您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“Android AlertDialog實例分析”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“Android AlertDialog實例分析”吧!
AlertDialog可以在當前的界面上顯示一個對話框,這個對話框是置頂于所有界面元素之上的,能夠屏蔽掉其他控件的交互能力,因此AlertDialog一般是用于提示一些非常重要的內容或者警告信息。
首先,我們來了解一下AlertDialog的大體創建順序。與TextView、Button這些控件稍有不同,AlertDialog并不是初始化(findViewById)之后就直接調用各種方法了。仔細想想AlertDialog的使用場景, 它并不像TextView和Button那些控件似的一般都是固定在界面上,而是在某個時機才會觸發出來(比如用戶點擊了某個按鈕或者斷網了)。所以AlertDialog并不需要到布局文件中創建,而是在代碼中通過構造器(AlertDialog.Builder)來構造標題、圖標和按鈕等內容的。
1.創建構造器AlertDialog.Builder的對象;
2.通過構造器對象調用setTitle、setMessage、setIcon等方法構造對話框的標題、信息和圖標等內容;
3.根據需要調用setPositive/Negative/NeutralButton()方法設置正面按鈕、負面按鈕和中立按鈕;
4.調用構造器對象的create方法創建AlertDialog對象;
5.AlertDialog對象調用show方法,讓對話框在界面上顯示。
注:AlertDialog.Builder自己也有一個show方法,可以顯示對話框,所以上面的第4、第5步可以簡化為一步。
下面,我們就來創建幾種常用的AlertDialog吧。新建一個工程,在activity_main.xml布局文件上放置五個按鈕,點擊按鈕就會有相應的對話框彈出。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.fd.alertdialog.MainActivity"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_normal_dialog" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="普通對話框" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_item_dialog" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="普通列表對話框" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_single_choice" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="單選對話框" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_multi_choice" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="復選對話框" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_custom_dialog" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="自定義對話框" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.fd.alertdialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AlertDialog;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
