(values);const createValues = (creator, length = 10) => Array.from({ length }, creator);
function createUser(v, index) {
return {
name: `user-${index}`,
age: (Math.random() * 100) >> 0, // 取整
};
}
const users = createValues(createUser, 100);
console.log("users:", users);const arr = [1, 2, 3];
arr.splice(0);
console.log("splice:", arr); // []
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
arr1.length = 0;
console.log("length:", arr1); // []const arr = [
"apple",
"banana",
1,
1,
3,
3,
undefined,
undefined,
,
,
NaN,
NaN,
null,
null,
"true",
true,
{ a: 1 },
];
const arr1 = Array.from(new Set(arr)); // 正常去重
console.log("set:", arr1);對于數組里面對象去重
function uniqueArray(arr) {
return Array.from(new Set(arr));
}
const arr = [{ a: 1 }, { a: 1 }];
console.log("set 不同引用:", uniqueArray(arr));
const obj1 = { a: 1 };
const arr2 = [obj1, obj1];
console.log("set 同一引用:", uniqueArray(arr2));如果我們想認為兩個對象里面的 a 屬性的值相同就認為是同一數組的話,可以使用 filter
function uniqueArray(arr = [], key) {
const keyValues = new Set();
let val;
return arr.filter((obj) => {
val = obj[key];
if (keyValues.has(val)) {
return false;
}
keyValues.add(val);
return true;
});
}
const arr = [{ a: 1 }, { a: 1 }, { a: 2 }];
console.log("filter 去重:", uniqueArray(arr, "a")); // filter 去重: [ { a: 1 }, { a: 2 } ]Array.prototype.filter + includes判斷
但是會存在性能和引用類型相同的判斷的問題
const arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
const arr2 = [3, 2, 0];
function intersectSet(arr1, arr2) {
return [...new Set(arr1)].filter((item) => arr2.includes(item));
}
const values = intersectSet(arr1, arr2);
console.log(values); // [ 0, 2 ]我們可以這樣做:
// 引用類型
function intersect(arr1, arr2, key) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.forEach((val) => map.set(val[key]));
return arr2.filter((val) => map.has(val[key]));
}
// 原始數據類型
function intersectBase(arr1, arr2) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.forEach((val) => map.set(val));
return arr2.filter((val) => map.has(val));
}
const arr1 = [{ p: 0 }, { p: 1 }, { p: 2 }];
const arr2 = [{ p: 3 }, { p: 2 }, { p: 1 }];
const result = intersect(arr1, arr2, "p");
console.log("result:", result); // result: [ { p: 2 }, { p: 1 } ]
const arr3 = [0, 1, 2];
const arr4 = [3, 2, 0];
const result1 = intersectBase(arr3, arr4);
console.log("result1:", result1); // result1: [ 2, 0 ]性能比對:
function createData(length) {
return Array.from({ length }, (val, i) => {
return ~~(Math.random() * length);
});
}
function intersectSet(arr1, arr2) {
return [...new Set(arr1)].filter((item) => arr2.includes(item));
}
// 原始數據類型
function intersectMap(arr1, arr2) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.forEach((val) => map.set(val));
return arr2.filter((val) => {
return map.has(val);
});
}
console.time("createData");
const data1 = createData(100000);
const data2 = createData(100000);
console.timeEnd("createData");
console.time("intersectMap");
intersectMap(data1, data2);
console.timeEnd("intersectMap");
console.time("intersectSet");
intersectSet(data1, data2);
console.timeEnd("intersectSet");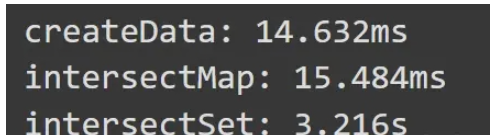
// 引用類型
function difference(arr1, arr2, key) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.forEach((val) => map.set(val[key]));
