您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
您好,登錄后才能下訂單哦!
這篇文章給大家分享的是有關MyBatis工作原理的示例分析的內容。小編覺得挺實用的,因此分享給大家做個參考,一起跟隨小編過來看看吧。
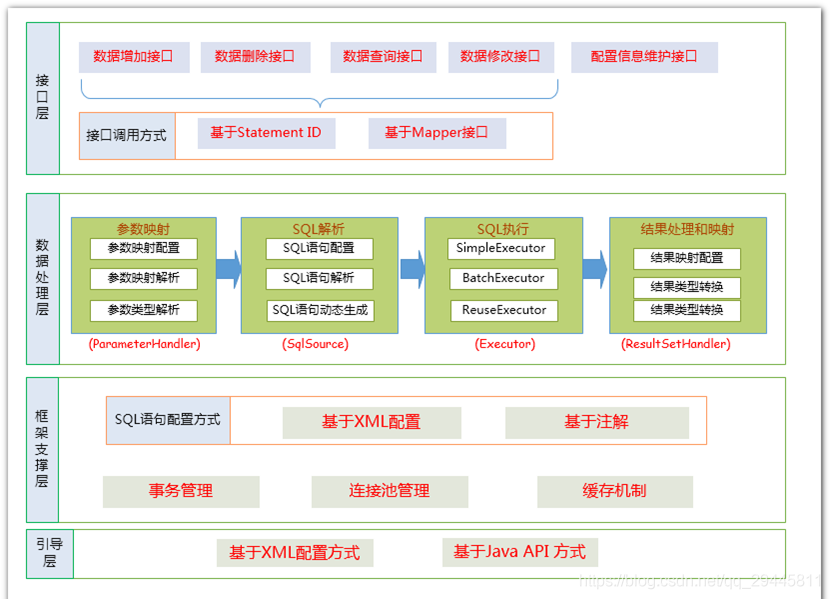
Mybatis分層框架圖
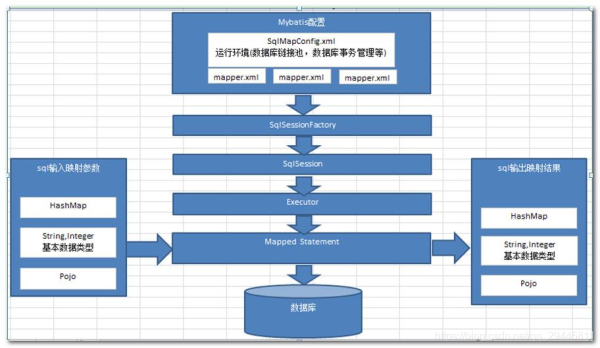
Mybatis工作原理圖
源碼分析:一般都是從helloworld入手
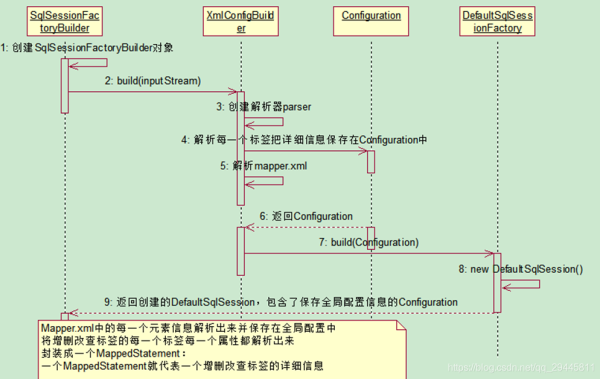
1、根據xml配置文件(全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml)創建一個SqlsessionFactory對象,mybatis-config.xml有數據源一些環境信息
2、sql映射文件EmployeeMapper.xml配置了每一個sql,以及sql的封裝規則等。
3、將sql映射文件注冊在全局配置文件中
4、寫代碼:
根據全局配置文件得到sqlsessionFactory
使用SqlSession工程進行crud、sqlseesion就代表和數據庫進行會話,用完close
使用sql標識告知mybatis來執行哪個sql,sql都是保存在sql映射文件中
測試類SqlSessionFactoryBuilder處打斷點
/**
* 1、根據xml配置文件(全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml)創建一個SqlsessionFactory對象,mybatis-config.xml有數據源一些環境信息
* 2、sql映射文件EmployeeMapper.xml配置了每一個sql,以及sql的封裝規則等。
* 3、將sql映射文件注冊在全局配置文件中
* 4、寫代碼:
* 4.1.根據全局配置文件得到sqlsessionFactory
