您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
Mybatis接口沒有實現類為什么可以執行增刪改查,很多新手對此不是很清楚,為了幫助大家解決這個難題,下面小編將為大家詳細講解,有這方面需求的人可以來學習下,希望你能有所收獲。
一、前言介紹
MyBatis 是一款非常優秀的持久層框架,相對于IBatis更是精進了不少。與此同時它還提供了很多的擴展點,比如最常用的插件;語言驅動器,執行器,對象工廠,對象包裝器工廠等等都可以擴展。那么,如果想成為一個有深度的男人(程序猿),還是應該好好的學習一下這款開源框架的源碼,以此可以更好的領會設計模式的精髓(面試?)。其實可能平常的業務開發中,并不會去深究各個框架的源代碼,也常常會聽到即使不會也可以開發代碼。但!每個人的目標不同,就像;代碼寫的好工資加的少(沒有bug怎么看出你工作嘞!),好!為了改變世界,開始分析嘍!
在分析之前先出一個題,看看你適合看源碼不;
@Test public void test(){ B b = new B(); b.scan(); //我的輸出結果是什么? } static class A { public void scan(){ doScan(); } protected void doScan(){ System.out.println("A.doScan"); } } static class B extends A { @Override protected void doScan() { System.out.println("B.doScan"); } }其實無論你的答案對錯,都不影響你對源碼的分析。只不過,往往在一些框架中會有很多的設計模式和開發技巧,如果上面的代碼在你平時的開發中幾乎沒用過,那么可能你暫時更多的還是開發著CRUD的功能(莫慌,我還寫過PHP呢)。
接下來先分析Mybatis單獨使用時的源碼執行過程,再分析Mybatis+Spring整合源碼,好!開始。
二、案例工程
為了更好的分析,我們創建一個Mybaits的案例工程,其中包括;Mybatis單獨使用、Mybatis+Spring整合使用
itstack-demo-mybatis └── src ├── main │ ├── java │ │ └── org.itstack.demo │ │ ├── dao │ │ │ ├── ISchool.java │ │ │ └── IUserDao.java │ │ └── interfaces │ │ ├── School.java │ │ └── User.java │ ├── resources │ │ ├── mapper │ │ │ ├── School_Mapper.xml │ │ │ └── User_Mapper.xml │ │ ├── props │ │ │ └── jdbc.properties │ │ ├── spring │ │ │ ├── mybatis-config-datasource.xml │ │ │ └── spring-config-datasource.xml │ │ ├── logback.xml │ │ ├── mybatis-config.xml │ │ └── spring-config.xml │ └── webapp │ └── WEB-INF └── test └── java └── org.itstack.demo.test ├── MybatisApiTest.java └── SpringApiTest.java
三、環境配置
JDK1.8
IDEA 2019.3.1
mybatis 3.4.6 {不同版本源碼略有差異和bug修復}
mybatis-spring 1.3.2 {以下源碼分析會說代碼行號,注意不同版本可能會有差異}
四、(mybatis)源碼分析
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis</artifactId> <version>3.4.6</version> </dependency>
Mybatis的整個源碼還是很大的,以下主要將部分核心內容進行整理分析,以便于后續分析Mybatis與Spring整合的源碼部分。簡要包括;容器初始化、配置文件解析、Mapper加載與動態代理。
1. 從一個簡單的案例開始
要學習Mybatis源碼,最好的方式一定是從一個簡單的點進入,而不是從Spring整合開始分析。SqlSessionFactory是整個Mybatis的核心實例對象,SqlSessionFactory對象的實例又通過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder對象來獲得。SqlSessionFactoryBuilder對象可以從XML配置文件加載配置信息,然后創建SqlSessionFactory。如下例子:
MybatisApiTest.java
public class MybatisApiTest { @Test public void test_queryUserInfoById() { String resource = "spring/mybatis-config-datasource.xml"; Reader reader; try { reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource); SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader); SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession(); try { User user = session.selectOne("org.itstack.demo.dao.IUserDao.queryUserInfoById", 1L); System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(user)); } finally { session.close(); reader.close(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }dao/IUserDao.java
public interface IUserDao { User queryUserInfoById(Long id); }spring/mybatis-config-datasource.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development"> <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/itstack?useUnicode=true"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123456"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/User_Mapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
如果一切順利,那么會有如下結果:
{"age":18,"createTime":1571376957000,"id":1,"name":"花花","updateTime":1571376957000}從上面的代碼塊可以看到,核心代碼;SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader),負責Mybatis配置文件的加載、解析、構建等職責,直到最終可以通過SqlSession來執行并返回結果。
2. 容器初始化
從上面代碼可以看到,SqlSessionFactory是通過SqlSessionFactoryBuilder工廠類創建的,而不是直接使用構造器。容器的配置文件加載和初始化流程如下:

流程核心類
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder
XMLConfigBuilder
XPathParser
Configuration
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder { public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) { return build(reader, null, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment) { return build(reader, environment, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, Properties properties) { return build(reader, null, properties); } public SqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(reader, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { reader.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) { return build(inputStream, null, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment) { return build(inputStream, environment, null); } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties) { return build(inputStream, null, properties); } public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) { try { XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties); return build(parser.parse()); } catch (Exception e) { throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); try { inputStream.close(); } catch (IOException e) { // Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error. } } } public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) { return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config); } }從上面的源碼可以看到,SqlSessionFactory提供三種方式build構建對象;
字節流:java.io.InputStream
字符流:java.io.Reader
配置類:org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration
