您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“HttpClient連接池及重試機制是什么”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
HttpClient 是Apache Jakarta Common 下的子項目,可以用來提供高效的、最新的、功能豐富的支持 HTTP 協議的客戶端編程工具包,基于標準的java語言。
支持HTTP和HTTPS協議
實現了HTTP的方法,GET,POST,PUT,DELETE等方法。
連接管理器支持多線程的應用。
可以設置連接超時
使用HttpClient發送請求,接收響應可以分為一下幾步:
創建HttpClient對象
創建請求方法的實例,并且指定URL
發送請求參數,GET請求和POST請求發送參數的方式有所不同
調用HttpClient對象的execute方法,返回HttpResponse對象
調用HttpResponse的getAllHeaders()、getHeaders(String name)等方法可獲取服務器的響應頭;調用HttpResponse的getEntity()方法可獲取HttpEntity對象,該對象包裝了服務器的響應內容
連接釋放。無論成功與否,必須釋放連接
筆者用到的版本是4.5.5,由于是maven工程,需要在pom文件引入對應的坐標。
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.5.5</version> </dependency>
package cn.htjc.customer.util;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy;
import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder;
import org.apache.http.config.Registry;
import org.apache.http.config.RegistryBuilder;
import org.apache.http.conn.socket.ConnectionSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.socket.PlainConnectionSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.TrustSelfSignedStrategy;
import org.apache.http.entity.ContentType;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.protocol.HttpContext;
import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContextBuilder;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.SocketTimeoutException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
public class HttpClientUtil {
// utf-8字符編碼
private static final String CHARSET_UTF_8 = "utf-8";
// HTTP內容類型。相當于form表單的形式,提交數據
private static final String CONTENT_TYPE_FORM_URL = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
// 連接管理器
private static PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager pool;
// 請求配置
private static RequestConfig requestConfig;
static {
try {
log.info("初始自定義HttpClient......開始");
SSLContextBuilder builder = new SSLContextBuilder();
builder.loadTrustMaterial(null, new TrustSelfSignedStrategy());
SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslsf = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(builder.build());
// 配置同時支持 HTTP 和 HTPPS
Registry<ConnectionSocketFactory> socketFactoryRegistry = RegistryBuilder.<ConnectionSocketFactory>create()
.register("http", PlainConnectionSocketFactory.getSocketFactory())
.register("https", sslsf).build();
// 初始化連接管理器
pool = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager(
socketFactoryRegistry);
// 設置連接池的最大連接數
pool.setMaxTotal(200);
// 設置每個路由上的默認連接個數
pool.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20);
// 根據默認超時限制初始化requestConfig
// 客戶端從服務器讀取數據的timeout
int socketTimeout = 1000;
// 客戶端和服務器建立連接的timeout
int connectTimeout = 10000;
// 從連接池獲取連接的timeout
int connectionRequestTimeout = 10000;
//設置請求超時時間
requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom().setConnectionRequestTimeout(
connectionRequestTimeout).setSocketTimeout(socketTimeout).setConnectTimeout(
connectTimeout).build();
log.info("初始自定義HttpClient......結束");
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("初始自定義HttpClient......失敗");
}
}
private HttpClientUtil() {
}
private static CloseableHttpClient getHttpClient() {
// 狀態碼是503的時候,該策略生效
ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy serviceUnavailableRetryStrategy = new ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy() {
@Override
public boolean retryRequest(HttpResponse httpResponse, int i, HttpContext httpContext) {
if (i < 3) {
log.info("ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy========================"+i);
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public long getRetryInterval() {
return 2000L;
}
};
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
// 設置連接池管理
.setConnectionManager(pool)
// 設置請求配置
.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig)
// 設置重試次數
.setRetryHandler(new DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler())
.setServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy(serviceUnavailableRetryStrategy)
.build();
return httpClient;
}
public static String doGet(String url, Map<String, String> param) {
// 創建Httpclient對象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = getHttpClient();
String resultString = "";
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 創建uri
URIBuilder builder = new URIBuilder(url);
if (param != null) {
for (String key : param.keySet()) {
builder.addParameter(key, param.get(key));
}
}
URI uri = builder.build();
// 創建http GET請求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
// 執行請求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 判斷返回狀態是否為200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
resultString = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), CHARSET_UTF_8);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return resultString;
}
public static String doGet(String url) {
return doGet(url, null);
}
public static String doPost(String url, Map<String, String> param) {
// 創建Httpclient對象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = getHttpClient();
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
String resultString = "";
try {
// 創建Http Post請求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
// 創建參數列表
if (param != null) {
List<NameValuePair> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String key : param.keySet()) {
paramList.add(new BasicNameValuePair(key, param.get(key)));
}
// 模擬表單
UrlEncodedFormEntity entity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(paramList, CHARSET_UTF_8);
entity.setContentType(CONTENT_TYPE_FORM_URL);
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
}
// 執行http請求main
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
resultString = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), CHARSET_UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return resultString;
}
public static String doPost(String url) {
return doPost(url, null);
}
public static String doPostJson(String url, String json) {
// 創建Httpclient對象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = getHttpClient();
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
String resultString = "";
try {
// 創建Http Post請求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
// 創建請求內容
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(json, ContentType.APPLICATION_JSON);
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
// 執行http請求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
resultString = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), CHARSET_UTF_8);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
response.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return resultString;
}
}代碼中出現了@Slf4j,作用是引入log,手動打印日志。這個注解是lombok的注解。
解釋一下,什么是Route?