return arr2.filter((val) => !map.has(val[key]));
}
// 原始數據類型
function differenceBase(arr1, arr2) {
const map = new Map();
arr1.forEach((val) => map.set(val));
return arr2.filter((val) => !map.has(val));
}
const arr1 = [{ p: 0 }, { p: 1 }, { p: 2 }];
const arr2 = [{ p: 3 }, { p: 2 }, { p: 1 }];
const result = difference(arr1, arr2, "p");
console.log("result:", result); // result: [ { p: 3 } ]
const arr3 = [0, 1, 2];
const arr4 = [3, 2, 0];
const result1 = differenceBase(arr3, arr4);
console.log("result1:", result1); // result1: [ 3 ]const array = [false, 0, undefined, , "", NaN, 9, true, undefined, null, "test"]; const newArray = array.filter(Boolean); console.log(newArray); // [ 9, true, 'test' ]
const numArray = [1, 3, 8, 666, 22, 9982, 11, 0];
const max = Math.max.apply(Math, numArray);
const min = Math.min.apply(Math, numArray);
console.log("max:", max + ",min:" + min); // max: 9982,min:0
console.log(Math.max(...numArray)); // 9982
console.log(Math.min(...numArray)); // 0來看一個實際的例子,我們去獲取用戶對象中最大和最小的年齡:
const createValues = (creator, length = 10) => Array.from({ length }, creator);
function createUser(v, index) {
return {
name: `user-${index}`,
age: (Math.random() * 100) >> 0,
};
}
const users = createValues(createUser, 10);
const ages = users.map((u) => u.age);
const max = Math.max.apply(Math, ages);
const min = Math.min.apply(Math, ages);
console.log(ages);
console.log("max:", max + ",min:" + min);作用∶頁面傳遞參數
規律∶地址url問號(?)拼接的鍵值對
URLSearchParams:
const urlSP = new URLSearchParams(location.search);
function getQueryString(key) {
return urlSP.get(key);
}
// 獲取頁面上查詢參數 words 和 wordss 的值
console.log("words:", getQueryString("words"));
console.log("wordss:", getQueryString("wordss"));URL:
const urlObj = new URL(location.href);
function getQueryString(key) {
return urlObj.searchParams.get(key);
}
// urlObj.searchParams instanceof URLSearchParams 為 true,證明是其實例
console.log("words:", getQueryString("words"));
console.log("wordss:", getQueryString("wordss"));使用 reduce 手寫查詢:
const urlObj = location.search
.slice(1)
.split("&")
.filter(Boolean)
.reduce((obj, cur) => {
const arr = cur.split("=");
if (arr.length != 2) {
return obj;
}
obj[decodeURIComponent(arr[0])] = decodeURIComponent(arr[1]);
return obj;
}, {});
function getQueryString(key) {
return urlObj[key];
}
console.log("words:", getQueryString("words"));
console.log("wordss:", getQueryString("wordss"));優惠1:9折
優惠2:200減50
草民版:
function discount(x) {
return x * 0.9;
}
function reduce(x) {
return x > 200 ? x - 50 : x;
}
const print = console.log;
// 享受九折
print(reduce(discount(100))); // 90
// 享受九折 + 滿減
print(reduce(discount(250))); // 175黃金版:
function discount(x) {
return x * 0.9;
}
function reduce(x) {
return x > 200 ? x - 50 : x;
}
function getPriceMethod(discount, reduce) {
return function _getPrice(x) {
return reduce(discount(x));
};
}
const method = getPriceMethod(discount, reduce);
const print = console.log;
print(method(100));
print(method(250));王者版:
function compose(...funcs) {
if (funcs.length === 0) {
return (arg) => arg;
}
return funcs.reduce(
(a, b) =>
(...args) =>
a(b(...args))
);
}
function discount(x) {
console.log("discount");
return x * 0.9;
}
function reduce(x) {
console.log("reduce");
