您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“Java實現常用的三種加密算法是什么”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“Java實現常用的三種加密算法是什么”這篇文章吧。
編程中常見的加密算法有以下幾種,它們在不同場景中分別有應用。除信息摘要算法外,其它加密方式都會需要密鑰。
信息摘要算法
對稱加密算法
非對稱加密算法
密鑰(key,又常稱金鑰)是指某個用來完成加密、解密、完整性驗證等密碼學應用的秘密信息。
加解密中的密鑰:對稱加密中共享相同的密鑰,非對稱加密中分公鑰和私鑰,公鑰加密私鑰解密。
消息認證碼和數字簽名中的密鑰:在消息認證碼中,消息發送方和接收方使用共享密鑰進行認證。在數字簽名中,簽名使用私鑰,而驗證使用公鑰。
會話密鑰和主密鑰:每次通信只使用一次的密鑰稱為會話密鑰(session key)。相對于會話密鑰,重復使用的密鑰稱為主密鑰(master key)。
密碼一般是由用戶生成,具有可讀性,可以記憶和存儲,常用于軟件管理,而密鑰是供實現加密算法的軟件使用,不需要具備可讀性(不過在編程中為了方便閱讀都進行Base64)。我們也可以通過密碼來生成密鑰。
生成密鑰:可以用隨機數生成密鑰,也可以用口令生成密鑰。
配送密鑰:可采用事先共享密鑰、使用密鑰分配中心、使用公鑰密碼、使用Diffie-Hellman密鑰交換。
更新密鑰
保存密鑰
作廢密鑰
jdk 中 jce (Java Cryptography Extension) 包含了加密相關的所有API。
生成對稱加密算法的密鑰

public static SecretKey generateKey(int keySize) {
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
try {
keyGenerator = KeyGenerator.getInstance("AES");
keyGenerator.init(keySize);
return keyGenerator.generateKey();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// ignore
return null;
}
}生成對稱非對稱加密算法的密鑰
/**
* 生成非對稱密鑰對
*
* @param keySize 密鑰大小
* @param random 指定隨機來源,默認使用 JCAUtil.getSecureRandom()
* @return 非對稱密鑰對
* @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException NoSuchAlgorithm
*/
public static PPKeys genKeysRSA(int keySize, SecureRandom random) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException {
KeyPairGenerator generator = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("RSA");
if (null != random) {
generator.initialize(keySize, random);
} else {
generator.initialize(keySize);
}
KeyPair pair = generator.generateKeyPair();
PPKeys keys = new PPKeys();
PublicKey publicKey = pair.getPublic();
PrivateKey privateKey = pair.getPrivate();
keys.setPublicKey(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(publicKey.getEncoded()));
keys.setPrivateKey(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(privateKey.getEncoded()));
return keys;
}密鑰協商(Diffie-Hellman)
密鑰協商是一種協議,兩方或多方在通過該協議建立相同的共享密鑰,然后通訊內容進行對稱加密傳輸,而不需要交換密鑰。
大致過程:每一方生成一個公私鑰對并將公鑰分發給其它方,當都獲得其他方的公鑰副本后就可以離線計算共享密鑰。
Java中提供了 KeyAgreement 可以實現密鑰協商。
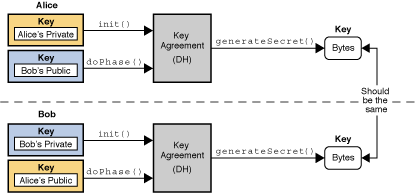
Alice 和 Bob 分別用他們的私鑰初始化自己的密鑰協商對象 KeyAgreement ,調用init() 方法;
然后將通信的每一方的公鑰 傳入執行 doPhase(Key key, boolean lastPhase) ;
各方生成共享密鑰 generateSecret()。
public static void diffieHellman() throws Exception {
AlgorithmParameterGenerator dhParams = AlgorithmParameterGenerator.getInstance("DH");
dhParams.init(1024);
KeyPairGenerator keyGen = KeyPairGenerator.getInstance("DH");
keyGen.initialize(dhParams.generateParameters().getParameterSpec(DHParameterSpec.class), new SecureRandom());
KeyAgreement aliceKeyAgree = KeyAgreement.getInstance("DH");
KeyPair alicePair = keyGen.generateKeyPair();
KeyAgreement bobKeyAgree = KeyAgreement.getInstance("DH");
KeyPair bobPair = keyGen.generateKeyPair();
aliceKeyAgree.init(alicePair.getPrivate());
bobKeyAgree.init(bobPair.getPrivate());
aliceKeyAgree.doPhase(bobPair.getPublic(), true);
bobKeyAgree.doPhase(alicePair.getPublic(), true);
boolean agree = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(aliceKeyAgree.generateSecret()).equals(
Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(bobKeyAgree.generateSecret())
);
System.out.println(agree);
}信息摘要算法又叫加密散列算法,加密過程不需要密鑰,常見的加密散列算法有MD系列和SHA系列。
一個理想的加密散列函數應該具備以下特性:
任何信息傳入后,輸出的總是長度固定;
消息摘要看起來是“隨機的”,這樣根據原始信息就很難推測出值;
好的散列函數碰撞概率應該極低,也就是不同信息傳入后得到相同值的概率;
MD5信息摘要算法(MD5 Message-Digest Algorithm),一種被廣泛使用的加密散列函數,輸出出一個128位(16字節)的散列值(hash value),MD5最初設計為加密散列函數,而目前發現它存在大量漏洞,所以不建議直接用作加密,不過在非加密場景下如:數據完整性校驗,文件完整性校驗它仍然有廣泛的應用。
public static String md5(String content) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
byte[] bytes = digest.digest(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return Hex.encodeHexString(bytes);
