您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章為大家展示了SpringBoot中對MongoDB的基本操作是怎樣的,內容簡明扼要并且容易理解,絕對能使你眼前一亮,通過這篇文章的詳細介紹希望你能有所收獲。
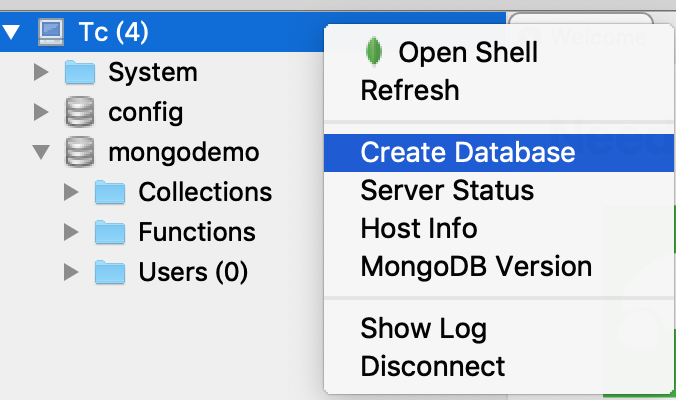
首先 在MongoDB 操作客戶端 Robo 3T 中 創建數據庫:
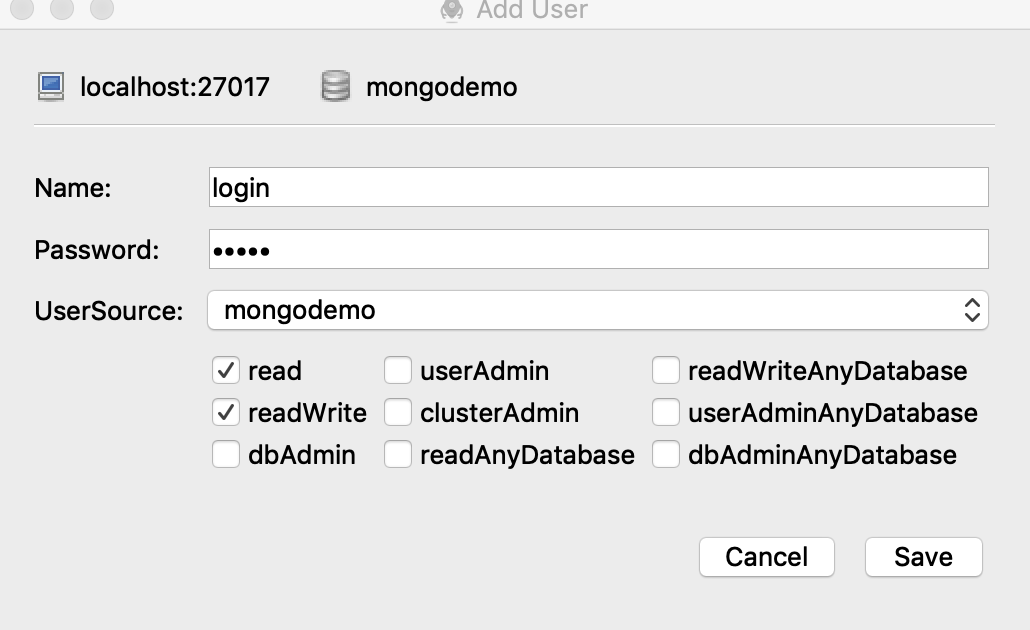
增加用戶User:
創建 Collections 集合(類似mysql 中的 表):
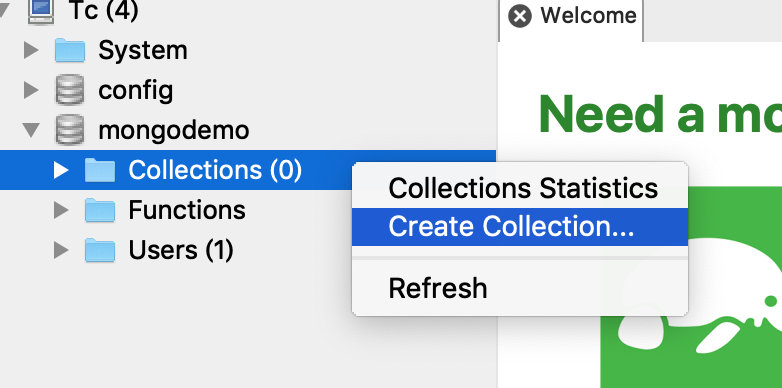
后面我們大部分都是基于創建的Collection “collectiondemo”操作的。
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <version> 2.1.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
spring.data.mongodb.host=localhost spring.data.mongodb.port=27017 spring.data.mongodb.database=mongodemo spring.data.mongodb.username=login spring.data.mongodb.password=login
定義 MongoTemplate
@Autowired private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate; private static String COLLECTION_DEMO = "collectiondemo";
