您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家介紹C語言動態順序表實例代碼怎么編寫,內容非常詳細,感興趣的小伙伴們可以參考借鑒,希望對大家能有所幫助。
順序表是用一段物理地址連續的存儲單元依次存儲數據元素的線性結構。一般情況下用數組存儲。在數組上完成數據的增刪查改。
代碼解析:
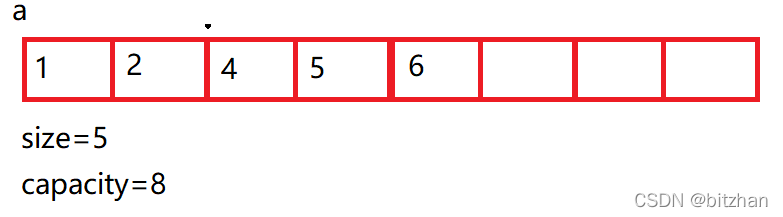
1. 首先對一些頭文件的引用和創建一個結構體,結構體包含一個數組,size表示該數組目前有多少個元素,capacity表示目前數組能存多少個元素。例如:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
DataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;2.創建一個順序表
SL sl;
注意這里的參數得是指針,形參是實參的一份臨時拷貝,所以得把地址傳給函數才能改變值。
void SeqListInit(SL* sl)
{
sl->a = NULL;
sl->size = 0;
sl->capacity = 0;
}寫尾插函數之前我們得先判斷一下數組空間是否夠。例如下面的例子。
所以我們要先檢查空間是否滿了,滿了就擴容
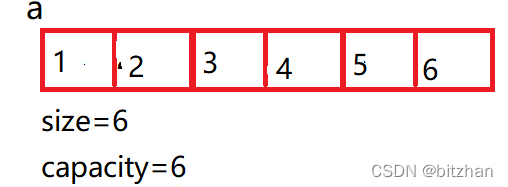
將這個判斷空間函數命名為 void CheckSpace(SL* sl) (這是動態順序表區別于靜態順序表最主要的部分)
void CheckSpace(SL* sl)
{
if (sl->size == sl->capacity)
{
//因為capacity一開始等于0,所以先給capacity一個值
int newcapacity = sl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : sl->capacity * 2;
DataType* tmp = (DataType*)realloc(sl->a, sizeof(DataType)*newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("開辟失敗\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
sl->capacity = newcapacity;
sl->a = tmp;
}
}
}尾插函數:
void SeqListPushBack(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
CheckSpace(sl);
sl->a[sl->size] = x;
sl->size++;
} 
void SeqListPushFront(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
//因為插入的時候都要檢查空間是不是滿了,滿了就擴容
CheckSpace(sl);
for (int end = sl->size - 1; end >= 0; end--)
{
sl->a[end + 1] = sl->a[end];
}
sl->a[0] = x;
sl->size++;
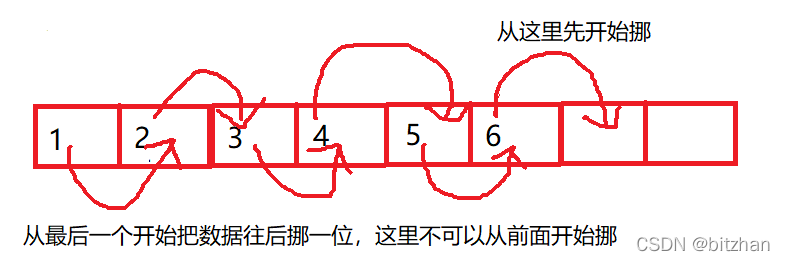
}挪數據對應著for循環的代碼,最后再給數組的第一個位置賦值。別忘了對size+1.