那么,字節流、字符流都會創建配置文件解析類:XMLConfigBuilder,并通過parser.parse()生成Configuration,最后調用配置類構建方法生成SqlSessionFactory。
XMLConfigBuilder.java
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder { private boolean parsed; private final XPathParser parser; private String environment; private final ReflectorFactory localReflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory(); ... public XMLConfigBuilder(Reader reader, String environment, Properties props) { this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props); } ... }XMLConfigBuilder對于XML文件的加載和解析都委托于XPathParser,最終使用JDK自帶的javax.xml進行XML解析(XPath)
XPathParser(Reader reader, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver)
1. reader:使用字符流創建新的輸入源,用于對XML文件的讀取
2. validation:是否進行DTD校驗
3. variables:屬性配置信息
4. entityResolver:Mybatis硬編碼了new XMLMapperEntityResolver()提供XML默認解析器
XMLMapperEntityResolver.java
public class XMLMapperEntityResolver implements EntityResolver { private static final String IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM = "mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-config.dtd"; private static final String MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD = "org/apache/ibatis/builder/xml/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"; /* * Converts a public DTD into a local one * * @param publicId The public id that is what comes after "PUBLIC" * @param systemId The system id that is what comes after the public id. * @return The InputSource for the DTD * * @throws org.xml.sax.SAXException If anything goes wrong */ @Override public InputSource resolveEntity(String publicId, String systemId) throws SAXException { try { if (systemId != null) { String lowerCaseSystemId = systemId.toLowerCase(Locale.ENGLISH); if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_CONFIG_SYSTEM)) { return getInputSource(MYBATIS_CONFIG_DTD, publicId, systemId); } else if (lowerCaseSystemId.contains(MYBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM) || lowerCaseSystemId.contains(IBATIS_MAPPER_SYSTEM)) { return getInputSource(MYBATIS_MAPPER_DTD, publicId, systemId); } } return null; } catch (Exception e) { throw new SAXException(e.toString()); } } private InputSource getInputSource(String path, String publicId, String systemId) { InputSource source = null; if (path != null) { try { InputStream in = Resources.getResourceAsStream(path); source = new InputSource(in); source.setPublicId(publicId); source.setSystemId(systemId); } catch (IOException e) { // ignore, null is ok } } return source; } }Mybatis依賴于dtd文件進行進行解析,其中的ibatis-3-config.dtd主要是用于兼容用途
getInputSource(String path, String publicId, String systemId)的調用里面有兩個參數publicId(公共標識符)和systemId(系統標示符)
XPathParser.java
public XPathParser(Reader reader, boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) { commonConstructor(validation, variables, entityResolver); this.document = createDocument(new InputSource(reader)); } private void commonConstructor(boolean validation, Properties variables, EntityResolver entityResolver) { this.validation = validation; this.entityResolver = entityResolver; this.variables = variables; XPathFactory factory = XPathFactory.newInstance(); this.xpath = factory.newXPath(); } private Document createDocument(InputSource inputSource) { // important: this must only be called AFTER common constructor try { DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); factory.setValidating(validation); factory.setNamespaceAware(false); factory.setIgnoringComments(true); factory.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(false); factory.setCoalescing(false); factory.setExpandEntityReferences(true); DocumentBuilder builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder(); builder.setEntityResolver(entityResolver); builder.setErrorHandler(new ErrorHandler() { @Override public void error(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { throw exception; } @Override public void fatalError(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { throw exception; } @Override public void warning(SAXParseException exception) throws SAXException { } }); return builder.parse(inputSource); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error creating document instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }從上到下可以看到主要是為了創建一個Mybatis的文檔解析器,最后根據builder.parse(inputSource)返回Document
得到XPathParser實例后,接下來在調用方法:this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props);
XMLConfigBuilder.this(new XPathParser(reader, true, props, new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), environment, props); private XMLConfigBuilder(XPathParser parser, String environment, Properties props) { super(new Configuration()); ErrorContext.instance().resource("SQL Mapper Configuration"); this.configuration.setVariables(props); this.parsed = false; this.environment = environment; this.parser = parser; }3. 其中調用了父類的構造函數