public static String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private int chedkedItem = 0;
private String name;
private String pwd;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
bindView();
}
private void bindView() {
Button btn_normal_dialog = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_normal_dialog);
Button btn_item_dialog = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_item_dialog);
Button btn_single_choice = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_single_choice);
Button btn_multi_choice = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_multi_choice);
Button btn_custom_dialog = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_custom_dialog);
btn_normal_dialog.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_item_dialog.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_single_choice.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_multi_choice.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_custom_dialog.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_normal_dialog:
tipDialog(); //提示對話框
break;
case R.id.btn_item_dialog:
itemListDialog(); //列表對話框
break;
case R.id.btn_single_choice:
singleChoiceDialog(); //單選對話框
break;
case R.id.btn_multi_choice:
multiChoiceDialog(); //多選對話框
break;
case R.id.btn_custom_dialog:
customDialog(); //自定義對話框
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}代碼比較簡單,這里就不做詳細講解了。接下來看一下各個對話框的具體代碼。
提示對話框應該是最常見的AlertDialog了,其上主要是提示標題,消息主體,底部“取消”、“確定”等按鈕。
/**
* 提示對話框
*/
public void tipDialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setTitle("提示:");
builder.setMessage("這是一個普通對話框,");
builder.setIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
builder.setCancelable(true); //點擊對話框以外的區域是否讓對話框消失
//設置正面按鈕
builder.setPositiveButton("確定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你點擊了確定", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