return x > 200 ? x - 50 : x;
}
function discountPlus(x) {
console.log("discountPlus");
return x * 0.95;
}
// 從后往前執行傳入的函數
const getPrice = compose(discountPlus, reduce, discount);
const print = console.log;
print(getPrice(200));
print(getPrice(250));打印結果如下圖:
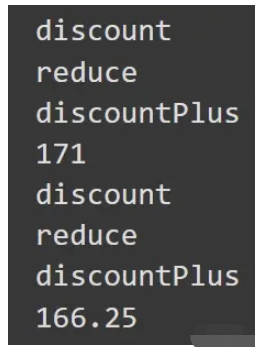
function runPromises(promiseCreators, initData) {
return promiseCreators.reduce(function (promise, next) {
return promise.then((data) => next(data));
}, Promise.resolve(initData));
}
function login(data) {
console.log("login: data", data);
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
return resolve({
token: "token",
});
}, 500);
});
}
function getUserInfo(data) {
console.log("getUserInfo: data", data);
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
return resolve({
name: "user-1",
id: 988,
});
}, 300);
});
}
function getOrders(data) {
console.log("getOrders: data", data);
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
return resolve([
{
orderId: 1,
productId: 100,
price: 100,
},
]);
}, 100);
});
}
const initData = { name: "name", pwd: "pwd" };
Promise.resolve(initData)
.then((data) => login(data))
.then((data) => getUserInfo(data))
.then((data) => getOrders(data))
.then((data) => console.log("orders", data));
// 使用 reduce 封裝的 runPromises 方法,確保返回 Promise 且執行結果是下一個函數的入參
runPromises([login, getUserInfo, getOrders], initData).then((res) => {
console.log("res", res);
});const hasOwn = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
function group(arr, fn) {
// 不是數組
if (!Array.isArray(arr)) {
return arr;
}
// 不是函數
if (typeof fn !== "function") {
throw new TypeError("fn必須是一個函數");
}
let v;
return arr.reduce((obj, cur, index) => {
v = fn(cur, index);
if (!hasOwn.call(obj, v)) {
obj[v] = [];
}
obj[v].push(cur);
return obj;
}, {});
}
// 按照長度分組
let result = group(["apple", "pear", "orange", "peach"], (v) => v.length);
console.log(result);
// 按照份數分組
result = group(
[
{
name: "tom",
score: 60,
},
{
name: "Jim",
score: 40,
},
{
name: "Nick",
score: 88,
},
],
(v) => v.score >= 60
);
console.log(result);打印結果如下:
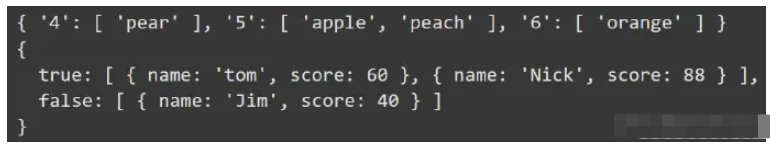
判斷是否是數組
const arr = ["1"];
console.log("isArray:", Array.isArray(arr));非基本使用:
const arr = ["1"];
const proxy = new Proxy(arr, {});
console.log("isArray:", Array.isArray(proxy)); // true為什么上面 Array.isArray 判斷代理對象是否數組返回 true 呢?
const arr = ["1"];
const proxy = new Proxy(arr, {});
const log = console.log;
log("__proto__:", proxy.__proto__ === Array.prototype); // __proto__: true
log("instanceof:", proxy instanceof Array); // instanceof: true
log("toString", Object.prototype.toString.call(Proxy)); // toString [object Function]
log("Proxy.prototype:", Proxy.prototype); // Proxy.prototype: undefined
log("proxy instanceof Proxy:", proxy instanceof Proxy); // 報錯
實際 Array.isArray 判斷的是 Proxy里面的 target 屬性

接下來我們真正手寫下 Array.isArray 的方法
Object.prototype.toString
Array.isArray = function (obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj) === "[object Array]";
};
const arr = ["1"];
const proxy = new Proxy(arr, {});
console.log(Array.isArray(arr));
console.log(Array.isArray(proxy));instanceof
Array.isArray = function (obj) {
if (typeof obj !== "object" || obj === null) {
return false;
}
