您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
本篇內容介紹了“Android 4.0 Launcher源碼是什么”的有關知識,在實際案例的操作過程中,不少人都會遇到這樣的困境,接下來就讓小編帶領大家學習一下如何處理這些情況吧!希望大家仔細閱讀,能夠學有所成!
首先先畫了個圖來再來闡述一下WorkSpace的結構。如下圖:
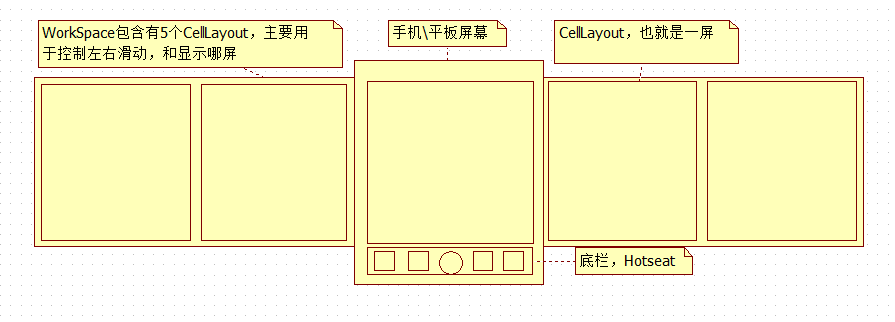
點擊查看大圖
桌面的左右滑動功能主要是在PagedView類中實現的,而WorkSpace是PagedView類的子類,所以會繼承PagedView中的方法。當我們的手指點擊WorkSpace時,首先就會觸發PageView中的onInterceptTouchEvent()方法,會根據相應的條件來判斷是否對Touch事件進行攔截,如果onInterceptTouchEvent()方法返回為true,則會對Touch事件進行攔截,PageView類的onTouch方法會進行響應從而得到調用。如果返回false,就分兩鐘情況:(1)我們是點擊在它的子控鍵上進行滑動時,比如我們是點擊在桌面的圖標上進行左右滑動的,workspace則會把Touch事件分發給它的子控件。(2)而如果僅僅是點擊到桌面的空白出Touch事件就不會發生響應。
在我們手指***次觸摸到屏幕時,首先會對onInterceptTouchEvent中的事件進行判斷,如果是按下事件(MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN), 則會記錄按下時的X坐標、Y坐標等等數據,同時改變現在Workspace的狀態為滾動狀態(OUCH_STATE_SCROLLING),這時會返回ture,把事件交給onTouchEvent函數來處理,onTouchEvent中同樣會對事件類型進行判斷,當事件方法為(otionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)的時候,就可以開始顯示滾動的指示條了(就是Hotseat上顯示第幾屏的屏點)。當我們按著屏幕不放進行滑動的時候,又會在onInterceptTouchEvent進行事件攔截,但是現在的事件類型變為了 MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE,因為是移動的操作,所以會在攔截的時候取消桌面長按的事件的響應,同時轉到onTouchEvent中對ACTION_MOVE事件的響應中,判斷我們移動了多少距離,使用scrollBy方法來對桌面進行移動,并刷新屏幕。***我們放開手后會觸發onTouchEvent中的MotionEvent.ACTION_UP事件,這時會根據滑動的情況來判斷是朝左滑動還是朝右滑動,如果手指只滑動了屏幕寬度的少一半距離,則會彈回原來的頁面,滑動多于屏幕寬度的一半則會進行翻頁。同時要注意無論在什么情況下觸發了WorkSpace滑動的事件,則系統會不斷調用computeScroll()方法,我們重寫這個方法同時在這個方法中調用刷新界面等操作。
滑動過程中所要注意的主要方法如下,具體見代碼注釋。
//對Touch事件進行攔截 主要用于在攔截各種Touch事件時,設置mTouchState的各種狀態 @Override public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { /* * This method JUST determines whether we want to intercept the motion. * If we return true, onTouchEvent will be called and we do the actual * scrolling there. * 這個方法僅僅決定了我們是否愿意去對滑動事件進行攔截,如果返回為true,則會調用onTouchEvent我們將會在那里進行事件處理 */ //對滑動的速率進行跟蹤。 acquireVelocityTrackerAndAddMovement(ev); // Skip touch handling if there are no pages to swipe // 如果沒有頁面,則跳過操作。 if (getChildCount() <= 0) return super.onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); /* * Shortcut the most recurring case: the user is in the dragging * state and he is moving his finger. We want to intercept this * motion. * shortcut最常見的情況是:用戶處于拖動的狀態下,同時在移動它的手指,這時候我們需要攔截這個動作。 * */ final int action = ev.getAction(); //如果是在MOVE的情況下,則進行Touch事件攔截 if ((action == MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE) && (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING)) { return true; } switch (action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: { /* * mIsBeingDragged == false, otherwise the shortcut would have caught it. Check * whether the user has moved far enough from his original down touch. * 如果mIsBeingDragged==false ,否則快捷方式應該捕獲到該事件,檢查一下用戶從它點擊的地方位移是否足夠 */ if (mActivePointerId != INVALID_POINTER) { //根據移動的距離判斷是翻頁還是移動一段位移,同時設置lastMotionX或者mTouchState這些值。同時取消桌面長按事件。 determineScrollingStart(ev); break; } // if mActivePointerId is INVALID_POINTER, then we must have missed an ACTION_DOWN // event. in that case, treat the first occurence of a move event as a ACTION_DOWN // i.e. fall through to the next case (don't break) // (We sometimes miss ACTION_DOWN events in Workspace because it ignores all events // while it's small- this was causing a crash before we checked for INVALID_POINTER) // 如果mActivePointerId 是 INVALID_POINTER,這時候我們應該已經錯過了ACTION_DOWN事件。