public abstract class BaseBuilder { protected final Configuration configuration; protected final TypeAliasRegistry typeAliasRegistry; protected final TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry; public BaseBuilder(Configuration configuration) { this.configuration = configuration; thisthis.typeAliasRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry(); thisthis.typeHandlerRegistry = this.configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); } }4. XMLConfigBuilder創建完成后,sqlSessionFactoryBuild調用parser.parse()創建Configuration
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder { public Configuration parse() { if (parsed) { throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once."); } parsed = true; parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); return configuration; } }3. 配置文件解析
這一部分是整個XML文件解析和裝載的核心內容,其中包括;
屬性解析propertiesElement
加載settings節點settingsAsProperties
載自定義VFS loadCustomVfs
解析類型別名typeAliasesElement
加載插件pluginElement
加載對象工廠objectFactoryElement
創建對象包裝器工廠objectWrapperFactoryElement
加載反射工廠reflectorFactoryElement
元素設置settingsElement
加載環境配置environmentsElement
數據庫廠商標識加載databaseIdProviderElement
加載類型處理器typeHandlerElement
(核心)加載mapper文件mapperElement
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration")); private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) { try { //issue #117 read properties first //屬性解析propertiesElement propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties")); //加載settings節點settingsAsProperties Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings")); //加載自定義VFS loadCustomVfs loadCustomVfs(settings); //解析類型別名typeAliasesElement typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases")); //加載插件pluginElement pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins")); //加載對象工廠objectFactoryElement objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory")); //創建對象包裝器工廠objectWrapperFactoryElement objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory")); //加載反射工廠reflectorFactoryElement reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory")); //元素設置 settingsElement(settings); // read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631 //加載環境配置environmentsElement environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments")); //數據庫廠商標識加載databaseIdProviderElement databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider")); //加載類型處理器typeHandlerElement typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers")); //加載mapper文件mapperElement mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers")); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e); } }所有的root.evalNode()底層都是調用XML DOM方法:Object evaluate(String expression, Object item, QName returnType),表達式參數expression,通過XObject resultObject = eval( expression, item )返回最終節點內容,可以參考http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybati...,如下;
<!ELEMENT configuration (properties?, settings?, typeAliases?, typeHandlers?, objectFactory?, objectWrapperFactory?, reflectorFactory?, plugins?, environments?, databaseIdProvider?, mappers?)> <!ELEMENT databaseIdProvider (property*)> <!ATTLIST databaseIdProvider type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT properties (property*)> <!ATTLIST properties resource CDATA #IMPLIED url CDATA #IMPLIED > <!ELEMENT property EMPTY> <!ATTLIST property name CDATA #REQUIRED value CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT settings (setting+)> <!ELEMENT setting EMPTY> <!ATTLIST setting name CDATA #REQUIRED value CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT typeAliases (typeAlias*,package*)> <!ELEMENT typeAlias EMPTY> <!ATTLIST typeAlias type CDATA #REQUIRED alias CDATA #IMPLIED > <!ELEMENT typeHandlers (typeHandler*,package*)> <!ELEMENT typeHandler EMPTY> <!ATTLIST typeHandler javaType CDATA #IMPLIED jdbcType CDATA #IMPLIED handler CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT objectFactory (property*)> <!ATTLIST objectFactory type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT objectWrapperFactory EMPTY> <!ATTLIST objectWrapperFactory type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT reflectorFactory EMPTY> <!ATTLIST reflectorFactory type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT plugins (plugin+)> <!ELEMENT plugin (property*)> <!ATTLIST plugin interceptor CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT environments (environment+)> <!ATTLIST environments default CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT environment (transactionManager,dataSource)> <!ATTLIST environment id CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT transactionManager (property*)> <!ATTLIST transactionManager type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT dataSource (property*)> <!ATTLIST dataSource type CDATA #REQUIRED > <!ELEMENT mappers (mapper*,package*)> <!ELEMENT mapper EMPTY> <!ATTLIST mapper resource CDATA #IMPLIED url CDATA #IMPLIED class CDATA #IMPLIED > <!ELEMENT package EMPTY> <!ATTLIST package name CDATA #REQUIRED >
mybatis-3-config.dtd 定義文件中有11個配置文件,如下;
properties?,
settings?,
typeAliases?,
typeHandlers?,
objectFactory?,
objectWrapperFactory?,
reflectorFactory?,
plugins?,
environments?,
databaseIdProvider?,
mappers?