return obj instanceof Array;
};
const arr = ["1"];
const proxy = new Proxy(arr, {});
console.log(Array.isArray(arr));
console.log(Array.isArray(proxy));其實還有很多方法可以判斷其數據類型,比如 constructor、isPrototypeOf等,不過我還是更推薦上面兩種
作用:返回一個新的 Array Iterator 對象,該對象包含數組中每個索引的鍵/值對
const arr = ["a", "b", "c"];
const iter = arr.entries();
console.log("iter:", iter);
// next函數訪問
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
// for of迭代
for (let [k, v] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(k, v);
}打印結果如下:
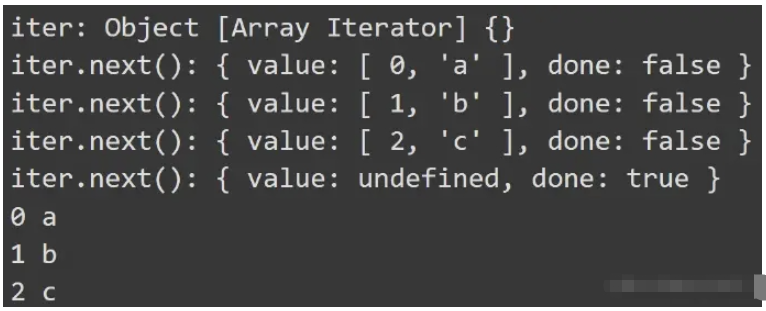
done 表示遍歷是否結束,value 返回當前遍歷的值
自己來實現下這個方法:
Array.prototype.entries = function () {
// 轉換對象(引用數據類型返回自身)
const O = Object(this);
let index = 0;
const length = O.length;
return {
next() {
if (index < length) {
return { value: [index, O[index++]], done: false };
}
return { value: undefined, done: true };
},
};
};
const arr = ["a", "b", "c"];
const iter = arr.entries();
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
console.log("iter.next():", iter.next());
// 不能正常執行,因為如果要能 for...of 遍歷需要去實現 Symbol.iterator
for (let [k, v] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(`k:${k}`, `v:${v}`);
}下面添加 Symbol.iterator 方法返回 next 即可for...of
Array.prototype.entries = function () {
const O = Object(this);
let index = 0;
const length = O.length;
function next() {
if (index < length) {
return { value: [index, O[index++]], done: false };
}
return { value: undefined, done: true };
}
return {
next,
[Symbol.iterator]() {
return {
next,
};
},
};
};數組還有 Array.prototype.keys,Array.prototype.keys,如果我們像上面這樣寫等于每個方法里面都要實現[Symbol.iterator],我們可以抽離其邏輯,代碼如下:
Array.prototype[Symbol.iterator] = function () {
const O = Object(this);
let index = 0;
const length = O.length;
function next() {
if (index < length) {
return { value: O[index++], done: false };
}
return { value: undefined, done: true };
}
return {
next,
};
};
Array.prototype.entries = function () {
const O = Object(this);
const length = O.length;
let entries = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
entries.push([i, O[i]]);
}
const itr = this[Symbol.iterator].bind(entries)();
return {
next: itr.next,
[Symbol.iterator]() {
return itr;
},
};
};
Array.prototype.keys = function () {
const O = Object(this);
const length = O.length;
let keys = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
keys.push([i]);
}
const itr = this[Symbol.iterator].bind(keys)();
return {
next: itr.next,
[Symbol.iterator]() {
return itr;
},
};
};
Array.prototype.values = function () {
const O = Object(this);
const length = O.length;
let keys = [];
for (let i = 0; i < length; i++) {
keys.push([O[i]]);
}
const itr = this[Symbol.iterator].bind(keys)();
return {
next: itr.next,
[Symbol.iterator]() {
return itr;
},
};
};
const arr = ["a", "b", "c"];
var iter = arr.entries();
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
for (let [k, v] of arr.entries()) {
console.log(`k:${k}`, `v:${v}`);
}
var iter = arr.keys();
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
for (let k of arr.keys()) {
console.log(`k:${k}`);
}
var iter = arr.values();
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
console.log("iter.next().value:", iter.next().value);
for (let k of arr.values()) {
console.log(`k:${k}`);
