您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
Exploit自動生成引擎Rex的示例分析,針對這個問題,這篇文章詳細介紹了相對應的分析和解答,希望可以幫助更多想解決這個問題的小伙伴找到更簡單易行的方法。
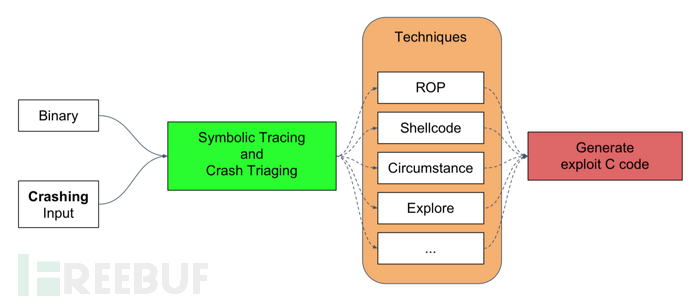
Exploit 自動生成引擎 Rex 在硬件模擬器 QEMU 與二進制分析平臺 angr 的基礎上,通過 Concolic Execution 實現 Exploit 的自動生成。將待分析的應用程序及導致應用程序崩潰的 Crash 作為系統輸入,Rex 將復現崩潰路徑,并對崩潰時的寄存器狀態及內存布局進行分析,判斷 Crash 的可利用性,并自動生成 Exploit。
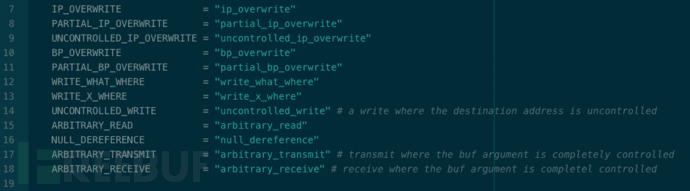
源碼中對漏洞類型的定義:
安裝 Rex 存在兩種方式:1)安裝 Mechaphish,安裝文檔;2)僅安裝 Rex,安裝文檔。二者的差別在于 Mechaphish 包含漏洞挖掘模塊 Driller、自動利用模塊 Rex、自動補丁模塊 Patcherex 以及 ropchain 生成模塊 angrop。由于各模塊之間相互獨立,因此本文選擇僅安裝自動利用模塊 Rex。本地環境采用 Ubuntu 16.04.5 Desktop(64 bit)。部署過程中,Rex 所需依賴如下:
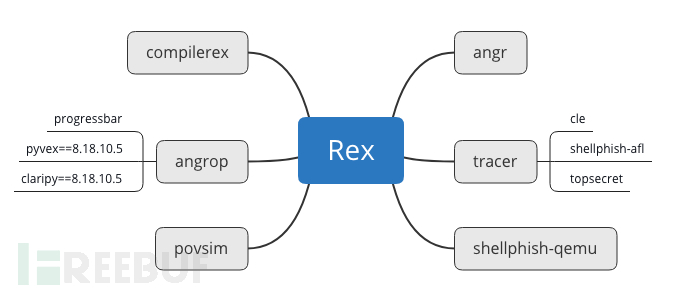
依賴過程中部分路徑需要調整,根據提示信息修改即可。各個依賴所承擔的功能如下:
| 組件名稱 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| angr | A powerful and user-friendly binary analysis platform! |
| tracer | Utilities for generating dynamic traces. |
| angrop | angrop is a rop gadget finder and chain builder. |
| compilerex | POV templates and compilation support for CGC binaries. compilerex is a hacky cgc binary compiler |
| shellphish-qemu | Shellphish's pip-installable package of QEMU |
| povsim | POV simulation for CGC. |
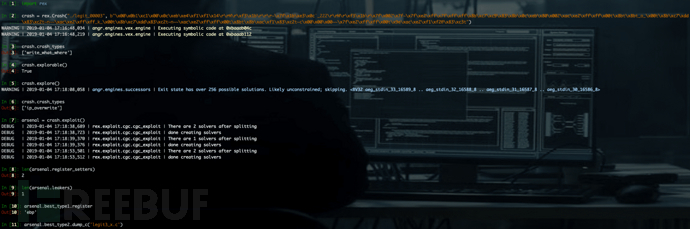
安裝完成后,使用以下代碼對 Rex 的功能進行測試。
# triage a crash
>>> crash = rex.Crash("./legit_00003", b"\x00\x0b1\xc1\x00\x0c\xeb\xe4\xf1\xf1\x14\r\rM\r\xf3\x1b\r\r\r~\x7f\x1b\xe3\x0c`_222\r\rM\r\xf3\x1b\r\x7f\x002\x7f~\x7f\xe2\xff\x7f\xff\xff\x8b\xc7\xc9\x83\x8b\x0c\xeb\x80\x002\xac\xe2\xff\xff\x00t\x8bt\x8bto\x00t\x8b\xc7\xdd\x83\xc2t~n\xac\xe2\xff\xffk\x00t\x8b\xc7\xdd\x83\xc2t~n\xac\xe2\xff\xff\x00t\x8bt\x8b\xac\xf1\x83\xc2t~c\x00\x00\x00~~\x7f\xe2\xff\xff\x00t\x9e\xac\xe2\xf1\xf2@\x83\xc3t")
>>> crash.crash_types
['write_what_where']
>>> crash.explorable()
True
explore the crash by setting segfaulting pointers to sane values and re-tracing
>>> crash.explore()
now we can see that we control instruction pointer
>>> crash.crash_types
'ip_overwrite'
generate exploits based off of this crash
