您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“elasticsearch源碼index action實現方式是什么”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“elasticsearch源碼index action實現方式是什么”吧!
上一篇從結構上分析了action的,本篇將以index action為例仔分析一下action的實現方式。
再概括一下action的作用:對于每種功能(如index)action都會包括兩個基本的類*action(IndexAction)和Transport*action(TransportIndexAction),前者類中會有一個實例(IndexAction INSTANCE = new IndexAction())這個實例用于client綁定對應的TransportAction(registerAction(IndexAction.INSTANCE, TransportIndexAction.class)),綁定過程發送在ActionModuel中。
另外在Action類中還會定義一個action的名字(String NAME = "indices:data/write/index")這個名字用于TransportService綁定對于的handle,用于處理NettyTransport接收到的信息。TransportAction的是最終的邏輯處理者,當接收到請求時,會首先判斷本節點能否處理,如果能夠處理則調用相關的方法處理得到結果返回,否則將通過NettyTransport轉發該請求到對應的node進行處理。所有的Transport的結構都是這種類型。
首先看一下TransportAction的類圖,所的Transport*action都繼承自于它。
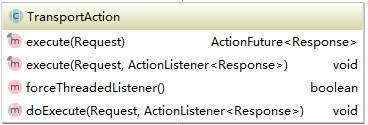
它主要由兩個方法execute和doExecute,execute方法有兩種實現,第一種實現需要自行添加actionListener。最終的邏輯都在doExecute方法中,這個方法在各個功能模塊中實現。以下是TransportIndexAction的繼承關系:
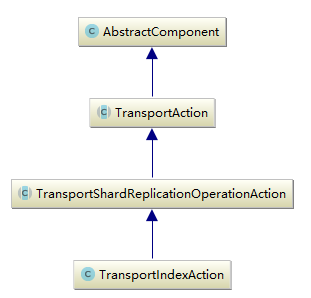
實現上由于功能劃分的原因,TransportIndexAction直接繼承自TranspShardReplicationOperationAction,這個抽象類中的方法是所有需要操作shard副本的功能action的父,因此它的實現還包括delete,bulk等功能action。它實現了多個內部類,這些內部類用來輔助完成相關的功能。這里主要說一下OperationTransportHandler,ReplicaOperationTransportHandler及AsyncShardOperationAction三個子類。
如下所示:
class OperationTransportHandler extends BaseTransportRequestHandler<Request> {
//繼承自BaseTransportRequestHanlder
………………
@Override
public void messageReceived(final Request request, final TransportChannel channel) throws Exception {
// no need to have a threaded listener since we just send back a response
request.listenerThreaded(false);
// if we have a local operation, execute it on a thread since we don't spawn
request.operationThreaded(true);
//調用Transport的execute方法,通過channel返回結果
execute(request, new ActionListener<Response>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Response result) {
try {
channel.sendResponse(result);
} catch (Throwable e) {
onFailure(e);
}
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable e) {
try {
channel.sendResponse(e);
} catch (Throwable e1) {
logger.warn("Failed to send response for " + actionName, e1);
}
}
});
}看過NettyTransport請求發送和處理的同學一定對這個代碼不陌生,這就是elasticsearch節點間處理信息的典型模式。當請求通過NettyTransport發送到本節點時會根據請求的action名稱找到對應的handler,使用對應的handler來處理該請求。這個handler就對應著“indices:data/write/index”,可以看到它調用execute方法來處理。它的注冊時在TransportShardReplicationOperationAction構造函數中完成的。
知道了OperationTransportHandler,ReplicaOperationTransportHandler就好理解了它的實現方式跟前者完全一樣,對應的action名稱加了一個“[r]”,它的作用是處理需要在副本上進行的操作,代碼如下所示:
class ReplicaOperationTransportHandler extends BaseTransportRequestHandler<ReplicaOperationRequest> {
……………………
@Override
public void messageReceived(final ReplicaOperationRequest request, final TransportChannel channel) throws Exception {
try {
shardOperationOnReplica(request);
} catch (Throwable t) {
failReplicaIfNeeded(request.shardId.getIndex(), request.shardId.id(), t);
throw t;
}
channel.sendResponse(TransportResponse.Empty.INSTANCE);
}
}可以看到代碼結構非常像,只是調用了副本操作的方法shardOperationOnReplica,這個方法在這TransportShardReplicationOperationAction中是抽象的,它的實現在各個子類中,例如deleteaction中實現了對于delete請求如何在副本上處理。
分析完這兩個handle是不是對于action的處理過程有了一定的眉目了呢?但是這才是冰山一角,這兩個Handler是用來接收來自其它節點的請求,如果請求的正好是本節點該如何處理呢?這些邏輯都在AsyncShardOperationAction類中。首先看一下它的內部結構:
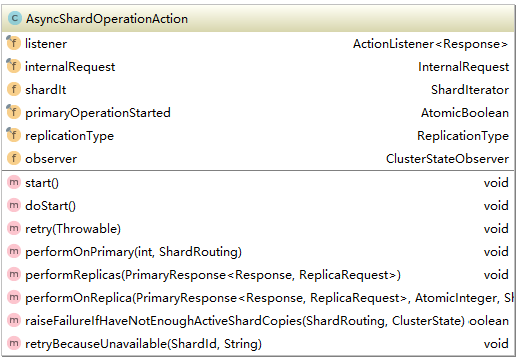
因為TransportShardReplicationOperationAction的所有子類都是對索引的修改,會引起數據不一致,因此它的操作流程都是現在primaryShard上操作然后是Replicashard上操作。代碼如下所示:
protected void doStart() throws ElasticsearchException {
try {
//檢查是否有阻塞
ClusterBlockException blockException = checkGlobalBlock(observer.observedState());
if (blockException != null) {
if (blockException.retryable()) {
