溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“C++如何實現通訊錄功能”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在C++如何實現通訊錄功能問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”C++如何實現通訊錄功能”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
簡介:通訊錄由一個擁有者以及通訊信息組成。
基本功能:增刪改查
擁有者和通訊信息的基礎結構相同,由struct構成
struct Person {
int m_id;
string m_name;
string m_tele;//手機號碼可以作為id,但是過于長(11位)
//string m_addr;
Person& operator = (const Person& r) {
if (this == &r) return *this;
m_id = r.m_id;
m_name = r.m_name;
m_tele = r.m_tele;
return *this;
}
};Person:id+姓名+手機號。還可以添加需要的信息,例如:地址、性別
重載了一個=操作符
通訊錄建立class AddressList
class AddressList {
private:
Person owner;//通訊錄擁有者
vector<Person> information;//通訊錄:好友的信息組成
public:
AddressList();
AddressList(const Person&, const vector<Person>& info = {});
AddressList(const AddressList&);
void Add(const Person&);//添加一個好友信息至通訊錄
void Delete();//通過姓名刪除
//通過電話號碼刪除
void Modify();//輸入id 修改姓名and號碼
void Search(int);//1:id搜索
//2:姓名搜索
//3:號碼指定搜索
void Print()const;
//查看通訊錄所有信息:僅顯示id和姓名,詳細信息輸入id查看
};cpp:
#include "AddressList.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
AddressList::AddressList() {}
AddressList::AddressList(const Person& r, const vector<Person>& info) {
owner = r;
for (const auto& i : info) {
information.push_back(i);
}
}
AddressList::AddressList(const AddressList& r) {
owner = r.owner;
for (const auto& i : r.information) {
information.push_back(i);
}
}
void AddressList::Add(const Person& p) {
//添加一個好友信息至通訊錄
//首先確認不存在:id+tele
for (const auto& it : information) {
if (p.m_id == it.m_id) {
cout << "Id已存在,添加失敗!\n";
return;
}
else if (p.m_tele == it.m_tele) {
cout << "Telephone已存在,添加失敗!\n";
return;
}
}
information.push_back(p);
}
void AddressList::Delete() {
//通過姓名刪除
//略:通過電話號碼刪除
string name;
cout << "姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "查找到信息如下:";
auto it = information.begin();
vector<int> info;//存儲下標
for (int i(0); it != information.end(); ++it,++i) {
if (it->m_name == name) info.push_back(i);
}
if (info.size() == 0) {
cout << "No such name.\n";
return;
}
for (const auto& i : info) {
cout << i << ":\t" << information[i].m_id << '\t' << information[i].m_name
<< '\t' << information[i].m_tele << endl;
}
int ind;
cout << "輸入下標(第一列)刪除信息:";
cin>>ind;
for (const auto& i : info) {
if (i == ind) {
information.erase(information.begin() + i);
return;
}
}
cout << "輸入信息錯誤,刪除失敗!\n";
}
void AddressList::Modify() {
//輸入id:修改姓名and號碼
long id;
cout << "Id:"; cin >> id;
cout << "查找到信息如下:\n";
auto it = information.begin();
for (; it != information.end(); ++it) {
if (it->m_id == id) {
cout << it->m_id << '\t' << it->m_name << '\t' << it->m_tele << endl;
break;
}
}
if (it == information.end()) {
cout << "No such Id.\n";
return;
}
cout << "修改信息:\n";
string name;
