您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Java8并發新特性CompletableFuture怎么使用”的相關知識,小編通過實際案例向大家展示操作過程,操作方法簡單快捷,實用性強,希望這篇“Java8并發新特性CompletableFuture怎么使用”文章能幫助大家解決問題。
各位小伙伴是否有一種感覺,整天大量時間沉迷于業務開發的同時,缺少對于一些技術更新的關注,忽略掉了很多實用又簡單的方法,以往我們做異步任務的時候都習慣于使用Callable或者Runnable接口去實現,今天我們就來聊聊與之不同的CompletableFuture類。
CompletableFuture針對Future接口做了改進,相比Callable/Runnable接口它支持多任務進行鏈式調用、組合、多任務并發處理。很多時候我們在設計過程中會想在一個異步任務執行完成后,直接獲取它的結果傳遞給下一個任務繼續執行后續的流程,這時候CompletableFuture的作用就來了。
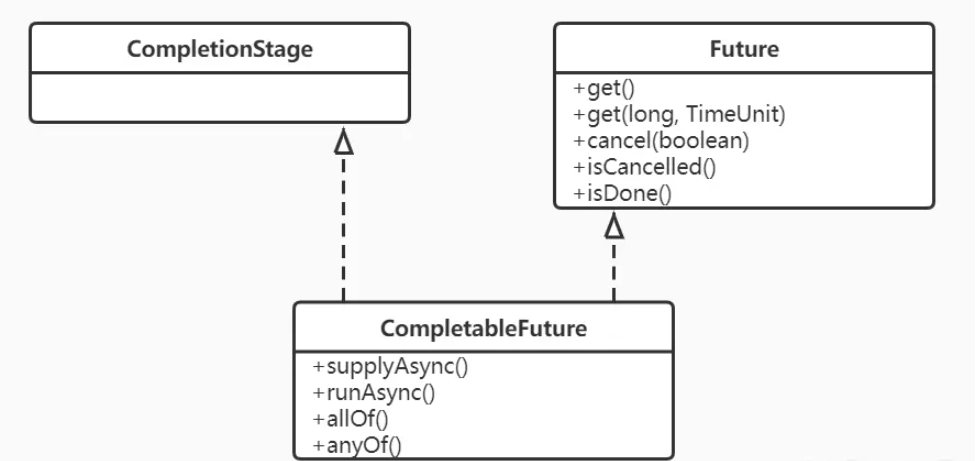
CompletableFuture類關系圖:
從以下類圖可以看到,CompletableFuture實現了Future和CompletionStage兩個接口,Future提供了獲取任務執行結果和任務執行狀態的功能。 CompletionStage表示一個任務的執行階段,提供了諸多方法支持了多任務的聚合功能。
supplyAsync與runAsync主要用于構建異步事件。
supplyAsync:帶有返回值的異步任務,支持在默認線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool()中完成異步任務,也可以使用自定義線程池執行異步任務,結果返回一個新的CompletableFuture,返回結果類型U。最終的任務執行結果可通過返回CompletableFuture對象的 get()/join() 方法獲取返回值。
// 使用默認線程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {...}
// 使用自定義線程池Executor
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor) {...}
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> supplyAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing supplyAsync task ...");
return "this is supplyAsync";
});
// 進入阻塞獲取異步任務結果
log.info(supplyAsyncFuture.get()); // 輸出結果:this is supplyAsyncrunAsync:不帶返回值的異步任務,支持在默認線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool()中完成異步任務,也可以使用自定義線程池執行異步任務,結果返回一個新的CompletableFuture,返回結果類型為Void,也就是無返回值。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {...}
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor) {...}
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<Void> runAsyncFuture = CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing runAsync task ...");
});
runAsyncFuture.get();allOf:多個CompletableFuture任務并發執行,所有CompletableFuture任務完成時,返回一個新的CompletableFuture對象,其返回值為Void,也就是無返回值。
public static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {...}
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
// allOf,可傳遞返回值不同類型的future,最終結果按自己設計預期處理即可
CompletableFuture<String> cf11 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing supplyAsync task cf11 ...");
return "this is supplyAsync";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf12 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing supplyAsync task cf12 ...");
return "this is supplyAsync";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> allOfFuture = CompletableFuture.allOf(cf11, cf12);
allOfFuture.get();anyOf:多個CompletableFuture任務并發執行,只要有一個CompletableFuture任務完成時,就會返回一個新的CompletableFuture對象,并返回該CompletableFuture執行完成任務的返回值。
public static CompletableFuture<Object> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs) {...}
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf21 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing supplyAsync task cf21 ...");
return "this is supplyAsync cf21";
});
CompletableFuture<String> cf22 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
log.info("executing supplyAsync task cf22 ...");
return "this is supplyAsync cf22";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> anyOfFuture = CompletableFuture.anyOf(cf21, cf22);
log.info("{}", anyOfFuture.get()); // 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync cf21或cf22join()和get()方法都是CompletableFuture對象基于阻塞的方式來獲取異步任務執行結果。
get方法會拋出顯示異常必須捕獲處理,任務允許被中斷拋出InterruptedException異常,通過帶有超時時間的阻塞方式獲取異步任務執行結果,超時等待無結果則中斷任務拋出TimeoutException異常。
join方法會拋出未檢查異常,與get()方法不同的是join()方法不允許被中斷。
// 可中斷,可設置超時時間