以上每個配置都是可選。最終配置內容會保存到org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration,如下;
public class Configuration { protected Environment environment; // 允許在嵌套語句中使用分頁(RowBounds)。如果允許使用則設置為false。默認為false protected boolean safeRowBoundsEnabled; // 允許在嵌套語句中使用分頁(ResultHandler)。如果允許使用則設置為false。 protected boolean safeResultHandlerEnabled = true; // 是否開啟自動駝峰命名規則(camel case)映射,即從經典數據庫列名 A_COLUMN 到經典 Java 屬性名 aColumn 的類似映射。默認false protected boolean mapUnderscoreToCamelCase; // 當開啟時,任何方法的調用都會加載該對象的所有屬性。否則,每個屬性會按需加載。默認值false (true in ≤3.4.1) protected boolean aggressiveLazyLoading; // 是否允許單一語句返回多結果集(需要兼容驅動)。 protected boolean multipleResultSetsEnabled = true; // 允許 JDBC 支持自動生成主鍵,需要驅動兼容。這就是insert時獲取mysql自增主鍵/oracle sequence的開關。注:一般來說,這是希望的結果,應該默認值為true比較合適。 protected boolean useGeneratedKeys; // 使用列標簽代替列名,一般來說,這是希望的結果 protected boolean useColumnLabel = true; // 是否啟用緩存 {默認是開啟的,可能這也是你的面試題} protected boolean cacheEnabled = true; // 指定當結果集中值為 null 的時候是否調用映射對象的 setter(map 對象時為 put)方法,這對于有 Map.keySet() 依賴或 null 值初始化的時候是有用的。 protected boolean callSettersOnNulls; // 允許使用方法簽名中的名稱作為語句參數名稱。 為了使用該特性,你的工程必須采用Java 8編譯,并且加上-parameters選項。(從3.4.1開始) protected boolean useActualParamName = true; //當返回行的所有列都是空時,MyBatis默認返回null。 當開啟這個設置時,MyBatis會返回一個空實例。 請注意,它也適用于嵌套的結果集 (i.e. collectioin and association)。(從3.4.2開始) 注:這里應該拆分為兩個參數比較合適, 一個用于結果集,一個用于單記錄。通常來說,我們會希望結果集不是null,單記錄仍然是null protected boolean returnInstanceForEmptyRow; // 指定 MyBatis 增加到日志名稱的前綴。 protected String logPrefix; // 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具體實現,未指定時將自動查找。一般建議指定為slf4j或log4j protected Class <? extends Log> logImpl; // 指定VFS的實現, VFS是mybatis提供的用于訪問AS內資源的一個簡便接口 protected Class <? extends VFS> vfsImpl; // MyBatis 利用本地緩存機制(Local Cache)防止循環引用(circular references)和加速重復嵌套查詢。 默認值為 SESSION,這種情況下會緩存一個會話中執行的所有查詢。 若設置值為 STATEMENT,本地會話僅用在語句執行上,對相同 SqlSession 的不同調用將不會共享數據。 protected LocalCacheScope localCacheScope = LocalCacheScope.SESSION; // 當沒有為參數提供特定的 JDBC 類型時,為空值指定 JDBC 類型。 某些驅動需要指定列的 JDBC 類型,多數情況直接用一般類型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 protected JdbcType jdbcTypeForNull = JdbcType.OTHER; // 指定對象的哪個方法觸發一次延遲加載。 protected Set<String> lazyLoadTriggerMethods = new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(new String[] { "equals", "clone", "hashCode", "toString" })); // 設置超時時間,它決定驅動等待數據庫響應的秒數。默認不超時 protected Integer defaultStatementTimeout; // 為驅動的結果集設置默認獲取數量。 protected Integer defaultFetchSize; // SIMPLE 就是普通的執行器;REUSE 執行器會重用預處理語句(prepared statements); BATCH 執行器將重用語句并執行批量更新。 protected ExecutorType defaultExecutorType = ExecutorType.SIMPLE; // 指定 MyBatis 應如何自動映射列到字段或屬性。 NONE 表示取消自動映射;PARTIAL 只會自動映射沒有定義嵌套結果集映射的結果集。 FULL 會自動映射任意復雜的結果集(無論是否嵌套)。 protected AutoMappingBehavior autoMappingBehavior = AutoMappingBehavior.PARTIAL; // 指定發現自動映射目標未知列(或者未知屬性類型)的行為。這個值應該設置為WARNING比較合適 protected AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior = AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.NONE; // settings下的properties屬性 protected Properties variables = new Properties(); // 默認的反射器工廠,用于操作屬性、構造器方便 protected ReflectorFactory reflectorFactory = new DefaultReflectorFactory(); // 對象工廠, 所有的類resultMap類都需要依賴于對象工廠來實例化 protected ObjectFactory objectFactory = new DefaultObjectFactory(); // 對象包裝器工廠,主要用來在創建非原生對象,比如增加了某些監控或者特殊屬性的代理類 protected ObjectWrapperFactory objectWrapperFactory = new DefaultObjectWrapperFactory(); // 延遲加載的全局開關。當開啟時,所有關聯對象都會延遲加載。特定關聯關系中可通過設置fetchType屬性來覆蓋該項的開關狀態。 protected boolean lazyLoadingEnabled = false; // 指定 Mybatis 創建具有延遲加載能力的對象所用到的代理工具。MyBatis 3.3+使用JAVASSIST protected ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new JavassistProxyFactory(); // #224 Using internal Javassist instead of OGNL // MyBatis 可以根據不同的數據庫廠商執行不同的語句,這種多廠商的支持是基于映射語句中的 databaseId 屬性。 protected String databaseId; ... }以上可以看到,Mybatis把所有的配置;resultMap、Sql語句、插件、緩存等都維護在Configuration中。這里還有一個小技巧,在Configuration還有一個StrictMap內部類,它繼承于HashMap完善了put時防重、get時取不到值的異常處理,如下;
