您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要介紹“hadoop rpc客戶端初始化和調用過程怎么實現”,在日常操作中,相信很多人在hadoop rpc客戶端初始化和調用過程怎么實現問題上存在疑惑,小編查閱了各式資料,整理出簡單好用的操作方法,希望對大家解答”hadoop rpc客戶端初始化和調用過程怎么實現”的疑惑有所幫助!接下來,請跟著小編一起來學習吧!
DFSClient的初始化主要看其構造函數,其中rpc部分我們主要關注屬性final ClientProtocol namenode,DFSClient的文件系統操作都是由他代理完成,構造函數中的關鍵代碼如下:
public DFSClient(URI nameNodeUri, ClientProtocol rpcNamenode,
Configuration conf, FileSystem.Statistics stats)
throws IOException {
proxyInfo = NameNodeProxies.createProxy(conf, nameNodeUri,ClientProtocol.class);
this.dtService = proxyInfo.getDelegationTokenService();
this.namenode = proxyInfo.getProxy();
}顯然,DFSClient中的namenode是一個代理類。
接著NameNodeProxies類的createProxy方法,下面給出了NameNodeProxies中需要用到的一些方法:
public class NameNodeProxies {
public static <T> ProxyAndInfo<T> createProxy(Configuration conf,
URI nameNodeUri, Class<T> xface) throws IOException {
return createNonHAProxy(conf, NameNode.getAddress(nameNodeUri), xface,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser(), true);
}
public static <T> ProxyAndInfo<T> createNonHAProxy(
Configuration conf, InetSocketAddress nnAddr, Class<T> xface,
UserGroupInformation ugi, boolean withRetries) throws IOException {
proxy = (T) createNNProxyWithClientProtocol(nnAddr, conf, ugi,withRetries);
return new ProxyAndInfo<T>(proxy, dtService);
}
/**
這部分是重點
*/
private static ClientProtocol createNNProxyWithClientProtocol(
InetSocketAddress address, Configuration conf, UserGroupInformation ugi,
boolean withRetries) throws IOException {
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB proxy = RPC.getProtocolProxy(
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class, version, address, ugi, conf,
NetUtils.getDefaultSocketFactory(conf),
org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client.getTimeout(conf), defaultPolicy).getProxy();
proxy = (ClientNamenodeProtocolPB) RetryProxy.create(
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class,
new DefaultFailoverProxyProvider<ClientNamenodeProtocolPB>(
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB.class, proxy),
methodNameToPolicyMap,
defaultPolicy);
return new ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB(proxy);
}
}該類中前面兩個方法做跳轉用,直接看createNNProxyWithClientProtocol方法,這里兩行很關鍵的代碼,proxy實例的初始化,這里先提示注意前一行中的getProxy() 對于這個方法是需要注意的,這樣也保證了類型的一致。
這時候就不得不調出RPC這個類來看看他是怎么生成proxy的實例的了,看代碼:ProtobufRpcEngineProtobufRpcEngineProtobufRpcEngineProtobufRpcEngine
public class RPC {
public static <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProtocolProxy(Class<T> protocol,
long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr,
UserGroupInformation ticket,
Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory,
int rpcTimeout,
RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy) throws IOException {
if (UserGroupInformation.isSecurityEnabled()) {
SaslRpcServer.init(conf);
}
return getProtocolEngine(protocol,conf).getProxy(protocol, clientVersion,
addr, ticket, conf, factory, rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy);
}
}
RPC中還是需要進一步的跳轉,但是這里需要注意,getProtocolEngine這個方法,這里做一個說明,查看
RpcEngine的依賴,看圖:
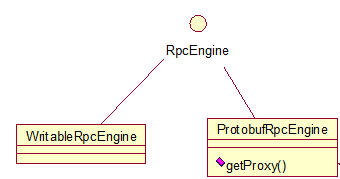 在我的2.4.1的hadoop的版本中,hadoop的序列化框架已經用了Protobuf,所以getProtocolEngine方法得到的是ProtobufRpcEngine類的一個實例,那好,我們進一步跟蹤ProtobufRpcEngine類的getProxy方法,看代碼:
在我的2.4.1的hadoop的版本中,hadoop的序列化框架已經用了Protobuf,所以getProtocolEngine方法得到的是ProtobufRpcEngine類的一個實例,那好,我們進一步跟蹤ProtobufRpcEngine類的getProxy方法,看代碼:
public class ProtobufRpcEngine implements RpcEngine {
public <T> ProtocolProxy<T> getProxy(Class<T> protocol, long clientVersion,
InetSocketAddress addr, UserGroupInformation ticket, Configuration conf,
SocketFactory factory, int rpcTimeout, RetryPolicy connectionRetryPolicy
) throws IOException {
final Invoker invoker = new Invoker(protocol, addr, ticket, conf, factory,
rpcTimeout, connectionRetryPolicy);
return new ProtocolProxy<T>(protocol, (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
