您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“Python+OpenCV怎么解決彩色圖亮度不均衡問題”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在Python+OpenCV怎么解決彩色圖亮度不均衡問題問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”Python+OpenCV怎么解決彩色圖亮度不均衡問題”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
也就是把圖像重新縮放到指定的范圍內
# 對比度拉伸 p1, p2 = np.percentile(img, (0, 70)) # numpy計算多維數組的任意百分比分位數 rescale_img = np.uint8((np.clip(img, p1, p2) - p1) / (p2 - p1) * 255)
其中,numpy的percentile函數可以計算多維數組的任意百分比分位數,因為我的圖片中整體偏暗,我就把原圖灰度值的0% ~ 70%縮放到0 ~255
使用以下公式進行映射:
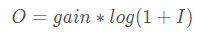
# 對數變換 log_img = np.zeros_like(img) scale, gain = 255, 1.5 for i in range(3): log_img[:, :, i] = np.log(img[:, :, i] / scale + 1) * scale * gain
使用以下公式進行映射:
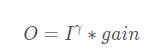
# gamma變換 gamma, gain, scale = 0.7, 1, 255 gamma_img = np.zeros_like(img) for i in range(3): gamma_img[:, :, i] = ((img[:, :, i] / scale) ** gamma) * scale * gain
使用直方圖均衡后的圖像具有大致線性的累積分布函數,其優點是不需要參數。
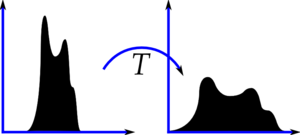
其原理為,考慮這樣一個圖像,它的像素值被限制在某個特定的值范圍內,即灰度范圍不均勻。所以我們需要將其直方圖縮放遍布整個灰度范圍(如下圖所示,來自維基百科),這就是直方圖均衡化所做的(簡單來說)。這通常會提高圖像的對比度。
這里使用OpenCV來演示。
# 直方圖均衡化 equa_img = np.zeros_like(img) for i in range(3): equa_img[:, :, i] = cv.equalizeHist(img[:, :, i])
這是一種自適應直方圖均衡化方法
OpenCV提供了該方法。
# 對比度自適應直方圖均衡化 clahe_img = np.zeros_like(img) clahe = cv.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8)) for i in range(3): clahe_img[:, :, i] = clahe.apply(img[:, :, i])
使用Matplotlib顯示上述幾種方法的結果:

可以看到,前四種方法效果都差不多,都有一個問題亮的地方過于亮,這是因為他們考慮的是全局對比度,而且因為我們使用的彩色圖像原因,使用log變換的結果圖中有部分區域色彩失真。最后一種CLAHE方法考慮的是局部對比度,所以效果會好一點。
因為圖像是彩色的,這里我只繪制了R通道的直方圖(紅色線)及其累積分布函數(黑色線)
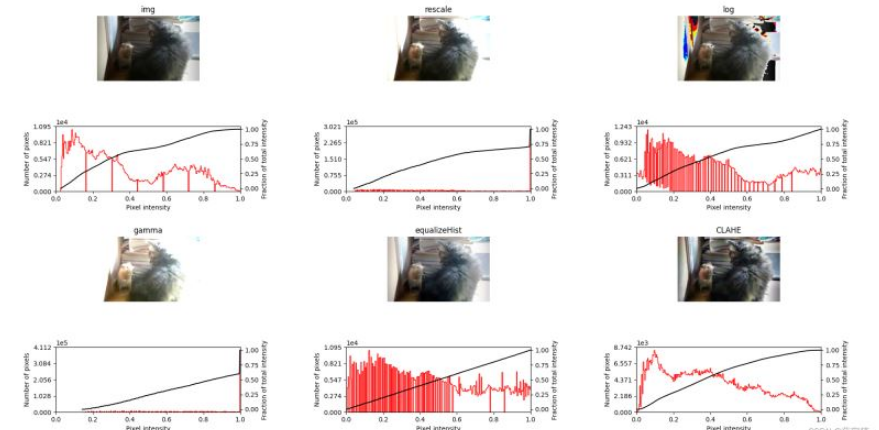
可以看到均衡后的圖像具有大致線性的累積分布函數。
總之,經過以上的探索,我最終決定使用CLAHE均衡后的結果,感覺是比之前的好了點
import cv2.cv2 as cv
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plot_img_and_hist(image, axes, bins=256):
"""Plot an image along with its histogram and cumulative histogram.
