您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇文章給大家分享的是有關如何進行Planning 模塊源代碼分析,小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家學習,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章后可以有所收獲,話不多說,跟著小編一起來看看吧。
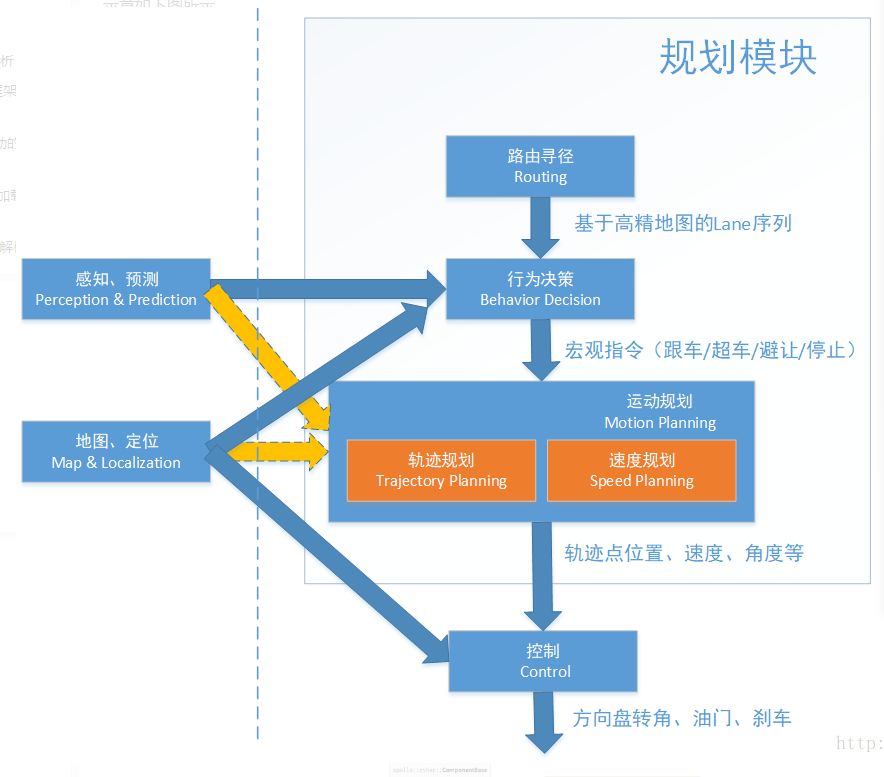
規劃(Planning)模塊位于命名空間:apollo::planning,其作用在于構建無人車從起點到終點的局部行駛路徑,具體而言,就是給定導航地圖、導航路徑、當前定位點、車輛狀態、 周邊目標的感知及預測信息,規劃模塊計算出可供控制模塊執行的一條安全且舒適的行駛路徑。
規劃模塊輸出的路徑是局部路徑而非全局路徑。舉例,如無人車需從長沙智能駕駛研究院行駛至長沙高鐵南站,首先需借助Routing模塊輸出全局導航路徑,接下來才是規劃模塊基于全局導航路徑進行一小段、一小段具體行駛路徑的規劃。
規劃模塊的作用是根據感知預測的結果,當前的車輛信息和路況規劃出一條車輛能夠行駛的軌跡,這個軌跡會交給控制模塊,控制模塊通過油門,剎車和方向盤使得車輛按照規劃的軌跡運行。
規劃模塊的軌跡是短期軌跡,即車輛短期內行駛的軌跡,長期軌跡是Routing模塊規劃出的導航軌跡,即起點到目的地的軌跡,規劃模塊會先生成導航軌跡,然后根據導航軌跡和路況的情況,沿著短期軌跡行駛,直到目的地。
規劃模塊內部結構及其與其他模塊的交互示意如下圖所示。
根據各功能模塊的啟動過程的分析,Planning模塊的主入口為:
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
2 google::SetUsageMessage("we use this program to load dag and run user apps.");
3
4 // parse the argument
5 ModuleArgument module_args;
6 module_args.ParseArgument(argc, argv);
7
8 // initialize cyber
9 apollo::cyber::Init(argv[0]);
10
11 // start module
12 ModuleController controller(module_args);
13 if (!controller.Init()) {
14 controller.Clear();
15 AERROR << "module start error.";
16 return -1;
17 }
18
19 apollo::cyber::WaitForShutdown();
20 controller.Clear();
21 AINFO << "exit mainboard.";
22
23 return 0;
24}Main函數十分簡單,首先是解析參數,初始化Cyber環境,接下來創建一個ModuleController類對象controller,之后調用controller.Init()啟動相關功能模塊。進入Cyber RT的消息循環,等待cyber::WaitForShutdown()返回,清理資源并退出Main函數。ModuleController::Init()函數內部調用了ModuleController::LoadAll()函數:
1bool ModuleController::LoadAll() {
2 const std::string work_root = common::WorkRoot();
3 const std::string current_path = common::GetCurrentPath();
4 const std::string dag_root_path = common::GetAbsolutePath(work_root, "dag");
5
6 for (auto& dag_conf : args_.GetDAGConfList()) {
7 std::string module_path = "";
8 if (dag_conf == common::GetFileName(dag_conf)) {
9 // case dag conf argument var is a filename
10 module_path = common::GetAbsolutePath(dag_root_path, dag_conf);