//設置反面按鈕
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你點擊了取消", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
//設置中立按鈕
builder.setNeutralButton("保密", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "你選擇了中立", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); //創建AlertDialog對象
//對話框顯示的監聽事件
dialog.setOnShowListener(new DialogInterface.OnShowListener() {
@Override
public void onShow(DialogInterface dialog) {
Log.e(TAG, "對話框顯示了");
}
});
//對話框消失的監聽事件
dialog.setOnCancelListener(new DialogInterface.OnCancelListener() {
@Override
public void onCancel(DialogInterface dialog) {
Log.e(TAG, "對話框消失了");
}
});
dialog.show(); //顯示對話框
}具體介紹一下用到的方法吧:
- setTitle:設置對話框的標題,比如“提示”、“警告”等;
- setMessage:設置對話框要傳達的具體信息;
- setIcon: 設置對話框的圖標;
- setCancelable: 點擊對話框以外的區域是否讓對話框消失,默認為true;
- setPositiveButton:設置正面按鈕,表示“積極”、“確認”的意思,第一個參數為按鈕上顯示的文字,下同;
- setNegativeButton:設置反面按鈕,表示“消極”、“否認”、“取消”的意思;
- setNeutralButton:設置中立按鈕;
- setOnShowListener:對話框顯示時觸發的事件;
- setOnCancelListener:對話框消失時觸發的事件。
當然,這些設置并不是非要不可,而是根據自己需要而定。比如標題、圖標這些就可要可不要。
效果如下圖所示:
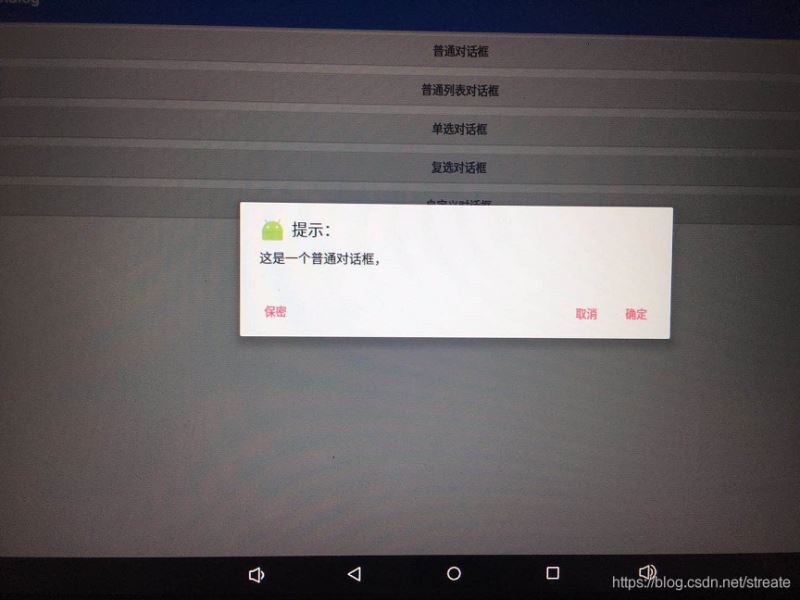
你或許會有這樣的疑問:既然底部那些按鈕的文字和點擊事件的內容都是我們自己來寫的,那不是可以把正面按鈕的內容和反面按鈕的內容互換嗎?看看運行后的效果圖就會發現,反面按鈕是在正面按鈕的左邊的,所以考慮到用戶的操作習慣和代碼的語義,我們最好還是按照API來寫。
列表對話框的內容就是一列顯示內容,需要用到構造器的setItems方法,參數一是列表數據,參數二是點擊監聽接口,我們要實現這樣一個小功能,用戶在點擊某一項時彈出一個Toast提示選中項的內容。
代碼如下所示:
/**
* 列表對話框
*/
private void itemListDialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setTitle("選擇你喜歡的課程:");
builder.setCancelable(true);
final String[] lesson = new String[]{"語文", "數學", "英語", "化學", "生物", "物理", "體育"};
builder.setIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
builder.setIcon(R.mipmap.tab_better_pressed)
.setItems(lesson, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "你選擇了" + lesson[which], Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}).create();