it may take several minutes
>>> arsenal = crash.exploit()
we generated a type 1 POV for every register
>>> len(arsenal.register_setters) # we generate one circumstantial register setter, one shellcode register setter
2
and one Type 2 which can leak arbitrary memory
>>> len(arsenal.leakers)
1
exploits are graded based on reliability, and what kind of defenses they can
bypass, the two best exploits are put into the 'best_type1' and 'best_type2' attributes
>>> arsenal.best_type1.register
'ebp'
exploits can be dumped in C, Python, or as a compiled POV
>>> arsenal.best_type2.dump_c('legit3_x.c')
>>> arsenal.best_type2.dump_python('legit3_x.py')
>>> arsenal.best_type2.dump_binary('legit3_x.pov')
also POVs can be tested against a simulation of the CGC architecture
>>> arsenal.best_type1.test_binary()
True測試結果如下:
查看 Rex 源碼的目錄結構:
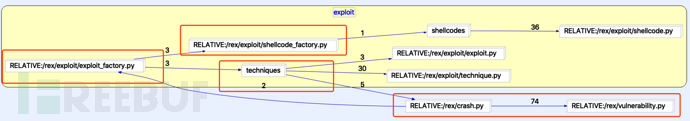
分析各類之間的依賴關系,從邏輯上大致可分為四部分: 1)Exploit_factory:調用各模塊,負責自動生成 Exploit; 2)Crash:復現崩潰路徑,判定 Crash 的可利用性; 3)Technique:對于可利用的 Crash,采用針對性的技術,生成 Exploit; 4)Shellcode_factory:shellcode 倉庫,根據需要選用合適的 Shellcode。
下文重點對 Crash 可利用性判定部分進行分析。
Rex 以 Concolic Execution 的方式復現 crash 路徑,分析崩潰時寄存器狀態及內存布局,并對 crash 的可利用性進行判定,相關功能代碼集中在 Crash.py 中。對原理感興趣的同學可以參考論文《SoK: (State of) The Art of War: Offensive Techniques in Binary Analysis》,以下是對論文原文的引用:
Vulnerable States. Unlike AEG/Mayhem, but similar to AXGEN, we generate exploits by performing concolic execution on crashing program inputs using angr. We drive concolic execution forward, forcing it to follow the same path as a dynamic trace gathered by concretely executing the crashing input applied to the program. Concolic execution is stopped at the point where the program crashed, and we inspect the symbolic state to determine the cause of the crash and measure exploitability. By counting the number of symbolic bits in certain registers, we can triage a crash into a number of categories such as frame pointer overwrite, instruction pointer overwrite, or arbitrary write, among others.