Route的概念可以理解為客戶端機器到目標機器的一條線路,例如使用HttpClient的實現來分別請求 www.163.com 的資源和 www.sina.com 的資源就會產生兩個route。缺省條件下對于每個Route,HttpClient僅維護2個連接,總數不超過20個連接。
1 為什么要使用http連接池?
延遲降低,如果不使用連接池,每次發起的http請求都會重新建立tcp連接(三次握手),用完就會關閉連接(4次握手),采用連接池則會減少這不是分時間的消耗。連接池管理的對象都是長連接。
支持更大的并發,由于連接池只適用于請求經常訪問同一主機(或同一端口的情況),連接池避免了反復建立連接,搶占端口資源的情況,如果沒用連接池,可能導致連接建立不了。
2 設置超時時間
首先要明白三個概念:socketTimeout,connectTimeout,connectionRequestTimeout。
socketTimeout:客戶端和服務器讀取數據的timeout
connectTimeout:客戶端和服務器建立連接的timeout
connectionRequestTimeout:從連接池獲取連接的timeout
3 解釋:一次http請求
一次http請求,必定會有三個階段,一:建立連接;二:數據傳送;三,斷開連接。
當建立連接在規定的時間內(ConnectionTimeOut )沒有完成,那么此次連接就結束了。后續的SocketTimeOutException就一定不會發生。只有當連接建立起來后,
也就是沒有發生ConnectionTimeOutException ,才會開始傳輸數據,如果數據在規定的時間內(SocketTimeOut)傳輸完畢,則斷開連接。否則,觸發SocketTimeOutException。
上面說了這么多,就是為了引出下面的重試問題。由于項目中要訪問外部接口,訪問接口的時候,偶爾會出現SocketTimeOutException:Read timed out,其實就是客戶端讀取服務器的數據超時了。
使用PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager得到的InternalHttpClient實例,是抽象類CloseableHttpClient的一個實現。
看一下ClientExecChain接口的實現類
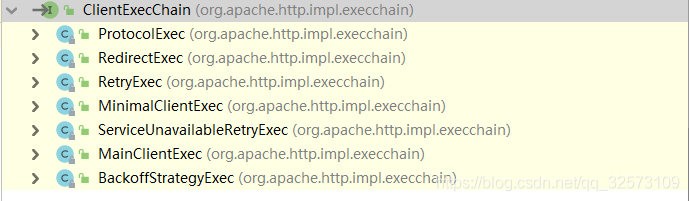
簡單看一下build()方法
public CloseableHttpClient build() {
// 省略一些代碼
// 添加MainClientExec
ClientExecChain execChain = this.createMainExec(requestExecCopy, (HttpClientConnectionManager)connManagerCopy, (ConnectionReuseStrategy)reuseStrategyCopy, (ConnectionKeepAliveStrategy)keepAliveStrategyCopy, new ImmutableHttpProcessor(new HttpRequestInterceptor[]{new RequestTargetHost(), new RequestUserAgent(userAgentCopy)}), (AuthenticationStrategy)targetAuthStrategyCopy, (AuthenticationStrategy)proxyAuthStrategyCopy, (UserTokenHandler)userTokenHandlerCopy);
execChain = this.decorateMainExec(execChain);
// 添加ProtocolExec
ClientExecChain execChain = new ProtocolExec(execChain, httpprocessorCopy);
ClientExecChain execChain = this.decorateProtocolExec(execChain);
// Add request retry executor, if not disabled
if (!automaticRetriesDisabled) {
HttpRequestRetryHandler retryHandlerCopy = this.retryHandler;
if (retryHandlerCopy == null) {
retryHandlerCopy = DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler.INSTANCE;
}
execChain = new RetryExec(execChain, retryHandlerCopy);
}
// 省去部分代碼
// 如果不為空,添加ServiceUnavailableRetryExec
ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy serviceUnavailStrategyCopy = this.serviceUnavailStrategy;
if (serviceUnavailStrategyCopy != null) {
execChain = new ServiceUnavailableRetryExec((ClientExecChain)execChain, serviceUnavailStrategyCopy);
}
// 添加RedirectExec
if (!this.redirectHandlingDisabled) {
authSchemeRegistryCopy = this.redirectStrategy;
if (authSchemeRegistryCopy == null) {
authSchemeRegistryCopy = DefaultRedirectStrategy.INSTANCE;
}
execChain = new RedirectExec((ClientExecChain)execChain, (HttpRoutePlanner)routePlannerCopy, (RedirectStrategy)authSchemeRegistryCopy);
}
// 省去部分代碼
return new InternalHttpClient((ClientExecChain)execChain, (HttpClientConnectionManager)connManagerCopy, (HttpRoutePlanner)routePlannerCopy, cookieSpecRegistryCopy, (Lookup)authSchemeRegistryCopy, (CookieStore)defaultCookieStore, (CredentialsProvider)defaultCredentialsProvider, this.defaultRequestConfig != null ? this.defaultRequestConfig : RequestConfig.DEFAULT, closeablesCopy);