//設置正面按鈕
builder.setPositiveButton("確定", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
//設置反面按鈕
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); //創建AlertDialog對象
dialog.show(); //顯示對話框
}運行后的效果如下所示:
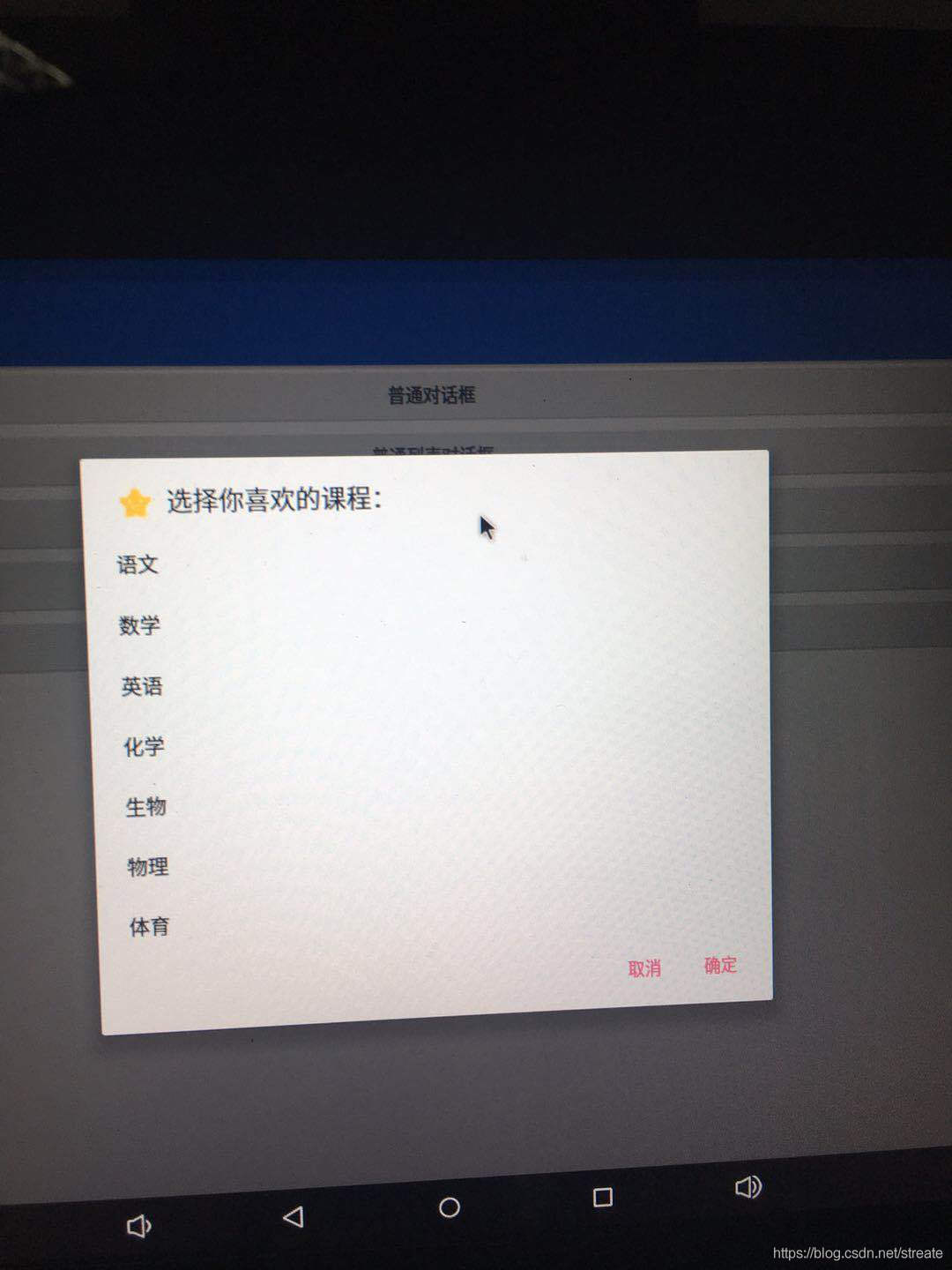
單選對話框的內容就是一個單項選擇列表,需要用到setSingleChoiceItems方法,參數一是列表數據,參數二是默認選中的item,參數三則是點擊監聽接口,我們要實現這樣一個小功能,用戶在選好某一項之后記下其選擇,下次點開對話框時就默認選中該項。
/**
* 單選對話框
*/
public void singleChoiceDialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setTitle("你現在居住地是:");
final String[] cities = {"北京", "上海", "廣州", "深圳", "杭州", "天津", "成都"};
builder.setSingleChoiceItems(cities, chedkedItem, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "你選擇了" + cities[which], Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
chedkedItem = which;
}
});
builder.setPositiveButton("確認", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); //創建AlertDialog對象
dialog.show(); //顯示對話框
}運行后的效果如下所示:
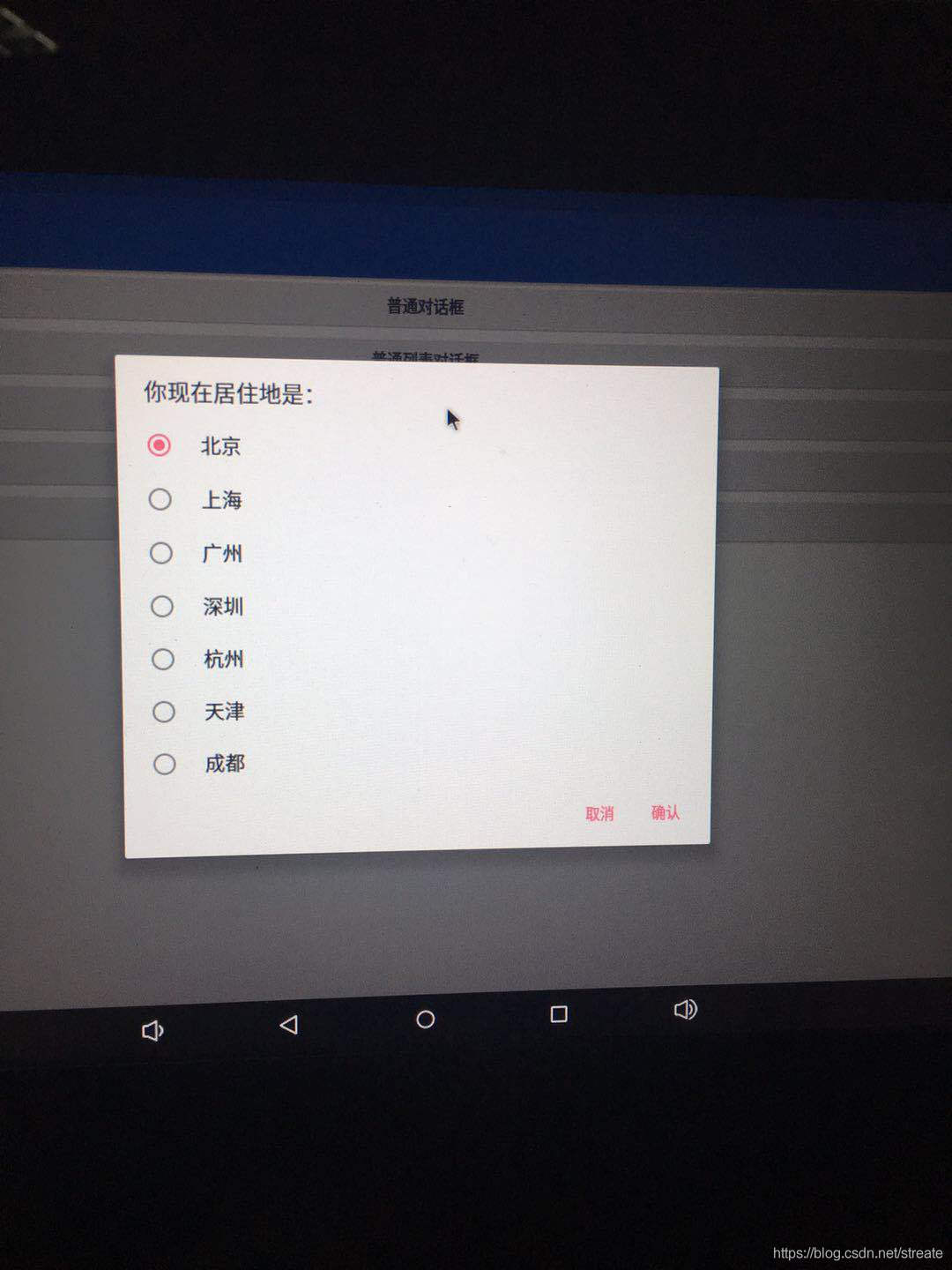
你可能會把checkedItem的賦值放在確定按鈕的點擊事件中,這一看似乎沒什么問題,但是這樣是錯誤的!仔細閱讀谷歌的API文檔就知道了,setSingleChoiceItems 方法中實現的onClick方法中which表示的是當前選中的列表中的item下標,而setPositiveButton和setNegativeButton方法那里的which表示的卻是按鈕的種類,正面按鈕中的which值是-1,反面按鈕的是-2,與列表的item是沒有關系的。
例子中的保存選中item的方法有問題的,當Activity被銷毀之后重新創建的話數據就會丟失,要想持久化保存的話要用sharedpreferences或者數據庫。
復選對話框是一個可以重復選中的列表,與單選對話框有點像,不過調用的是setMultiChoiceItems方法,而且多了一個布爾值參數isChecked,表示當前點擊的item是否被選中。
我們創建一個集合,將點擊選中的item添加到集合中,取消勾選的話就從集合中移除,點擊確認按鈕后就將選中內容顯示出來。
/**
* 復選對話框
*/
public void multiChoiceDialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
builder.setTitle("請選擇你喜歡的顏色:");
final String[] colors = {"紅色", "橙色", "黃色", "綠色", "藍色", "靛色", "紫色"};
final List<String> myColors = new ArrayList<>();
builder.setMultiChoiceItems(colors, null, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) {