protected static class StrictMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> { private static final long serialVersionUID = -4950446264854982944L; private final String name; public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) { super(initialCapacity, loadFactor); this.name = name; } public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity) { super(initialCapacity); this.name = name; } public StrictMap(String name) { super(); this.name = name; } public StrictMap(String name, Map<String, ? extends V> m) { super(m); this.name = name; } }(核心)加載mapper文件mapperElement
Mapper文件處理是Mybatis框架的核心服務,所有的SQL語句都編寫在Mapper中,這塊也是我們分析的重點,其他模塊可以后續講解。
XMLConfigBuilder.parseConfiguration()->mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { // 如果要同時使用package自動掃描和通過mapper明確指定要加載的mapper,一定要確保package自動掃描的范圍不包含明確指定的mapper,否則在通過package掃描的interface的時候,嘗試加載對應xml文件的loadXmlResource()的邏輯中出現判重出錯,報org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException異常,即使xml文件中包含的內容和mapper接口中包含的語句不重復也會出錯,包括加載mapper接口時自動加載的xml mapper也一樣會出錯。 if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource"); String url = child.getStringAttribute("url"); String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class"); if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) { ErrorContext.instance().resource(url); InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url); XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments()); mapperParser.parse(); } else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) { Class<?> mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass); configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface); } else { throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one."); } } } } }Mybatis提供了兩類配置Mapper的方法,第一類是使用package自動搜索的模式,這樣指定package下所有接口都會被注冊為mapper,也是在Spring中比較常用的方式,例如:
<mappers> <package name="org.itstack.demo"/> </mappers>
另外一類是明確指定Mapper,這又可以通過resource、url或者class進行細分,例如;
<mappers> <mapper resource="mapper/User_Mapper.xml"/> <mapper class=""/> <mapper url=""/> </mappers>
4. Mapper加載與動態代理
通過package方式自動搜索加載,生成對應的mapper代理類,代碼塊和流程,如下;
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception { if (parent != null) { for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) { if ("package".equals(child.getName())) { String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name"); configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage); } else { ... } } } }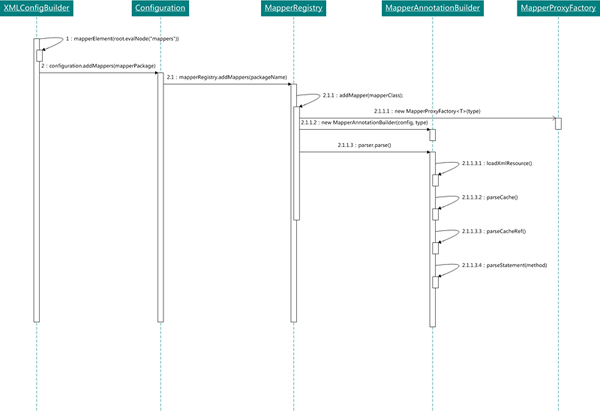
Mapper加載到生成代理對象的流程中,主要的核心類包括;
XMLConfigBuilder
Configuration
MapperRegistry
MapperAnnotationBuilder
MapperProxyFactory
MapperRegistry.java
解析加載Mapper
public void addMappers(String packageName, Class<?> superType) { // mybatis框架提供的搜索classpath下指定package以及子package中符合條件(注解或者繼承于某個類/接口)的類,默認使用Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()返回的加載器,和spring的工具類殊途同歸。 ResolverUtil<Class<?>> resolverUtil = new ResolverUtil<Class<?>>(); // 無條件的加載所有的類,因為調用方傳遞了Object.class作為父類,這也給以后的指定mapper接口預留了余地 resolverUtil.find(new ResolverUtil.IsA(superType), packageName); // 所有匹配的calss都被存儲在ResolverUtil.matches字段中 Set<Class<? extends Class<?>>> mapperSet = resolverUtil.getClasses(); for (Class<?> mapperClass : mapperSet) { //調用addMapper方法進行具體的mapper類/接口解析 addMapper(mapperClass); } }生成代理類:MapperProxyFactory