} catch (final NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
}安全散列算法(Secure Hash Algorithm,縮寫為SHA)是一個加密散列函數家族,是FIPS(美國聯邦信息處理標準)所認證的安全散列算法。能計算出一個數字消息所對應到的,長度固定的字符串(又稱消息摘要)的算法。且若輸入的消息不同,它們對應到不同字符串的機率很高。
它們分別包含 SHA-0、SHA-1、SHA-2、SHA-3,其中 SHA-0、SHA-1 輸出長度是160位,SHA-2 包含 SHA-224、SHA-256、SHA-384、SHA-512、SHA-512/224、SHA-512/256,我們平時常用 SHA-256 。
public static String sha256(String content) {
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256);
byte[] bytes = digest.digest(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
return Hex.encodeHexString(bytes);
} catch (final NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
}
}對稱加密算法,雙方持有相同密鑰進行加解密,常見的對稱加密算法:DES 3DES AES128 AES192 AES256。理解對稱加密需要先明白下面幾個概念:
分組密碼模式:將明文切割進行加密,再將密文拼接到一起。比如AES中會將明文數據切割為大小16字節的數據塊,最后一塊不夠16字節時,使用Padding模式進行補充。
填充(Padding):它有三種模式PKCS5、PKCS7和NOPADDING,PKCS5用缺少的字節數來填充,比如缺少5個字節就填充5個數字5,PKCS7缺少的字節數用0來填充。如果數據剛好是16的整數倍,PKCS5和PKCS7會再補充一個16字節數據來區分填充和有效數據,NOPADDING模式不需要填充。
初始化向量:初始向量IV的作用是使加密更加安全可靠,在分組密碼模式下IV大小對應數據塊長度。
加密模式:四種加密模式分別是:ECB(電子密碼本模式)、CBC(密碼分組鏈接模式)、CFB、OFB。ECB模式是僅僅使用明文和密鑰來加密數據,所以該模式下不需要Padding,安全性也較弱,CBC模式數據分塊并且使用傳入IV依次進行異或操作,安全性也相對較高,所以目前一般都選擇CBC模式。
加密密鑰:不同加密算法密鑰長度不同,比如:DES 默認長度56位,3DES默認長度168位,也支持128位,AES默認128位,也支持192位,256位。我們一般根據密碼生成密鑰,密碼長度需要滿足算法密鑰長度。
DES 是對稱加密算法領域中的典型算法,因為密鑰默認長度為56 bit,所以密碼長度需要大于 8 byte,DESKeySpec 取前 8 byte 進行密鑰制作。
public static String encryptDES(byte[] content, String password) {
try {
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
DESKeySpec desKeySpec = new DESKeySpec(password.getBytes());
SecretKeyFactory secretKeyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
SecretKey secretKey = secretKeyFactory.generateSecret(desKeySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretKey, random);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(content));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String decryptDES(String content, String password) throws Exception {
SecureRandom random = new SecureRandom();
DESKeySpec desKeySpec = new DESKeySpec(password.getBytes());
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DES");
SecretKey secretKey = keyFactory.generateSecret(desKeySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DES");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretKey, random);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(content)));
}3DES(即Triple DES)。是DES算法的加強,它使用3條56位的密鑰對數據進行三次加密。它以DES為基本模塊,通過組合分組方法設計出分組加密算法。比起最初的DES,3DES更為安全。密鑰默認長度 168 bit, 密碼需要大于24 byte,IV 是 8 byte 的隨機數字和字母數組。
public static String encrypt3DESECB(String content, String key, String iv) {
try {
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
DESedeKeySpec dks = new DESedeKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DESede");
SecretKey secretkey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secretkey, ivSpec);
return Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(cipher.doFinal(content.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String decrypt3DESECB(String content, String key, String iv) {
try {
IvParameterSpec ivSpec = new IvParameterSpec(iv.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
DESedeKeySpec dks = new DESedeKeySpec(key.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
SecretKeyFactory keyFactory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("DESede");
SecretKey secretkey = keyFactory.generateSecret(dks);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("DESede/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secretkey, ivSpec);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(content)), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}AES 高級數據加密標準,能夠有效抵御已知的針對DES算法的所有攻擊,默認密鑰長度為128 bit,還可以供選擇 192 bit,256 bit。AES-128 AES-192 AES-256