* 4.2.使用SqlSession工程進行crud,sqlseesion就代表和數據庫進行會話,用完close
* 4.3.使用sql標識告知mybatis來執行哪個sql,sql都是保存在sql映射文件中
*
* @throws IOException
*/
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//2、獲取SqlSession實例,能直接執行已經映射了的sql語句,selectOne:sql唯一標識,執行sql要用到的參數
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
Employee employee = openSession.selectOne("com.ming.dao.EmployeeMapper.getEmpByID", 1);
System.out.println(employee);
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}1、獲取SqlsessionFactory對象
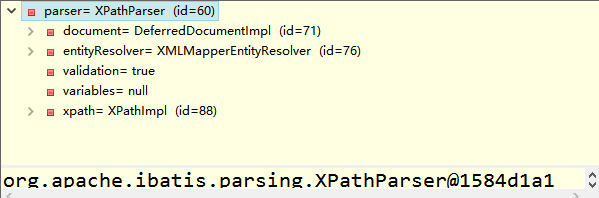
XPathParser作用:用dom解析mybatis-config.xml標簽的configuration標簽
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
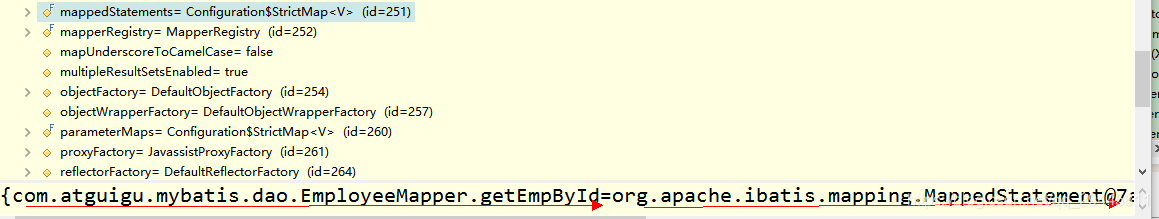
一個MappedStatement對象代表一個增刪改查標簽的詳細信息(id sqlResource等)
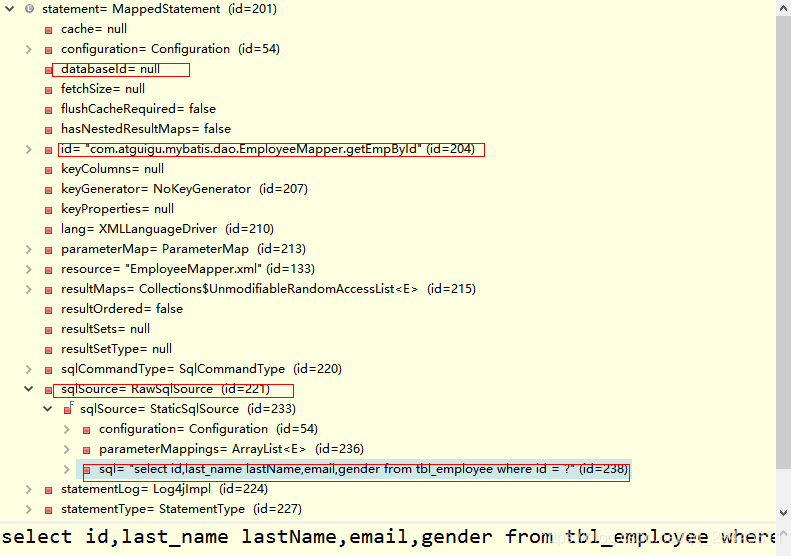
全局configuation的一個重要屬性MappedStatement
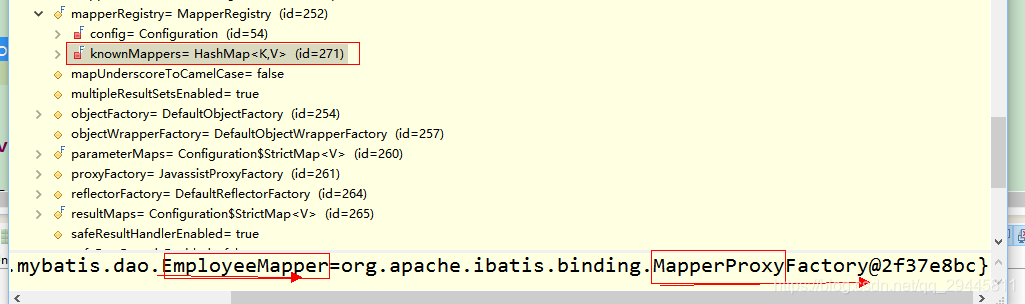
KonwnMappers生成一個Mapper接口的代理工廠
總結:
第一步:根據mybatis-config.xml全局配置文件創建SqlSessionFactory對象、就是把配置文件的詳細信息解析保存在了configuration對象中,返回包含了configuration的defaultSqsessionFactory對象
注意:mappedSatement對象代表一個增刪改查的詳細標簽
2、獲取sqlsession對象
mybatis-openSession
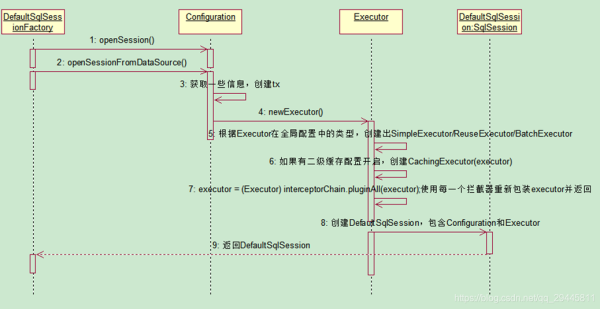
總結:
返回sqlsession的實現類defaultSqlsession對象,defaultSqlsession對象包含了executor和configuration,Executor(四大對象)對象會在這一步被創建
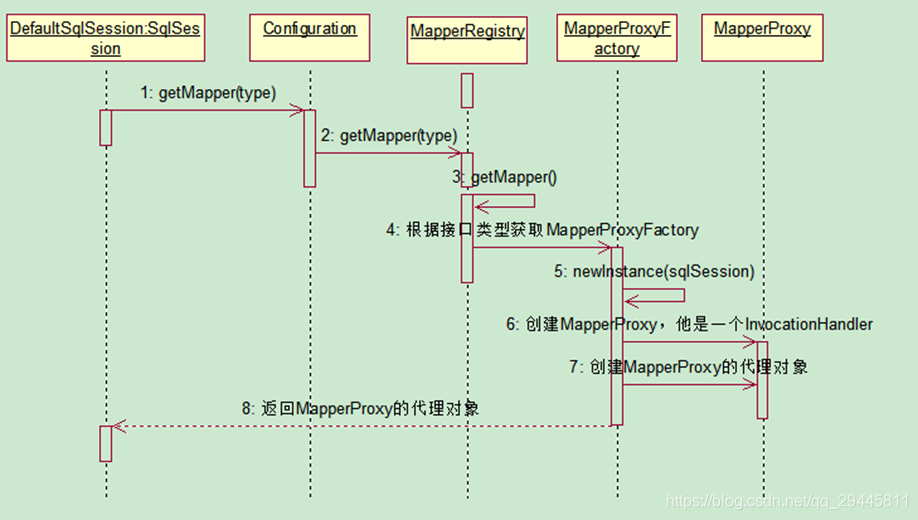
3、獲取Mapper接口代理對象(MapperProxy)

返回getMapper接口的代理對象、包含了SqlSession對象
4、執行增刪改查方法
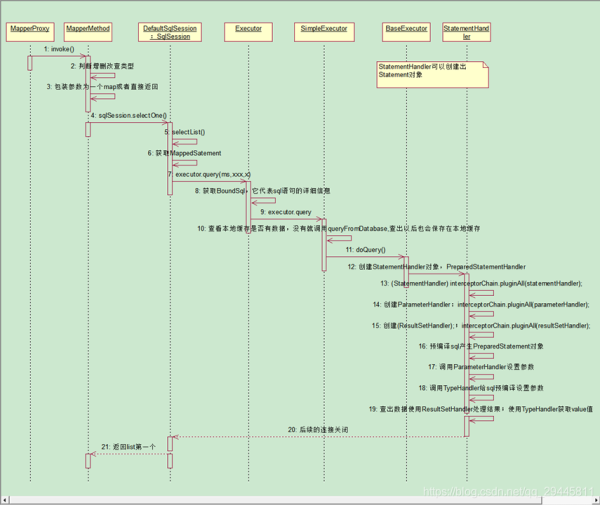
查詢流程
@Test
public void testInterface() throws IOException {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
EmployeeMapper employeeMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmployeeMapper.class);
Employee employee = employeeMapper.getEmpByID(1);
System.out.println(employee);
Employee employee2 = employeeMapper.getEmpByID(5);
System.out.println(employee2);
System.out.println(employee==employee2);
}finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
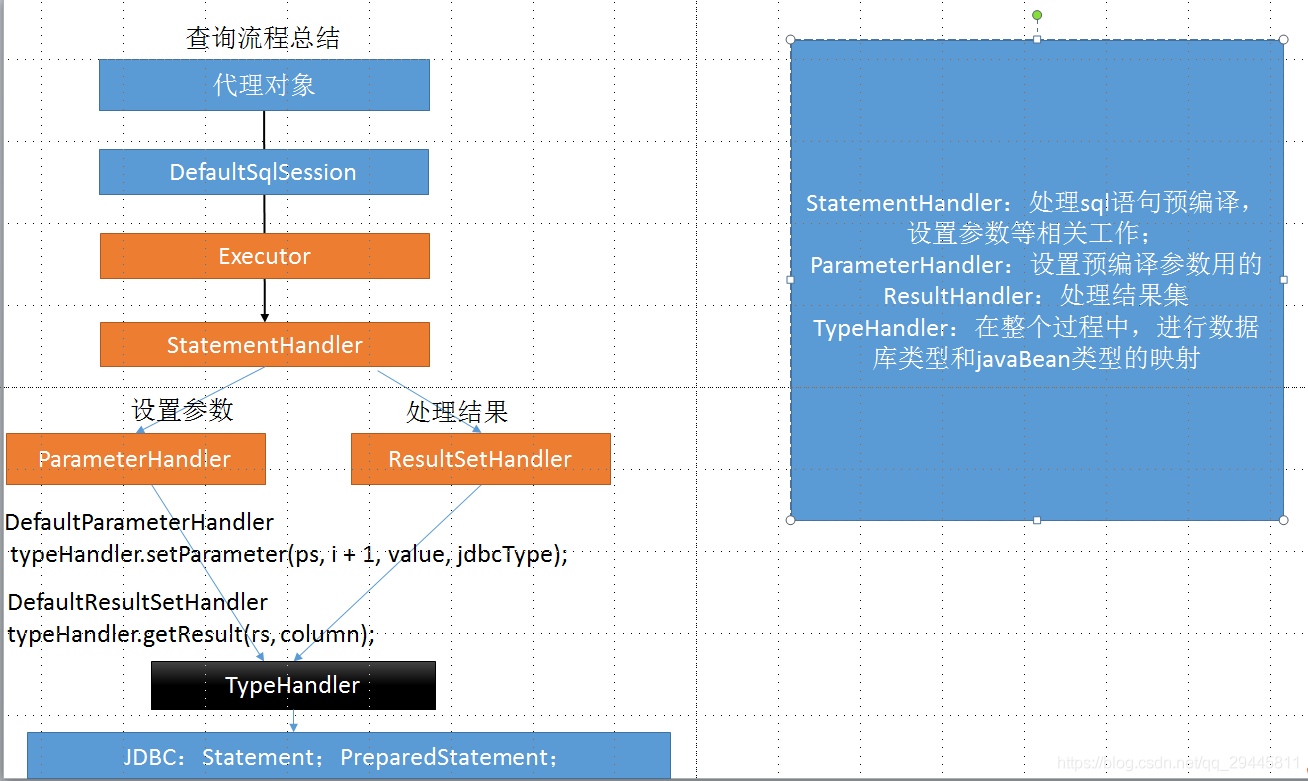
1、根據配置文件(全局、SQL映射文件)初始化出configuration對象
2、創建一個defaultSqlSession對象,它里面包含configuration和executor(根據配置文件中的defaultEXecutorType創建出對應的Executor)
3、defaultSqlSession.getMapper()獲取Mapper接口對應的MapperProxy
4、MapperProxy里面有defaultSqlSession
5、執行增刪改查方法:
調用的是defaultSqlsesion的增刪改查(會調用Executor的crud)
會創建一個statementhandler對象(同時也會創建出parameterHandler和resultSetHandler)
調用StatementHandler的prepareStatement()方法進行預編譯handler.prepare()和參數設置handler.parameterize(stmt)
設置完成后調用StatementHandler的增刪改查方法query()
參數預編譯完成后使用resultSetHandler封裝結果集
注意:四大對象每個創建的時候都有一個interceptorChain.pluginAll()方法
例如StatementHandler 對象的創建
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}感謝各位的閱讀!關于“MyBatis工作原理的示例分析”這篇文章就分享到這里了,希望以上內容可以對大家有一定的幫助,讓大家可以學到更多知識,如果覺得文章不錯,可以把它分享出去讓更多的人看到吧!
免責聲明:本站發布的內容(圖片、視頻和文字)以原創、轉載和分享為主,文章觀點不代表本網站立場,如果涉及侵權請聯系站長郵箱:is@yisu.com進行舉報,并提供相關證據,一經查實,將立刻刪除涉嫌侵權內容。