您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要為大家展示了“java基礎之string類的示例分析”,內容簡而易懂,條理清晰,希望能夠幫助大家解決疑惑,下面讓小編帶領大家一起研究并學習一下“java基礎之string類的示例分析”這篇文章吧。
對于String在之前已經學習過了基本使用,就是表示字符串,那么當時使用的形式采取了直接賦值:
public class StringText{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str =new String( "Hello"); //構造方法
System.out.print(str);
}
}對于String而言肯定是一個類,那么程序之中出現的str應該就是這個類的對象,那么就證明以上的賦值操作實際上就表示要為String類的對象進行實例化操作。
但String畢竟是一個類,那么類之中一定會存在構造方法,String類的構造:
public class StringText{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str =new String( "Hello"); //構造方法
System.out.print(str);
}
}發現現在也可以通過構造方法為String類對象實例化。
如果現在有兩個int型變量,如果想要知道是否相等,使用“==”進行驗證。
public class StringText{
public static void main(String args[]){
int x = 10;
int y = 10;
System.out.print(x==y);
}
}換成String
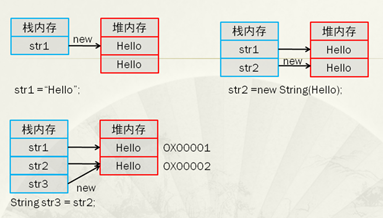
public class StringText{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = new String("Hello");
String str3 = str2; //引用傳遞
System.out.print(str1== str2); //false
System.out.print(str1== str3); //false
System.out.print(str2== str3); //ture
}
}
現在使用了“==”的確是完成了相等的判斷,但是最終判斷的是兩個對象(現在的對象是字符串)判斷是否相等,屬于數值判斷------判斷的是兩個對象的內存地址數值,并沒有判斷內容,而想要完成字符串內容的判斷,則就必須使用到String類的操作方法:public Boolean equals(String str)(將方法暫時變了)
public class StringText{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = new String("Hello");
String str3 = str2; //引用傳遞
System.out.print(str1.equals(str2)); //ture
System.out.print(str2.equals(str3)); //ture
System.out.print(str2.equals(str3)); //ture
}
}如果在程序之中定義了字符串(使用“””),那么這個就表示一個String對象,因為在各個語言之中沒有關于字符串數據類型的定義,而Java將其簡單的處理了,所以感覺上存在了字符串數據類型。
**范例:**驗證字符串是對象的概念
public class NiMing{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Hello";
System.out.print("Hello".equals(str)); //通過字符串調用方法
}
}匿名對象可以調用類之中的方法與屬性,以上的字符串可以調用了equals()方法,那么它一定是一個對象。
**小技巧:**關于字符串與字符串常量的判斷
例如:在實際工作之中會有這樣一種操作,要求用戶輸入一個內容,之后判斷此內容是否與指定內容相同。
public class NiMing{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Hello";
if(str.equals("Hello")){
System.out.print("條件滿足");
}
}
}但,既然數據是用戶自己輸入,那么就有可能沒有輸入內容。
public class TestDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = null;
if(str.equals("Hello")){
System.out.print("條件滿足");
}
}
}
//報錯
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NullPointerException
at NiMing.main(TestDemo1.java:4)
//現在將代碼反過來操作:
public class TestDemo1{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = null;
if("Hello".equals(str)){
System.out.print("條件滿足");
}
}
}因為字符串常量是匿名對象,匿名對象不可能為null。
String str = "Hello"; //定義字符串
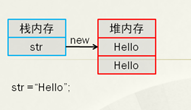
發現現在只開辟額一塊堆內存空間和一塊棧內存空間。
String str = new String("Hello");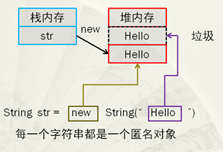
使用構造方法賦值的方式開辟的字符串對象,實際上會開辟兩塊空間,其中有一塊空間就愛那個成為垃圾。
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = new String("Hello");
String str2 = "Hello"; //入池
String str3 = "Hello"; //使用池中對象
System.out.print(str1==str2); //false
System.out.print(str2==str3); // ture
System.out.print(str1==str3); // false
}
}通過上面的程序可以發現,使用構造方法實例化String對象,不會入池,只能自己使用。可是在String類之中為了方便操作提供了一種稱為手工入池的方法:public String intern()。
public class TestDemo2{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = new String("Hello").intern(); //手工入池
String str2 = "Hello"; //入池
String str3 = "Hello"; //使用池中對象
System.out.print(str1==str2); //ture System.out.print(str2==str3); //ture
System.out.print(str1==str3); //ture
}
}字符串類的操作特點決定:字符串不可能去修改里面的內容。
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Hello";
str += "World";
str += "!!!";
