您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容主要講解“如何理解責任鏈模式”,感興趣的朋友不妨來看看。本文介紹的方法操作簡單快捷,實用性強。下面就讓小編來帶大家學習“如何理解責任鏈模式”吧!
責任鏈模式英文解釋為:
Avoid coupling the sender of a request to its receiver bygiving more than one object a chance to handle the request.Chainthe receiving objects and pass the request along the chain until anobject handles it.
責任鏈模式(Chain of Responsibility Pattern)將鏈中每一個節點都看作一個對象,每個節點處理的請求均不同,且內部自動維護下一個節點對象。當一個請求從鏈式的首端發出時,會沿著責任鏈預設的路徑依次傳遞到每一個節點對象,直至被鏈中的某個對象處理為止,屬于行為型設計模式。
責任鏈模式通用代碼
Java實現責任鏈設計模式如下:
public abstract class Handler { protected Handler nextHandler = null; public abstract void handle(); public Handler getNextHandler() { return nextHandler; } public void setNextHandler(Handler nextHandler) { this.nextHandler = nextHandler; } } public class HandlerA extends Handler{ @Override public void handle() { if(nextHandler == null){ System.out.println("HandlerA handle ..."); }else{ nextHandler.handle(); } } } public class HandlerB extends Handler{ @Override public void handle() { if(nextHandler == null){ System.out.println("HandlerB handle ..."); }else{ nextHandler.handle(); } } } public class HandlerC extends Handler{ @Override public void handle() { if(getNextHandler() == null){ System.out.println("HandlerC handle ..."); }else{ getNextHandler().handle(); } } } //測試 public class Client{ public static void main(String[] args) { Handler handlerA = new HandlerA(); Handler handlerB = new HandlerB(); handlerA.setNextHandler(handlerB); handlerA.handle(); } }運行結果:
HandlerC handle ...
從上面代碼,我們可以畫出UML圖:
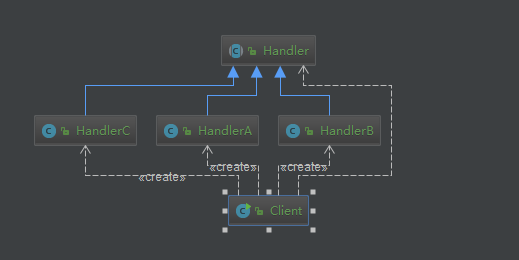
從UML圖中,我們又可以看出,責任鏈模式中有兩個非常重要的角色:
(1)、抽象處理者角色(Handler)
定義處理請求的接口。接口可以也可以給出一個方法以設定和返回對下個對象引用。這個角色通常由一個Java抽象類或者Java接口實現。
(2)、具體處理者角色(HandlerA、HandlerB、HandlerC)
具體處理者接到請求后,可以選擇將請求處理掉,或者將請求傳給下個對象。由于具體處理者持有對下家的引用。
優點:請求和處理分開,兩者解耦,提供系統的靈活性。
缺點:性能能問,一個鏈非常長的時候,非常耗時。因為我們避免建立很長的鏈。
在日常生活中,責任鏈模式是比較常見的。我們平時處理工作中的一些事務,往往是各部門協同合作來完成某一個任務的。而每個部門都有各自的職責,因此,很多時候事情完成一半,便會轉交到下一個部門,直到所有部門都審批通過,事情才能完成。
責任鏈模式主要解耦了請求與處理,客戶只需將請求發送到鏈上即可,不需要關心請求的具體內容和處理細節,請求會自動進行傳遞,直至有節點對象進行處理。
責任鏈模式主要適用于以下應用場景:
多個對象可以處理同一請求,但具體由哪個對象處理則在運行時動態決定。
在不明確指定接收者的情況下,向多個對象中的一個提交請求。
可動態指定一組對象處理請求。
下面我們來對,前面的案例:OA上請假流程做一個Java代碼的實現。
抽象處理者:領導類
public abstract class Leader { private Leader next; public void setNext(Leader next) { this.next = next; } public Leader getNext() { return next; } //處理請求的方法 public abstract void handleRequest(double LeaveDays); }項目負責人
public class ProjectLeader extends Leader { @Override public void handleRequest(double LeaveDays) { if (LeaveDays <= 0.5) { System.out.println("項目負責人批準您請假" + LeaveDays + "天。"); } else { if (getNext() != null) { getNext().handleRequest(LeaveDays); } else { System.out.println("請假天數太多,沒有人批準該假條!"); } } } }技術總監
public class TechnicalDirectorLeader extends Leader { @Override public void handleRequest(double LeaveDays) { if (LeaveDays <= 1) { System.out.println("技術總監批準您請假" + LeaveDays + "天。"); } else { if (getNext() != null) { getNext().handleRequest(LeaveDays); } else { System.out.println("請假天數太多,沒有人批準該假條!"); } } } }Boss
public class BossLeader extends Leader { @Override public void handleRequest(double LeaveDays) { if (LeaveDays >= 2 && LeaveDays <= 30) { System.out.println("Boss批準您請假" + LeaveDays + "天。"); } else { if (getNext() != null) { getNext().handleRequest(LeaveDays); } else { System.out.println("請假天數太多,沒有人批準該假條!"); } } } }發起審批
public class LeaveApproval { public static void main(String[] args) { //組裝責任鏈 Leader projectLeader = new ProjectLeader(); Leader technicalDirectorLeader = new TechnicalDirectorLeader(); Leader bossLeader = new BossLeader(); projectLeader.setNext(technicalDirectorLeader); technicalDirectorLeader.setNext(bossLeader); //請假兩天,提交請假流程,開啟審批環節, projectLeader.handleRequest(2); } }審批結果
Boss批準您請假2.0天。
如果請假天數是31天,審批結果
請假天數太多,沒有人批準該假條!
