您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Java阻塞隊列的原理和使用場景”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
在數據結構中,隊列遵循FIFO(先進先出)原則。在java中,Queue接口定義了定義了基本行為,由子類完成實現,常見的隊列有ArrayDeque、LinkedList等,這些都是非線程安全的,在java 1.5中新增了阻塞隊列,當隊列滿時,添加元素的線程呈阻塞狀態;當隊列為空時,獲取元素的線程呈阻塞狀態。
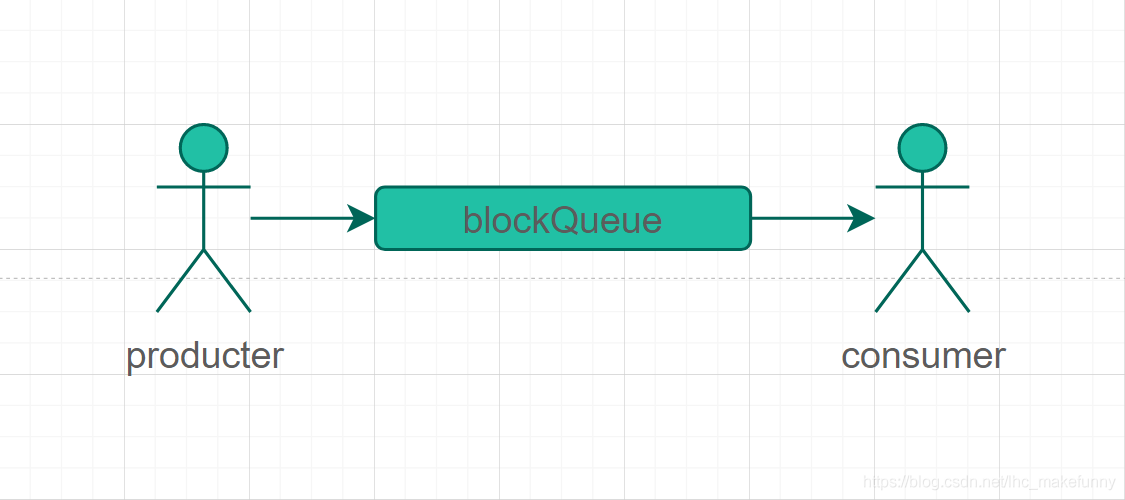
生產者將元素添加到隊列中,消費中獲取數據后完成數據處理。兩者通過隊列解決了生產者和消費者的耦合關系;當生產者的生產速度與消費者的消費速度不一致時,可以通過大道緩沖的目的。
線程池
在線程池中,當工作線程數大于等于corePoolSize時,后續的任務后添加到阻塞隊列中;
在java中,BlockingQueue接口定義了阻塞隊列的行為,常用子類是ArrayBlockingQueue和LinkedBlockingQueue。
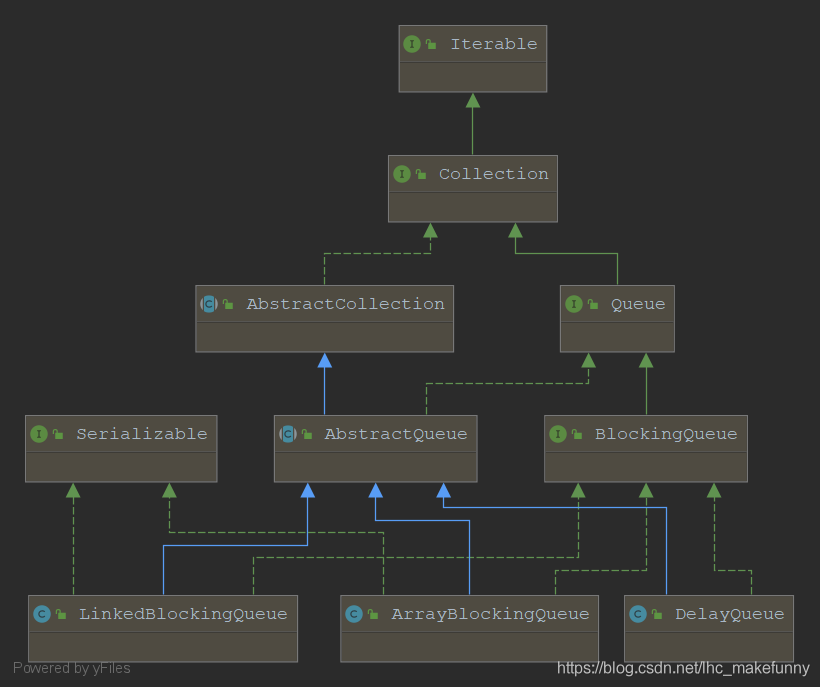
BlockingQueue繼承了Queue接口,擁有其全部特性。在BlockingQueue的java doc中對其中的操作方法做了匯總
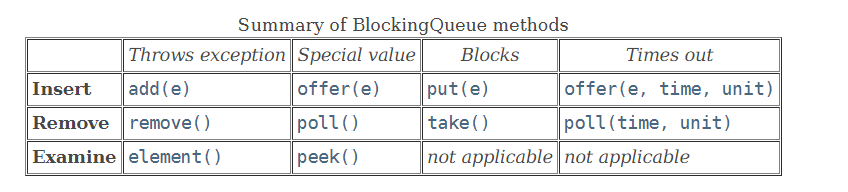
插入元素
add(e):當隊列已滿時,再添加元素會拋出異常IllegalStateException
offer(e):添加成功,返回true,否則返回false
put:(e):當隊列已滿時,再添加元素會使線程變為阻塞狀態
offer(e, time,unit):當隊列已滿時,在末尾添加數據,如果在指定時間內沒有添加成功,返回false,反之是true
刪除元素
remove(e):返回true表示已成功刪除,否則返回false
poll():如果隊列為空返回null,否則返回隊列中的第一個元素
take():獲取隊列中的第一個元素,如果隊列為空,獲取元素的線程變為阻塞狀態
poll(time, unit):當隊列為空時,線程被阻塞,如果超過指定時間,線程退出
檢查元素
element():獲取隊頭元素,如果元素為null,拋出NoSuchElementException
peek():獲取隊頭元素,如果隊列為空返回null,否則返回目標元素
底層基于數組的有界阻塞隊列,在構造此隊列時必須指定容量;
構造函數
// 第一個
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
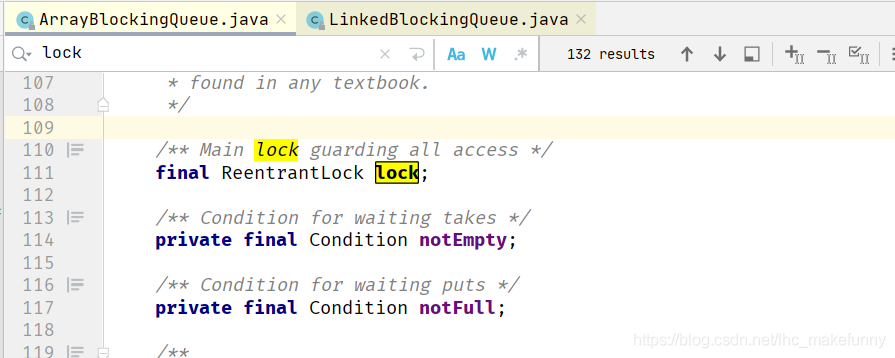
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 第二個
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
// 第三個
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}capacity:隊列的初始容量
fair:線程訪問隊列的公平性。如果為true按照FIFO的原則處理,反之;默認為falsec:
已有元素的集合,類型于合并兩個數組
put()方法
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 檢查元素是否為null
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 獲取鎖
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果當前隊列為空,變為阻塞狀態