if (isChecked) {
myColors.add(colors[which]);
} else {
myColors.remove(colors[which]);
}
}
});
builder.setPositiveButton("確認", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
String result = "";
for (String color : myColors) {
result += color + "、";
}
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "你選擇了: " + result, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("取消", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
myColors.clear();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); //創建AlertDialog對象
dialog.show(); //顯示對話框
}運行后效果圖如下所示:
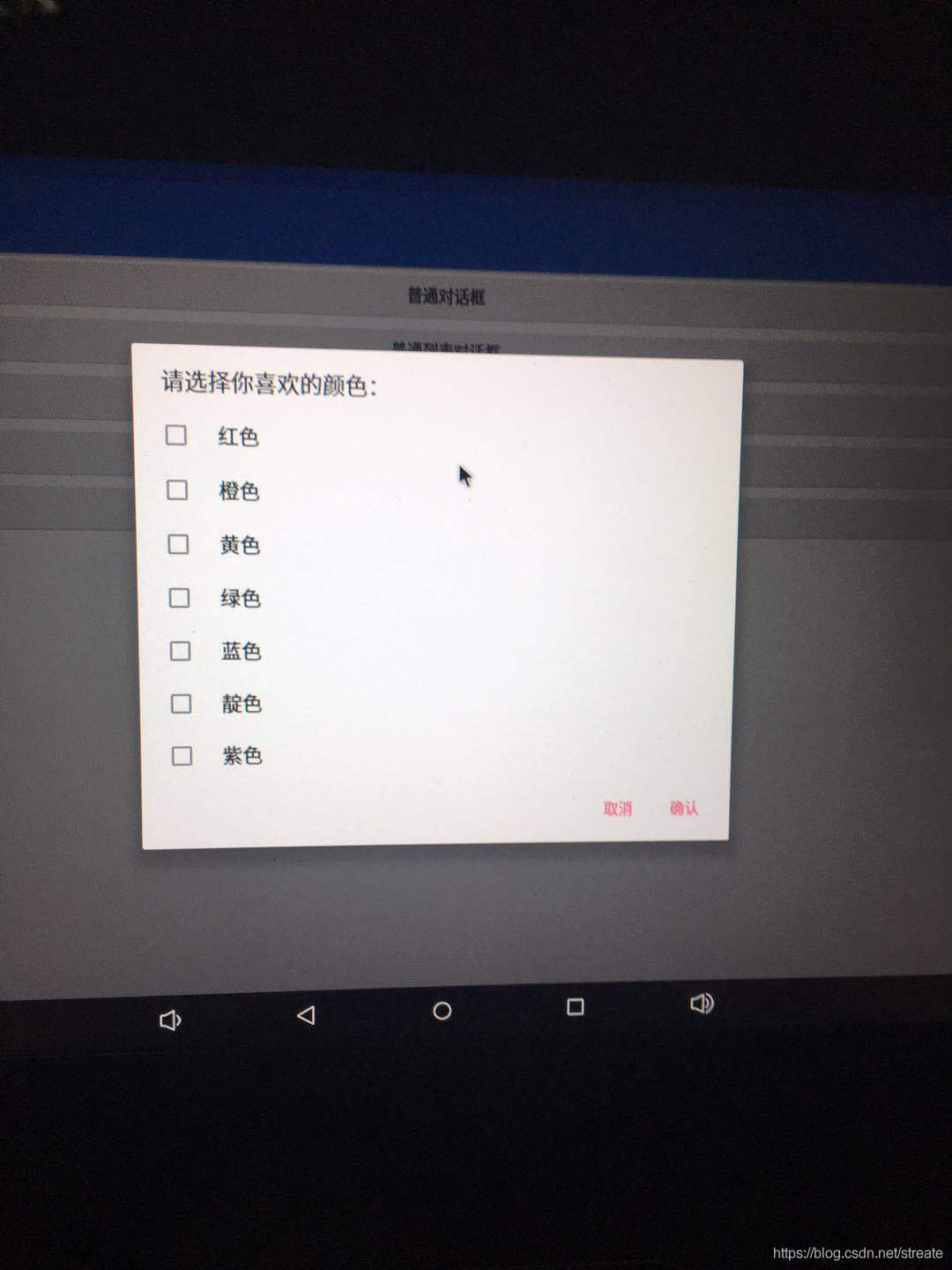
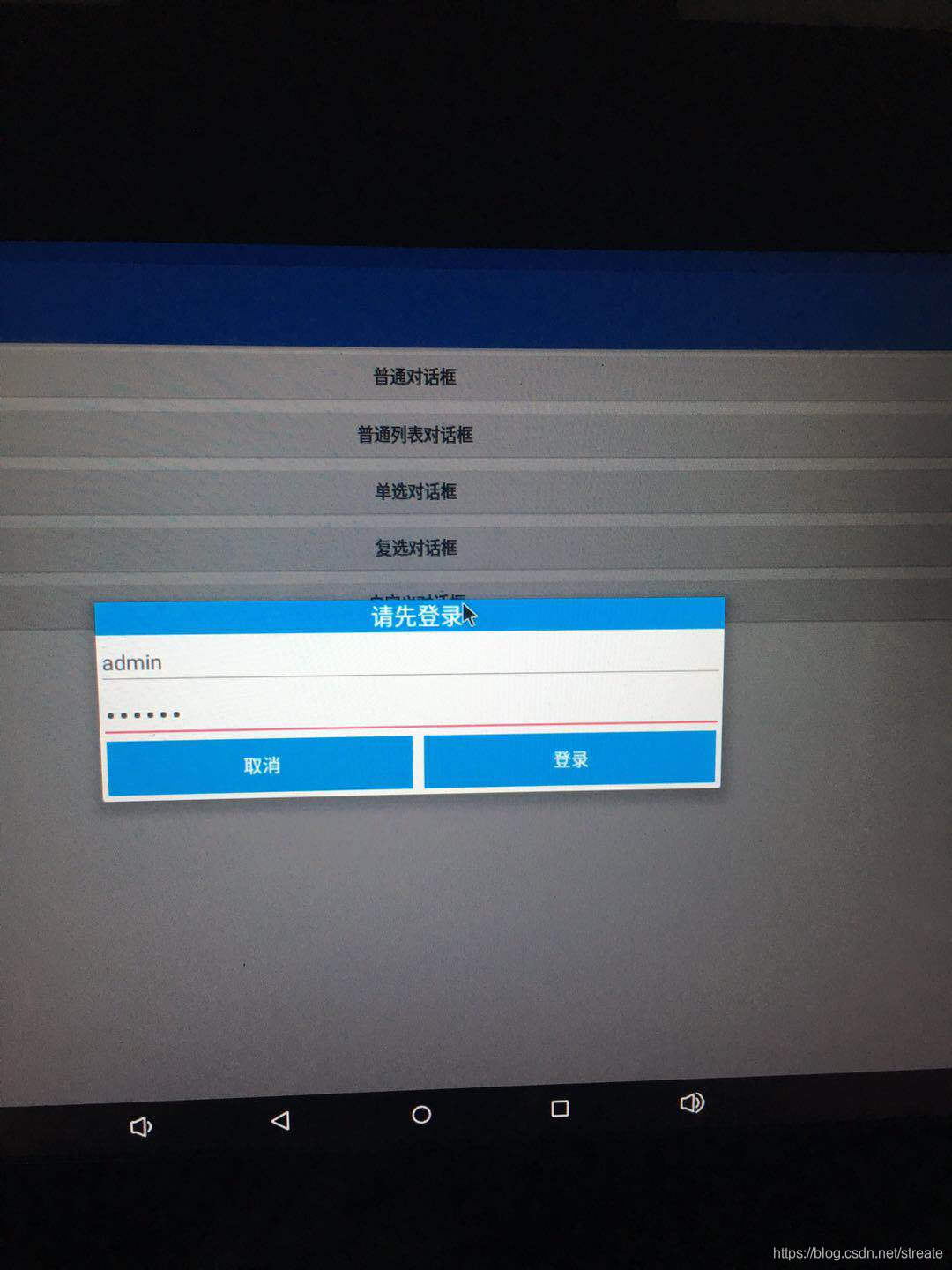
有時候,只顯示簡單的標題和信息是滿足不了我們的要求,比如我們要實現一個登錄對話框的話,那就需要在對話框上放置EditText輸入框了。AlertDialog早就為我們準備好了setView方法,只要往里面放進我們需要的對話框的View對象就可以了。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="請輸入你的賬戶名:" android:textSize="18sp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_pwd" android:inputType="textPassword" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="請輸入密碼:" android:textSize="18sp" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="5dp" android:orientation="horizontal" android:paddingLeft="5dp" android:paddingRight="5dp"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_cancel" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginRight="10dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="#169ee5" android:text="取消" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="16sp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_login" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="#169ee5" android:text="登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="16sp" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
setView方法是通過AlertDialog的對象調用的,所以這里的代碼順序會稍有不同:我們要先創建AlertDialog對象和View對象,然后再去初始化對話框中的控件。
/**
* 自定義登錄對話框