11 } else if (dag_conf[0] == '/') {
12 // case dag conf argument var is an absolute path
13 module_path = dag_conf;
14 } else {
15 // case dag conf argument var is a relative path
16 module_path = common::GetAbsolutePath(current_path, dag_conf);
17 if (!common::PathExists(module_path)) {
18 module_path = common::GetAbsolutePath(work_root, dag_conf);
19 }
20 }
21 AINFO << "Start initialize dag: ">上述函數處理一個dag_conf配置文件循環,讀取配置文件中的所有dag_conf,并逐一調用bool ModuleController::LoadModule(const std::string& path)函數加載功能模塊。
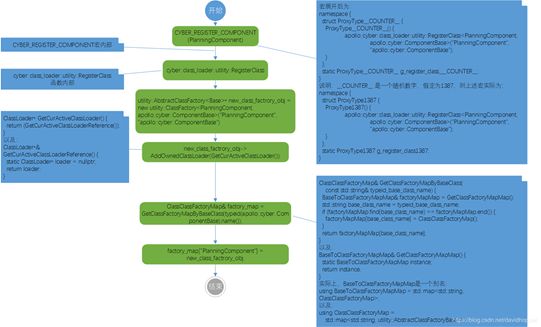
進一步展開:
1#define CLASS_LOADER_REGISTER_CLASS_INTERNAL(Derived, Base, UniqueID) \
2 namespace { \
3 struct ProxyType##UniqueID { \
4 ProxyType##UniqueID() { \
5 apollo::cyber::class_loader::utility::RegisterClass( \
6 #Derived, #Base); \
7 } \
8 }; \
9 static ProxyType##UniqueID g_register_class_##UniqueID; \
10 }將PlanningComponent代入,最終得到:
1 namespace {
2 struct ProxyType__COUNTER__ {
3 ProxyType__COUNTER__() {
4 apollo::cyber::class_loader::utility::RegisterClass<planningcomponent, apollo::cyber::componentbase>(
5 "PlanningComponent", "apollo::cyber::ComponentBase");
6 }
7 };
8 static ProxyType__COUNTER__ g_register_class___COUNTER__;
9 }
</planningcomponent, apollo::cyber::componentbase>創建一個模板類utility::ClassFactory<derived, base=""></derived,>對象new_class_factrory_obj,為其添加類加載器,設置加載庫的路徑,將工廠類對象加入到ClassClassFactoryMap對象factory_map統一管理。通過該函數,Cyber使用工廠方法模式完成產品類對象的創建:
第一部分介紹模塊主入口時,提及bool ModuleController::LoadModule(const std::string& path)函數,正是該函數動態創建出了apollo::planning::PlanningComponent類對象。
函數內部調用分析如下:
1bool ModuleController::LoadModule(const std::string& path) {
2 DagConfig dag_config;
3 if (!common::GetProtoFromFile(path, &dag_config)) {
4 AERROR << "Get proto failed, file: ">上述函數從磁盤配置文件讀取配置信息,并調用bool ModuleController::LoadModule(const DagConfig& dag_config)函數加載功能模塊:
1bool ModuleController::LoadModule(const DagConfig& dag_config) {
2 const std::string work_root = common::WorkRoot();
3
4 for (auto module_config : dag_config.module_config()) {
5 std::string load_path;
6 // ...