protocol.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{protocol}, invoker), false);
}
}對java的動態代理有點了解的人看到Proxy.newProxyInstance這個方法應該都很清楚這就是生成一個遠程代理類實例(特別注意:在NameNodeProxies類的createNNProxyWithClientProtocol方法中getProxy方法拿到的對象也就是這個對象),其中的invoker參數,確實我們不能忽略的,因為他暗藏玄機,java的動態代理中,invoker的類需要實現InvocationHandler接口,該接口只聽過一個方法invoke,共代理類使用,及通過Proxy.newProxyInstance生成的代理類,在使用的時候是通過InvocationHandler的invoke方法來起作用的。好吧,現在我們可以順便看看在ProtobufRpcEngine類的getProxy方法中invoker局部變量的類依賴圖:,顯然有剛才提到的實現關系,現在再讓我們看看Invoker的內部,包括構造函數和invoke方法:
private Invoker(Class<?> protocol, Client.ConnectionId connId,
Configuration conf, SocketFactory factory) {
this.remoteId = connId;
this.client = CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory, RpcResponseWrapper.class);
this.protocolName = RPC.getProtocolName(protocol);
this.clientProtocolVersion = RPC
.getProtocolVersion(protocol);
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)
throws ServiceException {
val = (RpcResponseWrapper) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER,
new RpcRequestWrapper(rpcRequestHeader, theRequest), remoteId);
}在構造函數請注意一個屬性client,他的類型正式 org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client,而且在invoke方法中發起遠程調用的正是這個client屬性,能夠讀到這里的同學,相信應該比較清楚了,在DFSClient中發起遠程訪問的就是這個Client類的實例。
關于DFSClient的初始化階段中關于rpc的部分,總結一句,就是創建一個namenode的代理對象,供后續的文件系統操作調用。
DFSClient提供了相當豐富的API供客戶端操作hadoop的文件系統,這里以 getFileLinkInfo為例,講解rpc客戶端的調用過程。注意:如果是FileSystem類的話,請使用方法getFileLinkStatus,他對DFSClient提供的getFileLinkInfo做了一層包裝,僅此而已。
直接看DFSClient中的代碼:
public HdfsFileStatus getFileLinkInfo(String src) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
try {
return namenode.getFileLinkInfo(src);
} catch(RemoteException re) {
throw re.unwrapRemoteException(AccessControlException.class,
UnresolvedPathException.class);
}
}
很簡答的一行代碼,通過namenode屬性的調用操作完成,看了DFSClient的初始化過程,我們很容易知道namenode的實例化類是ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB,繼續看調用過程,代碼轉到了ClientNamenodeProtocolTranslatorPB中:
@Override
public HdfsFileStatus getFileLinkInfo(String src)
throws AccessControlException, UnresolvedLinkException, IOException {
GetFileLinkInfoRequestProto req = GetFileLinkInfoRequestProto.newBuilder()
.setSrc(src).build();
try {
GetFileLinkInfoResponseProto result = rpcProxy.getFileLinkInfo(null, req);
return result.hasFs() ?
PBHelper.convert(rpcProxy.getFileLinkInfo(null, req).getFs()) : null;
} catch (ServiceException e) {
throw ProtobufHelper.getRemoteException(e);
}
}
這時候我們會發現一個屬性rpcProxy,再回過頭看看NameNodeProxies類的createProxy方法,我們就可以很清楚的知道,rpcProxy就是那個能發起遠程調用的代理類,它封裝了Invoker對象,當然就也有了使用Client類的能力,很好,這里我們稍微總結下,在DFSClient類中,調用getFileLinkInfo方法,最終就是通過Client的call方法,發起遠程訪問,獲取數據。
這時候,我們可以進一步來探討下Hadoop中RPC的Client類了,下面我把Client類主要的部分抽取出來了,看下面的代碼:
public class Client {
Call createCall(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest) {
return new Call(rpcKind, rpcRequest);
}
public Writable call(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest,
ConnectionId remoteId, int serviceClass) throws IOException {
final Call call = createCall(rpcKind, rpcRequest);
Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call, serviceClass);
connection.sendRpcRequest(call); // send the rpc request
return call.getRpcResponse();
}
private class Connection extends Thread {
private void receiveRpcResponse() {
}
public void sendRpcRequest(final Call call)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
}
}
}看了DFSclient的初始化部分,我們就可以知道,DFSClient的遠程調用,是通過Client的call方法起作用的。其實Client的call方法已經很能夠說明問題了,先封裝一個call,然后獲取連接,再得到結果。簡單的說Client就是這樣了。可以在稍微復雜一點,在Client的call方法中,封裝了call后,getConnection的方法不僅是獲取一個連接,同時會啟動連接代表的線程,這個線程的作用就是等待請求的完成,完成后,將結果寫到call中(該過程天內各國Connection的receiveRpcRespoce方法完成),在call方法中獲取連接后,會發送請求的參數到namenode的服務端,等待namenode處理完畢,Connection的receiveRpcRespoce方法寫返回結果,最后call方法中返回結果。大概的過程就是這個樣子了。
到此,關于“hadoop rpc客戶端初始化和調用過程怎么實現”的學習就結束了,希望能夠解決大家的疑惑。理論與實踐的搭配能更好的幫助大家學習,快去試試吧!若想繼續學習更多相關知識,請繼續關注億速云網站,小編會繼續努力為大家帶來更多實用的文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。