*/
public void customDialog() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
final AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
View dialogView = View.inflate(MainActivity.this, R.layout.activity_custom, null);
dialog.setView(dialogView);
dialog.show();
final EditText et_name = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.et_name);
final EditText et_pwd = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.et_pwd);
final Button btn_login = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btn_login);
final Button btn_cancel = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel);
btn_login.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
name = et_name.getText().toString();
pwd = et_pwd.getText().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name) || TextUtils.isEmpty(pwd)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用戶名或密碼不能為空!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用戶名:" + name + "\n" + "用戶密碼:" + pwd, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
}運行后的效果圖如下所示:
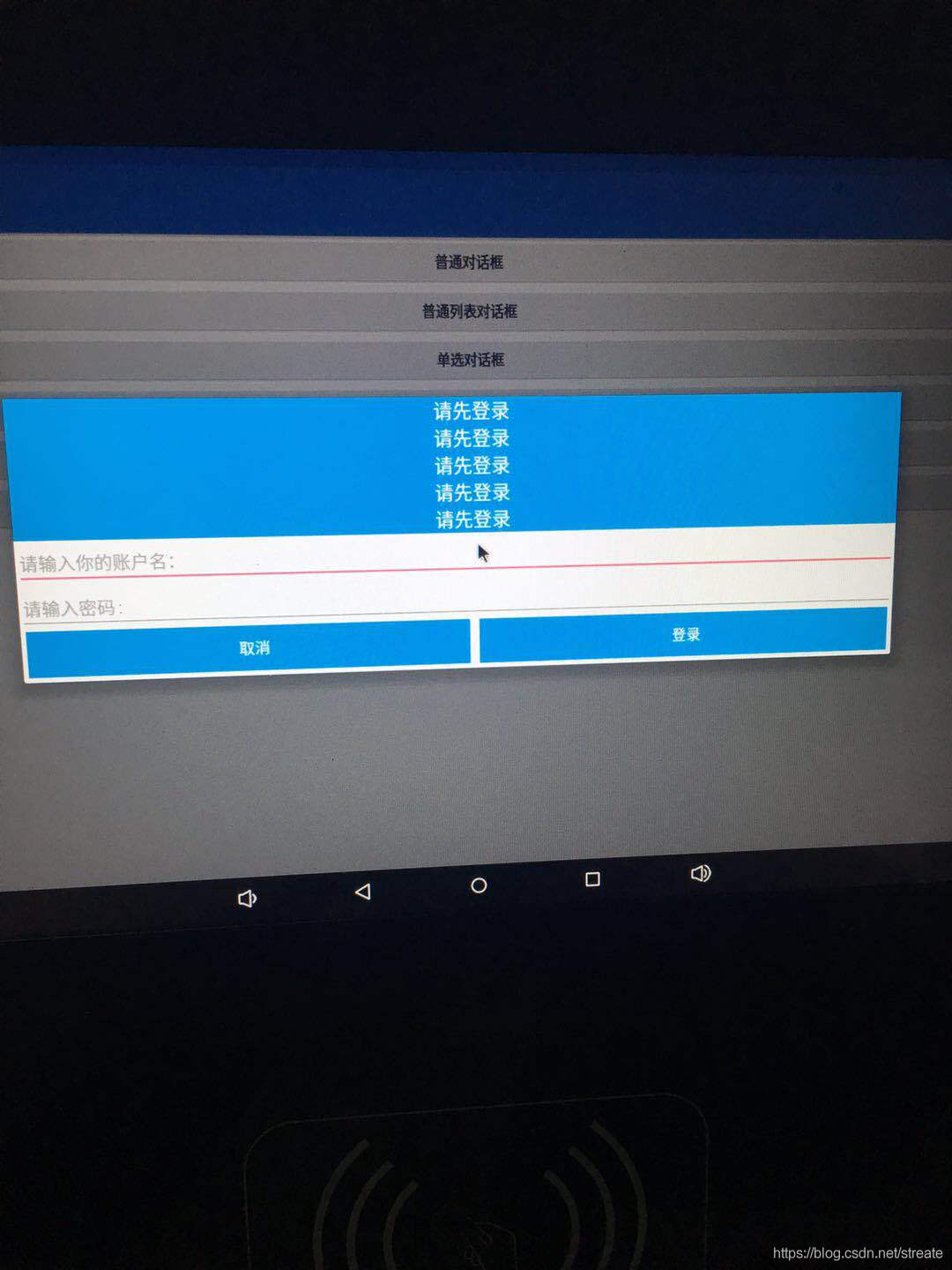
7.1 系統dialog的寬度默認是固定的,即使你自定義布局怎么修改寬度也不起作用,高度可根據布局自動調節。如果想修改彈出窗體大小,可以使用下面這段代碼來實現改變對話框的寬高。這段代碼必須在dialog.show()方法之后調用才有效。
//此處設置位置窗體大小, dialog.getWindow().setLayout(width,height);
創建新的布局文件activity_layout.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView4" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView3" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#169ee5" android:gravity="center" android:text="請先登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="20sp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="請輸入你的賬戶名:" android:textSize="18sp" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/et_pwd" android:inputType="textPassword" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="請輸入密碼:" android