}自上而下,創建了不同的ClientExecChain實例。注意:創建對象的順序就是執行器鏈的順序
在構造CloseableHttpClient實例的時候,判斷是否關閉了自動重試功能,automaticRetriesDisabled默認是false。如果沒有指定執行器鏈,就用RetryExec。默認的重試策略是DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler。
如果重寫了ServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy接口,或者使用了DefaultServiceUnavailableRetryStrategy,ServiceUnavailableRetryExec也會加入到執行器鏈里。
同理,redirectHandlingDisabled默認是false,RedirectExec也會加入到執行器鏈,并且會最先執行。
前面已經看到我們使用的HttiClient本質上是InternalHttpClient,這里看下他的執行發送數據的方法。
@Override
protected CloseableHttpResponse doExecute(
final HttpHost target,
final HttpRequest request,
final HttpContext context) throws IOException, ClientProtocolException {
//省略一些代碼
return this.execChain.execute(route, wrapper, localcontext, execAware);
}
}首先經過RedirectExec,RedirectExec里面調用ServiceUnavailableRetryExec的excute(),進入ServiceUnavailableRetryExec后,調用RetryExec的excute(),進入發到RetryExec后,調用ProtocolExec的execute(),最后調用MainClientExec的excute()。
執行器鏈結束后,執行HttpRequestExecutor的excute(),excute()方法調用了自己的doSendRequest()。
之后一步一步的返回,遇到異常進行處理。
下面是RetryExec發送請求的部分
public CloseableHttpResponse execute(HttpRoute route,
HttpRequestWrapper request,
HttpClientContext context,
HttpExecutionAware execAware) throws IOException, HttpException {
// 參數檢驗
Args.notNull(route, "HTTP route");
Args.notNull(request, "HTTP request");
Args.notNull(context, "HTTP context");
// 獲取請求頭的全部信息
Header[] origheaders = request.getAllHeaders();
// 初始化請求次數為1
int execCount = 1;
while(true) {
try {
// 調用基礎executor執行http請求
return this.requestExecutor.execute(route, request, context, execAware);
} catch (IOException var9) {
// 發生IO異常的時候,判斷上下文是否已經中斷,如果中斷則拋異常退出
if (execAware != null && execAware.isAborted()) {
this.log.debug("Request has been aborted");
throw var9;
}
// 根據重試策略,判斷當前執行狀況是否要重試,如果是則進入下面邏輯
if (!this.retryHandler.retryRequest(var9, execCount, context)) {
if (var9 instanceof NoHttpResponseException) {
NoHttpResponseException updatedex = new NoHttpResponseException(route.getTargetHost().toHostString() + " failed to respond");
updatedex.setStackTrace(var9.getStackTrace());
throw updatedex;
}
throw var9;
}
// 日志
if (this.log.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.log.info("I/O exception (" + var9.getClass().getName() + ") caught when processing request to " + route + ": " + var9.getMessage());
}
// 日志
if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.log.debug(var9.getMessage(), var9);
}
// 判斷當前請求是否可以重復發起
if (!RequestEntityProxy.isRepeatable(request)) {
this.log.debug("Cannot retry non-repeatable request");
throw new NonRepeatableRequestException("Cannot retry request with a non-repeatable request entity", var9);
}
// 設置請求頭
request.setHeaders(origheaders);
// 日志
if (this.log.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.log.info("Retrying request to " + route);
}
++execCount;
}
}
}當發生IOException,判斷是否要重試。如果重試則記錄相應的次數,如果不重試,就拋出異常并且退出。