默認 AES-128 ,使用 PBEKeySpec 生成固定大小的密鑰。
public static String encryptAES128(String plainText, String password, String salt) throws Exception {
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1");
byte[] saltBytes = salt.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
// AES-128 密鑰長度為128bit
PBEKeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(
password.toCharArray(),
saltBytes,
1000,
128
);
SecretKey secretKey = factory.generateSecret(spec);
SecretKeySpec secret = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
AlgorithmParameters params = cipher.getParameters();
IvParameterSpec iv = params.getParameterSpec(IvParameterSpec.class);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, secret, iv);
byte[] encryptedTextBytes = cipher.doFinal(plainText.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String encodedText = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(encryptedTextBytes);
String encodedIV = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(iv.getIV());
String encodedSalt = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(saltBytes);
return encodedSalt + "." + encodedIV + "." + encodedText;
}
public static String decryptAES128(String encryptedText, String password) throws Exception {
String[] fields = encryptedText.split("\\.");
byte[] saltBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(fields[0]);
byte[] ivBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(fields[1]);
byte[] encryptedTextBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(fields[2]);
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("PBKDF2WithHmacSHA1");
PBEKeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(
password.toCharArray(),
saltBytes,
1000,
128
);
SecretKey secretKey = factory.generateSecret(spec);
SecretKeySpec secret = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, secret, new IvParameterSpec(ivBytes));
byte[] decryptedTextBytes;
try {
decryptedTextBytes = cipher.doFinal(encryptedTextBytes);
return new String(decryptedTextBytes);
} catch (IllegalBlockSizeException | BadPaddingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}使用 AES-256 時可能會出現下面異常:
java.security.InvalidKeyException: Illegal key size
JDK 1.8.0_161 及以上版本默認已經啟用無限強度加密:
static {
java.security.Security.setProperty("crypto.policy", "unlimited");
}JDK 1.8.0_161以前版本需要手動安裝 jce 策略文件(下載地址)
非對稱加密使用一對密鑰,公鑰用作加密,私鑰則用作解密。關于密鑰大小,截至2020年,公開已知的最大RSA密鑰是破解的是829位的RSA-250,建議至少使用 2048 位密鑰。

public static String encrypt(byte[] publicKey, String plainText) {
X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(publicKey);
KeyFactory kf;
try {
kf = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
PublicKey publicKeySecret = kf.generatePublic(keySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, publicKeySecret);
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plainText.getBytes());
return new String(Base64.getEncoder().encode(encryptedBytes));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Rsa encrypt error ", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static String decrypt(byte[] privateKey, String encryptedText) {
PKCS8EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new PKCS8EncodedKeySpec(privateKey);
KeyFactory kf;
try {
kf = KeyFactory.getInstance("RSA");
PrivateKey privateKeySecret = kf.generatePrivate(keySpec);
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("RSA/ECB/PKCS1Padding");
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, privateKeySecret);
return new String(cipher.doFinal(Base64.getDecoder().decode(encryptedText)), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Rsa decrypt error ", e);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}以上是“Java實現常用的三種加密算法是什么”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。