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {...}
public T get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException,
ExecutionException, TimeoutException {...}
/**
* 不可中斷
*/
public T join() {...}CompletionStage表示一個任務的執行階段,每個任務都會返回一個CompletionStage對象,可以對多個CompletionStage對象進行串行、并行或者聚合的方式來進行下階段的操作,也就是說實現異步任務的回調功能。CompletionStage總共提供了38個方法來實現多個CompletionStage任務的各種操作, 接下來我們就針對這些方法分類來了解一下。
以下類型均有三種使用方式:
thenAccept:方法名不帶Async的使用主線程同步執行回調函數,不做異步處理
thenAcceptAsync:方法名帶Async,但是無executor參數的,使用默認線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool異步執行任務
thenAcceptAsync:方法名帶Async,有executor參數的,使用自定義線程池異步執行任務
依賴單個任務完成(thenAccept):由上一個CompletionStage任務執行完成的結果傳遞到action進行回調處理,即僅僅消費了上一個CompletionStage任務的返回值,回調處理結果無返回值。
// 不使用線程池,僅依賴當前線程執行,不做異步
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action);
// 使用默認線程池ForkJoinPool.commonPool執行任務
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action);
// 使用自定義線程池執行任務
public CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync")
.thenAcceptAsync((result) -> {
log.info("{} thenAcceptAsync", result);
}).join();
// 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync thenAcceptAsync依賴兩個任務都完成(thenAcceptBoth):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,必須都完成了才執行action回調處理,即僅僅消費了兩個CompletionStage任務的返回值,回調處理結果無返回值。
/**
* 額外多了CompletionStage參數表示CompletionStage任務依賴的另一個CompletionStage任務
* action接收兩個參數,分別表示兩個CompletionStage任務的返回值
*/
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
// 原理同上,使用默認線程池執行異步任務
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action);
// 原理同上,使用自定義線程池執行異步任務
public <U> CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiConsumer<? super T, ? super U> action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf311 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf311");
CompletableFuture<String> cf312 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf312");
cf311.thenAcceptBothAsync(cf312, (r1, r2) -> {
log.info("{} and {}", r1, r2);
}).join();
// 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync cf311 and this is supplyAsync cf312依賴兩個任務中的任何一個完成(acceptEither):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,只要其中一個先完成了就攜帶返回值執行action回調處理,即僅僅消費了優先完成的CompletionStage任務的返回值,回調處理結果無返回值。
/**
* 類似thenAcceptBothAsync,只不過acceptEither只需兩個任務中的其中一個完成即可回調action
* action中的值為兩個任務中先執行完任務的返回值
*/
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Consumer<? super T> action);
public CompletionStage<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Consumer<? super T> action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf311 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf311");
CompletableFuture<String> cf312 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf312");
cf311.acceptEitherAsync(cf312, (r) -> {
log.info(r); // 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync cf311或cf312
}).join();依賴單個任務完成(thenApply):由上一個CompletionStage任務執行完成的結果傳遞到action進行回調處理,即不止消費了上一個CompletaionStage任務的返回值,同時回調處理結果也有返回值
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApply(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn); public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T,? extends U> fn, Executor executor); // ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================ CompletableFuture<String> cf32 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync") .thenApplyAsync(result -> result + " and thenApplyAsync"); log.info(cf32.join()); // 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync and thenApplyAsync