logger.trace("cluster is blocked ({}), scheduling a retry", blockException.getMessage());
retry(blockException);
return;
} else {
throw blockException;
}
}
//檢測是否是創建索引
if (resolveIndex()) {
internalRequest.concreteIndex(observer.observedState().metaData().concreteSingleIndex(internalRequest.request().index(), internalRequest.request().indicesOptions()));
} else {
internalRequest.concreteIndex(internalRequest.request().index());
}
// check if we need to execute, and if not, return
if (!resolveRequest(observer.observedState(), internalRequest, listener)) {
return;
}
//再次檢測是否有阻塞
blockException = checkRequestBlock(observer.observedState(), internalRequest);
if (blockException != null) {
if (blockException.retryable()) {
logger.trace("cluster is blocked ({}), scheduling a retry", blockException.getMessage());
retry(blockException);
return;
} else {
throw blockException;
}
}
shardIt = shards(observer.observedState(), internalRequest);
} catch (Throwable e) {
listener.onFailure(e);
return;
}
//查找primaryShard
boolean foundPrimary = false;
ShardRouting shardX;
while ((shardX = shardIt.nextOrNull()) != null) {
final ShardRouting shard = shardX;
// we only deal with primary shardIt here...
if (!shard.primary()) {
continue;
}
if (!shard.active() || !observer.observedState().nodes().nodeExists(shard.currentNodeId())) {
logger.trace("primary shard [{}] is not yet active or we do not know the node it is assigned to [{}], scheduling a retry.", shard.shardId(), shard.currentNodeId());
retryBecauseUnavailable(shardIt.shardId(), "Primary shard is not active or isn't assigned to a known node.");
return;
}
if (!primaryOperationStarted.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return;
}
foundPrimary = true;
//primaryShard就在本地,直接進行相關操作
if (shard.currentNodeId().equals(observer.observedState().nodes().localNodeId())) {
try {
if (internalRequest.request().operationThreaded()) {
internalRequest.request().beforeLocalFork();
threadPool.executor(executor).execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
performOnPrimary(shard.id(), shard);
} catch (Throwable t) {
listener.onFailure(t);
}
}
});
} else {
performOnPrimary(shard.id(), shard);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
listener.onFailure(t);
}
} else {//primaryShard在其它節點上,將請求通過truansport發送到對應的節點。
DiscoveryNode node = observer.observedState().nodes().get(shard.currentNodeId());
transportService.sendRequest(node, actionName, internalRequest.request(), transportOptions, new BaseTransportResponseHandler<Response>() {
@Override
public Response newInstance() {
return newResponseInstance();
}
@Override
public String executor() {
return ThreadPool.Names.SAME;
}
@Override
public void handleResponse(Response response) {
listener.onResponse(response);
}
@Override
public void handleException(TransportException exp) {
// if we got disconnected from the node, or the node / shard is not in the right state (being closed)
if (exp.unwrapCause() instanceof ConnectTransportException || exp.unwrapCause() instanceof NodeClosedException ||
retryPrimaryException(exp)) {
primaryOperationStarted.set(false);
internalRequest.request().setCanHaveDuplicates();
// we already marked it as started when we executed it (removed the listener) so pass false
// to re-add to the cluster listener
logger.trace("received an error from node the primary was assigned to ({}), scheduling a retry", exp.getMessage());
retry(exp);
} else {
listener.onFailure(exp);
}
}
});
}
break;
}
………………
}這就是對應請求的處理過程。
void performOnPrimary(int primaryShardId, final ShardRouting shard) {
……
PrimaryResponse<Response, ReplicaRequest> response = shardOperationOnPrimary(clusterState, new PrimaryOperationRequest(primaryShardId, internalRequest.concreteIndex(), internalRequest.request()));