//單例模式 final 不可變的對象,線程安全
public static final DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler INSTANCE = new DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler();
//重試次數
private final int retryCount;
//如果一個請求發送成功過,是否還會被再次發送
private final boolean requestSentRetryEnabled;
// 不允許重試的異常類
private final Set<Class<? extends IOException>> nonRetriableClasses;
// 默認重試3次,請求發送成功,不在發送
public DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler() {
this(3, false);
}
public DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler(final int retryCount, final boolean requestSentRetryEnabled) {
this(retryCount, requestSentRetryEnabled, Arrays.asList(
InterruptedIOException.class,
UnknownHostException.class,
ConnectException.class,
SSLException.class));
}
protected DefaultHttpRequestRetryHandler(
final int retryCount,
final boolean requestSentRetryEnabled,
final Collection<Class<? extends IOException>> clazzes) {
super();
this.retryCount = retryCount;
this.requestSentRetryEnabled = requestSentRetryEnabled;
this.nonRetriableClasses = new HashSet<Class<? extends IOException>>();
for (final Class<? extends IOException> clazz: clazzes) {
this.nonRetriableClasses.add(clazz);
}
}通過構造函數,可以看出:
重試3次請求成功,就不再重試InterruptedIOException、UnknownHostException、ConnectException、SSLException,發生這4種異常不重試
重試3次
請求成功,就不再重試
InterruptedIOException、UnknownHostException、ConnectException、SSLException,發生這4種異常不重試
關于默認的重試策略
如果超過三次不進行重試
以上4中異常及其子類不進行重試
同一個請求在異步任務中已經停止,不進行重試
冪等的方法可以進行重試,比如get,含有http body都可以認為是非冪等
請求沒有發送成功,可以進行重試
問題來了,發送成功的請求是怎么樣的?
下面的代碼在HttpCoreContext里面,HttpCoreContext是HttpContext的實現類
public static final String HTTP_REQ_SENT = "http.request_sent";
public boolean isRequestSent() {
final Boolean b = getAttribute(HTTP_REQ_SENT, Boolean.class);
return b != null && b.booleanValue();
}當前httpContext中的http.request_sent設置為true,則認為已經發送成功。
HttpRequestExecutor的excute(),調用了自己的doSendRequest()。
protected HttpResponse doSendRequest(HttpRequest request,
HttpClientConnection conn,
HttpContext context) throws IOException, HttpException {
// 參數檢驗
Args.notNull(request, "HTTP request");
Args.notNull(conn, "Client connection");
Args.notNull(context, "HTTP context");
HttpResponse response = null;
// 將連接放入上下文
context.setAttribute("http.connection", conn);
// 在請求發送之前,將http.request_sent放入上下文context的屬性中,值為false
context.setAttribute("http.request_sent", Boolean.FALSE);
// 將request的header放入連接中
conn.sendRequestHeader(request);
// 如果是post/put這種有body的請求,要先進行判斷
if (request instanceof HttpEntityEnclosingRequest) {
boolean sendentity = true;
// 獲取http協議版本號
ProtocolVersion ver = request.getRequestLine().getProtocolVersion();
// 滿足100-continue,并且http協議不是1.0
if (((HttpEntityEnclosingRequest)request).expectContinue() && !ver.lessEquals(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_0)) {
// 刷新當前連接,發送數據
conn.flush();
// Checks if response data is available from the connection
if (conn.isResponseAvailable(this.waitForContinue)) {
// Receives the request line and headers of the next response available from this connection.