基于 mongoTemplate 操作
@PostMapping("/insertDocument")
public void insertDocument(String document) {
//獲取集合
MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO);
Document parse = Document.parse(document);
//插入文檔
collection.insertOne(parse);
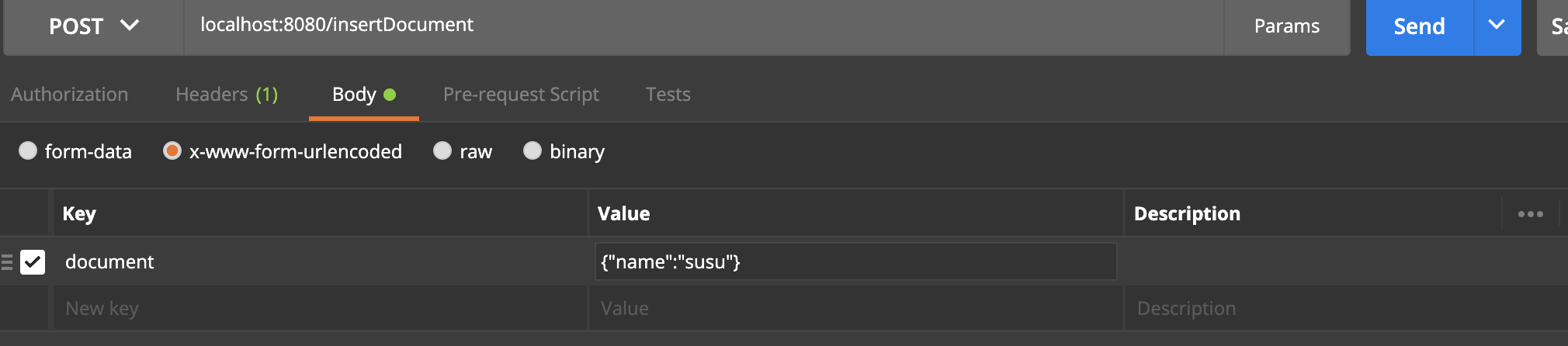
}postman 測試參數:
在 Robo 中 可以查詢到:
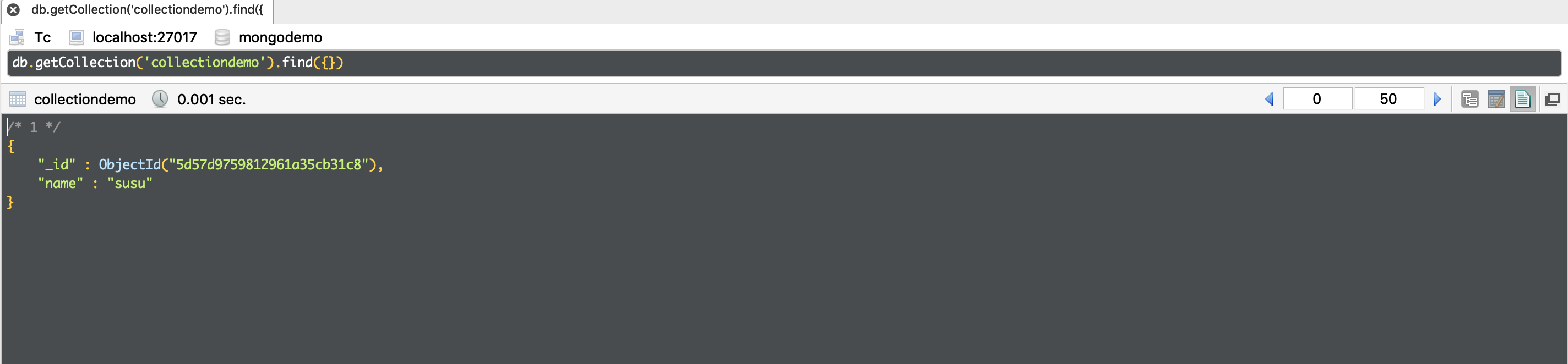
添加數據成功 ,其中 ObjectId是一個12字節的 BSON 類型字符串, 由
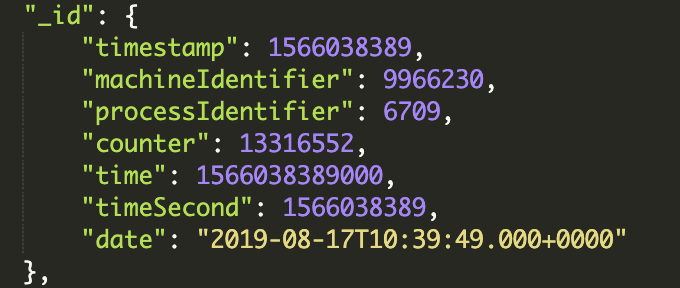
組成
@PutMapping("/updateDocument")
public Long updateDocument(String queryDocument, String ducument) {
MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO);
BasicDBObject queryParse = BasicDBObject.parse(queryDocument);
BasicDBObject parse = BasicDBObject.parse(ducument);
