溫馨提示×
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
點擊 登錄注冊 即表示同意《億速云用戶服務條款》
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
小編給大家分享一下Python卷積神經網絡圖片分類框架的示例分析,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后都有所收獲,下面讓我們一起去探討吧!
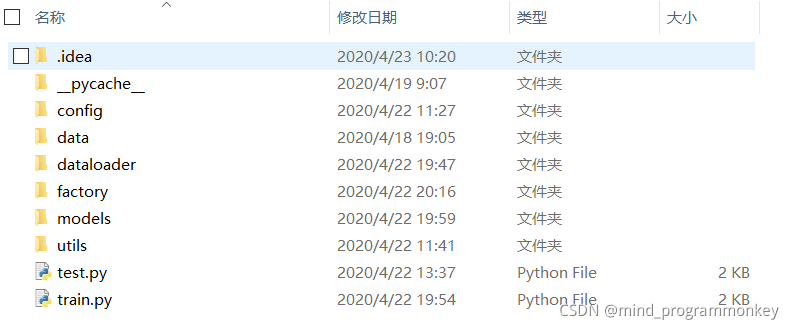
在config文件夾下的config.py中主要定義數據集的位置,訓練輪數,batch_size以及本次選用的模型。
# 定義訓練集和測試集的路徑 train_data_path = "./data/train/" train_anno_path = "./data/train.csv" test_data_path = "./data/test/" # 定義多線程 num_workers = 8 # 定義batch_size大小 batch_size = 8 # 定義訓練輪數 epochs = 20 # 定義k折交叉驗證 k = 5 # 定義模型選擇 # inception_v3_google inceptionv4 # vgg16 # resnet50 resnet101 resnet152 resnext50_32x4d resnext101_32x8d wide_resnet50_2 wide_resnet101_2 # senet154 se_resnet50 se_resnet101 se_resnet152 se_resnext50_32x4d se_resnext101_32x4d # nasnetalarge pnasnet5large # densenet121 densenet161 densenet169 densenet201 # efficientnet-b0 efficientnet-b1 efficientnet-b2 efficientnet-b3 efficientnet-b4 efficientnet-b5 efficientnet-b6 efficientnet-b7 # xception # squeezenet1_0 squeezenet1_1 # mobilenet_v2 # mnasnet0_5 mnasnet0_75 mnasnet1_0 mnasnet1_3 # shufflenet_v2_x0_5 shufflenet_v2_x1_0 model_name = "vgg16" # 定義分類類別 num_classes = 102 # 定義圖片尺寸 img_width = 320 img_height = 320
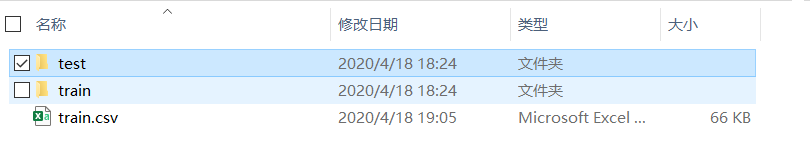
data文件夾存放了train和test圖片信息。
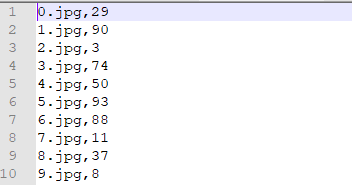
在train.csv中的存放圖片名稱以及對應的標簽
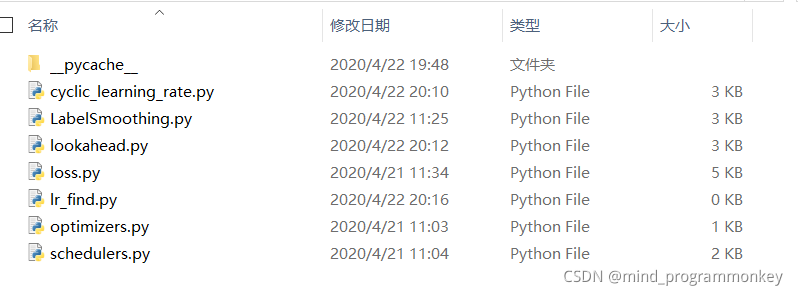
dataloader里面主要有data.py和data_augmentation.py文件。其中一個用于讀取數據,另外一個用于數據增強操作。
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torch.utils.data.dataset import Dataset
import numpy as np
import PIL
from torchvision import transforms
from config import config
import os
import cv2
# 定義DataSet和Transform
# 將df轉換成標準的numpy array形式
def get_anno(path, images_path):
data = []
with open(path) as f:
for line in f:
idx, label = line.strip().split(',')
data.append((os.path.join(images_path, idx), int(label)))
return np.array(data)
# 定義讀取trainData,讀取df文件
# 通過df的idx,來獲取image_path和label
class trainDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data, transform=None):
self.data = data
self.transform = transform
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_path, label = self.data[idx]
img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
#img = cv2.imread(img_path)
#img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
return img, int(label)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
# 通過文件路徑來讀取測試圖片
class testDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, img_path, transform=None):
self.img_path = img_path
if transform is not None:
self.transform = transform
else:
self.transform = None
def __getitem__(self, index):
img = Image.open(self.img_path[index]).convert('RGB')
# img = cv2.imread(self.img_path[index])
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
if self.transform is not None:
img = self.transform(img)
return img
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_path)
# train_transform = transforms.Compose([
# transforms.Resize([config.img_width, config.img_height]),
# transforms.RandomRotation(10),
# transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.3, contrast=0.2),
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
# transforms.ToTensor(), # range [0, 255] -> [0.0,1.0]
# transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# ])
train_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Pad(4, padding_mode='reflect'),
transforms.RandomRotation(10),
transforms.RandomResizedCrop([config.img_width, config.img_height]),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
val_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop([config.img_width, config.img_height]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop([config.img_width, config.img_height]),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])import random
from __future__ import division
import cv2
import numpy as np
from numpy import random
import math
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
# 固定角度隨機旋轉
class FixedRotation(object):
def __init__(self, angles):
self.angles = angles
def __call__(self, img):
return fixed_rotate(img, self.angles)
def fixed_rotate(img, angles):
angles = list(angles)
angles_num = len(angles)
index = random.randint(0, angles_num - 1)
return img.rotate(angles[index])
