您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章主要講解了“怎么使用TFserving”,文中的講解內容簡單清晰,易于學習與理解,下面請大家跟著小編的思路慢慢深入,一起來研究和學習“怎么使用TFserving”吧!
1.什么是TFserving
當你訓好你的模型,需要提供給外部使用的時候,你就需要把模型部署到線上,并提供合適的接口給外部調用。你可能會考慮一些問題:
用什么來部署
怎么提供api接口
多個模型GPU資源如何分配
線上模型如何更新而服務不中斷
目前流行的深度學習框架Tensorflow和Pytorch, Pytorch官方并沒有提供合適的線上部署方案;Tensorflow則提供了TFserving方案來部署線上模型推理。另外,Model Server for Apache MXNet 為MXNet模型提供推理服務。
本文為TFServing的使用指南。如果你是pytorch或者MXNet模型,也可以通過ONNX轉成TFserving的模型,部署在TFServing上。
那什么是TFserving?
TFserving是Google 2017推出的線上推理服務;采用C/S架構,客戶端可通過gRPC和RESTfull API與模型服務進行通信。
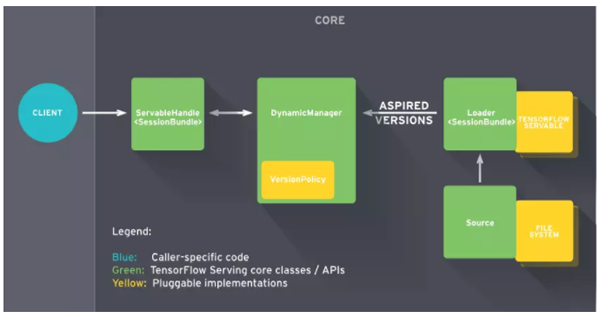
TFServing的特點:
支持模型版本控制和回滾:Manager會進行模型的版本的管理
支持并發,實現高吞吐量
開箱即用,并且可定制化
支持多模型服務
支持批處理
支持熱更新:Source加載本地模型,通知Manager有新的模型需要加載,Manager檢查模型的版本,通知Source創建的Loader進行加載模型
支持分布式模型
2.TFserving安裝
強烈建議采用docker方式安裝TFserving,安裝依賴docker和nvidia-docker(TFserving的gpu需要)
docker 安裝
#安裝yum-utils工具和device-mapper相關依賴包 yum install -y yum-utils \ device-mapper-persistent-data \ lvm2 #添加docker-ce stable版本的倉庫 yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #更新yum緩存文件 yum makecache fast #查看所有可安裝的docker-ce版本 yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r # 安裝docker-ce yum install docker-ce-17.12.1.ce-1.el7.centos #允許開機啟動docker-ce服務 systemctl enable docker.service #啟動Docker-ce服務 systemctl start docker #運行測試容器hello-world docker run --rm hello-world
nvidia-docker 安裝
# 安裝nvidia-docker2 yum install -y nvidia-docker2-2.0.3-1.docker17.12.1.ce # 重啟docker服務 service docker restart
安裝TFserving
docker pull tensorflow/serving:latest-gpu # 可以選擇其他版本如 docker pull tensorflow/serving:1.14.0-rc0-gpu
注意:docker版本和nvidia-docker要匹配
目前最新的nvidia-docker需要Docker為19.03 可參考官方https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker
nvidia-docker2 支持Docker版本低于19.03的其他版本(需>=1.12),現有服務器有18.09,1.17,1.13 https://github.com/NVIDIA/nvidia-docker/wiki/Installation-(version-2.0)
3.TFserving使用說明
3.1 模型轉換
TFserving的模型需要轉換成TFserving的格式, 不支持通常的checkpoint和pb格式。
TFserving的模型包含一個.pb文件和variables目錄(可以為空),導出格式如下:.
├── 1 │ ├── saved_model.pb │ └── variables ├── 2 │ ├── saved_model.pb │ └── variables
不同的深度學習框架的轉換路徑:
(1) pytorch(.pth)--> onnx(.onnx)--> tensorflow(.pb) --> TFserving (2) keras(.h6)--> tensorflow(.pb) --> TFserving (3) tensorflow(.pb) --> TFserving
這里詳細介紹下pb轉換成TFserving模型
import tensorflow as tf def create_graph(pb_file): """Creates a graph from saved GraphDef file and returns a saver.""" # Creates graph from saved graph_def.pb. with tf.gfile.FastGFile(pb_file, 'rb') as f: graph_def = tf.GraphDef() graph_def.ParseFromString(f.read()) _ = tf.import_graph_def(graph_def, name='') def pb_to_tfserving(pb_file, export_path, pb_io_name=[], input_node_name='input', output_node_name='output', signature_name='default_tfserving'): # pb_io_name 為 pb模型輸入和輸出的節點名稱, # input_node_name為轉化后輸入名 # output_node_name為轉化后輸出名 # signature_name 為簽名 create_graph(pb_file) # tensor_name_list = [tensor.name for tensor in tf.get_default_graph().as_graph_def().node] input_name = '%s:0' % pb_io_name[0] output_name = '%s:0' % pb_io_name[1] with tf.Session() as sess: in_tensor = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name(input_name) out_tensor = sess.graph.get_tensor_by_name(output_name) builder = tf.saved_model.builder.SavedModelBuilder(export_path) ## export_path導出路徑 inputs = {input_node_name: tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(in_tensor)} outputs = {output_node_name: tf.saved_model.utils.build_tensor_info(out_tensor)} signature = tf.saved_model.signature_def_utils.build_signature_def( inputs, outputs, method_name=tf.saved_model.signature_constants.PREDICT_METHOD_NAME) builder.add_meta_graph_and_variables( sesssess=sess, tags=[tf.saved_model.tag_constants.SERVING], signature_def_map={signature_name: signature}, clear_devices=True) ## signature_name為簽名,可自定義 builder.save() pb_model_path = 'test.pb' pb_to_tfserving(pb_model_path, './1', pb_io_name=['input_1_1','output_1'],signature_name='your_model')3.2 TFserving配置和啟動
模型導出后,同一個模型可以導出不同的版本(版本后數字),可以TFserving配置中指定模型和指定版本。TFserving的模型是通過模型名稱和簽名來唯一定位。TFserving 可以配置多個模型,充分利用GPU資源。
模型配置