在這種情況下,把 // ***次發生移動的事件當作ACTION——DOWN事件,直接進入下一個情況下。 // 我們有時候會錯過workspace中的ACTION_DOWN事件,因為在workspace變小的時候會忽略掉所有的事件。 } case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: { final float x = ev.getX(); final float y = ev.getY(); // Remember location of down touch // 記錄按下的位置 mDownMotionX = x; mLastMotionX = x; mLastMotionY = y; mLastMotionXRemainder = 0; mTotalMotionX = 0; //Return the pointer identifier associated with a particular pointer data index is this event. //The identifier tells you the actual pointer number associated with the data, //accounting for individual pointers going up and down since the start of the current gesture. //返回和這個事件關聯的觸點數據id,計算單獨點的id會上下浮動,因為手勢的起始位置揮發聲改變。 mActivePointerId = ev.getPointerId(0); mAllowLongPress = true; /* * If being flinged and user touches the screen, initiate drag; * otherwise don't. mScroller.isFinished should be false when * being flinged. * 如果被拖動同時用戶觸摸到了屏幕,就開始初始化拖動,否則便不會。 * 當拖動完成后mScroller.isFinished就應該設置為false. * */ final int xDist = Math.abs(mScroller.getFinalX() - mScroller.getCurrX()); final boolean finishedScrolling = (mScroller.isFinished() || xDist < mTouchSlop); if (finishedScrolling) { //標記為TOUCH_STATE_REST狀態 mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; //取消滾動動畫 mScroller.abortAnimation(); } else { //狀態為TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING; } // check if this can be the beginning of a tap on the side of the pages // to scroll the current page // 檢測此事件是不是開始于點擊頁面的邊緣來對當前頁面進行滾動。 if (mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_PREV_PAGE && mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_NEXT_PAGE) { if (getChildCount() > 0) { //根據觸點的點位來判斷是否點擊到上一頁,從而更新相應的狀態 if (hitsPreviousPage(x, y)) { mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_PREV_PAGE; } else if (hitsNextPage(x, y)) { mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_NEXT_PAGE; } } } break; } case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: //觸點不被相應時,所做的動作 mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; mAllowLongPress = false; mActivePointerId = INVALID_POINTER; //釋放速率跟蹤 releaseVelocityTracker(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP: onSecondaryPointerUp(ev); releaseVelocityTracker(); break; } /* * The only time we want to intercept motion events is if we are in the * drag mode. * 我們唯一會去對移動事件進行攔截的情況時我們在拖動模式下 */ if(DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onInterceptTouchEvent "+(mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_REST)); //只要是mTouchState的狀態不為TOUCH_STATE_REST,那么就進行事件攔截 return mTouchState != TOUCH_STATE_REST; }onTouchEvent方法,詳細見代碼注釋:
@Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) { // Skip touch handling if there are no pages to swipe // 如果沒有子頁面,就直接跳過 if (getChildCount() <= 0) return super.onTouchEvent(ev); acquireVelocityTrackerAndAddMovement(ev); final int action = ev.getAction(); switch (action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: /* * If being flinged and user touches, stop the fling. isFinished * will be false if being flinged. * 如果在滑動的過程中下用戶又點擊桌面,則取消滑動,從而響應當前的點擊。 * 在滑動的isFinished將返回false. */ if (!mScroller.isFinished()) { mScroller.abortAnimation(); } // Remember where the motion event started mDownMotionX = mLastMotionX = ev.getX(); mLastMotionXRemainder = 0; mTotalMotionX = 0; mActivePointerId = ev.getPointerId(0); //主要用來顯示滾動條,表明要開始滾動了,這里可以進行調整,滾動條時逐漸顯示還是立刻顯示。 if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING) { pageBeginMoving(); } break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING) { // Scroll to follow the motion event final int pointerIndex = ev.findPointerIndex(mActivePointerId); final float x = ev.getX(pointerIndex); final float deltaX = mLastMotionX + mLastMotionXRemainder - x; //總共移動的距離 mTotalMotionX += Math.abs(deltaX); // Only scroll and update mLastMotionX if we have moved some discrete amount. We // keep the remainder because we are actually testing if we've moved from the last // scrolled position (which is discrete). // 如果我們移動了一小段距離,我們則移動和更新mLastMotionX 。我們保存Remainder變量是因為會檢測我們 //是否是從***的滾動點位移動的。 if (Math.abs(deltaX) >= 1.0f) { mTouchX += deltaX; mSmoothingTime = System.nanoTime() / NANOTIME_DIV; if (!mDeferScrollUpdate) { scrollBy((int) deltaX, 0); if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "onTouchEvent().Scrolling: " + deltaX); } else { invalidate(); } mLastMotionX = x; mLastMotionXRemainder = deltaX - (int) deltaX; } else { //Trigger the scrollbars to draw. When invoked this method starts an animation to fade the //scrollbars out after a default delay. If a subclass provides animated scrolling, //the start delay should equal the duration of the scrolling animation. //觸發scrollbar進行繪制。 使用這個方法來啟動一個動畫來使scrollbars經過一段時間淡出。如果子類提供了滾動的動畫,則 //延遲的時間等于動畫滾動的時間。 awakenScrollBars(); } } else { determineScrollingStart(ev); } break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING) { final int activePointerId = mActivePointerId; final int pointerIndex = ev.findPointerIndex(activePointerId); final float x = ev.getX(pointerIndex); final VelocityTracker velocityTracker = mVelocityTracker; velocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaximumVelocity); int velocityX = (int) velocityTracker.getXVelocity(activePointerId); final int deltaX = (int) (x - mDownMotionX); final int pageWidth = getScaledMeasuredWidth(getPageAt(mCurrentPage)); // 屏幕的寬度*0.4f boolean isSignificantMove = Math.abs(deltaX) > pageWidth * SIGNIFICANT_MOVE_THRESHOLD; final int snapVelocity = mSnapVelocity; mTotalMotionX += Math.abs(mLastMotionX + mLastMotionXRemainder - x); boolean isFling = mTotalMotionX > MIN_LENGTH_FOR_FLING && Math.abs(velocityX) > snapVelocity; // In the case that the page is moved far to one direction and then is flung // in the opposite direction, we use a threshold to determine whether we should // just return to the starting page, or if we should skip one further. // 這鐘情況是頁面朝一個方向移動了一段距離,然后又彈回去了。我們使用一個閥值來判斷是進行翻頁還是返回到初始頁面 boolean returnToOriginalPage = false; if (Math.abs(deltaX) > pageWidth * RETURN_TO_ORIGINAL_PAGE_THRESHOLD && Math.signum(velocityX) != Math.signum(deltaX) && isFling) { returnToOriginalPage = true; } int finalPage; // We give flings precedence over large moves, which is why we short-circuit our // test for a large move if a fling has been registered. That is, a large // move to the left and fling to the right will register as a fling to the right. //朝右移動 