如果size等于0了就說明順序表中沒有數據了,所以
void SeqListPopBack(SL* sl)
{
assert(sl->size > 0);
sl->size--;
}從第二個數據開始整體往前挪以為就可以了。(要從前面開始挪):
void SeqListPopFront(SL* sl)
{
for (int i = 1; i < sl->size; i++)
{
sl->a[i - 1] = sl->a[i];
}
sl->size--;
}首先pos不能小于現有的數據個數。
第二判斷空間,滿了就擴容。
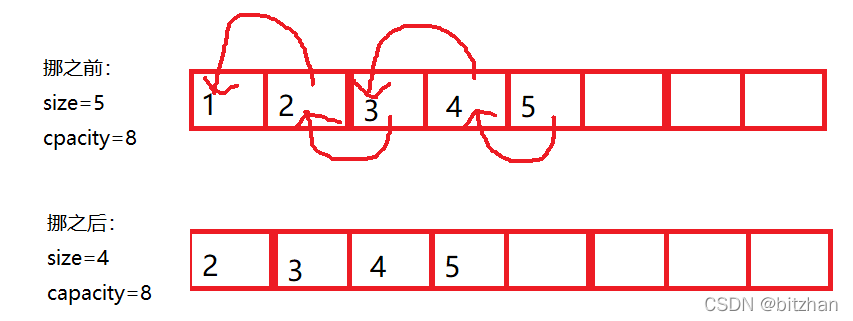
第三:從第pos個位置的數據開始(這里第pos個位置的數據在數組中的下標是pos-1) 將后面的數據整體往后挪一位。
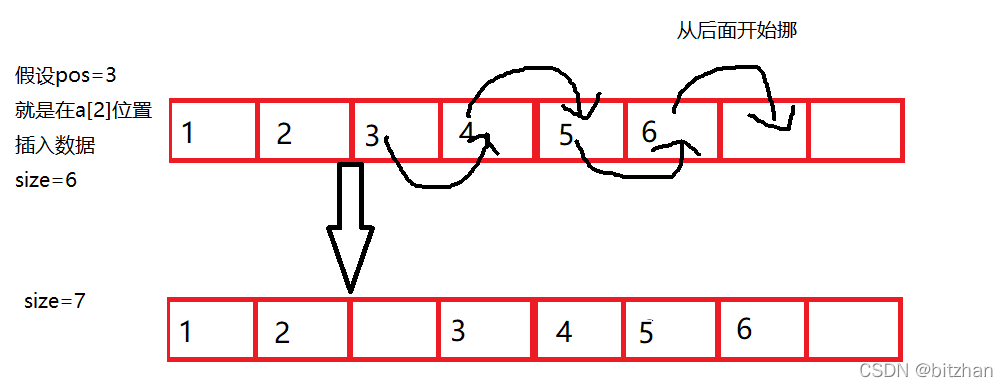
第四:再這個位置賦值,別忘了對size++;
void SeqListInsert(SL* sl, int pos, DataType x)
{
//查看空間
assert(pos <= sl->size);
CheckSpace(sl);
for (int end = sl->size-1; end >= pos-1; end--)//這里不能用sl->size--
{
sl->a[end+1] = sl->a[end];
}
sl->a[pos - 1] = x;
sl->size++;
}首先pos不能小于現有數據個數
第二:將從第pos個位置的數據開始到最后一個數據往前挪一位
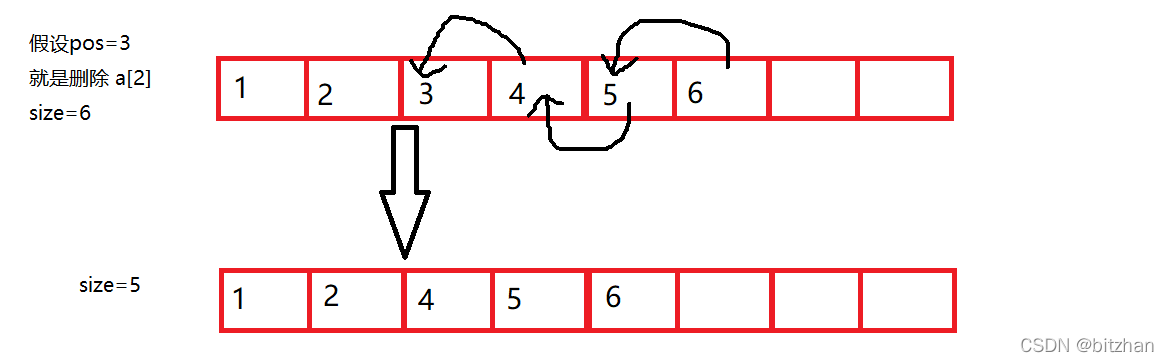
第三:對size--
void SeqListErase(SL* sl, int pos)
{
assert(pos <=sl->size);
for (int i = pos; i < sl->size; i++)
{
sl->a[i - 1] = sl->a[i];
}
sl->size--;
}一:pos不能小于現有數據個數
二:賦值。第pos個位置的數據在數組中下標是pos-1。(因為數組下表從0開始)
void SeqListModify(SL* sl, int pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos <= sl->size);
sl->a[pos - 1] = x;
}遍歷一遍看是否有這個數據,有就返回數據是第幾個元素。(這里我不是返回該數據在數組中的下標,我是返回 下標+1)
這里我沒有考慮如果有兩個一樣的數據的情況。
int SeqListFind(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sl->size;i++)
{
if (sl->a[i] == x)
{
i++;
printf("在第%d個位置\n", i);
return i;
}
}
printf("沒有此數據\n");
return -1;
}釋放sl->a之后要對它置空,因為指針free之后,free函數只是把指針指向的內存空間釋放了,即內存中存儲的值,但是并沒有將指針的值賦為NULL,指針仍然指向這塊內存。
void SeqListDestory(SL* sl)
{
free(sl->a);
sl->a = NULL;
sl->size = 0;
sl->capacity = 0;
}void SeqListPrint(SL* sl)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sl->size;i++)
{
printf("%d ", sl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}菜單寫的比較簡單。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int DataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
DataType* a;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL;
void SeqListInit(SL* sl)
{
sl->a = NULL;
sl->size = 0;
sl->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListPrint(SL* sl)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sl->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", sl->a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void CheckSpace(SL* sl)
{
if (sl->size == sl->capacity)
{
//因為capacity一開始等于0,所以先給capacity一個值
int newcapacity = sl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : sl->capacity * 2;
DataType* tmp = (DataType*)realloc(sl->a, sizeof(DataType)*newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("開辟失敗\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
sl->capacity = newcapacity;
sl->a = tmp;
}
}
}
void SeqListPushBack(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
//看空間是不是滿了,滿了就擴容
//if (sl->size == sl->capacity)
//{
// //因為capacity一開始等于0,所以先給capacity一個值
// int newcapacity = sl->capacity == 0 ? 4 : sl->capacity * 2;
// DataType* tmp = (DataType*)realloc(sl->a, sizeof(DataType)*newcapacity);
// if (tmp == NULL)
// {
// printf("開辟失敗\n");
// exit(-1);