while (count == items.length)
notFull.await();
// 反之,就添加元素
enqueue(e);
} finally {
// 解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
}
private void enqueue(E x) {
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
count++;
// 此時隊列不為空,喚醒消費者
notEmpty.signal();
}take()方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 獲取鎖
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果隊列為空,消費者變為阻塞狀態
while (count == 0)
notEmpty.await();
// 不為空,就獲取數據
return dequeue();
} finally {
// 解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
}
private E dequeue() {
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
// 獲取隊頭元素x
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
items[takeIndex] = null;
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
count--;
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
// 此時隊列沒有滿,同時生產者繼續添加數據
notFull.signal();
return x;
}底層基于單向鏈表的無界阻塞隊列,如果不指定初始容量,默認為Integer.MAX_VALUE,否則為指定容量
構造函數
// 不指定容量
public LinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
// 指定容量
public LinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}
// 等同于合并數組
public LinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
int n = 0;
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (n == capacity)
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
++n;
}
count.set(n);
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}put()方法
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
// 元素為空,拋出異常
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
// 獲取隊列中的數據量
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
// 獲取鎖
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 隊列滿了,變為阻塞狀態
while (count.get() == capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
// 將目標元素添加到鏈表的尾端
enqueue(node);
// 總數增加
c = count.getAndIncrement();
// 隊列還沒有滿,繼續添加元素
if (c + 1 < capacity)
notFull.signal();
} finally {
// 解鎖
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0)
signalNotEmpty();
}take()方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
// 獲取隊列中的工作數
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
// 獲取鎖
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
// 如果隊列為空,變為阻塞狀態
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
// 獲取隊頭元素
x = dequeue();
// 遞減
c = count.getAndDecrement();
// 通知消費者
if (c > 1)
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
// 解鎖
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c == capacity)
//
signalNotFull();
return x;
}相同點
兩者都是通過Condition通知生產者和消費者完成元素的添加和獲取
都可以指定容量
不同點
ArrayBlockingQueue基于數據,LinkedBlockingQueue基于鏈表
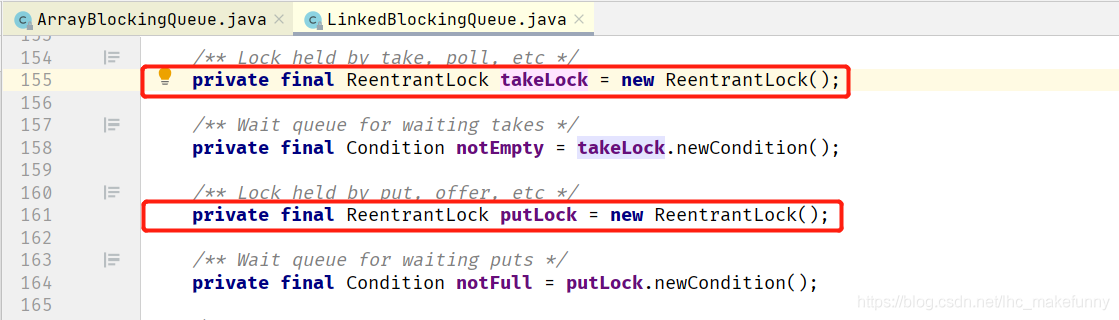
ArrayBlockingQueue內有一把鎖,LinkedBlockingQueue內有兩把鎖
自己動手實現一個阻塞隊列
通過分析源碼可以知道,阻塞隊列其實是通過通知機制Condition完成生產者和消費的互通。也可以通過Object類中的wait()和notify、notifyAll實現。下面是自己寫的一個阻塞隊列
public class BlockQueue {
// 對象鎖
public static final Object LOCK = new Object();
// 控制變量的值 來通知雙方
public boolean condition;
public void put() {
synchronized (LOCK) {
while (condition) {
try {
// 滿了
System.out.println("put 隊列滿了,開始阻塞");
LOCK.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
condition = true;
System.out.println("put 改為true,喚醒消費者");
LOCK.notifyAll();
}
}
public void take() {
synchronized (LOCK) {
while (!condition) {
// 沒滿
System.out.println("take 隊列沒滿,開始阻塞");
try {
LOCK.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
condition = false;
System.out.println("take 改為false,喚醒生產者");
LOCK.notifyAll();
}
}
}“Java阻塞隊列的原理和使用場景”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。