if (((isSignificantMove && deltaX > 0 && !isFling) || (isFling && velocityX > 0)) && mCurrentPage > 0) { finalPage = returnToOriginalPage ? mCurrentPage : mCurrentPage - 1; snapToPageWithVelocity(finalPage, velocityX); //朝左移動 } else if (((isSignificantMove && deltaX < 0 && !isFling) || (isFling && velocityX < 0)) && mCurrentPage < getChildCount() - 1) { finalPage = returnToOriginalPage ? mCurrentPage : mCurrentPage + 1; snapToPageWithVelocity(finalPage, velocityX); //尋找離屏幕中心最近的頁面移動 } else { snapToDestination(); } } //直接移動到前一頁 else if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_PREV_PAGE) { // at this point we have not moved beyond the touch slop // (otherwise mTouchState would be TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING), so // we can just page int nextPage = Math.max(0, mCurrentPage - 1); if (nextPage != mCurrentPage) { snapToPage(nextPage); } else { snapToDestination(); } } //直接移動到下一頁 else if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_NEXT_PAGE) { // at this point we have not moved beyond the touch slop // (otherwise mTouchState would be TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING), so // we can just page int nextPage = Math.min(getChildCount() - 1, mCurrentPage + 1); if (nextPage != mCurrentPage) { snapToPage(nextPage); } else { snapToDestination(); } } else { onUnhandledTap(ev); } mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; mActivePointerId = INVALID_POINTER; releaseVelocityTracker(); break; //對事件不響應 case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL: if (mTouchState == TOUCH_STATE_SCROLLING) { snapToDestination(); } mTouchState = TOUCH_STATE_REST; mActivePointerId = INVALID_POINTER; releaseVelocityTracker(); break; case MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_UP: onSecondaryPointerUp(ev); break; } return true; }***有個小知識點要搞清楚,不少網友都問到過我。就是scrollTo和scrollBy的區別。我們查看View類的源代碼如下所示,mScrollX記錄的是當前View針對屏幕坐標在水平方向上的偏移量,而mScrollY則是記錄的時當前View針對屏幕在豎值方向上的偏移量。
從以下代碼我們可以得知,scrollTo就是把View移動到屏幕的X和Y位置,也就是絕對位置。而scrollBy其實就是調用的 scrollTo,但是參數是當前mScrollX和mScrollY加上X和Y的位置,所以ScrollBy調用的是相對于mScrollX和mScrollY的位置。我們在上面的代碼中可以看到當我們手指不放移動屏幕時,就會調用scrollBy來移動一段相對的距離。而當我們手指松開后,會調用 mScroller.startScroll(mUnboundedScrollX, 0, delta, 0, duration); 來產生一段動畫來移動到相應的頁面,在這個過程中系統回不斷調用computeScroll(),我們再使用scrollTo來把View移動到當前Scroller所在的絕對位置。
/** * Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be * invalidated. * @param x the x position to scroll to * @param y the y position to scroll to */ public void scrollTo(int x, int y) { if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) { int oldX = mScrollX; int oldY = mScrollY; mScrollX = x; mScrollY = y; invalidateParentCaches(); onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY); if (!awakenScrollBars()) { invalidate(true); } } } /** * Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be * invalidated. * @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally * @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically */ public void scrollBy(int x, int y) { scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y); }“Android 4.0 Launcher源碼是什么”的內容就介紹到這里了,感謝大家的閱讀。如果想了解更多行業相關的知識可以關注億速云網站,小編將為大家輸出更多高質量的實用文章!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。