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { // 對于mybatis mapper接口文件,必須是interface,不能是class if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { // 為mapper接口創建一個MapperProxyFactory代理 knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type)); // It's important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try. MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } }在MapperRegistry中維護了接口類與代理工程的映射關系,knownMappers;
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
MapperProxyFactory.java
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> { private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>(); public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } public Class<T> getMapperInterface() { return mapperInterface; } public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() { return methodCache; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); } }如上是Mapper的代理類工程,構造函數中的mapperInterface就是對應的接口類,當實例化時候會獲得具體的MapperProxy代理,里面主要包含了SqlSession。
五、(mybatis-spring)源碼分析
<dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId> <version>1.3.2</version> </dependency>
作為一款好用的ORM框架,一定是蘿莉臉(單純)、御姐心(強大),鋪的了床(屏蔽與JDBC直接打交道)、暖的了房(速度性能好)!鑒于這些優點幾乎在國內互聯網大部分開發框架都會使用到Mybatis,尤其在一些需要高性能的場景下需要優化sql那么一定需要手寫sql在xml中。那么,準備好了嗎!開始分析分析它的源碼;
1. 從一個簡單的案例開始
與分析mybatis源碼一樣,先做一個簡單的案例;定義dao、編寫配置文件、junit單元測試;
SpringApiTest.java
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:spring-config.xml") public class SpringApiTest { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringApiTest.class); @Resource private ISchoolDao schoolDao; @Resource private IUserDao userDao; @Test public void test_queryRuleTreeByTreeId(){ School ruleTree = schoolDao.querySchoolInfoById(1L); logger.info(JSON.toJSONString(ruleTree)); User user = userDao.queryUserInfoById(1L); logger.info(JSON.toJSONString(user)); } }spring-config-datasource.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 1.數據庫連接池: DriverManagerDataSource 也可以使用DBCP2--> <bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="${db.jdbc.driverClassName}"/> <property name="url" value="${db.jdbc.url}"/> <property name="username" value="${db.jdbc.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${db.jdbc.password}"/> </bean> <!-- 2.配置SqlSessionFactory對象 --> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean"> <!-- 注入數據庫連接池 --> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> <!-- 配置MyBaties全局配置文件:mybatis-config.xml --> <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/> <!-- 掃描entity包 使用別名 --> <property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="org.itstack.demo.po"/> <!-- 掃描sql配置文件:mapper需要的xml文件 --> <property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mapper/*.xml"/> </bean> <!-- 3.配置掃描Dao接口包,動態實現Dao接口,注入到spring容器中 --> <bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer"> <!-- 注入sqlSessionFactory --> <property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/> <!-- 給出需要掃描Dao接口包,多個逗號隔開 --> <property name="basePackage" value="org.itstack.demo.dao"/> </bean> </beans>如果一切順利,那么會有如下結果:
{"address":"北京市海淀區頤和園路5號","createTime":1571376957000,"id":1,"name":"北京大學","updateTime":1571376957000} {"age":18,"createTime":1571376957000,"id":1,"name":"花花","updateTime":1571376957000}從上面單元測試的代碼可以看到,兩個沒有方法體的注解就這么神奇的執行了我們的xml中的配置語句并輸出了結果。其實主要得益于以下兩個類;
org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean
org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer
2. 掃描裝配注冊(MapperScannerConfigurer)
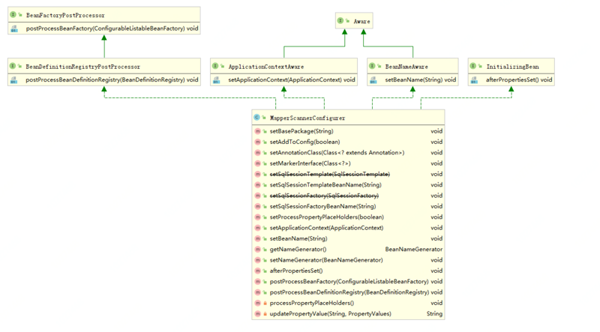
MapperScannerConfigurer為整個Dao接口層生成動態代理類注冊,啟動到了核心作用。這個類實現了如下接口,用來對掃描的Mapper進行處理:
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
InitializingBean
ApplicationContextAware
BeanNameAware
整體類圖如下;
執行流程如下;
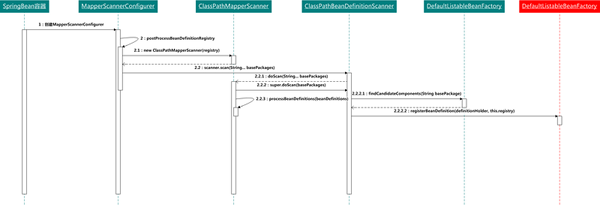
上面的類圖+流程圖,其實已經很清楚的描述了MapperScannerConfigurer初始化過程,但對于頭一次看的新人來說依舊是我太難了,好繼續!