Concolic Execution 原理請感興趣的同學自行查閱。angr 在實現 concolic execution 時,需要提供 crash_addr。

因此,通過 QEMU 加載二進制程序及 PoC,以獲取 crash_addr。相關功能在 Tracer 模塊中實現。
Crash.py 中調用 Tracer 模塊的代碼如下:
tracer_args={
'ld_linux': os.path.join(bin_location, 'tests/i386/ld-linux.so.2'),'library_path': os.path.join(bin_location, 'tests/i386')}
r = tracer.QEMURunner(binary=binary, input=input_data, argv=argv, trace_timeout=trace_timeout, **tracer_args)在獲取 crash_addr 之后,對 angr 進行配置,并執行 Concolic Execution。 其中,較為關鍵的配置包括:初始狀態設定、State Plugin 選擇、路徑探索策略。
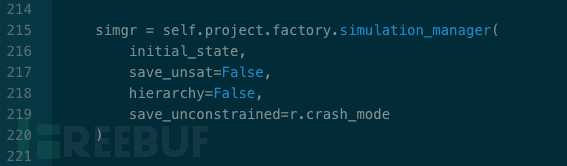
(1)初始狀態設定
配置 simulation_manager 中的 save_unconstrained 參數。 其中 r 為 tracer.QEMURunner() 返回值,當 PoC 成功觸發崩潰時 r.crash_mode 為 True,失敗時為 False。
通過 full_init_state()方法,設置程序的初始狀態:
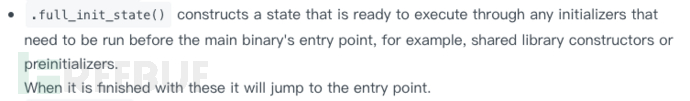
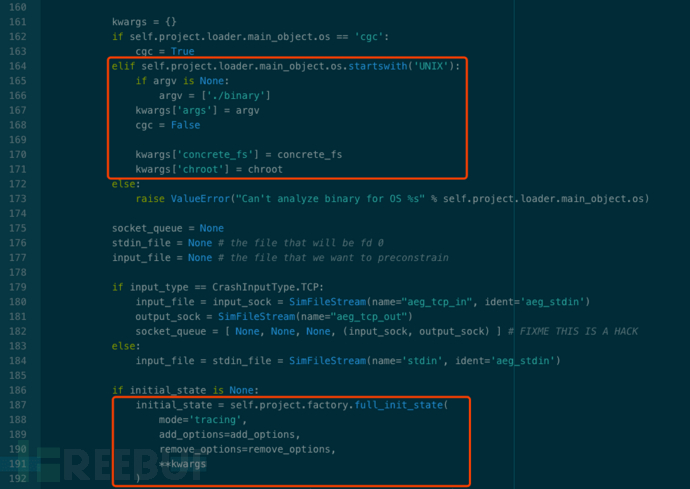
設置 tracing 模式:mode = ‘tracing’

add_options:
| Option name | Description |
|---|---|
| so.MEMORY_SYMBOLIC_BYTES_MAP | Maintain a mapping of symbolic variable to which memory address it "really" corresponds to, at the paged memory level? |
| so.TRACK_ACTION_HISTORY | track the history of actions through a path (multiple states). This action affects things on the angr level |
| so.CONCRETIZE_SYMBOLIC_WRITE_SIZES | Concretize the sizes of symbolic writes to memory |
| so.CONCRETIZE_SYMBOLIC_FILE_READ_SIZES | Concreteize the sizes of file reads |
| so.TRACK_MEMORY_ACTIONS | Keep a SimAction for each memory read and write |
remove_options:
由于 ‘tracing’ 模式下預制了一些選項,因此在優化策略時,不僅需要add_options,而且需要 remove_options。定義在./angr/sim_options.py中:
| Option name | Description |
|---|---|
| so.TRACK_CONSTRAINT_ACTIONS | Keep a SimAction for each constraint added |
| so.LAZY_SOLVES | Don't check satisfiability until absolutely necessary |
| so.ALL_FILES_EXIST | Attempting to open an unkown file will result in creating it with a symbolic length |
| so.TRACK_REGISTER_ACTIONS | Keep a SimAction for each register read and write |
| so.TRACK_TMP_ACTIONS | Keep a SimAction for each temporary variable read and write |
| so.TRACK_JMP_ACTIONS | Keep a SimAction for each jump or branch |
| so.ACTION_DEPS | Track dependencies in SimActions |
| so.SIMPLIFY_MEMORY_WRITES | Run values stored to memory through z3's simplification |
設置約束條件:
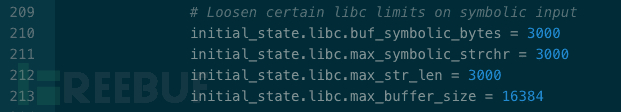
SimState 屬于 angr 核心概念之一,并被設計為插件式的架構,可以根據分析任務的不同,選用針對性的插件。Rex 默認選用了 'posix' 與 'preconstrainer'。插件源碼位于./angr/state_plugins/目錄下。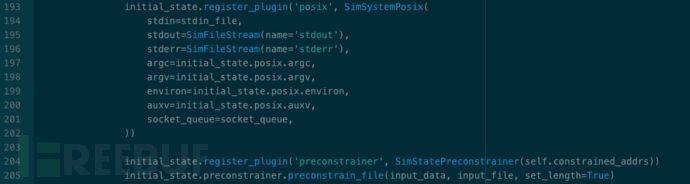
SimSystemPosix( ):
Data storage and interaction mechanisms for states with an environment conforming to posix.Available as state.posix.