UpdateResult result = collection.updateOne(queryParse, new BasicDBObject("$set",parse));
return result.getModifiedCount();
}輸入參數:
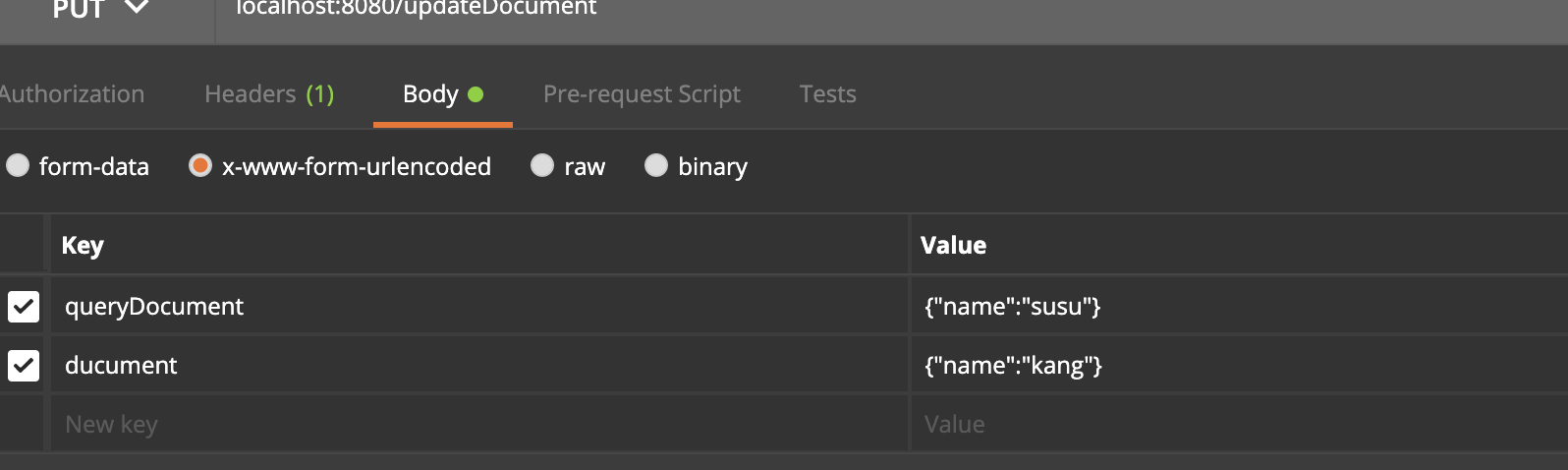
可以看到:

但有個問題,當參數中 key 在 mongodb 不存在時,會自己創建:
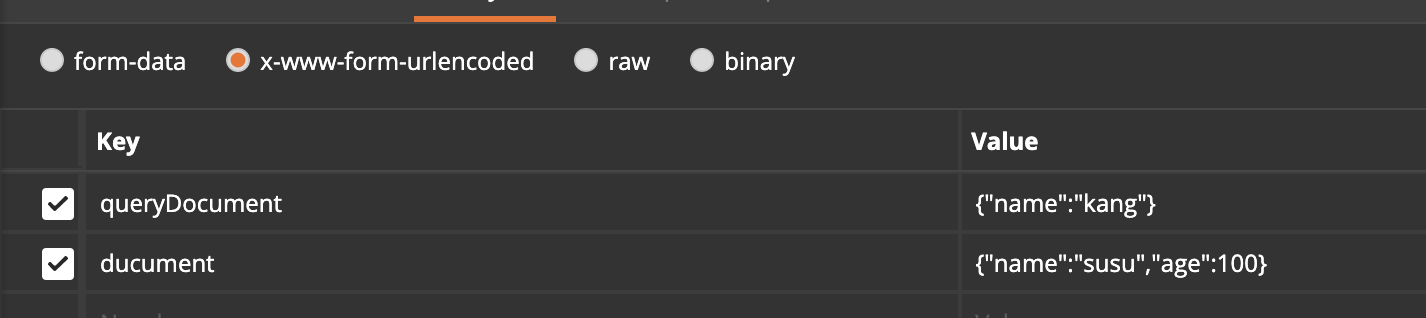
之前mongodb并沒有 age 字段,現在可以看到:

這可能對有些業務場景,對key要求嚴格的 就無法通過這個滿足條件 ,此時mongodb 中 可以用$exists 解決:
@PutMapping("/updateDocumentOnlyHave")
public Long updateDocumentOnlyHave(String id, String ducument) {
MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO);
BasicDBObject parse = BasicDBObject.parse(ducument);
Set<String> keySet = parse.keySet();
BasicDBObject dbObject = new BasicDBObject();
dbObject.put("id",id);
for (String key : keySet) {
dbObject.put(key, new BasicDBObject("$exists",true));
}
UpdateResult result = collection.updateOne(dbObject, new BasicDBObject("$set",parse));
return result.getModifiedCount();
} @GetMapping("/listDocuments")
public List<Document> findDocuments() {
MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO);
FindIterable<Document> documents = collection.find();
List<Document> listDocuments = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
listDocuments.add(document);
}
return listDocuments;
} @DeleteMapping("/deleteDocument")
public DeleteResult deleteDocument(String name) {
MongoCollection<Document> collection = mongoTemplate.getCollection(COLLECTION_DEMO);
DeleteResult result = collection.deleteOne(new BasicDBObject("name", name));
return result;
}上述內容就是SpringBoot中對MongoDB的基本操作是怎樣的,你們學到知識或技能了嗎?如果還想學到更多技能或者豐富自己的知識儲備,歡迎關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。