"""
ax_img, ax_hist = axes
ax_cdf = ax_hist.twinx()
# Display image
ax_img.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax_img.set_axis_off()
# Display histogram
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
for i in range(1):
ax_hist.hist(image[:, :, i].ravel(), bins=bins, histtype='step', color=colors[i])
ax_hist.ticklabel_format(axis='y', style='scientific', scilimits=(0, 0))
ax_hist.set_xlabel('Pixel intensity')
ax_hist.set_xlim(0, 255) # 這里范圍為0~255 如果使用img_as_float,則這里為0~1
ax_hist.set_yticks([])
# Display cumulative distribution
for i in range(1):
hist, bins = np.histogram(image[:, :, i].flatten(), 256, [0, 256])
cdf = hist.cumsum()
cdf = cdf * float(hist.max()) / cdf.max()
ax_cdf.plot(bins[1:], cdf, 'k')
ax_cdf.set_yticks([])
return ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf
def plot_all(images, titles, cols):
"""
輸入titles、images、以及每一行多少列,自動計算行數、并繪制圖像和其直方圖
:param images:
:param titles:
:param cols: 每一行多少列
:return:
"""
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
img_num = len(images) # 圖片的個數
rows = int(np.ceil(img_num / cols) * 2) # 上圖下直方圖 所以一共顯示img_num*2個子圖
axes = np.zeros((rows, cols), dtype=object)
axes = axes.ravel()
axes[0] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, 1) # 先定義第一個img 單獨拿出來定義它是為了下面的sharex
# 開始創建所有的子窗口
for i in range(1, img_num): #
axes[i + i // cols * cols] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i + i // cols * cols + 1, sharex=axes[0],
sharey=axes[0])
for i in range(0, img_num):
axes[i + i // cols * cols + cols] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i + i // cols * cols + cols + 1)
for i in range(0, img_num): # 這里從1開始,因為第一個在上面已經繪制過了
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(images[i],
(axes[i + i // cols * cols], axes[i + i // cols * cols + cols]))
ax_img.set_title(titles[i])
y_min, y_max = ax_hist.get_ylim()
ax_hist.set_ylabel('Number of pixels')
ax_hist.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, y_max, 5))
ax_cdf.set_ylabel('Fraction of total intensity')
ax_cdf.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, 1, 5))
# prevent overlap of y-axis labels
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close(fig)
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = cv.imread('catandmouse.png', cv.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)[:, :, :3]
img = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
gray = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# 對比度拉伸
p1, p2 = np.percentile(img, (0, 70)) # numpy計算多維數組的任意百分比分位數
rescale_img = np.uint8((np.clip(img, p1, p2) - p1) / (p2 - p1) * 255)
# 對數變換
log_img = np.zeros_like(img)
scale, gain = 255, 1.5
for i in range(3):
log_img[:, :, i] = np.log(img[:, :, i] / scale + 1) * scale * gain
# gamma變換
gamma, gain, scale = 0.7, 1, 255
gamma_img = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
gamma_img[:, :, i] = ((img[:, :, i] / scale) ** gamma) * scale * gain
# 彩色圖直方圖均衡化
# 直方圖均衡化
equa_img = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
equa_img[:, :, i] = cv.equalizeHist(img[:, :, i])
# 對比度自適應直方圖均衡化
clahe_img = np.zeros_like(img)
clahe = cv.createCLAHE(clipLimit=2.0, tileGridSize=(8, 8))
for i in range(3):
clahe_img[:, :, i] = clahe.apply(img[:, :, i])
titles = ['img', 'rescale', 'log', 'gamma', 'equalizeHist', 'CLAHE']
images = [img, rescale_img, log_img, gamma_img, equa_img, clahe_img]
plot_all(images, titles, 3)from skimage import exposure, util, io, color, filters, morphology
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
def plot_img_and_hist(image, axes, bins=256):
"""Plot an image along with its histogram and cumulative histogram.
