您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
今天就跟大家聊聊有關使用python怎么比較字符串是否一樣,可能很多人都不太了解,為了讓大家更加了解,小編給大家總結了以下內容,希望大家根據這篇文章可以有所收獲。
示例
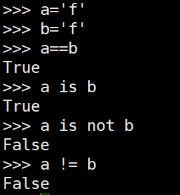
如果兩個字符串末尾有其他符號,比如回車‘\n',print的時候無法發現的,所以需要strip:
a=a.strip() b=b.strip() if a==b: print "True"
這是因為兩個字符串來自不同的內存塊,內存地址不一樣
id() 函數用于獲取對象的內存地址。
(ob1 is ob2) 等價于 (id(ob1) == id(ob2)) id函數可以獲得對象的內存地址,如果兩個對象的內存地址是一樣的,那么這兩個對象肯定是一個對象。和is是等價的.
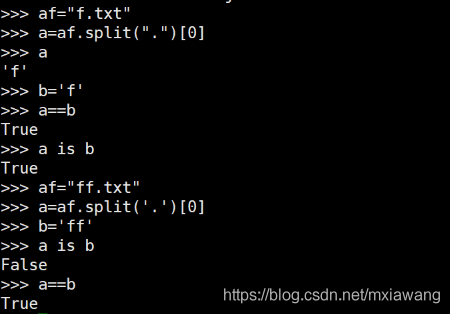
原理比較復雜,如下:
In [1]: def bar(self, x): ...: return self.x + y ...: In [2]: class Foo(object): ...: x = 9 ...: def __init__(self ,x): ...: self.x = x ...: bar = bar ...: In [3]: foo = Foo(5) In [4]: foo.bar is Foo.bar Out[4]: False In [5]: id(foo.bar) == id(Foo.bar) Out[5]: True
真實情況是當執行.操作符的時候,實際是生成了一個proxy對象,foo.bar is Foo.bar的時候,兩個對象順序生成,放在棧里相比較,由于地址不同肯定是False,但是id(foo.bar) ==id(Foo.bar)的時候就不同了,首先生成foo.bar,然后計算foo.bar的地址,計算完之后foo.bar的地址之后,就沒有任何對象指向foo.bar了,所以foo.bar對象就會被釋放。然后生成Foo.bar對象,由于foo.bar和Foo.bar所占用的內存大小是一樣的,所以又恰好重用了原先foo.bar的內存地址,所以id(foo.bar) == id(Foo.bar)的結果是True。
下面內容由郵件Leo Jay大牛提供,他解釋的更加通透。
用id(expression a) == id(expression b)來判斷兩個表達式的結果是不是同一個對象的想法是有問題的。
foo.bar 這種形式叫 attribute reference [1],它是表達式的一種。foo是一個instance object,bar是一個方法,這個時候表達式foo.bar返回的結果叫method object [2]。
根據文檔:
When an instance attribute is referenced that isn't a data attribute, its class is searched. If the name denotes a valid class attribute that is a function object, a method object is created by packing (pointers to) the instance object and the function object just found together in an abstract object: this is the method object.
foo.bar本身并不是簡單的名字,而是表達式的計算結果,是一個 method object,在id(foo.bar)這樣的表達式里,method object只是一個臨時的中間變量而已,對臨時的中間變量做id是沒有意義的。
一個更明顯的例子是,
print id(foo.bar) == id(foo.__init__) 輸出的結果也是True
看 id 的文檔[3]:
Return the “identity” of an object. This is an integer (or long integer) which is guaranteed to be unique and constant for this object during its lifetime. Two objects with non-overlapping lifetimes may have the same id() value. CPython implementation detail: This is the address of the object in memory.
只有你能保證對象不會被銷毀的前提下,你才能用 id 來比較兩個對象。所以,如果你非要比的話,得這樣寫:
fb = foo.bar Fb = Foo.bar print id(fb) == id(Fb)
即把兩個表達式的結果綁定到名字上,再來比是不是同一個對象,你才能得到正確的結果。
is表達式 [4] 也是一樣的,你現在得到了正確的結果,完全是因為 CPython 現在的實現細節決定的。
現在的is的實現,是左右兩邊的對象都計算出來,然后再比較這兩個對象的地址是否一樣。
萬一哪天改成了,先算左邊,保存地址,把左邊釋放掉,再算右邊,再比較的話,你的is的結果可能就錯了。
官方文檔里也提到了這個問題 [5]。
我認為正確的方法也是像id那樣,先把左右兩邊都計算下來,并顯式綁定到各自的名字上,然后再用is判斷。
cmp() 函數則是相當于 <,==,> 但是在 Python3 中,cmp() 函數被移除了,所以我以后還是避免少用這個函數。
#-*-conding:utf-8-*-
i='新聞';
m=input();
if i==m:
print('yes');
else:
print('no');
input();if second_company_name == u'中外運長航' or second_company_name == u'長航集團': print(u'忽略中外運長航和長航集團的子公司') continue
在 if 判斷語句中非常有用吶!
#!/usr/bin/python
# Filename: if.py
number = 23
guess = int(raw_input('Enter an integer : '))
if guess == number:
print 'Congratulations, you guessed it.' # New block starts here
print "(but you do not win any prizes!)" # New block ends here
elif guess < number:
print 'No, it is a little higher than that' # Another block
# You can do whatever you want in a block ...
else:
print 'No, it is a little lower than that'
# you must have guess > number to reach here
print 'Done'
# This last statement is always executed, after the if statement is executed```
## strip 去掉字符串其他符號
str1 = str1.strip() #去掉字符串中其他符號包括換行符等等
str2 = str2.strip()
if str2 == str1:
... #自己的代碼
## == 與 is的區別python中,使用==來比較兩個**對象的值**是否相等,而java 則使用== 比較兩個**對象**是否是同一對象
譬如,java中比較字符串,一般使用equal 方法,來比較兩個對象的值是否相等,而不使用==
相比較的,python 使用**is** 來比較兩個對象是否是同一對象。
is 用來判斷是否是同一個對象,is 是種很特殊的語法,你在其它的語言應該不會見到這樣的用法。
官方文檔解釋:
```python The operators ``is`` and ``is not`` test for object identity: ``x is y`` is true if and only if *x* and *y* are the same object. ``x is not y`` yields the inverse truth value. cmp(...) cmp(x, y) -> integer Return negative if x<y, zero if x==y, positive if x>y.
>>> a='abc' >>> b='abc' >>> a is b True >>> id(a) == id(b) True >>> >``` (Java 中直接賦值的字符串也可用 == 來判斷,但是使用 new 實例化的對象則需要使用equals(String s) 來判斷) ## 判斷數字相等不要用 is 操作符 ```python >>> a = 256 >>> b = 256 >>> id(a) 9987148 >>> id(b) 9987148 >>> a = 257 >>> b = 257 >>> id(a) 11662816 >>> id(b) 11662828
為什么兩次 is 返回的是不同結果?不是應該都是 true 嗎?
因為 string pooling (或叫intern)。 is 相等代表兩個對象的 id 相同(從底層來看的話,可以看作引用同一塊內存區域)。 至于為什么 “ABC” 被 intern 了而 “a bc” 沒有,這是 Python 解析器實現決定的,可能會變。
== 用來判斷兩個對象的值是否相等(跟 Java 不同,Java 中 == 用來判斷是否是同一個對象)。
看完上述內容,你們對使用python怎么比較字符串是否一樣有進一步的了解嗎?如果還想了解更多知識或者相關內容,請關注億速云行業資訊頻道,感謝大家的支持。
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。