7 class_loader_manager_.LoadLibrary(load_path);
8 for (auto& component : module_config.components()) {
9 const std::string& class_name = component.class_name();
10 std::shared_ptr base =
11 class_loader_manager_.CreateClassObj(class_name);
12 if (base == nullptr) {
13 return false;
14 }
15
16 if (!base->Initialize(component.config())) {
17 return false;
18 }
19 component_list_.emplace_back(std::move(base));
20 }
21
22 // ...
23 }
24 return true;
25}工廠類對象指針找到后,使用classobj = factory->CreateObj();就順理成章地將PlanningComponent類對象創建出來了。
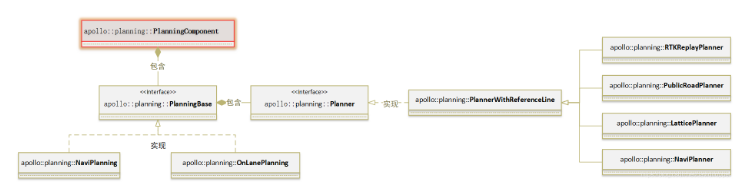
PublicRoadPlanner算法從Routing模塊輸出的高精地圖Lane序列獲得全局導航路徑。
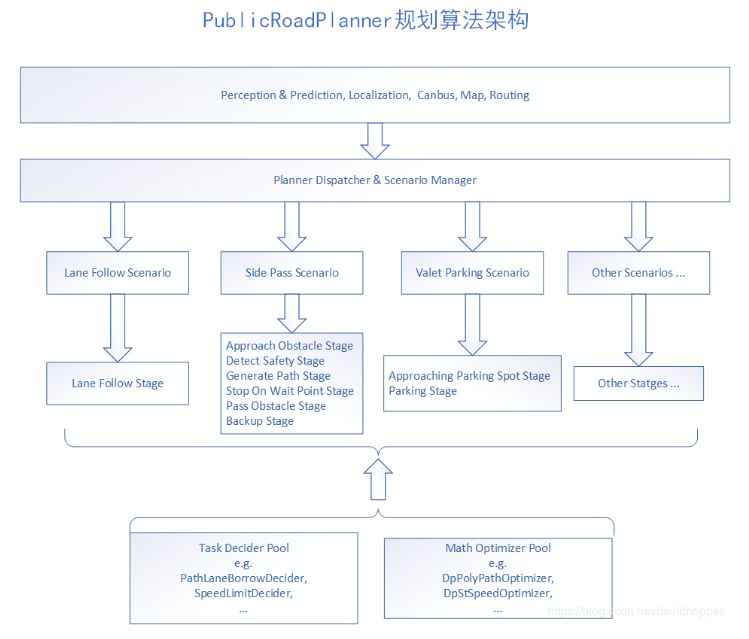
基于場景、階段和任務的理念進行規劃,優點是能合理有效地應對每種場景,易于擴充,并且基于配置文件動態增減場景、階段及使用的任務,靈活性強;缺點是可能會遺漏一些特殊場景,但可通過不斷擴充新的場景加以解決。
該算法的主要執行流程如下:

可借助GDB調試命令對上述執行流程進行更為深入的理解,例如TrafficLightProtectedStageApproach階段的PathLaneBorrowDecider任務的調用堆棧,從下往上看,對于任意一個任務的調用流程一目了然:
#0 apollo::planning::PathLaneBorrowDecider::Process (this=0x7f8c28294460, frame=0x7f8c38029f70,
2 reference_line_info=0x7f8c3802b140) at modules/planning/tasks/deciders/path_lane_borrow_decider/path_lane_borrow_decider.cc:39
3#1 0x00007f8c0468b7c8 in apollo::planning::Decider::Execute (this=0x7f8c28294460, frame=0x7f8c38029f70,
4 reference_line_info=0x7f8c3802b140) at modules/planning/tasks/deciders/decider.cc:31
5#2 0x00007f8c065c4a01 in apollo::planning::scenario::Stage::ExecuteTaskOnReferenceLine (this=0x7f8c28293eb0,
6 planning_start_point=..., frame=0x7f8c38029f70) at modules/planning/scenarios/stage.cc:96
7#3 0x00007f8c06e721da in apollo::planning::scenario::traffic_light::TrafficLightProtectedStageApproach::Process (
8 this=0x7f8c28293eb0, planning_init_point=..., frame=0x7f8c38029f70) at
9 modules/planning/scenarios/traffic_light/protected/stage_approach.cc:48
10#4 0x00007f8c067f1732 in apollo::planning::scenario::Scenario::Process (
11 this=0x7f8c2801bf20, planning_init_point=..., frame=0x7f8c38029f70)
12 at modules/planning/scenarios/scenario.cc:76
13#5 0x00007f8c186e153a in apollo::planning::PublicRoadPlanner::Plan (
14 this=0x23093de0, planning_start_point=..., frame=0x7f8c38029f70,
15 ptr_computed_trajectory=0x7f8b9a5fbed0) at modules/planning/planner/public_road/public_road_planner.cc:51
16#6 0x00007f8c19ee5937 in apollo::planning::OnLanePlanning::Plan (
17 this=0x237f3b0, current_time_stamp=1557133995.3679764, stitching_trajectory=std::vector of length 1,
18 capacity 1 = {...}, ptr_trajectory_pb=0x7f8b9a5fbed0) at modules/planning/on_lane_planning.cc:436
19#7 0x00007f8c19ee40fa in apollo::planning::OnLanePlanning::RunOnce (
20 this=0x237f3b0, local_view=..., ptr_trajectory_pb=0x7f8b9a5fbed0) at modules/planning/on_lane_planning.cc:304
21#8 0x00007f8c1ab0d494 in apollo::planning::PlanningComponent::Proc (
22 this=0x1d0f310, prediction_obstacles=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b840164f8,
23 chassis=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b84018a08,
24 localization_estimate=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b8400d3b8) at modules/planning/planning_component.cc:134