SimStatePreconstrainer( ):
This state plugin manages the concept of preconstraining - adding constraints which you would like to remove later.:param constrained_addrs : SimActions for memory operations whose addresses should be constrained during crash analysis
路徑搜索策略的選擇,對符號執行來說舉足輕重。由于 Rex 在采用 Concolic Execution,因此設置了 'Tracer'、'Oppologist' 兩種路徑搜索策略。

angr 內置的路徑搜索方法存儲于 ./angr/exploration_techniques/ 目錄下。Crash.py 中調用代碼如下:

_triage_crash() 中根據 eip、ebp 中符號變量的個數,及發生崩潰時的操作,對 Crash 類型進行判定。
def _triage_crash(self):
ip = self.state.regs.ip
bp = self.state.regs.bp
# any arbitrary receives or transmits
# TODO: receives
zp = self.state.get_plugin('zen_plugin') if self.os == 'cgc' else None
if zp is not None and len(zp.controlled_transmits):
l.debug("detected arbitrary transmit vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.ARBITRARY_TRANSMIT)
# we assume a symbolic eip is always exploitable
if self.state.solver.symbolic(ip):
# how much control of ip do we have?
if self._symbolic_control(ip) >= self.state.arch.bits:
l.info("detected ip overwrite vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.IP_OVERWRITE)
else:
l.info("detected partial ip overwrite vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.PARTIAL_IP_OVERWRITE)
return
if self.state.solver.symbolic(bp):
# how much control of bp do we have
if self._symbolic_control(bp) >= self.state.arch.bits:
l.info("detected bp overwrite vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.BP_OVERWRITE)
else:
l.info("detected partial bp overwrite vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.PARTIAL_BP_OVERWRITE)
return
# if nothing obvious is symbolic let's look at actions
# grab the all actions in the last basic block
symbolic_actions = [ ]
if self._t is not None and self._t.last_state is not None:
recent_actions = reversed(self._t.last_state.history.recent_actions)
state = self._t.last_state
# TODO: this is a dead assignment! what was this supposed to be?
else:
recent_actions = reversed(self.state.history.actions)
state = self.state
for a in recent_actions:
if a.type == 'mem':
if self.state.solver.symbolic(a.addr):
symbolic_actions.append(a)
# TODO: pick the crashing action based off the crashing instruction address,
# crash fixup attempts will break on this
#import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
for sym_action in symbolic_actions:
if sym_action.action == "write":
if self.state.solver.symbolic(sym_action.data):
l.info("detected write-what-where vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.WRITE_WHAT_WHERE)
else:
l.info("detected write-x-where vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.WRITE_X_WHERE)
self.violating_action = sym_action
break
if sym_action.action == "read":
# special vulnerability type, if this is detected we can explore the crash further
l.info("detected arbitrary-read vulnerability")
self.crash_types.append(Vulnerability.ARBITRARY_READ)
self.violating_action = sym_action
break
return關于Exploit自動生成引擎Rex的示例分析問題的解答就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,如果你還有很多疑惑沒有解開,可以關注億速云行業資訊頻道了解更多相關知識。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。