您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇“MicroPython如何實現智能小車”文章的知識點大部分人都不太理解,所以小編給大家總結了以下內容,內容詳細,步驟清晰,具有一定的借鑒價值,希望大家閱讀完這篇文章能有所收獲,下面我們一起來看看這篇“MicroPython如何實現智能小車”文章吧。
1.效果展示
2.材料準備
TPYBoard v102 1塊
藍牙串口模塊 1個
TPYBoard v102小車擴展板(包含4個車輪,4個電機)
18650電池 2節
數據線 1條
杜邦線 若干
藍牙APP
3.藍牙模塊
藍牙( Bluetooth):是一種無線技術標準,可實現固定設備、移動設備和樓宇個人域網之間的短距離數據交換(使用2.4-2.485GHz的ISM波段的UHF無線電波)。
我們在此使用的藍牙模塊(HC-06)已經在內部實現了藍牙協議,不用我們再去自己開發調試協議。這類模塊一般都是借助于串口協議通信,因此我們只需借助串口將我們需要發送的數據發送給藍牙模塊,藍牙模塊會自動將數據通過藍牙協議發送給配對好的藍牙設備。
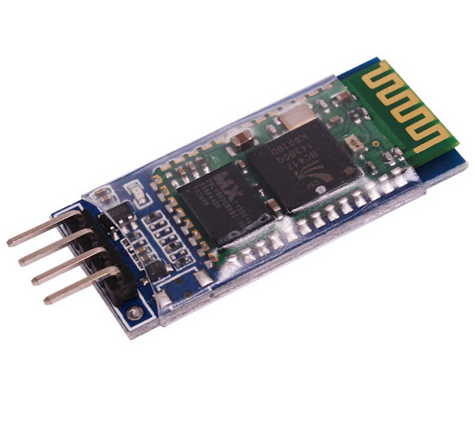

4.單片機-TPYBoard v102
TPYBoard v102 是遵循MIT協議,由TurnipSmart公司制作的一款MicroPython開發板,它基于STM32F405單片機,通過USB接口進行數據傳輸。該開發板內置4個LED燈、一個加速度傳感器,可在3V-10V之間的電壓正常工作。讓你會Python就能做極客, 用Python控制硬件,支持Python語言的開發板。比樹莓派更小巧,更簡單,更便宜,比Arduino更強大,更加容易編程。
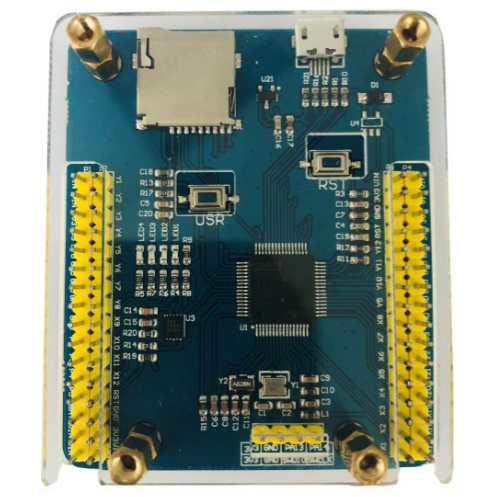
小車擴展板
以TPYBoard v102開發板為主控板,小車擴展板具有四路PWM調速電機、8個可控LED、1個蜂鳴器、5路舵機接口、1個藍牙接口、1個PS2無線接口、引出TPYBoard v102開發板全部針腳,可裝載循跡模塊、超聲波模塊、機械手臂、紅外接收頭,兼容入門級電機和專業級電機,兩節18650單獨供電。

源代碼
我們只需要把TPYBoard v102 插小車擴展板上,把藍牙模塊插上,把程序寫入就行,下面是main.py源程序
# main.py -- put your code here!
from pyb import Pin
from pyb import UART
N1 = Pin('Y1', Pin.OUT_PP)
N2 = Pin('Y2', Pin.OUT_PP)
N3 = Pin('Y3', Pin.OUT_PP)
N4 = Pin('Y4', Pin.OUT_PP)
N5 = Pin('Y6', Pin.OUT_PP)
N6 = Pin('Y7', Pin.OUT_PP)
N7 = Pin('Y8', Pin.OUT_PP)
N8 = Pin('Y9', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_red=Pin('Y5', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_right=Pin('Y12', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_left=Pin('Y11', Pin.OUT_PP)
led_red.value(1)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(0)
blue=UART(1,9600,timeout=100)
def go(speed):
M1_0=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1, pulse_width=(speed*200)+10000)
M1_1=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2, pulse_width=0)
M2_0=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3, pulse_width=(speed*100)+5000)
M2_1=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4, pulse_width=0)
M3_0=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6, pulse_width=(speed*220)+10000)
M3_1=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7, pulse_width=0)
M4_0=pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9, pulse_width=(speed*50)+5000)
M4_1=pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8, pulse_width=0)
led_red.value(0)
def back(speed):
M1_0=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1, pulse_width=0)
M1_1=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2, pulse_width=(speed*200)+10000)
M2_0=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3, pulse_width=0)
M2_1=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4, pulse_width=(speed*100)+10000)
M3_0=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6, pulse_width=0)
M3_1=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7, pulse_width=(speed*200)+10000)
M4_0=pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9, pulse_width=0)
M4_1=pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8, pulse_width=(speed*100)+10000)
led_red.value(1)
def stop():
M1_0=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1, pulse_width=0)
M1_1=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2, pulse_width=0)
M2_0=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3, pulse_width=0)
M2_1=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4, pulse_width=0)
M3_0=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6, pulse_width=0)
M3_1=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7, pulse_width=0)
M4_0=pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8, pulse_width=0)
M4_1=pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9, pulse_width=0)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(0)
led_red.value(1)
def left(speed):
M1_0=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1, pulse_width=(speed*30)+10000)
M1_1=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2, pulse_width=0)
M2_0=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3, pulse_width=(speed*100)+10000)
M2_1=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4, pulse_width=0)
M3_0=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6, pulse_width=(speed*30)+10000)
M3_1=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7, pulse_width=0)
M4_0=pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9, pulse_width=(speed*100)+10000)
M4_1=pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8, pulse_width=0)
led_right.value(1)
led_left.value(0)
def right(speed):
M1_0=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y1, pulse_width=(speed*200)+20000)
M1_1=pyb.Timer(8, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y2, pulse_width=0)
M2_0=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y3, pulse_width=(speed*200)+3000)
M2_1=pyb.Timer(4, freq=10000).channel(4, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y4, pulse_width=0)
M3_0=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(1, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y6, pulse_width=(speed*100)+20000)
M3_1=pyb.Timer(1, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y7, pulse_width=0)
M4_0=pyb.Timer(2, freq=10000).channel(3, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y9, pulse_width=(speed*100)+3000)
M4_1=pyb.Timer(12, freq=10000).channel(2, pyb.Timer.PWM, pin=pyb.Pin.board.Y8, pulse_width=0)
led_right.value(0)
led_left.value(1)
while True:
if blue.any()>0:
data=blue.read().decode()
print(data)
if data.find('0')>-1:
#stop
stop()
print('stop')
if data.find('1')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).on()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).off()
#-------------
go(5)
print('go')
if data.find('2')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).on()
pyb.LED(4).off()
#-------------
back(5)
if data.find('3')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).on()
left(5)
if data.find('4')>-1:
pyb.LED(2).off()
pyb.LED(3).off()
pyb.LED(4).on()
right(5)以上就是關于“MicroPython如何實現智能小車”這篇文章的內容,相信大家都有了一定的了解,希望小編分享的內容對大家有幫助,若想了解更多相關的知識內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。