performReplicas(response);
…………
}以上就是performOnPrimary方法的部分代碼,首先調用外部類的shardOperationOnPrimary方法,該方法實現在各個子類中,在TransportIndexAction中的實現如下所示:
@Override
protected PrimaryResponse<IndexResponse, IndexRequest> shardOperationOnPrimary(ClusterState clusterState, PrimaryOperationRequest shardRequest) throws Throwable {
final IndexRequest request = shardRequest.request;
// 查看是否需要routing
IndexMetaData indexMetaData = clusterState.metaData().index(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex());
MappingMetaData mappingMd = indexMetaData.mappingOrDefault(request.type());
if (mappingMd != null && mappingMd.routing().required()) {
if (request.routing() == null) {
throw new RoutingMissingException(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex(), request.type(), request.id());
}
}
//調用indexserice執行對應的index操作
IndexService indexService = indicesService.indexServiceSafe(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex());
IndexShard indexShard = indexService.shardSafe(shardRequest.shardId.id());
SourceToParse sourceToParse = SourceToParse.source(SourceToParse.Origin.PRIMARY, request.source()).type(request.type()).id(request.id())
.routing(request.routing()).parent(request.parent()).timestamp(request.timestamp()).ttl(request.ttl());
long version;
boolean created;
try {
Engine.IndexingOperation op;
if (request.opType() == IndexRequest.OpType.INDEX) {
Engine.Index index = indexShard.prepareIndex(sourceToParse, request.version(), request.versionType(), Engine.Operation.Origin.PRIMARY, request.canHaveDuplicates());
if (index.parsedDoc().mappingsModified()) {
mappingUpdatedAction.updateMappingOnMaster(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex(), index.docMapper(), indexService.indexUUID());
}
indexShard.index(index);
version = index.version();
op = index;
created = index.created();
} else {
Engine.Create create = indexShard.prepareCreate(sourceToParse,
request.version(), request.versionType(), Engine.Operation.Origin.PRIMARY, request.canHaveDuplicates(), request.autoGeneratedId());
if (create.parsedDoc().mappingsModified()) {
mappingUpdatedAction.updateMappingOnMaster(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex(), create.docMapper(), indexService.indexUUID());
}
indexShard.create(create);
version = create.version();
op = create;
created = true;
}
if (request.refresh()) {
try {
indexShard.refresh("refresh_flag_index");
} catch (Throwable e) {
// ignore
}
}
// update the version on the request, so it will be used for the replicas
request.version(version);
request.versionType(request.versionType().versionTypeForReplicationAndRecovery());
assert request.versionType().validateVersionForWrites(request.version());
IndexResponse response = new IndexResponse(shardRequest.shardId.getIndex(), request.type(), request.id(), version, created);
return new PrimaryResponse<>(shardRequest.request, response, op);
} catch (WriteFailureException e) {
if (e.getMappingTypeToUpdate() != null) {
DocumentMapper docMapper = indexService.mapperService().documentMapper(e.getMappingTypeToUpdate());
if (docMapper != null) {
mappingUpdatedAction.updateMappingOnMaster(indexService.index().name(), docMapper, indexService.indexUUID());
}
}
throw e.getCause();
}
}上面的代碼就是index的執行過程,這一過程涉及到index的底層操作,這里就不展開,只是說明它在action中是如何實現的,后面會有詳細說明。接下來看在副本上的操作。副本可能有多個,因此首先調用了performReplicas方法,在這個方法中首先開始監聽集群的狀態,然后便利所有的副本進行處理,如果是異步則加入一個listener,否則同步執行返回結果。最后調用performReplica,在該方法中調用外部類的抽象方法shardOperationOnReplica。 這一過程比較簡單,這里就不再貼代碼,有興趣可以參考相關源碼。
到此,相信大家對“elasticsearch源碼index action實現方式是什么”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。