__all__ = ['Compose','RandomHflip', 'RandomUpperCrop', 'Resize', 'UpperCrop', 'RandomBottomCrop',"RandomErasing",
'BottomCrop', 'Normalize', 'RandomSwapChannels', 'RandomRotate', 'RandomHShift',"CenterCrop","RandomVflip",
'ExpandBorder', 'RandomResizedCrop','RandomDownCrop', 'DownCrop', 'ResizedCrop',"FixRandomRotate"]
def rotate_nobound(image, angle, center=None, scale=1.):
(h, w) = image.shape[:2]
# if the center is None, initialize it as the center of
# the image
if center is None:
center = (w // 2, h // 2)
# perform the rotation
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, scale)
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (w, h))
return rotated
def scale_down(src_size, size):
w, h = size
sw, sh = src_size
if sh < h:
w, h = float(w * sh) / h, sh
if sw < w:
w, h = sw, float(h * sw) / w
return int(w), int(h)
def fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, w, h, size=None):
out = src[y0:y0 + h, x0:x0 + w]
if size is not None and (w, h) != size:
out = cv2.resize(out, (size[0], size[1]), interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
return out
class FixRandomRotate(object):
def __init__(self, angles=[0,90,180,270], bound=False):
self.angles = angles
self.bound = bound
def __call__(self,img):
do_rotate = random.randint(0, 4)
angle=self.angles[do_rotate]
if self.bound:
img = rotate_bound(img, angle)
else:
img = rotate_nobound(img, angle)
return img
def center_crop(src, size):
h, w = src.shape[0:2]
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), size)
x0 = int((w - new_w) / 2)
y0 = int((h - new_h) / 2)
out = fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, size)
return out
def bottom_crop(src, size):
h, w = src.shape[0:2]
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), size)
x0 = int((w - new_w) / 2)
y0 = int((h - new_h) * 0.75)
out = fixed_crop(src, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, size)
return out
def rotate_bound(image, angle):
# grab the dimensions of the image and then determine the
# center
h, w = image.shape[:2]
(cX, cY) = (w // 2, h // 2)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cX, cY), angle, 1.0)
cos = np.abs(M[0, 0])
sin = np.abs(M[0, 1])
# compute the new bounding dimensions of the image
nW = int((h * sin) + (w * cos))
nH = int((h * cos) + (w * sin))
# adjust the rotation matrix to take into account translation
M[0, 2] += (nW / 2) - cX
M[1, 2] += (nH / 2) - cY
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(image, M, (nW, nH))
return rotated
class Compose(object):
def __init__(self, transforms):
self.transforms = transforms
def __call__(self, img):
for t in self.transforms:
img = t(img)
return img
class RandomRotate(object):
def __init__(self, angles, bound=False):
self.angles = angles
self.bound = bound
def __call__(self,img):
do_rotate = random.randint(0, 2)
if do_rotate:
angle = np.random.uniform(self.angles[0], self.angles[1])
if self.bound:
img = rotate_bound(img, angle)
else:
img = rotate_nobound(img, angle)
return img
class RandomBrightness(object):
def __init__(self, delta=10):
assert delta >= 0
assert delta <= 255
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
delta = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image = (image + delta).clip(0.0, 255.0)
# print('RandomBrightness,delta ',delta)
return image
class RandomContrast(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.9, upper=1.05):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
# expects float image
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
# print('contrast:', alpha)
image = (image * alpha).clip(0.0,255.0)
return image
class RandomSaturation(object):
def __init__(self, lower=0.8, upper=1.2):
self.lower = lower
self.upper = upper
assert self.upper >= self.lower, "contrast upper must be >= lower."
assert self.lower >= 0, "contrast lower must be non-negative."
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(self.lower, self.upper)
image[:, :, 1] *= alpha
# print('RandomSaturation,alpha',alpha)
return image
class RandomHue(object):
def __init__(self, delta=18.0):
assert delta >= 0.0 and delta <= 360.0
self.delta = delta
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
alpha = random.uniform(-self.delta, self.delta)
image[:, :, 0] += alpha
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] > 360.0] -= 360.0
image[:, :, 0][image[:, :, 0] < 0.0] += 360.0