整個請假流程為:
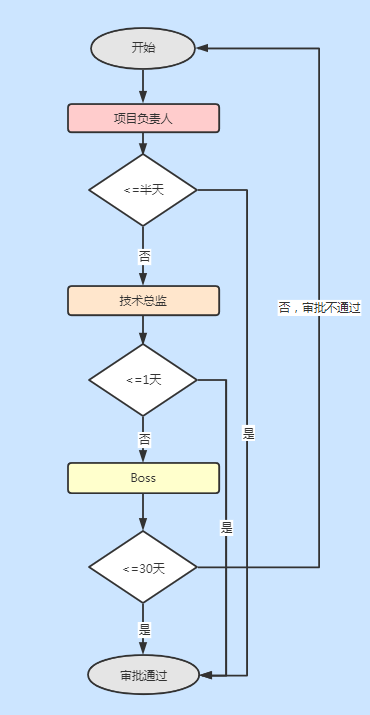
把這張流程圖改成縱向:
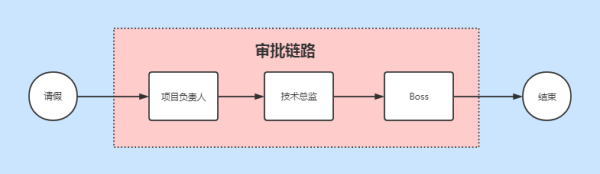
就這么一環套一環的,使用上面兩個例子和兩張圖來理解責任鏈模式是不是就更輕松了?
自己吹牛逼,沒什么用,下面來看看大神們是怎么使用責任鏈模式的。
在Spring、Mybatis等框架中,都用使用到責任鏈模式,下面先來看在Spring中是如何使用的。
在Spring MVC中的org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet類中:
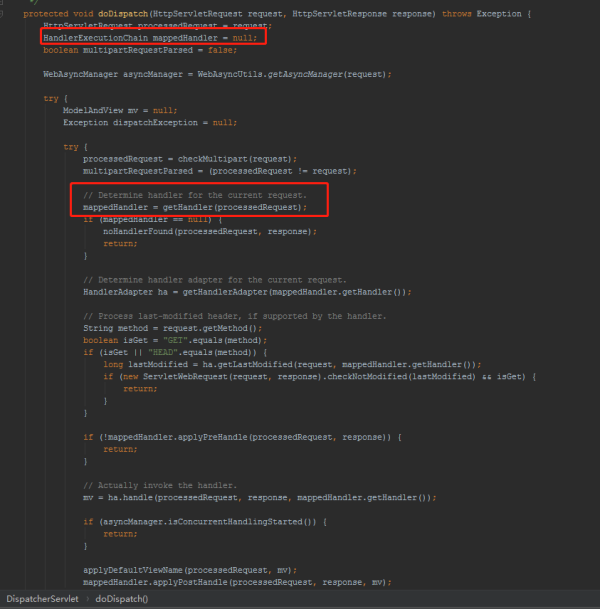
getHandler 方法的處理使用到了責任鏈模式,handlerMappings是之前 Spring 容器初始化好的,通過遍歷 handlerMappings查找與request匹配的 Handler, 這里返回 HandlerExecutionChain 對象。這個 HandlerExecutionChain對象到后面執行的時候再分析為什么返回的是這樣一個對象。
@Nullable protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { if (this.handlerMappings != null) { for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) { HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } } return null; }到此,相信大家對“如何理解責任鏈模式”有了更深的了解,不妨來實際操作一番吧!這里是億速云網站,更多相關內容可以進入相關頻道進行查詢,關注我們,繼續學習!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。