您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹了Go語言中CGO怎么用,具有一定借鑒價值,感興趣的朋友可以參考下,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章之后大有收獲,下面讓小編帶著大家一起了解一下。
package main
//
// 引用的C頭文件需要在注釋中聲明,緊接著注釋需要有import "C",且這一行和注釋之間不能有空格
//
/*
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void myprint(char* s) {
printf("%s\n", s);
}
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
func main() {
//使用C.CString創建的字符串需要手動釋放。
cs := C.CString("Hello World\n")
C.myprint(cs)
C.free(unsafe.Pointer(cs))
fmt.Println("call C.sleep for 3s")
C.sleep(3)
return
}運行:

hello.c
#include <stdio.h>
void hello()
{
printf("hello world\n");
}hello.h
#ifndef HELLO_H #define HELLO_H void hello(void); #endif
編譯:
gcc -c hello.c ar -cru libhello.a hello.o
package main
//使用#cgo定義庫路徑
/*
#cgo CFLAGS: -I .
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L . -lhello
#include "hello.h"
*/
import "C"
func main() {
C.hello()
}運行:

main.go
package main
//
//#include <stdio.h>
//int add(int a, int b);
//
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
)
//當使用export的時候,在同一個文件中就不能再定義其它的c函數了,不然會報錯。
//使用export導出函數給c語言調用。
//export GoAdd
func GoAdd(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
func main() {
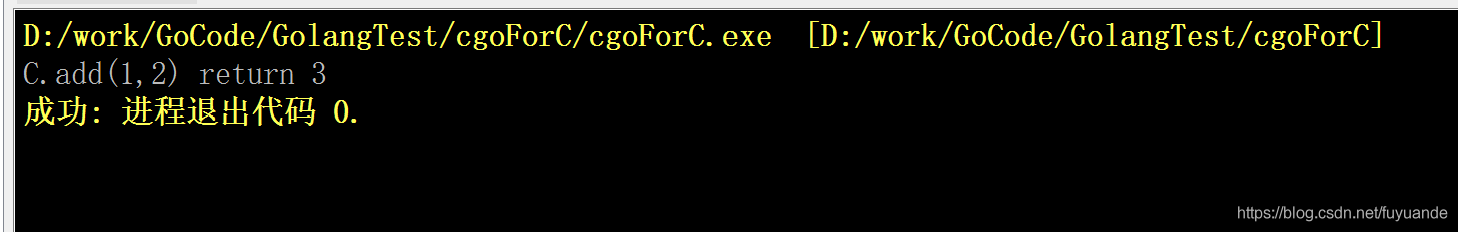
a := C.add(1, 2)
fmt.Printf("C.add(1,2) return %d\n", a)
}cfunc.go
package main
//
//int GoAdd(int a, int b);
//
//int add(int a, int b)
//{
// return GoAdd(a,b);
//}
//
import "C"運行:
還有一種使用方式,這種是我使用比較多的。就是傳遞函數指針,因為GO函數無法取址,因此需要寫個中間函數做個轉換操作,例子如下:
clibrary.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "clibrary.h"
//參數是函數指針
void some_c_func(callback_fcn callback)
{
int arg = 2;
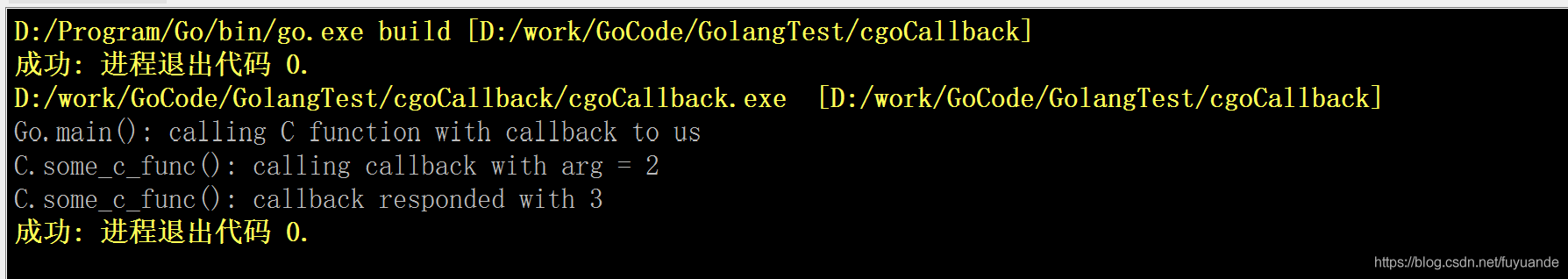
printf("C.some_c_func(): calling callback with arg = %d\n", arg);
int response = callback(2);
printf("C.some_c_func(): callback responded with %d\n", response);
}clibrary.h
#ifndef CLIBRARY_H #define CLIBRARY_H //定義函數指針 typedef int (*callback_fcn)(int); void some_c_func(callback_fcn); #endif
Go code:
package main
/*
#cgo CFLAGS: -I .
#cgo LDFLAGS: -L . -lclibrary
#include "clibrary.h"
int callOnMeGo_cgo(int in); // 聲明
*/
import "C"
import (
"fmt"
"unsafe"
)
//export callOnMeGo
func callOnMeGo(in int) int {
return in + 1
}
func main() {
fmt.Printf("Go.main(): calling C function with callback to us\n")
//使用unsafe.Pointer轉換
C.some_c_func((C.callback_fcn)(unsafe.Pointer(C.callOnMeGo_cgo)))
}中間函數:
package main
/*
#include <stdio.h>
int callOnMeGo(int);
// The gateway function
int callOnMeGo_cgo(int in)
{
printf("C.callOnMeGo_cgo(): called with arg = %d\n", in);
//調用GO函數
return callOnMeGo(in);
}
*/
import "C"運行:
開發注意事項:
1. 在注釋和import”C”之間不能有空行
2. 使用C.CString函數轉換GoString為CString時要手動釋放該字符串。
3. CGO不支持使用變參的函數,例如printf,如果要使用的話,可以寫個包裹函數m'yprintf,使用傳參的方式調用。
4. Go支持使用//export導出函數給C使用,但是有一點需要注意就是不能在export導出的同一個文件里定義c函數,不然會出現
multiple definition of "xxx"編譯錯誤,如果函數非常tiny的話,還有一個方法是使用static inline 來聲明該函數,如下:
package gocallback
import (
"fmt"
"sync"
)
/*
extern void go_callback_int(int foo, int p1);
// normally you will have to define function or variables
// in another separate C file to avoid the multiple definition
// errors, however, using "static inline" is a nice workaround
// for simple functions like this one.
static inline void CallMyFunction(int foo) {
go_callback_int(foo, 5);
}
*/
import "C"感謝你能夠認真閱讀完這篇文章,希望小編分享的“Go語言中CGO怎么用”這篇文章對大家有幫助,同時也希望大家多多支持億速云,關注億速云行業資訊頻道,更多相關知識等著你來學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。