string tele;
cout << "新的姓名:"; cin >> name;
cout << "新的號碼:"; cin >> tele;
char c;
cout << "確認?<y/n> ";
cin >> c;
if (c == 'y' || c == 'Y') {
it->m_name = name;
it->m_tele = tele;
return;
}
cout << "取消修改!\n";
return;
}
void AddressList::Search(int cho) {
//1:id搜索
//2:姓名搜索
//3:號碼指定搜索
int id;
string name;
string tele;
auto it = information.begin();
switch (cho) {
case 1:
cout << "Id:";
cin >> id;
cout << "搜索到的信息如下:\n";
for (it = information.begin(); it != information.end(); ++it) {
if (it->m_id == id) {
cout << it->m_id << '\t' << it->m_name << '\t' << it->m_tele << endl;
break;
}
}
break;
case 2:
cout << "Name:";
cin >> name;
cout << "搜索到的信息如下:\n";
for (it = information.begin(); it != information.end(); ++it) {
if (it->m_name == name)
cout << it->m_id << '\t' << it->m_name << '\t' << it->m_tele << endl;
}
break;
case 3:
cout << "Tele:";
cin >> tele;
cout << "搜索到的信息如下:\n";
for (it = information.begin(); it != information.end(); ++it) {
if (it->m_tele == tele) {
cout << it->m_id << '\t' << it->m_name << '\t' << it->m_tele << endl;
break;
}
}
break;
default:break;
}
}
void AddressList::Print()const {
cout << "ID:" << owner.m_id << endl;
cout << "Owner:" << owner.m_name << endl
<< "Tele:" << owner.m_tele << endl;
int n(information.size());
cout << "通訊錄人數:" << n << endl;
for (int i(0); i < n; ++i) {
cout << information[i].m_id << '\t' << information[i].m_name << endl;
}
while (1) {
cout << endl
<< "詳細信息,請輸入id:-1終止查看\n";
int id;
cin >> id;
if (id == -1) break;
bool b(false);
for (const auto& it : information) {
if (id == it.m_id) {
b = true;
cout << it.m_id << '\t' << it.m_name << '\t' << it.m_tele << endl;
break;
}
}
if (!b) {
cout << "No such Id.!" << endl;
}
}
}main.cpp:測試
#include"AddressList.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
Person p;
{
p.m_id = 0;
p.m_name = "一號";
p.m_tele = "11012011900";//任意
}
int I = 1;//m_id編號
AddressList addr(p);
{
cout << "0.退出\n"
<< "1.添加\n"
<< "2.刪除\n"
<< "3.修改\n"
<< "4.搜索\n"
<< "5.查看\n"
<< endl
<< endl;
}
int cho2;
bool b(true);
while (b) {
int cho;
int id;
string name;
string tele;
cout << "Your choose:";
cin >> cho;
switch (cho) {
case 0:
b = false;
break;
case 1:
cout << "添加信息:\n"
<< "姓名:";
cin >> name;
cout << "號碼:";
cin >> tele;
id = I++;
{
p.m_id = id;
p.m_name = name;
p.m_tele = tele;
}
addr.Add(p);
break;
case 2:
cout << "刪除信息:\n";
addr.Delete();
break;
case 3:
cout << "修改信息:\n";
addr.Modify();
break;
case 4:
cout << "搜索信息\n"
<< "1.Id\n"
<< "2.Name\n"
<< "3.Telephone\n";
cout << "Chosse:";
cin >> cho2;
addr.Search(cho2);
break;
case 5:
cout << "查看信息\n";
addr.Print();
break;
default:break;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}截圖:
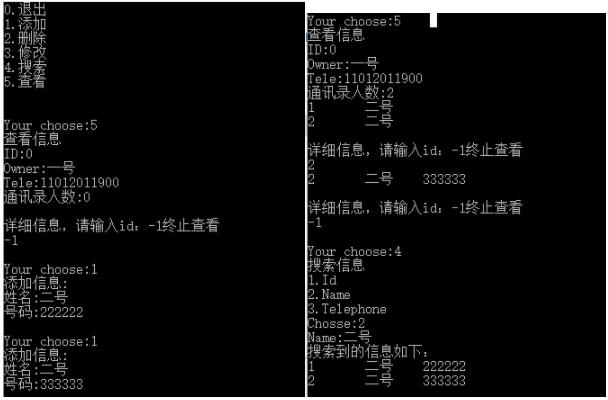
到此,關于“C++如何實現通訊錄功能”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。