依賴兩個任務都完成(thenCombine):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,必須都完成了才執行action回調處理,即不止消費了兩個CompletaionStage任務的返回值,同時回調處理結果也有返回值。
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn);
public <U,V> CompletionStage<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<? extends U> other,
BiFunction<? super T,? super U,? extends V> fn, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf321 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf321");
CompletableFuture<String> cf322 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf322");
CompletableFuture<String> thenCombineFuture = cf321.thenCombineAsync(cf322, (r1, r2) -> {
return r1 + " and " + r2;
});
log.info(thenCombineFuture.join());
// 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync cf321 and this is supplyAsync cf322依賴兩個任務中的任何一個完成(applyToEither):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,只要其中一個任務執行完成就會action回調處理,即不止消費了優先完成的CompletionStage的返回值,同時回調處理結果也有返回值。
// 原理同3.1的acceptEither,只不過applyToEither任務執行完成會返回一個帶有返回值的CompletionStage
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEither(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Function<? super T, U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<? extends T> other,
Function<? super T, U> fn, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf321 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf321");
CompletableFuture<String> cf322 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf322");
CompletableFuture<String> thenCombineFuture = cf321.applyToEitherAsync(cf322, (r) -> {
return r;
});
log.info(thenCombineFuture.join());
// 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync cf321或cf322依賴單個任務完成(thenRun):單個CompletionStage任務執行完成回調action處理,即執行action回調方法無參數,回調處理結果也無返回值。
// 上一個CompletionStage任務執行完成后直接回調action處理,無返回值
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(Runnable action);
// 同上,使用默認線程池執行action處理
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action);
// 同上,使用自定義線程池執行action處理
public CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
// TODO
}).thenRunAsync(() -> {
log.info("this is thenRunAsync"); // 輸出結果:this is thenRunAsync
}).join();依賴兩個任務都完成(runAfterBoth):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,必須兩個任務都完成才執行action回調處理,即執行action回調方法無參數,回調處理結果也無返回值。
// 原理同3.1的thenAcceptBoth,只不過runAfterBoth的action回調處理不接收參數且任務執行完成無返回值
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
// 同上,使用默認線程池執行action處理
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
// 同上,使用自定義線程池執行action處理
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf331 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf331");
CompletableFuture<String> cf332 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf332");
cf331.runAfterBoth(cf332, () -> {
log.info("this is runAfterBoth");
}).join();
// 輸出結果:this is runAfterBoth依賴兩個任務中的任何一個完成(runAfterEither):兩個CompletionStage任務并發執行,只需其中任何一個任務完成即可回調action處理,即執行action回調方法無參數,回調處理結果也無返回值。
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action);
public CompletionStage<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<?> other, Runnable action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> cf331 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf331");
CompletableFuture<String> cf332 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "this is supplyAsync cf332");
cf331.runAfterEitherAsync(cf332, () -> {
log.info("this is runAfterEitherAsync");
}).join();