response = conn.receiveResponseHeader();
// 判斷相應是否攜帶實體(是否有body)
if (this.canResponseHaveBody(request, response)) {
// Receives the next response entity available from this connection and attaches it to an existing HttpResponse object.
conn.receiveResponseEntity(response);
}
// 獲取請求狀態碼
int status = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (status < 200) {
if (status != 100) {
throw new ProtocolException("Unexpected response: " + response.getStatusLine());
}
response = null;
} else {
sendentity = false;
}
}
}
if (sendentity) {
// 通過連接發送請求實體
conn.sendRequestEntity((HttpEntityEnclosingRequest)request);
}
}
// Writes out all pending buffered data over the open connection.
conn.flush();
// 將http.request_sent置為true
context.setAttribute("http.request_sent", Boolean.TRUE);
return response;
}判斷是否攜帶實體的方法
protected boolean canResponseHaveBody(HttpRequest request, HttpResponse response) {
// 如果是head請求,返回false HEAD:只請求頁面首部
if ("HEAD".equalsIgnoreCase(request.getRequestLine().getMethod())) {
return false;
} else {
int status = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
return status >= 200 && status != 204 && status != 304 && status != 205;
}
}注:HttpEntityEnclosingRequest是一個接口
public interface HttpEntityEnclosingRequest extends HttpRequest {
// 詢問Server是否愿意接收數據
boolean expectContinue();
// 設置httpEntity
void setEntity(HttpEntity entity);
// 獲取httpEntity
HttpEntity getEntity();
}HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase是實現HttpEntityEnclosingRequest的抽象類
public abstract class HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase extends HttpRequestBase implements HttpEntityEnclosingRequest {
// HttpEntity其實相當于一個消息實體,內容是http傳送的報文,有多個實現類,常用StringEntity
private HttpEntity entity;
public HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase() {
}
public HttpEntity getEntity() {
return this.entity;
}
public void setEntity(HttpEntity entity) {
this.entity = entity;
}
// 判斷此請求是否應使用expect-continue
public boolean expectContinue() {
// 從請求頭獲取Except鍵值對
Header expect = this.getFirstHeader("Expect");
// 如果except不為空,并且內容是 100-continue時返回true
return expect != null && "100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(expect.getValue());
}
public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase clone = (HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase)super.clone();
if (this.entity != null) {
clone.entity = (HttpEntity)CloneUtils.cloneObject(this.entity);
}
return clone;
}
}下圖可以看出,HttpPost和HttpPut是HttpEntityEnclosingRequestBase的子類
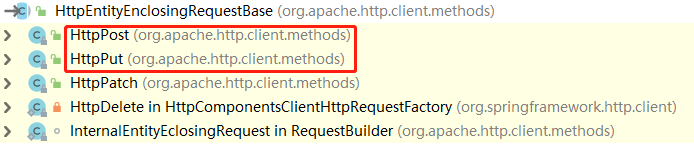
簡要分析一下,上述的操作過程
開始將http.request_sent設置為false
通過流flush數據到客戶端
然后將http.request_sent設置為true
顯然conn.flush()是可以發生異常的。注意:conn都是從連接池獲取的。
默認是開啟重試的,可以在創建HttpClientBuilder的時候,調用下面的方法關閉。
public final HttpClientBuilder disableAutomaticRetries() {
this.automaticRetriesDisabled = true;
return this;
}只有發生IOException才會發生重試
InterruptedIOException、UnknownHostException、ConnectException、SSLException,發生這4種異常不重試
get方法可以重試3次,post方法對應的socket流沒有被flush成功時可以重試3次
InterruptedIOException,線程中斷異常
UnknownHostException,找不到對應host
ConnectException,找到了host但是建立連接失敗。
SSLException,https認證異常
另外,我們還經常會提到兩種超時,連接超時與讀超時:
1. java.net.SocketTimeoutException: Read timed out
2. java.net.SocketTimeoutException: connect timed out
這兩種超時都是SocketTimeoutException,繼承自InterruptedIOException,屬于線程中斷異常,不會進行重試。
“HttpClient連接池及重試機制是什么”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。