25#9 0x00007f8c1abb46c4 in apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, < span="">
26 apollo::canbus::Chassis, apollo::localization::LocalizationEstimate, apollo::cyber::NullType>::Process (this=0x1d0f310,
27 msg0=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b840164f8, msg1=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b84018a08,
28 msg2=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b8400d3b8) at ./cyber/component/component.h:291
29#10 0x00007f8c1aba2698 in apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, < span="">
30 apollo::canbus::Chassis, apollo::localization::LocalizationEstimate, apollo::cyber::NullType>::Initialize(
31 apollo::cyber::proto::ComponentConfig const&)::{lambda(std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&,
32 std::shared_ptr const&, std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&)#2}::operator()
33 (std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&, std::shared_ptr const&,
34 std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&) const (__closure=0x2059a430,
35 msg0=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b840164f8, msg1=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b84018a08,
36 msg2=std::shared_ptr (count 4, weak 0) 0x7f8b8400d3b8) at ./cyber/component/component.h:378
37#11 0x00007f8c1abb4ad2 in apollo::cyber::croutine::RoutineFactory apollo::cyber::croutine::CreateRoutineFactory
38 <apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
39 apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis,
40 apollo::localization::LocalizationEstimate, apollo::cyber::NullType>::Initialize(
41 apollo::cyber::proto::ComponentConfig const&)::{lambda(std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&,
42 std::shared_ptr const&, std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&)#2}&>
43 (apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis,
44 apollo::localization::LocalizationEstimate, apollo::cyber::NullType>::Initialize(apollo::cyber::proto::ComponentConfig const&)::
45 {lambda(std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&, std::shared_ptr const&,
46 std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&)#2}&,
47 std::shared_ptr<apollo::cyber::data::datavisitor<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles,
48 apollo::canbus::Chassis, apollo::localization::LocalizationEstimate, apollo::cyber::NullType> > const&)::
49 {lambda()#1}::operator()() const::{lambda()#1}::operator()() const (__closure=0x2059a420) at ./cyber/croutine/routine_factory.h:108
50#12 0x00007f8c1ac0466a in std::_Function_handler<void (), apollo::cyber::croutine::routinefactory < span="">
51apollo::cyber::croutine::CreateRoutineFactory<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
52apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
53apollo::cyber::NullType>::Initialize(apollo::cyber::proto::ComponentConfig const&)::{lambda(std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&,
54std::shared_ptr const&, std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&)#2}&>