MapperScannerConfigurer.java & 部分截取
@Override public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) { processPropertyPlaceHolders(); } ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry); scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig); scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass); scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface); scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate); scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName); scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName); scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext); scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator); scanner.registerFilters(); scanner.scan(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS)); }實現了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry用于注冊Bean到Spring容器中
306行:new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry); 硬編碼類路徑掃描器,用于解析Mybatis的Mapper文件
317行:scanner.scan 對Mapper進行掃描。這里包含了一個繼承類實現關系的調用,也就是本文開頭的測試題。
ClassPathMapperScanner.java & 部分截取
@Override public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages); if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) { logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration."); } else { processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions); } return beanDefinitions; }優先調用父類的super.doScan(basePackages);進行注冊Bean信息
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.java & 部分截取
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry); if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate) } if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.regi beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; }優先調用了父類的doScan方法,用于Mapper掃描和Bean的定義以及注冊到DefaultListableBeanFactory。{DefaultListableBeanFactory是Spring中IOC容器的始祖,所有需要實例化的類都需要注冊進來,之后在初始化}
272行:findCandidateComponents(basePackage),掃描package包路徑,對于注解類的有另外的方式,大同小異
288行:registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);注冊Bean信息的過程,最終會調用到:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
ClassPathMapperScanner.java & 部分截取
**processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);** private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) { GenericBeanDefinition definition; for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) { definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + definition.getBeanClassName() + "' mapperInterface"); } // the mapper interface is the original class of the bean // but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); // issue #59 definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass()); definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig); boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false; if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) { definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) { if (explicitFactoryUsed) { logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored."); } definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) { if (explicitFactoryUsed) { logger.warn("Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored."); } definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate); explicitFactoryUsed = true; } if (!explicitFactoryUsed) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'."); } definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE); } } }163行:super.doScan(basePackages);,調用完父類方法后開始執行內部方法:processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions)
186行:definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(definition.getBeanClassName()); 設置BeanName參數,也就是我們的:ISchoolDao、IUserDao
187行:definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBean.getClass());,設置BeanClass,接口本身是沒有類的,那么這里將MapperFactoryBean類設置進來,最終所有的dao層接口類都是這個MapperFactoryBean
MapperFactoryBean.java & 部分截取
這個類有繼承也有接口實現,最好先了解下整體類圖,如下;
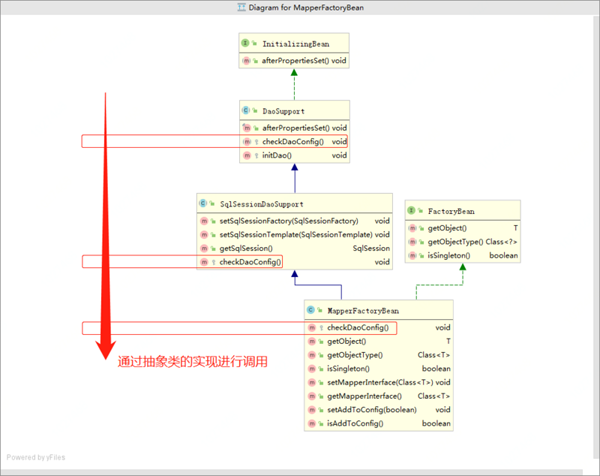
這個類就非常重要了,最終所有的sql信息執行都會通過這個類獲取getObject(),也就是SqlSession獲取mapper的代理類:MapperProxyFactory->MapperProxy
public class MapperFactoryBean<T> extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements FactoryBean<T> { private Class<T> mapperInterface; private boolean addToConfig = true; public MapperFactoryBean() { //intentionally empty } public MapperFactoryBean(Class<T> mapperInterface) { this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; } /** * 當SpringBean容器初始化時候會調用到checkDaoConfig(),他是繼承類中的抽象方法 * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override protected void checkDaoConfig() { super.checkDaoConfig(); notNull(this.mapperInterface, "Property 'mapperInterface' is required"); Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration(); if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) { try { configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("Error while adding the mapper '" + this.mapperInterface + "' to configuration.", e); throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } } } /** * {@inheritDoc} */ @Override public T getObject() throws Exception { return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface); } ... }72行:checkDaoConfig(),當SpringBean容器初始化時候會調用到checkDaoConfig(),他是繼承類中的抽象方法
95行:getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);,通過接口獲取Mapper(代理類),調用過程如下;
DefaultSqlSession.getMapper(Class<T> type),獲取Mapper
Configuration.getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession),從配置中獲取
MapperRegistry.getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession),從注冊中心獲取到實例化生成
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type); if (mapperProxyFactory == null) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry."); } try { return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession); } catch (Exception e) { throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e); } }mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);,通過反射工程生成MapperProxy
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy); } public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) { final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache); return newInstance(mapperProxy); }MapperProxy.java & 部分截取
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L; private final SqlSession sqlSession; private final Class<T> mapperInterface; private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache; public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) { this.sqlSession = sqlSession; this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface; this.methodCache = methodCache; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) { return method.invoke(this, args); } else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) { return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args); } } catch (Throwable t) { throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t); } final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method); return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args); } private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) { MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method); if (mapperMethod == null) { mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration()); methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod); } return mapperMethod; } @UsesJava7 private Object invokeDefaultMethod(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { final Constructor<MethodHandles.Lookup> constructor = MethodHandles.Lookup.class .getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, int.class); if (!constructor.isAccessible()) { constructor.setAccessible(true); } final Class<?> declaringClass = method.getDeclaringClass(); return constructor .newInstance(declaringClass, MethodHandles.Lookup.PRIVATE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PROTECTED | MethodHandles.Lookup.PACKAGE | MethodHandles.Lookup.PUBLIC) .unreflectSpecial(method, declaringClass).bindTo(proxy).invokeWithArguments(args); } ... }58行:final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);,從緩存中獲取MapperMethod
59行:mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);,執行SQL語句,并返回結果(到這關于查詢獲取結果就到骨頭(干)層了);INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、SELECT
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) { Object result; switch (command.getType()) { case INSERT: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param)); break; } case UPDATE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param)); break; } case DELETE: { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param)); break; } case SELECT: if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args); result = null; } else if (method.returnsMany()) { result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsMap()) { result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args); } else if (method.returnsCursor()) { result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args); } else { Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args); result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param); } break; case FLUSH: result = sqlSession.flushStatements(); break; default: throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName()); } if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) { throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName() + " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ")."); } return result; }以上對于MapperScannerConfigurer這一層就分析完了,從掃描定義注入到為Spring容器準備Bean的信息,代理、反射、SQL執行,基本就包括全部核心內容了,接下來在分析下SqlSessionFactoryBean
3. SqlSession容器工廠初始化(SqlSessionFactoryBean)
SqlSessionFactoryBean初始化過程中需要對一些自身內容進行處理,因此也需要實現如下接口;
FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>
InitializingBean -> void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception
ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent>
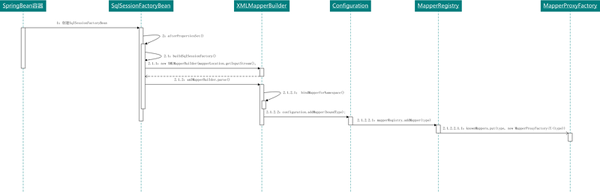
以上的流程其實已經很清晰的描述整個核心流程,但同樣對于新手上路會有障礙,那么!好,繼續!