:textSize="18sp" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="5dp" android:orientation="horizontal" android:paddingLeft="5dp" android:paddingRight="5dp"> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_cancel" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginRight="10dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="#169ee5" android:text="取消" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="16sp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_login" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="#169ee5" android:text="登錄" android:textColor="@android:color/white" android:textSize="16sp" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
代碼邏輯和6.2的代碼邏輯差不多,只是多了設置對話框寬度的調用 。
/**
* 修改對話框顯示的寬度
*/
public void customDialogDisplay() {
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this);
final AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
View dialogView = View.inflate(MainActivity.this, R.layout.activity_layout, null);
dialog.setView(dialogView);
dialog.show();
dialog.getWindow().setLayout(ScreenUtils.getScreenWidth(this)/4*3, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
final EditText et_name = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.et_name);
final EditText et_pwd = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.et_pwd);
final Button btn_login = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btn_login);
final Button btn_cancel = dialogView.findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel);
btn_login.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
name = et_name.getText().toString();
pwd = et_pwd.getText().toString();
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name) || TextUtils.isEmpty(pwd)) {
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用戶名或密碼不能為空!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
}
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "用戶名:" + name + "\n" + "用戶密碼:" + pwd, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
dialog.dismiss();
}
});
}ScreenUtils工具類代碼
public class ScreenUtils {
/**
* 獲取屏幕高度(px)
*/
public static int getScreenHeight(Context context) {
return context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels;
}
/**
* 獲取屏幕寬度(px)
*/
public static int getScreenWidth(Context context) {
return context.getResources().getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels;
}
}效果圖:
7.2 改變Android Dialog彈出后的Activity背景亮度:
在代碼中修改.lp.alpha大小,值的大小可根據自己要求設置。
// 設置屏幕背景變暗
private void setScreenBgDarken() {
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = getWindow().getAttributes();
lp.alpha = 0.5f;
lp.dimAmount = 0.5f;
getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
}
// 設置屏幕背景變亮
private void setScreenBgLight() {
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = getWindow().getAttributes();
lp.alpha = 1.0f;
lp.dimAmount = 1.0f;
getWindow().setAttributes(lp);
}7.3 如何控制彈窗彈出的位置:
一般都是在屏幕正中間彈出默認,但也可以控制從別的地方彈出,比如從底部彈出,可以這樣寫
private void popFromBottom(Dialog dialog) {
Window win = dialog.getWindow();
win.setGravity(Gravity.BOTTOM); // 這里控制彈出的位置
win.getDecorView().setPadding(0, 0, 0, 0);
WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = win.getAttributes();
lp.width = WindowManager.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
lp.height = WindowManager.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT;
dialog.getWindow().setBackgroundDrawable(null);
win.setAttributes(lp);
}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“Android AlertDialog實例分析”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對Android AlertDialog實例分析這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。