System.out.print(str);
}
}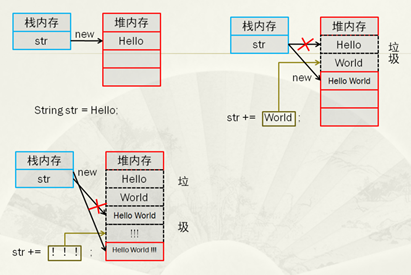
通過以上的代碼可以發現,字符串內容的更改,實際上改變的是字符串對象的引用過程,那么一下的代碼應該盡量避免:
public class TestDemo3{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Hello";
for(int x=0;x<1000;x++){
str += x;
}
System.out.print(str);
}
}字符串賦值只用直接賦值模式進行完成
字符串的比較采用equals()方法進行實現字
符串沒有特殊的情況不要改變太多
任何一個類的文檔由如下幾個部分組成
類的相關定義,包括這個類的名字,有哪些父類,有哪些接口。
類的相關簡介。包括基本使用
成員摘要(field):屬性就是一種成員,會列出所有成員的信息項
構造方法說明(Constructor),列出所有構造方法的信息
方法信息(Method),所有類中定義好的可以使用的方法
成員、構造、方法的詳細信息
字符串就是一個字符數組,所有在String類中有字符串轉變為字符數組,字符數組轉換為字符串的方法。
| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public String(char[] value) | 構造 | 將字符數組中的所有內容變為字符串 |
| public String(char[] value, int offset, int count) | 構造 | 將字符數組中的所有內容變為字符串 offset-開始 count-個數 |
| public char charAt(int index) | 普通 | 返回char指定字符的索引值 |
| public char[] toCharArray() | 普通 | 將字符串轉化為字符數組 |
public class TestDemo4{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Hello";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0));
//如果現在超過了字符串的長度,則會產生異常StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println(str.charAt(10));
}
}字符串和字符數組的轉化是重點
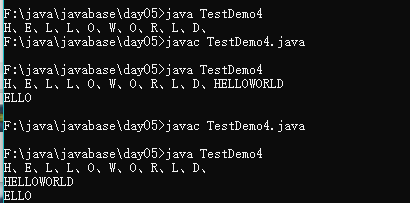
//字符串轉化為字符數組
public class TestDemo4{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "helloworld";
char data [] = str.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){
data[i] -= 32; //轉大寫字母簡化模式更簡單
System.out.print(data[i] + "、");
}
}
}//字符數組轉化為字符串
public class TestDemo4{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "helloworld";
char data [] = str.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){
data[i] -= 32; //轉大寫字母簡化模式更簡單
System.out.print(data[i] + "、");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println(new String(data));//字符串數組全部轉化為字符數組
System.out.println(new String(data,1,4));//字符串數組部分轉化為字符數組
}
}
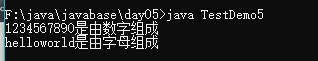
判斷字符串是否由數字組成
public class TestDemo5{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = "helloworld";
String str = "1234567890";
Judgenum(str);
Judgenum(str1);
}
public static void Judgenum(String str){
char data [] = str.toCharArray();
boolean judge = true;
for(int i = 0; i < data.length; i++){
if(data[i]>= '0' && data[i]<= '9'){
judge = false;
}
}
if(judge){
System.out.println(str+"是由字母組成");
}else
System.out.println(str+"是由數字組成");
}
}
| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public String(byte[] bytes) | 構造 | 將部分字節數組變為字符串 |
| public String(byte[] bytes, int offset,int length) | 構造 | 將部分字節數組變為字符串 bytes——要解碼為字符的字節 offset——要解碼的第一個字節的索引 length——要解碼的字節數 |
| public byte[] getBytes() | 普通 | 將字符串變為字節數組 |
| public byte[] getBytes(String charsetName) throws UnsupportedEncodingException | 普通 | 編碼轉換編碼 |
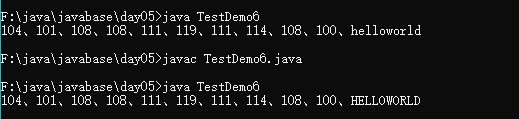
//將字符串通過字節流轉化為大寫
public class TestDemo6{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "helloworld";
byte data [] = str.getBytes();//字符串轉換為字節數組
for(int i = 0; i < data.length ; i++){
System.out.print(data[i]+"、");
data[i] -= 32;
}
System.out.println(new String(data));//字節數組轉化為字符串
}
}
一般情況下,在程序之中如果想要操作字節數組只有兩種情況:
**1、**需要進行編碼的轉化;
2、 數據要進行傳輸的時候。
**3、**二進制文件適合字節處理
| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public boolean equals(String anObject) | 普通 | 區分大小寫比較 |
| public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | 普通 | 不區分大小寫比較 |
| public int compareTo(String anotherString) | 普通 | 比較兩個字符串的大小關系 |
如果現在要比較兩個字符串的大小關系,那么就必須使用comepareTo()方法完成,而這個方法返回int型數據,而這個int型數據有三種結果:大于(返回結果大于0)、小于(返回結果小于0)、等于(返回結果為0).