# print('RandomHue,alpha:', alpha)
return image
class ConvertColor(object):
def __init__(self, current='BGR', transform='HSV'):
self.transform = transform
self.current = current
def __call__(self, image):
if self.current == 'BGR' and self.transform == 'HSV':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
elif self.current == 'HSV' and self.transform == 'BGR':
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
return image
class RandomSwapChannels(object):
def __call__(self, img):
if np.random.randint(2):
order = np.random.permutation(3)
return img[:,:,order]
return img
class RandomCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
h, w, _ = image.shape
new_w, new_h = scale_down((w, h), self.size)
if w == new_w:
x0 = 0
else:
x0 = random.randint(0, w - new_w)
if h == new_h:
y0 = 0
else:
y0 = random.randint(0, h - new_h)
out = fixed_crop(image, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
class RandomResizedCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size,scale=(0.49, 1.0), ratio=(1., 1.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
def __call__(self,img):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return cv2.resize(img,self.size)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
d=1
for attempt in range(10):
target_area = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1]) * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
if random.random() < 0.5:
new_h, new_w = new_w, new_h
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
x0 = random.randint(0, w - new_w)
y0 = (random.randint(0, h - new_h))//d
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size)
class DownCrop():
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.36,0.81)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.64,1.0)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = h-new_h
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class ResizedCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select,scale=(0.64, 1.0), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
d=1
if attr_idx == 2:
self.scale=(0.36,0.81)
d=2
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.81,1.0)
target_area = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0 * area
# aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# if random.random() < 0.5:
# new_h, new_w = new_w, new_h
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
x0 = (w - new_w)//2
y0 = (h - new_h)//d//2
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
# cv2.imshow('{}_img'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), img)
# cv2.imshow('{}_crop'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), out)
#
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class RandomHflip(object):
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
return cv2.flip(image, 1)
else:
return image
class RandomVflip(object):
def __call__(self, image):
if random.randint(2):
return cv2.flip(image, 0)
else:
return image
class Hflip(object):
def __init__(self,doHflip):
self.doHflip = doHflip
def __call__(self, image):
if self.doHflip:
return cv2.flip(image, 1)
else:
return image
class CenterCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size):
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
return center_crop(image, self.size)
class UpperCrop():
def __init__(self, size, scale=(0.09, 0.64)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
def __call__(self,img):
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/2.0
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = 0
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size)
class RandomUpperCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.09, 0.64), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.1 + (0.3 - 0.1) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
# new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), int((0.5+d)*dw)+1)
y0 = (random.randint(0, h - new_h))//10
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class RandomDownCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.36, 0.81), ratio=(3. / 4., 4. / 3.)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.ratio = ratio
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if random.random() < 0.2:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
if attr_idx == 0:
self.scale=(0.64,1.0)
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.1 + (0.3 - 0.1) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.ratio[0], self.ratio[1])
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
#
# new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
# new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), int((0.5+d)*dw)+1)
y0 = (random.randint((h - new_h)*9//10, h - new_h))
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
# cv2.imshow('{}_img'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), img)
# cv2.imshow('{}_crop'.format(idx2attr_map[attr_idx]), out)
#
# cv2.waitKey(0)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return center_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class RandomHShift(object):
def __init__(self, select, scale=(0.0, 0.2)):
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
do_shift_crop = random.randint(0, 2)
if do_shift_crop:
h, w, _ = img.shape
min_shift = int(w*self.scale[0])
max_shift = int(w*self.scale[1])
shift_idx = random.randint(min_shift, max_shift)
direction = random.randint(0,2)
if direction:
right_part = img[:, -shift_idx:, :]
left_part = img[:, :-shift_idx, :]
else:
left_part = img[:, :shift_idx, :]
right_part = img[:, shift_idx:, :]
img = np.concatenate((right_part, left_part), axis=1)
# Fallback
return img, attr_idx
class RandomBottomCrop(object):
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.4, 0.8)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
for attempt in range(10):
s = random.uniform(self.scale[0], self.scale[1])
d = 0.25 + (0.45 - 0.25) / (self.scale[1] - self.scale[0]) * (s - self.scale[0])
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
dh = h - new_h
x0 = random.randint(int((0.5-d)*dw), min(int((0.5+d)*dw)+1,dw))
y0 = (random.randint(max(0,int(0.8*dh)-1), dh))
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return bottom_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class BottomCrop():
def __init__(self, size, select, scale=(0.4, 0.8)):
self.size = size
self.scale = scale
self.select = select
def __call__(self,img, attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img, attr_idx
h, w, _ = img.shape
area = h * w
s = (self.scale[0]+self.scale[1])/3.*2.
target_area = s * area
new_w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
new_h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area)))
if new_w < w and new_h < h:
dw = w-new_w
dh = h-new_h
x0 = int(0.5*dw)
y0 = int(0.9*dh)
out = fixed_crop(img, x0, y0, new_w, new_h, self.size)
return out, attr_idx
# Fallback
return bottom_crop(img, self.size), attr_idx
class Resize(object):
def __init__(self, size, inter=cv2.INTER_CUBIC):
self.size = size
self.inter = inter
def __call__(self, image):
return cv2.resize(image, (self.size[0], self.size[0]), interpolation=self.inter)
class ExpandBorder(object):
def __init__(self, mode='constant', value=255, size=(336,336), resize=False):
self.mode = mode
self.value = value
self.resize = resize
self.size = size
def __call__(self, image):
h, w, _ = image.shape
if h > w:
pad1 = (h-w)//2
pad2 = h - w - pad1
if self.mode == 'constant':
image = np.pad(image, ((0, 0), (pad1, pad2), (0, 0)),
self.mode, constant_values=self.value)
else:
image = np.pad(image,((0,0), (pad1, pad2),(0,0)), self.mode)
elif h < w:
pad1 = (w-h)//2
pad2 = w-h - pad1
if self.mode == 'constant':
image = np.pad(image, ((pad1, pad2),(0, 0), (0, 0)),
self.mode,constant_values=self.value)
else:
image = np.pad(image, ((pad1, pad2), (0, 0), (0, 0)),self.mode)
if self.resize:
image = cv2.resize(image, (self.size[0], self.size[0]),interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
return image
class AstypeToInt():
def __call__(self, image, attr_idx):
return image.clip(0,255.0).astype(np.uint8), attr_idx
class AstypeToFloat():
def __call__(self, image, attr_idx):
return image.astype(np.float32), attr_idx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class Normalize(object):
def __init__(self,mean, std):
'''
:param mean: RGB order
:param std: RGB order
'''
self.mean = np.array(mean).reshape(3,1,1)
self.std = np.array(std).reshape(3,1,1)
def __call__(self, image):
'''
:param image: (H,W,3) RGB
:return:
'''
# plt.figure(1)
# plt.imshow(image)
# plt.show()
return (image.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255. - self.mean) / self.std