SqlSessionFactoryBean.java & 部分截取
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required"); notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required"); state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null), "Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together"); this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory(); }afterPropertiesSet(),InitializingBean接口為bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是繼承該接口的類,在初始化bean的時候都會執行該方法。
380行:buildSqlSessionFactory();內部方法構建,核心功能繼續往下看。
SqlSessionFactoryBean.java & 部分截取
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException { Configuration configuration; XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null; ... if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) { for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) { if (mapperLocation == null) { continue; } try { XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(), configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments()); xmlMapperBuilder.parse(); } catch (Exception e) { throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e); } finally { ErrorContext.instance().reset(); } if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'"); } } } else { if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found"); } } return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(configuration); }513行:for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) 循環解析Mapper內容
519行:XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(...) 解析XMLMapperBuilder
521行:xmlMapperBuilder.parse() 執行解析,具體如下;
XMLMapperBuilder.java & 部分截取
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder { private final XPathParser parser; private final MapperBuilderAssistant builderAssistant; private final Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments; private final String resource; private void bindMapperForNamespace() { String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace(); if (namespace != null) { Class<?> boundType = null; try { boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { //ignore, bound type is not required } if (boundType != null) { if (!configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) { // Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag // to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface // look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace); configuration.addMapper(boundType); } } } } }這里413行非常重要,configuration.addMapper(boundType);,真正到了添加Mapper到配置中心
MapperRegistry.java & 部分截取
public class MapperRegistry { public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) { if (type.isInterface()) { if (hasMapper(type)) { throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry."); } boolean loadCompleted = false; try { knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type)); // It's important that the type is added before the parser is run // otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the // mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try. MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type); parser.parse(); loadCompleted = true; } finally { if (!loadCompleted) { knownMappers.remove(type); } } } } }67行:創建代理工程knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<T>(type));
截至到這,MapperScannerConfigurer、SqlSessionFactoryBean,兩個類干的事情就相融合了;
第一個用于掃描Dao接口設置代理類注冊到IOC中,用于后續生成Bean實體類,MapperFactoryBean,并可以通過mapperInterface從Configuration獲取Mapper
另一個用于生成SqlSession工廠初始化,解析Mapper里的XML配置進行動態代理MapperProxyFactory->MapperProxy注入到Configuration的Mapper
最終在注解類的幫助下進行方法注入,等執行操作時候即可獲得動態代理對象,從而執行相應的CRUD操作
@Resource private ISchoolDao schoolDao; schoolDao.querySchoolInfoById(1L);
六、總結
分析過程較長篇幅也很大,不一定一天就能看懂整個流程,但當耐下心來一點點研究,還是可以獲得很多的收獲的。以后在遇到這類的異常就可以迎刃而解了,同時也有助于面試、招聘!
之所以分析Mybatis最開始是想在Dao上加自定義注解,發現切面攔截不到。想到這是被動態代理的類,之后層層往往下扒直到MapperProxy.invoke!當然,Mybatis提供了自定義插件開發。
以上的源碼分析只是對部分核心內容進行分析,如果希望了解全部可以參考資料;MyBatis 3源碼深度解析,并調試代碼。IDEA中還是很方便看源碼的,包括可以查看類圖、調用順序等。
mybatis、mybatis-spring中其實最重要的是將Mapper配置文件解析與接口類組裝成代理類進行映射,以此來方便對數據庫的CRUD操作。從源碼分析后,可以獲得更多的編程經驗(套路)。
看完上述內容是否對您有幫助呢?如果還想對相關知識有進一步的了解或閱讀更多相關文章,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝您對億速云的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。