}判斷數組是否含有某值,可判斷NaN
const arr = [1, 2, 3, { a: 1 }, null, undefined, NaN, ""];
console.log("includes null:", arr.includes(null)); // includes null: true
console.log("indexOf null:", arr.indexOf(null)); // indexOf null: 4
console.log("includes NaN:", arr.includes(NaN)); // includes NaN: true
console.log("indexOf NaN:", arr.indexOf(NaN)); // indexOf NaN: -1手寫該方法
Number.isNaN = function (param) {
if (typeof param === "number") {
return isNaN(param);
}
return false;
};
Array.prototype.includes = function (item, fromIndex) {
// call, apply調用,嚴格模式
if (this == null) {
throw new TypeError("無效的this");
}
let O = Object(this);
let len = O.length >> 0;
if (len <= 0) {
return false;
}
const isNAN = Number.isNaN(item);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (O[i] === item) {
return true;
} else if (isNAN && Number.isNaN(O[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const obj = { a: 3 };
const arr = [1, 2, 3, { a: 1 }, null, undefined, NaN, "", 0, obj, obj];
console.log("includes null:", arr.includes(null));
console.log("includes NaN:", arr.includes(NaN));其實 includes 還有第二個參數,表示從哪個下標開始檢查,我們也來寫寫該方法
注意參數的情況
轉為整數:TolntegerOrlnfinity
+lnfinity , -Infinity
可能為負數
Number.isNaN = function (params) {
if (typeof params === "number") {
return isNaN(params);
}
return false;
};
// 轉換整數
function ToIntegerOrInfinity(argument) {
const num = Number(argument);
// NaN 和 +0、-0
if (Number.isNaN(num) || num == 0) {
return 0;
}
if (num === Infinity || num == -Infinity) {
return num;
}
let inter = Math.floor(Math.abs(num));
if (num < 0) {
inter = -inter;
}
return inter;
}
Array.prototype.includes = function (item, fromIndex) {
// 嚴格模式
if (this == null) {
throw new TypeError("無效的this");
}
const O = Object(this);
const len = O.length >> 0;
if (len <= 0) {
return false;
}
let n = ToIntegerOrInfinity(fromIndex);
if (fromIndex === undefined) {
n = 0;
}
if (n === +Infinity) {
return false;
}
// 負無窮轉換為0
if (n === -Infinity) {
n = 0;
}
let k = n >= 0 ? n : len + n;
if (k < 0) {
k = 0;
}
const isNAN = Number.isNaN(item);
for (let i = k; i < len; i++) {
if (O[i] === item) {
return true;
} else if (isNAN && Number.isNaN(O[i])) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
};
const arr = ["a", "b", "c"];
console.log("arr include -100->0:", arr.includes("c", -100)); // true
console.log("arr include -100->0:", arr.includes("a", -1)); // false
console.log("arr include 1:", arr.includes("a", -Infinity)); // true
console.log("arr include 1:", arr.includes("a", Infinity)); // false有三個參數
arrayLike:類數組對象或者可遍歷對象(Map、Set)等
mapFn:可選參數,在最后生成數組后執行一次map方法后返回
thisArg:可選參數,實際是Array.from(obj).map(mapFn, thisArg)
特殊值處理
console.log("Array.from1:", Array.from({}));
console.log("Array.from2:", Array.from(""));
console.log("Array.from3:", Array.from({ a: 1, length: "10" }));
console.log("Array.from4:", Array.from({ a: 1, length: "ss" }));
console.log("Array.from5:", Array.from([NaN, null, undefined, 0]));
// 長度極限問題
// const max = Math.pow(2, 32);
// console.log("Array.from:", Array.from({ 0: 1, 1: 2, length: max - 1 })); // 極限
// console.log("Array.from:", Array.from({ 0: 1, 1: 2, length: max })); // 失敗執行結果如下:
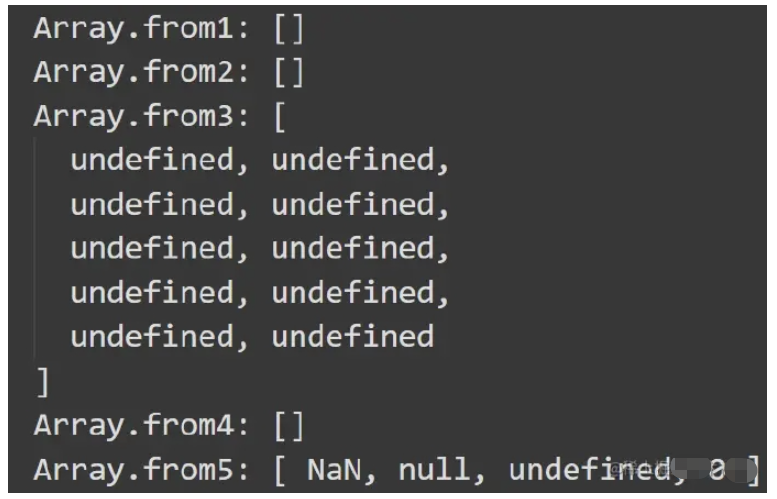
自己實現一個:
//類數組的特征