// }
// else
// {
// sl->a = tmp;
// }
//}
//封裝成一個函數
CheckSpace(sl);
sl->a[sl->size] = x;
sl->size++;
}
void SeqListPushFront(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
//因為插入的時候都要檢查空間是不是滿了,滿了就擴容
CheckSpace(sl);
for (int end = sl->size - 1; end >= 0; end--)
{
sl->a[end + 1] = sl->a[end];
}
sl->a[0] = x;
sl->size++;
}
void SeqListPopBack(SL* sl)
{
assert(sl->size > 0);
sl->size--;
}
void SeqListPopFront(SL* sl)
{
for (int i = 1; i < sl->size; i++)
{
sl->a[i - 1] = sl->a[i];
}
sl->size--;
}
void SeqListInsert(SL* sl, int pos, DataType x)
{
//查看空間
assert(pos <= sl->size);
CheckSpace(sl);
for (int end = sl->size - 1; end >= pos - 1; end--)//這里不能用sl->size--
{
sl->a[end + 1] = sl->a[end];
}
sl->a[pos - 1] = x;
sl->size++;
}
void SeqListErase(SL* sl, int pos)
{
assert(pos <= sl->size);
for (int i = pos; i < sl->size; i++)
{
sl->a[i - 1] = sl->a[i];
}
sl->size--;
}
void SeqListModify(SL* sl, int pos, DataType x)
{
assert(pos <= sl->size);
sl->a[pos - 1] = x;
}
int SeqListFind(SL* sl, DataType x)
{
for (int i = 0; i < sl->size; i++)
{
if (sl->a[i] == x)
{
i++;
printf("在第%d個位置\n", i);
return i;
}
}
printf("沒有此數據\n");
return -1;
}
void SeqListDestory(SL* sl)
{
free(sl->a);
sl->a = NULL;
sl->size = 0;
sl->capacity = 0;
}
void menu()
{
printf("******************************\n");
printf("*** 1.尾插數據 2.頭插數據 ***\n");
printf("*** 3.在第pos個位置插入數據***\n");
printf("*** 4.尾刪數據 5.頭刪數據 ***\n");
printf("*** 6.在第pos個位置刪除數據***\n");
printf("*** 7.修改第pos個位置的數據***\n");
printf("*** 8.查找數據 9.打印數據 ***\n");
printf("********** -1.退出 ***********\n");
printf("******************************\n");
}
int main()
{
SL sl;
SeqListInit(&sl);
int option = 0;
int x = 0;
int pos = 1;
while (option != -1)
{
menu();
scanf("%d", &option);
switch (option)
{
case 1:
printf("請輸入要插入的數據,以-1結束:\n");
do
{
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x != -1)
{
SeqListPushBack(&sl, x);
}
} while (x != -1);
break;
case 2:
printf("請輸入要插入的數據,以-1結束:\n");
do
{
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x != -1)
{
SeqListPushFront(&sl, x);
}
} while (x != -1);
break;
case 3:
printf("請輸入要插入的數據,要從第幾個插入,以非正正數結束\n");
do
{
scanf("%d", &x);
scanf("%d", &pos);
if (pos >= 0)
{
SeqListInsert(&sl, pos, x);
}
} while (pos >= 0);
break;
case 4:
SeqListPopBack(&sl);
break;
case 5:
SeqListPopFront(&sl);
break;
case 6:
printf("請輸入要刪除第幾個位置的數據,以非正正數結束\n");
do
{
scanf("%d", &pos);
if (pos>0)
{
SeqListErase(&sl, pos);
}
} while (pos>0);
break;
case 7:
printf("請輸入要修改的數據,要修改第幾個數據,以非正整數結束\n");
do
{
scanf("%d", &x);
scanf("%d", &pos);
if (pos>0)
{
SeqListInsert(&sl, pos, x);
}
} while (pos>0);
break;
case 8:
printf("請輸入需要查找的數據\n");
scanf("%d", &x);
SeqListFind(&sl, x);
break;
case 9:
SeqListPrint(&sl);
break;
case -1:
printf("退出\n");
break;
default:
printf("輸入錯誤,請重新輸入\n");
}
}
SeqListDestory(&sl);
return 0;
}關于C語言動態順序表實例代碼怎么編寫就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,可以學到更多知識。如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。