public class CompareTo{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str1 = "HELLO";
String str2= "hello";
System.out.println(str1.compareTo(str2));
}
}| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public boolean contains(String s) | 普通 | 判斷一個子字符串是否村存在 |
| public int indexOf(String str) | 普通 | 返回字符串中第一次出現字符串的索引 |
| public int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 普通 | 從指定地方開始查找子字符串的位置 |
| public int lastIndexOf(String str) | 普通 | 從后向前查找子字符串的位置 |
| public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 普通 | 從指定位置由后向前查找 |
| public boolean startsWith(String prefix) | 普通 | 從頭判斷是否以某字符串開頭 |
| public boolean startsWith(String prefix,int toffset) | 普通 | 從指定位置判斷是否以字符串開頭 |
| public boolean endsWith(String suffix) | 普通 | 判斷以某字符串結尾 |
public class TestDemo7{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "helloworld";
System.out.println(str.contains("world")); //true
//使用indexOf()進行查找
System.out.println(str.indexOf("world"));
System.out.println(str.indexOf("java"));
//JDK1,5之前這樣使用
if(str.indexOf() != -1){
System.out.println("可以查找到指定的內容");
}
}
}基本上所有的查找現在都是通過contains()方法完成。
需要注意的是,如果內容重復indexOf()它只能返回查找的第一個位置。
在進行查找的時候往往會判斷開頭或結尾。
public class TestDemo7{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "**@@helloworld##";
System.out.println(str.startsWith("**")); //true
System.out.println(str.startsWith("@@",2)); //true
System.out.println(str.endsWith("##")); //true
}
}| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public String replaceAll(String regex,String replacement) | 普通 | 替換所有的內容 |
| public String replaceFirst(String regex,String replacement) | 普通 | 替換首內容 |
public class TestDemo7{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "**@@helloworld##";
System.out.println(str.replaceAll("l","_")); //**@@he__owor_d##
}
}| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public String[] split(String regex) | 普通 | 將字符串全部拆分 |
| public String[] split(String regex,int limit) | 普通 | 將字符串部分拆分 |
public class TestDemo8{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "hello world hello zsr hello csdn";
String result [] = str.split(" "); //按照空格進行拆分
//hello、world、hello、zsr、hello、csdn、
for(int i = 0; i < result.length ; i++){
System.out.print(result[i]+"、");
}
System.out.println();
//部分拆分
String result1 [] = str.split(" ",3); //按照空格進行拆分
//第二個參數 從第幾個位置開始不進行拆分操作
//hello、world、hello zsr hello csdn、
for(int i = 0; i < result1.length ; i++){
System.out.print(result1[i]+"、");
}
}
}//拆分ip地址
public class TestDemo9{
//吳國發現內容無法拆分,就需要用到“\\”進行轉義
public static void main(String args[]){
//120
//11
//219
//223:57114
String str = "120.11.219.223:57114";
String result [] = str.split("\\.");
for(int i = 0 ; i < result.length ; i++){
System.out.println(result[i]);
}
}
}| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| public String substring(int beginIndex) | 普通 | 從指定位置截取到結尾 |
| public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex) | 普通 | 截取部分內容 |
public class TestDemo10{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "helloworld";
//world
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
//hello
System.out.println(str.substring(0,5));
}
}| 方法名稱 | 類型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Public String trim() | 普通 | 去掉左右空格,保留中間空格 |
| public String toUpperCase() | 普通 | 將全部字符串轉大寫 |
| public String toLowerCase() | 普通 | 將全部字符串轉小寫 |
| public String intern() | 普通 | 字符串入對象池 |
| public String concat() | 普通 | 字符串連接 |
1.現在給出了如下一個字符串格式:“姓名:成績|姓名:成績|姓名:成績”,例如:給定的字符串是:“Tom:90|Jerry:80|tony:89”,要求可以對以上數據進行處理,將數據按照如下的形式顯示:姓名:Tom,成績:90;
public class Exam1{
public static void main(String args[]){
String str = "Tom:90|Jerry:80|tony:89";
String data [] = str.split("\\|");
for(int i = 0 ; i < data.length ; i++){
String result [] = data[i].split(":");
System.out.print("姓名 = " + result[0] + ",");
System.out.println("年齡 = " + result[1]);
}
/*姓名 = Tom,年齡 = 90
姓名 = Jerry,年齡 = 80
姓名 = tony,年齡 = 89*/
}
}2.給定一個email地址,要求驗證其是否正確,提示:可以簡單的驗證一下,重點驗證“@”和“.”。標準如下:
1.email長度不短于5
2.@和.不能做開頭或結尾
3.@和.順序要有定義
public class Exam2{
public static void main(String args[]){
String email = "1016942589.@qqcom";
char date[] = email.toCharArray();
if (date.length>5&&email.startsWith("@")==false
&& email.startsWith(".")==false && email.endsWith("@")==false
&&email.endsWith(".")==false && email.indexOf(".") >email.indexOf("@"))
{System.out.println("正確");
}else{System.out.println("錯誤");}
}
}以上是“java基礎之string類的示例分析”這篇文章的所有內容,感謝各位的閱讀!相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望分享的內容對大家有所幫助,如果還想學習更多知識,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。