class RandomErasing(object):
def __init__(self, select,EPSILON=0.5,sl=0.02, sh=0.09, r1=0.3, mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]):
self.EPSILON = EPSILON
self.mean = mean
self.sl = sl
self.sh = sh
self.r1 = r1
self.select = select
def __call__(self, img,attr_idx):
if attr_idx not in self.select:
return img,attr_idx
if random.uniform(0, 1) > self.EPSILON:
return img,attr_idx
for attempt in range(100):
area = img.shape[1] * img.shape[2]
target_area = random.uniform(self.sl, self.sh) * area
aspect_ratio = random.uniform(self.r1, 1 / self.r1)
h = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area * aspect_ratio)))
w = int(round(math.sqrt(target_area / aspect_ratio)))
if w <= img.shape[2] and h <= img.shape[1]:
x1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[1] - h)
y1 = random.randint(0, img.shape[2] - w)
if img.shape[0] == 3:
# img[0, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
# img[1, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
# img[2, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = random.uniform(0, 1)
img[0, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[0]
img[1, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[1]
img[2, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[2]
# img[:, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(3, h, w))
else:
img[0, x1:x1 + h, y1:y1 + w] = self.mean[1]
# img[0, x1:x1+h, y1:y1+w] = torch.from_numpy(np.random.rand(1, h, w))
return img,attr_idx
return img,attr_idx
# if __name__ == '__main__':
# import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#
#
# class FSAug(object):
# def __init__(self):
# self.augment = Compose([
# AstypeToFloat(),
# # RandomHShift(scale=(0.,0.2),select=range(8)),
# # RandomRotate(angles=(-20., 20.), bound=True),
# ExpandBorder(select=range(8), mode='symmetric'),# symmetric
# # Resize(size=(336, 336), select=[ 2, 7]),
# AstypeToInt()
# ])
#
# def __call__(self, spct,attr_idx):
# return self.augment(spct,attr_idx)
#
#
# trans = FSAug()
#
# img_path = '/media/gserver/data/FashionAI/round2/train/Images/coat_length_labels/0b6b4a2146fc8616a19fcf2026d61d50.jpg'
# img = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(img_path),cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# img_trans,_ = trans(img,5)
# # img_trans2,_ = trans(img,6)
# print img_trans.max(), img_trans.min()
# print img_trans.dtype
#
# plt.figure()
# plt.subplot(221)
# plt.imshow(img)
#
# plt.subplot(222)
# plt.imshow(img_trans)
#
# # plt.subplot(223)
# # plt.imshow(img_trans2)
# # plt.imshow(img_trans2)
# plt.show()factory里面主要定義了一些學習率,損失函數,優化器等之類的。
models中主要定義了常見的分類模型。
import os
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from torchvision import transforms
import torch.utils.data
from dataloader.data import trainDataset,train_transform,val_transform,get_anno
from factory.loss import *
from models.model import Model
from config import config
import numpy as np
from utils import utils
from factory.LabelSmoothing import LSR
def train(model_type, prefix):
# df -> numpy.array()形式
data = get_anno(config.train_anno_path, config.train_data_path)
# 5折交叉驗證
skf = KFold(n_splits=config.k, random_state=233, shuffle=True)
for flod_idx, (train_indices, val_indices) in enumerate(skf.split(data)):
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
trainDataset(data[train_indices],
train_transform),
batch_size=config.batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=config.num_workers, pin_memory=True
)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
trainDataset(data[val_indices],
val_transform),
batch_size=config.batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=config.num_workers, pin_memory=True
)
#criterion = FocalLoss(0.5)
criterion = LSR()
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = Model(model_type, config.num_classes, criterion, device=device, prefix=prefix, suffix=str(flod_idx))
for epoch in range(config.epochs):
print('Epoch: ', epoch)
model.fit(train_loader)
model.validate(val_loader)
if __name__ == '__main__':
model_type_list = [config.model_name]
for model_type in model_type_list:
train(model_type, "resize")看完了這篇文章,相信你對“Python卷積神經網絡圖片分類框架的示例分析”有了一定的了解,如果想了解更多相關知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝各位的閱讀!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。