"""
image = util.img_as_float(image)
ax_img, ax_hist = axes
ax_cdf = ax_hist.twinx()
# Display image
ax_img.imshow(image, cmap=plt.cm.gray)
ax_img.set_axis_off()
# Display histogram
colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue']
for i in range(1):
ax_hist.hist(image[:, :, i].ravel(), bins=bins, histtype='step', color=colors[i])
ax_hist.ticklabel_format(axis='y', style='scientific', scilimits=(0, 0))
ax_hist.set_xlabel('Pixel intensity')
ax_hist.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax_hist.set_yticks([])
# Display cumulative distribution
for i in range(1):
img_cdf, bins = exposure.cumulative_distribution(image[:, :, i], bins)
ax_cdf.plot(bins, img_cdf, 'k')
ax_cdf.set_yticks([])
return ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf
def plot_all(images, titles, cols):
"""
輸入titles、images、以及每一行多少列,自動計算行數、并繪制圖像和其直方圖
:param images:
:param titles:
:param cols: 每一行多少列
:return:
"""
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
img_num = len(images) # 圖片的個數
rows = int(np.ceil(img_num / cols) * 2) # 上圖下直方圖 所以一共顯示img_num*2個子圖
axes = np.zeros((rows, cols), dtype=object)
axes = axes.ravel()
axes[0] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, 1) # 先定義第一個img 單獨拿出來定義它是為了下面的sharex
# 開始創建所有的子窗口
for i in range(1, img_num): #
axes[i + i // cols * cols] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i + i // cols * cols + 1, sharex=axes[0],
sharey=axes[0])
for i in range(0, img_num):
axes[i + i // cols * cols + cols] = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i + i // cols * cols + cols + 1)
for i in range(0, img_num): # 這里從1開始,因為第一個在上面已經繪制過了
ax_img, ax_hist, ax_cdf = plot_img_and_hist(images[i],
(axes[i + i // cols * cols], axes[i + i // cols * cols + cols]))
ax_img.set_title(titles[i])
y_min, y_max = ax_hist.get_ylim()
ax_hist.set_ylabel('Number of pixels')
ax_hist.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, y_max, 5))
ax_cdf.set_ylabel('Fraction of total intensity')
ax_cdf.set_yticks(np.linspace(0, 1, 5))
# prevent overlap of y-axis labels
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plt.close(fig)
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = io.imread('catandmouse.png')[:, :, :3]
gray = color.rgb2gray(img)
# 對比度拉伸
p1, p2 = np.percentile(img, (0, 70)) # numpy計算多維數組的任意百分比分位數
rescale_img = exposure.rescale_intensity(img, in_range=(p1, p2))
# 對數變換
# img = util.img_as_float(img)
log_img = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
log_img[:, :, i] = exposure.adjust_log(img[:, :, i], 1.2, False)
# gamma變換
gamma_img = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
gamma_img[:, :, i] = exposure.adjust_gamma(img[:, :, i], 0.7, 2)
# 彩色圖直方圖均衡化
equa_img = np.zeros_like(img, dtype=np.float64) # 注意直方圖均衡化輸出值為float類型的
for i in range(3):
equa_img[:, :, i] = exposure.equalize_hist(img[:, :, i])
# 對比度自適應直方圖均衡化
clahe_img = np.zeros_like(img, dtype=np.float64)
for i in range(3):
clahe_img[:, :, i] = exposure.equalize_adapthist(img[:, :, i])
# 局部直方圖均衡化 效果不好就不放了
selem = morphology.rectangle(50, 50)
loc_img = np.zeros_like(img)
for i in range(3):
loc_img[:, :, i] = filters.rank.equalize(util.img_as_ubyte(img[:, :, i]), footprint=selem)
# Display results
titles = ['img', 'rescale', 'log', 'gamma', 'equalizeHist', 'CLAHE']
images = [img, rescale_img, log_img, gamma_img, equa_img, clahe_img]
plot_all(images, titles, 3)到此,關于“Python+OpenCV怎么解決彩色圖亮度不均衡問題”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。