let maxSafeInteger = Math.pow(2, 32) - 1;
let ToIntegerOrInfinity = function (value) {
let number = Number(value);
if (isNaN(number)) {
return 0;
}
if (number === 0 || !isFinite(number)) {
return number;
}
return (number > 0 ? 1 : -1) * Math.floor(Math.abs(number));
};
let ToLength = function (value) {
let len = ToIntegerOrInfinity(value);
return Math.min(Math.max(len, 0), maxSafeInteger);
};
let isCallable = function (fn) {
return typeof fn === "function" || toStr.call(fn) === "[object Function]";
};
Array.from = function (arrayLike, mapFn, thisArg) {
let C = this;
//判斷對象是否為空
if (arrayLike == null) {
throw new TypeError("Array.from requires an array-like object - not null or undefined");
}
//檢查mapFn是否是方法
if (typeof mapFn !== "function" && typeof mapFn !== "undefined") {
throw new TypeError(mapFn + "is not a function");
}
let items = Object(arrayLike);
//判斷 length 為數字,并且在有效范圍內。
let len = ToLength(items.length);
if (len <= 0) return [];
let A = isCallable(C) ? Object(new C(len)) : new Array(len);
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let value = items[i];
if (mapFn) {
A[i] = typeof thisArg === "undefined" ? mapFn(value, i) : mapFn.call(thisArg, value, i);
} else {
A[i] = value;
}
}
return A;
};
console.log("Array.from1:", Array.from({ a: 1, length: "10" }));
console.log("Array.from2:", Array.from({ a: 1, length: "ss" }));
console.log(
"Array.from3:",
Array.from({ 0: 1, 1: 2, 4: 5, length: 4 }, (x) => x + x)
);
function MyArray(length) {
const len = length * 2;
return new Array(len);
}
function MyObject(length) {
return {
length,
};
}
console.log("Array.from:MyArray", Array.from.call(MyArray, { length: 5 }));
console.log("Array.from:MyObject", Array.from.call(MyObject, { length: 5 }));打印結果如下:

Array.prototype.flat
指定的深度遞歸遍歷數組,并將所有元素與遍歷到的子數組中的元素合并為一個新數組返回
const array = [1, 3, 4, [4, 5], [6, [7, 8]], [, ,], [undefined, null, NaN]];
console.log("flat 1:", array.flat(1));
console.log("flat 2:", array.flat(2));執行結果如下:

reduce + 遞歸
const array = [1, [1, , ,]];
const flat = (arr) => {
return arr.reduce((pre, cur) => {
return pre.concat(Array.isArray(cur) ? flat(cur) : cur);
}, []);
};
console.log(flat(array)); // [ 1, 1 ]上面的實現存在幾個弊端:
無法指定躺平深度
性能差的一批(遞歸 + concat)
丟數據(空值reduce無法遍歷)
正規軍入場:
let has = Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty;
let maxSafeInteger = Math.pow(2, 32) - 1;
let toInteger = function (value) {
const number = Number(value);
if (isNaN(number)) {
return 0;
}
if (number === 0 || !isFinite(number)) {
return number;
}
return (number > 0 ? 1 : -1) * Math.floor(Math.abs(number));
};
let toLength = function (value) {
let len = toInteger(value);
return Math.min(Math.max(len, 0), maxSafeInteger);
};
let push = Array.prototype.push;
Array.prototype.flat = function (deep) {
let O = Object(this);
let sourceLen = toLength(O.length);
let depthNum = 1;
if (deep !== undefined) {
depthNum = toLength(deep);
}
if (depthNum <= 0) {
return O;
}
let arr = [];
let val;
for (let i = 0; i < sourceLen; i++) {
if (has.call(O, i)) {
val = O[i];
if (Array.isArray(val)) {
push.apply(arr, val.flat(depthNum - 1));
} else {
arr.push(val);
}
} else {
arr.push(undefined);
}
}
return arr;
};
let array = [1, 3, [4, 5], [6, [7, 8, [9, , 10]]], [, ,], [undefined, null, NaN]];