// 輸出結果:this is runAfterEitherAsyncthenCompose:存在先后關系的兩個任務進行串行組合,由第一個CompletionStage任務執行結果作為參數傳遞給第二個CompletionStage任務,最終返回第二個CompletionStage。
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> supplyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "this is supplyAsync";
});
CompletableFuture<String> thenComposeFuture = supplyFuture.thenComposeAsync((r) -> {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return r + " and this is thenComposeAsync";
});
});
log.info(thenComposeFuture.join());
// 輸出結果:this is supplyAsync and this is thenComposeAsyncCompletionStage接口也支持類似我們常用的try-catch-finally中的finally的作用,無論這個任務的執行結果是正常還是出現異常的情況,都必須要去執行的一個代碼塊。在CompletionStage接口提供了以下兩種接口回調的形式(whenComplete、handle),并支持主線程同步執行同時也支持使用默認線程池,或者使用自定義線程池去異步執行最終的回調處理。例如我們一個事務操作,無論這段代碼執行是否成功,我們都必須要去關閉事務。
任務完成事件(whenComplete):結果無返回值,若出現異常執行完whenComplete回調處理完成后將中斷主線程的運行。
// 1.whenComplete回調函數中Throwable對象不對空代表出現異常,為空則表示無異常
public CompletionStage<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action);
public CompletionStage<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> action, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> whenCompleteFufute = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 100 / a;
return "this is supplyAsync normal";
}).whenCompleteAsync((r, th) -> {
if (th != null) {
log.error("this is whenCompleteAsync error");
}
else {
log.info("this is whenCompleteAsync success");
}
});
log.info(whenCompleteFufute.join()); // 輸出結果:this is whenCompleteAsync error任務完成回調事件(handle):結果有返回值,若出現異常執行完handle回調處理完成后將繼續執行主線程的后續操作,不中斷主線程運行。
// 2.handle回調函數中Throwable對象不對空代表出現異常,為空則表示無異常
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handle(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn);
public <U> CompletionStage<U> handleAsync(BiFunction<? super T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn, Executor executor);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> whenCompleteFufute = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 100 / a;
return "this is supplyAsync normal";
}).handleAsync((r, th) -> {
if (th != null) {
return "this is handleAsync error";
}
else {
return "this is handleAsync success";
}
});
log.info(whenCompleteFufute.join());
// 輸出結果:this is handleAsync error
log.info("main thread is running");
// 輸出結果:main thread is runningexceptionally:只要是個程序,就會有異常出現的情況,例如一個CompletionStage任務,如果執行過程中出現異常,我們為了保證異常情況下程序能夠正常處理業務邏輯,那么在這里我們就可以使用exceptionally進行異常回調處理。當CompletionStage任務出現異常時就會觸發回調exceptionally,否則CompletionStage任務正常執行業務不進行異常回調處理。
public CompletionStage<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn);
// ====================================demo華麗分割線============================================
CompletableFuture<String> exceptionallyFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
int a = 0;
int b = 10 / a; // 除數為0將拋異常
return "this is supplyAsync normal";
}).exceptionally(th -> {
log.error("exception:{}", th.getMessage());
return "this is exceptionally";
});
log.info(exceptionallyFuture.join()); // 輸出結果:this is exceptionally注:以下這兩種情況可能大家在實際開發過程中會比較少見,但還是得在這里做個提醒,以免到最后準備不充分出現設計上的缺陷。
當whenCompleteAsync與exceptionally同時使用時,若出現異常情況,由于exceptionally有返回值,所以優先執行whenCompleteAsync,后執行exceptionally。
當handleAsync與exceptionally同時出現時,由于handleAsync已經包含了exceptionally的所有操作,即handleAsync回調有返回值,且有Throwable異常對象能夠進行異常處理,所以這兩者同時出現時exceptionally將失效。
關于“Java8并發新特性CompletableFuture怎么使用”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道,小編每天都會為大家更新不同的知識點。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。