# models.config model_config_list { config { name: 'your_model' base_path: '/models/your_model/' model_platform: 'tensorflow' # model_version_policy { # specific { # versions: 42 # versions: 43 # } # } # version_labels { # key: 'stable' # value: 43 # } # version_labels { # key: 'canary' # value: 43 # } } config { name: "mnist", base_path: "/models/mnist", model_platform: "tensorflow", model_version_policy: { specific: { versions: 1, versions: 2 } } } # 可以通過model_version_policy 進行版本的控制啟動服務
# 建議把模型和配置文件放在docker外的本地路徑,如/home/tfserving/models, 通過-v 掛載到docker內部 # --model_config_file: 指定模型配置文件 # -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0: 指定GPU # -p 指定端口映射 8500為gRpc 8501為restful api端口 # -t 為docker鏡像 nvidia-docker run -it --privileged -d -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 -v /home/tfserving/models:/models -p 8500:8500 -p 8501:8501 \ -t tensorflow/serving:latest-gpu \ --model_config_file=/models/models.config # /home/tfserving/models 結構 ├── models.config └── your_model ├── 1 │ ├── saved_model.pb │ └── variables └── 2 ├── saved_model.pb └── variables # test curl http://192.168.0.3:8501/v1/models/your_model { "model_version_status": [ { "version": "2", "state": "AVAILABLE", "status": { "error_code": "OK", "error_message": "" } } ] } # 其他啟動方式 # 如果多個模型在不同的目錄,可以通過-mount 單獨加載 nvidia-docker run -it --privileged -d -e NVIDIA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 \ --mount type=bind,source=/home/tfserving/models/your_model,target=/models/your_model \ --mount type=bind,source=/home/tfserving/models/your_model/models.config,target=/models/models.config \ -p 8510:8500 -p 8501:8501 \ -t tensorflow/serving:latest-gpu \ --model_config_file=/models/models.config3.3 TFserving服務調用
客戶端可以通過gRpc和http方式調用TFserving服務模型,支持多種客戶端語言,這里提供python的調用方式; 調用都是通過模型名稱和簽名來唯一對應一個模型
gRpc調用, gRpc的端口是8500
# # -*-coding:utf-8 -*- import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow_serving.apis import predict_pb2 from tensorflow_serving.apis import prediction_service_pb2_grpc import grpc import time import numpy as np import cv2 class YourModel(object): def __init__(self, socket): """ Args: socket: host and port of the tfserving, like 192.168.0.3:8500 """ self.socket = socket start = time.time() self.request, selfself.stub = self.__get_request() end = time.time() print('initialize cost time: ' + str(end - start) + ' s') def __get_request(self): channel = grpc.insecure_channel(self.socket, options=[('grpc.max_send_message_length', 1024 * 1024 * 1024), ('grpc.max_receive_message_length', 1024 * 1024 * 1024)]) # 可設置大小 stub = prediction_service_pb2_grpc.PredictionServiceStub(channel) request = predict_pb2.PredictRequest() request.model_spec.name = "your_model" # model name request.model_spec.signature_name = "your_model" # model signature name return request, stub def run(self, image): """ Args: image: the input image(rgb format) Returns: embedding is output of model """ img = image[..., ::-1] self.request.inputs['input'].CopyFrom(tf.contrib.util.make_tensor_proto(img)) # images is input of model result = self.stub.Predict(self.request, 30.0) return tf.make_ndarray(result.outputs['output']) def run_file(self, image_file): """ Args: image_file: the input image file Returns: """ image = cv2.imread(image_file) image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) return self.run(image) if __name__ == '__main__': model = YourModel('192.168.0.3:8500') test_file = './test.jpg' result = model.run_file(test_file) print(result) # [8.014745e-05 9.999199e-01]restful api調用: restful端口是8501
import cv2 import requests class SelfEncoder(json.JSONEncoder): def default(self, obj): if isinstance(obj, np.ndarray): return obj.tolist() elif isinstance(obj, np.floating): return float(obj) elif isinstance(obj, bytes): return str(obj, encoding='utf-8'); return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj) image_file = '/home/tfserving/test.jpg' image = cv2.imread(image_file) image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) img = image[..., ::-1] input_data = { "signature_name": "your_model", "instances": img } data = json.dumps(input_data, cls=SelfEncoder, indent=None) result = requests.post("http://192.168.0.3:8501/v1/models/your_model:predict", datadata=data) eval(result .content) # {'predictions': [8.01474525e-05, 0.999919891]}感謝各位的閱讀,以上就是“怎么使用TFserving”的內容了,經過本文的學習后,相信大家對怎么使用TFserving這一問題有了更深刻的體會,具體使用情況還需要大家實踐驗證。這里是億速云,小編將為大家推送更多相關知識點的文章,歡迎關注!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。