55(apollo::cyber::Component<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
56apollo::cyber::NullType>::Initialize(apollo::cyber::proto::ComponentConfig const&)::{lambda(std::shared_ptr<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles> const&,
57std::shared_ptr const&, std::shared_ptr<apollo::localization::localizationestimate> const&)#2}&,
58std::shared_ptr<apollo::cyber::data::datavisitor<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
59apollo::cyber::NullType> > const&)::{lambda()#1}::operator()() const::{lambda()#1}>::_M_invoke(std::_Any_data const&) (__functor=...) at
60/usr/include/c++/4.8/functional:2071
61#13 0x00007f8c5f5b86e8 in std::function::operator()() const (this=0x205f1160) at /usr/include/c++/4.8/functional:2471
62#14 0x00007f8c57560cbc in apollo::cyber::croutine::CRoutine::Run (this=0x205f1148) at ./cyber/croutine/croutine.h:143
63#15 0x00007f8c5755ff55 in apollo::cyber::croutine::(anonymous namespace)::CRoutineEntry (arg=0x205f1148) at cyber/croutine/croutine.cc:43
</apollo::cyber::data::datavisitor<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
</apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
</apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
</apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
</void (), apollo::cyber::croutine::routinefactory <></apollo::cyber::data::datavisitor<apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles,
</apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis,
</apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis,
</apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, apollo::canbus::chassis, apollo::localization::localizationestimate,
</apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::localization::localizationestimate></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, <></apollo::prediction::predictionobstacles, <>所有規劃算法共用的流程略去不表,與PublicRoadPlanner規劃算法相關的有兩處,一處是PublicRoadPlanner::Init,另一處是PublicRoadPlanner::Plan。
下面來看場景更新函數ScenarioManager::Update的代碼:
1void ScenarioManager::Update(const common::TrajectoryPoint& ego_point,
2 const Frame& frame) {
3 CHECK(!frame.reference_line_info().empty());
4 Observe(frame);
5 ScenarioDispatch(ego_point, frame);
6}該函數包含兩個子函數:ScenarioManager::Observe和ScenarioManager::ScenarioDispatch,其中前者用于更新first_encountered_overlap_map_,代碼如下所示:
1void ScenarioManager::Observe(const Frame& frame) {
2 // init first_encountered_overlap_map_
3 first_encountered_overlap_map_.clear();
4 const auto& reference_line_info = frame.reference_line_info().front();
5 const auto& first_encountered_overlaps =
6 reference_line_info.FirstEncounteredOverlaps();
7 for (const auto& overlap : first_encountered_overlaps) {
8 if (overlap.first == ReferenceLineInfo::PNC_JUNCTION ||
9 overlap.first == ReferenceLineInfo::SIGNAL ||
10 overlap.first == ReferenceLineInfo::STOP_SIGN ||
11 overlap.first == ReferenceLineInfo::YIELD_SIGN) {
12 first_encountered_overlap_map_[overlap.first] = overlap.second;
13 }
14 }
15}以上就是如何進行Planning 模塊源代碼分析,小編相信有部分知識點可能是我們日常工作會見到或用到的。希望你能通過這篇文章學到更多知識。更多詳情敬請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。