console.log(array.flat(2));打印結果如下:
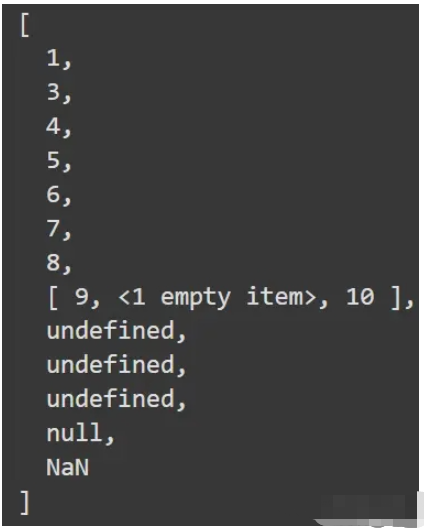
準備好兩條數據,對 uid 相同的數據進行合并
export const usersInfo = Array.from({ length: 200 }, (val, index) => {
return {
uid: `${index + 1}`,
name: `user-name-${index}`,
age: index + 10,
avatar: `http://www.my-avatar.com/${index + 1}`,
};
});
export const scoresInfo = Array.from({ length: 10 }, (val, index) => {
return {
uid: `${index + 1}`,
score: ~~(Math.random() * 10000),
comments: ~~(Math.random() * 10000),
stars: ~~(Math.random() * 1000),
};
});兩層for循環,通過key關聯
import * as data from "./data.js";
const { usersInfo, scoresInfo } = data;
console.time("merge data");
for (let i = 0; i < usersInfo.length; i++) {
let user: any = usersInfo[i];
for (let j = 0; j < scoresInfo.length; j++) {
let score = scoresInfo[j];
if (user.uid == score.uid) {
user.score = score.score;
user.comments = score.comments;
user.stars = score.stars;
}
}
}
console.timeEnd("merge data");
console.log(usersInfo);數組轉換為map對象。數組查找變為屬性查找
import * as data from "./data.js";
const { usersInfo, scoresInfo } = data;
console.time("merge data");
const scoreMap = scoresInfo.reduce((obj, cur) => {
obj[cur.uid] = cur;
return obj;
}, Object.create(null));
for (let i = 0; i < usersInfo.length; i++) {
const user: any = usersInfo[i];
const score = scoreMap[user.uid];
if (score != null) {
user.score = score.score;
user.comments = score.comments;
user.stars = score.stars;
}
}
console.timeEnd("merge data");
console.log(usersInfo);import * as data from "./data.js";
const { usersInfo, scoresInfo } = data;
console.time("merge data");
const scoreMap = scoresInfo.reduce((obj, cur) => {
obj[cur.uid] = cur;
return obj;
}, Object.create(null));
// 被合并數據的條數
const len = scoresInfo.length;
// 已合并的條數
let count = 0;
// 已遍歷的次數
let walkCount = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < usersInfo.length; i++) {
const user: any = usersInfo[i];
const score = scoreMap[user.uid];
walkCount++;
if (score != null) {
count++;
user.score = score.score;
user.comments = score.comments;
user.stars = score.stars;
if (count >= len) {
break;
}
}
}
console.timeEnd("merge data");
console.log(`合并完畢:遍歷次數${walkCount}, 實際命中次數${count}, 預期命中次數${len}`);
console.log(usersInfo);數據合并-基礎 hash 跳出-倒敘版
在跳出版的基礎上,一個是從前向后,一個是從后往前
適應場景∶分頁拉取數據,新數組添加在最后,倒敘更快
import * as data from "./data.js";
const { usersInfo, scoresInfo } = data;
console.time("merge data");
const scoreMap = scoresInfo.reduce((obj, cur) => {
obj[cur.uid] = cur;
return obj;
}, Object.create(null));
const len = scoresInfo.length;
let count = 0;
let walkCount = 0;
for (let i = usersInfo.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
const user: any = usersInfo[i];
const score = scoreMap[user.uid];
walkCount++;
if (score != null) {
count++;
user.score = score.score;
user.comments = score.comments;
user.stars = score.stars;
if (count >= len) {
break;
}
}
}
console.timeEnd("merge data");
console.log(`合并完畢:遍歷次數${walkCount}, 實際命中次數${count}, 預期命中次數${len}`);
console.log(usersInfo);以上就是“前端進階JS數組高級使用方法實例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家閱讀完這篇文章都有很大的收獲,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識,如果還想學習更多的知識,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。